目录
1.算法描述
2.仿真效果预览
3.MATLAB核心程序
4.完整MATLAB
1.算法描述
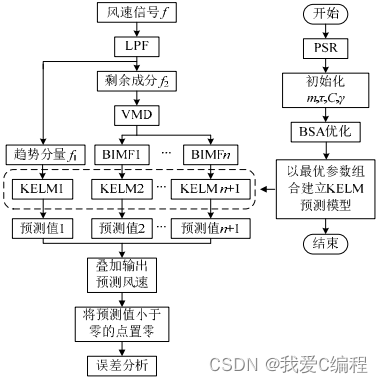
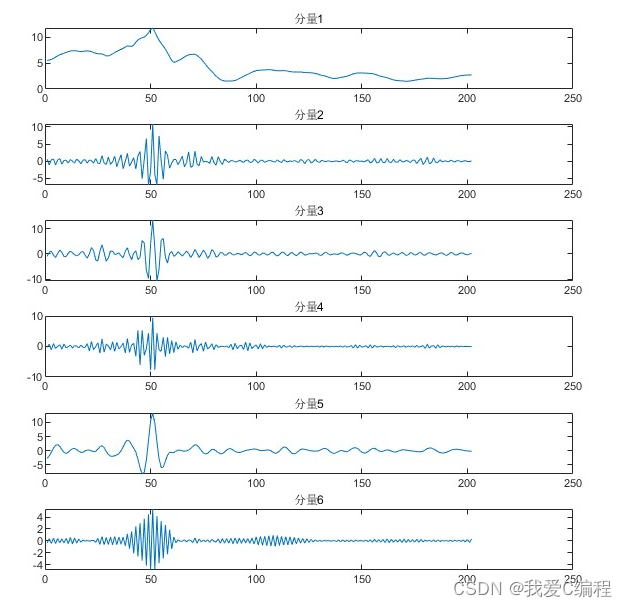
1).使用 LPF-VMD 对风速时间序列进行分解, 得到一个低频的趋势分量以及 n 个由 VMD 分解得 到的 BIMF。
2).对 LPF-VMD 分解得到的各分量分别建立 KELM 预测模型,采用 BSA 对模型中 4 个待定参 数进行联合优化。
3).以得到的最优参数组合建立 KELM 模型进 行预测。
4).各分量的预测结果叠加得到预测风速。
5).误差分析。
VMD(Variational mode decomposition)是一种自适应、完全非递归的模态变分和信号处理的方法。该技术具有可以确定模态分解个数的优点,其自适应性表现在根据实际情况确定所给序列的模态分解个数,随后的搜索和求解过程中可以自适应地匹配每种模态的最佳中心频率和有限带宽,并且可以实现固有模态分量(IMF)的有效分离、信号的频域划分、进而得到给定信号的有效分解成分,最终获得变分问题的最优解。它克服了EMD方法存在端点效应和模态分量混叠的问题,并且具有更坚实的数学理论基础,可以降低复杂度高和非线性强的时间序列非平稳性,分解获得包含多个不同频率尺度且相对平稳的子序列,适用于非平稳性的序列,VMD的核心思想是构建和求解变分问题。
核极限学习机(Kernel Based Extreme Learning Machine,KELM)是基于极限学习机(Extreme Learning Machine,ELM)并结合核函数所提出的改进算法,KELM 能够在保留 ELM 优点的基础上提高模型的预测性能。
鸟群算法模仿的生物行为可简化为如下规则:
(1) 每一只鸟自由选择觅食或保持警觉行为。
(2) 若选择觅食,每一只鸟即时记录并更新其所经过的最佳觅食位置,同时将此信息分享至整个种群,并记录种群最佳觅食位置。
(3) 若保持警觉,每只鸟均试图飞往种群的中心,此行为受种群间的竞争影响,食物储备多的鸟比储备少的有更大的概率飞往中心。
(4) 鸟群会周期性地飞往另一区域。鸟群之间会分享所寻觅的食物信息,这一习性使得种群更有利地生存下去。种群中食物储备最多的称为食物生产者,储备最少的称为乞食者,其它鸟随机作为 2 者之一。当鸟群从一个区域飞往另一区域,各只鸟的身份将发生改变。
(5) 生产者积极寻找食物,乞食者随机跟随一位生产者寻找食物。
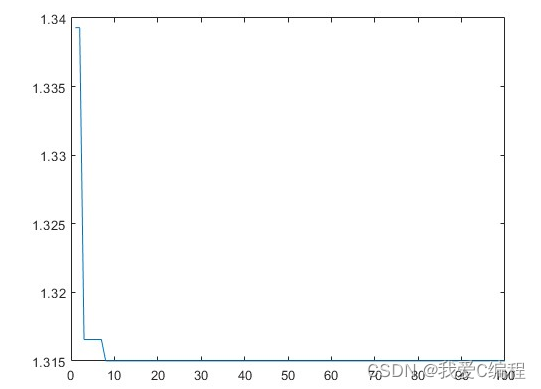
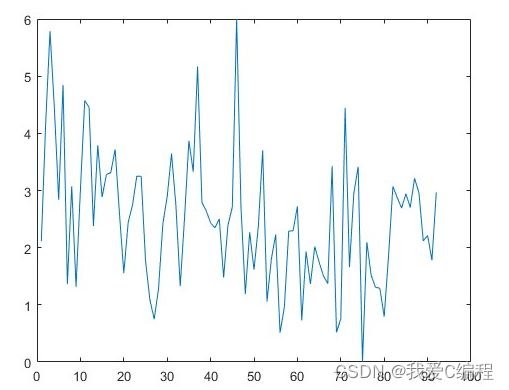
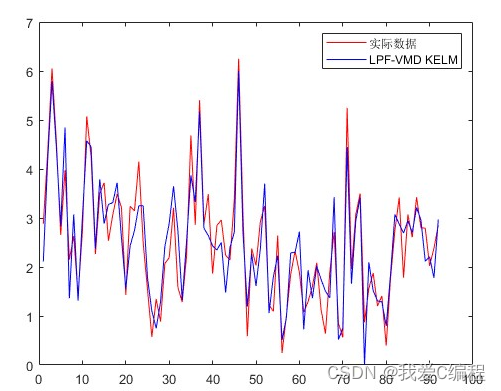
2.仿真效果预览
