ByteBuffer
- 1.创建方式
- 创建方式1:ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(int size);
- 2.创建方式2:ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(int size);
- 2.字符串转成ByteBuffer的3三种方式
- 方式1: 采用put()方法,读数据时需要调用flip()切换为读模式
- 方式2:以特定编码格式将String转换为ByteBuffer
- 方式3:调用ByteBuffer.wrap()
- 3.读写原理
1.创建方式
创建方式1:ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(int size);
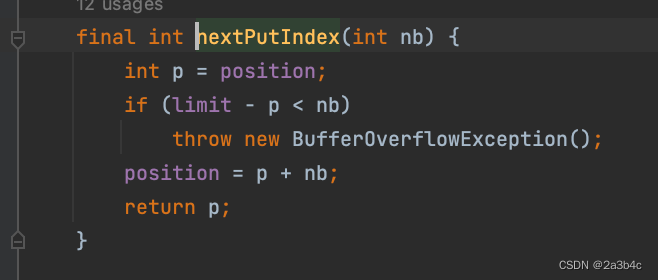
public static ByteBuffer getTimeBuffer(Tablet tablet) {
ByteBuffer timeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(tablet.getTimeBytesSize());
for (int i = 0; i < tablet.rowSize; i++) {
timeBuffer.putLong(tablet.timestamps[i]);
}
timeBuffer.flip();
return timeBuffer;
}
- buf缓冲区存储在堆内存中,内存开销在JVM中,受GC影响,会多拷贝一次,因为java程序收到的数据首先被系统内存所获取,然后再拷贝给JVM
2.创建方式2:ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(int size);
- buf在系统直接内存中创建,内存开销在JVM之外,读写效率高(不受GC影响,0拷贝),但是分配效率低,使用后若不释放,会造成内存泄漏
2.字符串转成ByteBuffer的3三种方式
方式1: 采用put()方法,读数据时需要调用flip()切换为读模式
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(int size);
buf.put(msg.getBytes());
方式2:以特定编码格式将String转换为ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
方式3:调用ByteBuffer.wrap()
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());
3.读写原理
Bytebuffer的数据读写主要采用三个参数来控制
-
1.position:起始下标
-
2.limit:限制下标
-
3.capacity:buffer的容量

一开始limit指向capacity,position指向0


写模式下,写数据时,position会不断前移

timeBuffer.flip();切换为读模式,limit位于position位置,position位置置于起始位置
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-aps5cc0u-1690883091607)(file:///Users/rongli/Library/Application%20Support/marktext/images/2023-08-01-17-36-56-image.png?msec=1690882616983)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ac363168b1f54274a1142a92f4b73e1c.png)
timeBuffer.clear();切换为写模式,采用清空缓冲区,将position置为0,limit为capacity
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ivWPsOsi-1690883091607)(file:///Users/rongli/Library/Application%20Support/marktext/images/2023-08-01-17-36-42-image.png?msec=1690882602657)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bd58c14a74af4a7e81d1d3e009f14d1a.png)
划重点:由此可见,读写模式由于共用相同的position等参数,因此,需要切换模式,才能正确的读写。
并且在发生一次写读(先写后读)切换后,需要调用clear()方法进行重置,才能进行一轮新的写读.
存在的问题:
读操作后,重新写,调用clear()会重置至0的问题,如果没有读完呢?
例如 存在接收到的数据是不完整的,无法进行读操作,那么需要在原来的基础上,继续写数据怎么办?
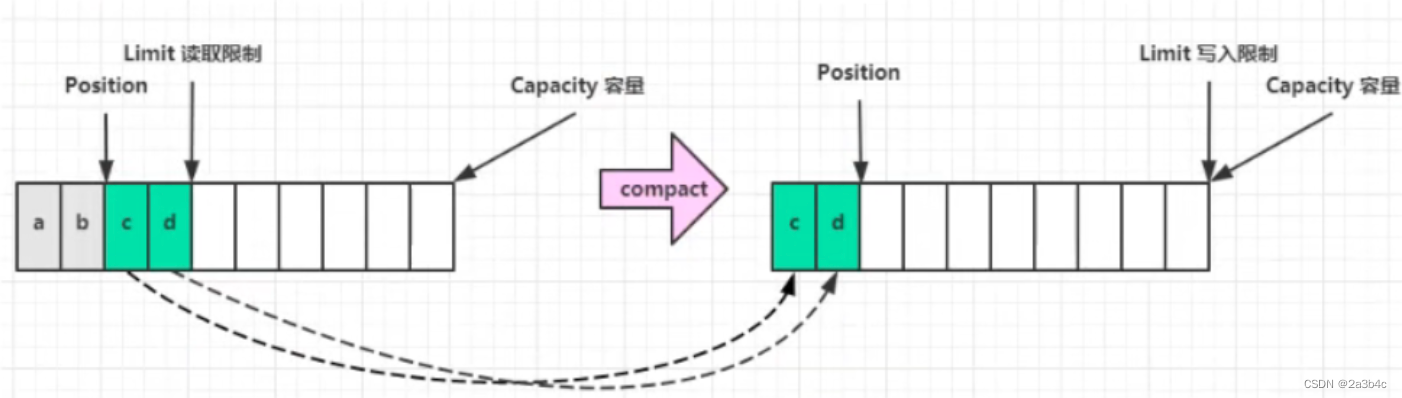
答案是 Buffer.compact() 切换到写入模式
五. 调用compact方法切换为写模式,在不清空缓冲区的前提下,继续写如信息,将未读取的数据前移,postion指针置为未读取数据的末尾下标,limit置为capacity
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-YIjrg6tP-1690883091607)(file:///Users/rongli/Library/Application%20Support/marktext/images/2023-08-01-17-44-34-image.png?msec=1690883074749)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5a716258f2694042bd5eaeacff289c3d.png)