matlab2022a仿真结果如下:
3.MATLAB核心程序
% set the parameters
lb= [1,1,1,1]; % Lower bounds
ub= [5,5,5,100]; % Upper bounds
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%Initialization
for i = 1 : pop
x( i, : ) = lb + (ub - lb) .* rand( 1, dim );
fit( i ) = FitFunc( x( i, : ) );
end
pFit = fit; % The individual's best fitness value
pX = x; % The individual's best position corresponding to the pFit
[ fMin, bestIndex ] = min( fit ); % fMin denotes the global optimum
% bestX denotes the position corresponding to fMin
bestX = x( bestIndex, : );
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Start the iteration.
for iteration = 1 : M
iteration
prob = rand( pop, 1 ) .* 0.2 + 0.8;%The probability of foraging for food
if( mod( iteration, FQ ) ~= 0 )
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Birds forage for food or keep vigilance
sumPfit = sum( pFit );
meanP = mean( pX );
for i = 1 : pop
if rand < prob(i)
x( i, : ) = x( i, : ) + c1 * rand.*(bestX - x( i, : ))+ ...
c2 * rand.*( pX(i,:) - x( i, : ) );
else
person = randiTabu( 1, pop, i, 1 );
x( i, : ) = x( i, : ) + rand.*(meanP - x( i, : )) * a1 * ...
exp( -pFit(i)/( sumPfit + realmin) * pop ) + a2 * ...
( rand*2 - 1) .* ( pX(person,:) - x( i, : ) ) * exp( ...
-(pFit(person) - pFit(i))/(abs( pFit(person)-pFit(i) )...
+ realmin) * pFit(person)/(sumPfit + realmin) * pop );
end
x( i, : ) = Bounds( x( i, : ), lb, ub );
fit( i ) = FitFunc( x( i, : ) );
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
else
FL = rand( pop, 1 ) .* 0.4 + 0.5; %The followed coefficient
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Divide the bird swarm into two parts: producers and scroungers.
[ans, minIndex ] = min( pFit );
[ans, maxIndex ] = max( pFit );
choose = 0;
if ( minIndex < 0.5*pop && maxIndex < 0.5*pop )
choose = 1;
end
if ( minIndex > 0.5*pop && maxIndex < 0.5*pop )
choose = 2;
end
if ( minIndex < 0.5*pop && maxIndex > 0.5*pop )
choose = 3;
end
if ( minIndex > 0.5*pop && maxIndex > 0.5*pop )
choose = 4;
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
if choose < 3
for i = (pop/2+1) : pop
x( i, : ) = x( i, : ) * ( 1 + randn );
x( i, : ) = Bounds( x( i, : ), lb, ub );
fit( i ) = FitFunc( x( i, : ) );
end
if choose == 1
x( minIndex,: ) = x( minIndex,: ) * ( 1 + randn );
x( minIndex, : ) = Bounds( x( minIndex, : ), lb, ub );
fit( minIndex ) = FitFunc( x( minIndex, : ) );
end
for i = 1 : 0.5*pop
if choose == 2 || minIndex ~= i
person = randi( [(0.5*pop+1), pop ], 1 );
x( i, : ) = x( i, : ) + (pX(person, :) - x( i, : )) * FL( i );
x( i, : ) = Bounds( x( i, : ), lb, ub );
fit( i ) = FitFunc( x( i, : ) );
end
end
else
for i = 1 : 0.5*pop
x( i, : ) = x( i, : ) * ( 1 + randn );
x( i, : ) = Bounds( x( i, : ), lb, ub );
fit( i ) = FitFunc( x( i, : ) );
end
if choose == 4
x( minIndex,: ) = x( minIndex,: ) * ( 1 + randn );
x( minIndex, : ) = Bounds( x( minIndex, : ), lb, ub );
fit( minIndex ) = FitFunc( x( minIndex, : ) );
end
for i = (0.5*pop+1) : pop
if choose == 3 || minIndex ~= i
person = randi( [1, 0.5*pop], 1 );
x( i, : ) = x( i, : ) + (pX(person, :) - x( i, : )) * FL( i );
x( i, : ) = Bounds( x( i, : ), lb, ub );
fit( i ) = FitFunc( x( i, : ) );
end
end
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Update the individual's best fitness vlaue and the global best one
for i = 1 : pop
if ( fit( i ) < pFit( i ) )
pFit( i ) = fit( i );
pX( i, : ) = x( i, : );
end
if( pFit( i ) < fMin )
fMin = pFit( i );
bestX = pX( i, : );
end
end
ff(iteration) = fMin;
end
figure;
plot(ff);
m = floor(bestX(1))+1;
if isnan(m)==1
m=5;
end
% 延迟时间
tau = floor(bestX(2))+1;
if isnan(tau)==1
tau=1;
end
% 惩罚系数 C
C = bestX(3);
if isnan(C)==1
C=1;
end
% 核参数?
Ker = bestX(4);
if isnan(Ker)==1
Ker=100;
end
%采用 BSA 对模型中 4 个待定参数进行联合优化。
save best.mat m tau C Ker
load S122.mat
%%
% 训练集――50个样本
train = S122(1:120,:);
% 测试集――1
test = S122(121:end,:);
02_101m4.完整MATLAB
V







![[附源码]计算机毕业设计付费自习室管理小程序Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1cee4fd785f546eb92e20b403a2a4b4d.png)