目录
四、SpringBoot自动配置原理
4.1 起步依赖原理
4.1.1 版本锁定
4.1.2 起步依赖
4.2 自动配置原理
4.2.1 @SpringBootApplication源码
4.2.2 @SpringBootConfiguration源码
4.2.3 @EnableAutoConfiguration源码
1)Registrar
2)AutoConfigurationImportSelector
4.2.4 @ComponentScan
1)AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter
2)TypeExcludeFilter
3)自定义排除器
4.3 自动配置类
4.3.1 自动配置类说明
4.3.2 @Conditional派生注解
4.3.3 自定义自动配置类
4.4 属性配置类
4.4.1 属性配置类说明
4.4.2 自定义属性配置类
4.5 自定义场景启动器
4.5.1 场景启动器包含内容
4.5.2 搭建自动配置工程
4.5.2.1 依赖
4.5.2.2 自动配置类
4.5.2.3 属性配置类
4.5.2.4 具体配置的类
4.5.2.5 spring.factories
4.5.3 搭建测试工程
4.5.3.1 依赖
4.5.2.2 Controller
4.5.2.3 application.yml
4.5.2.4 引导类
四、SpringBoot自动配置原理
4.1 起步依赖原理
4.1.1 版本锁定
SpringBoot项目都是继承于spring-boot-starter-parent工程的,我们点进去看看这个工程中配置了什么?
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>
...
<properties>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<resource.delimiter>@</resource.delimiter>
<maven.compiler.source>${java.version}</maven.compiler.source>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.target>${java.version}</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId>
<artifactId>kotlin-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${kotlin.version}</version>
</plugin>
...
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>我们发现spring-boot-starter-parent工程是继承于spring-boot-dependencies工程,在spring-boot-starter-parent工程中锁定了部分插件使用的版本:

我们继续点进spring-boot-dependencies工程:
<properties>
<activemq.version>5.15.3</activemq.version>
<antlr2.version>2.7.7</antlr2.version>
<appengine-sdk.version>1.9.63</appengine-sdk.version>
<artemis.version>2.4.0</artemis.version>
<aspectj.version>1.8.13</aspectj.version>
<assertj.version>3.9.1</assertj.version>
<atomikos.version>4.0.6</atomikos.version>
<bitronix.version>2.1.4</bitronix.version>
.....
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-actuator</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
....
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>从上面的spring-boot-starter-dependencies的pom.xml中我们可以发现,一部分坐标的版本、依赖管理、插件管理已经定义好,所以我们的SpringBoot工程继承spring-boot-starter-parent后已经具备版本锁定等配置了(解决了版本冲突问题)。
这些版本的搭配经过了SpringBoot官方团队的测试,我们在使用过程中,采用SpringBoot搭配的版本匹配,就避免了版本冲突、不稳定等因素;
4.1.2 起步依赖
在继承的父工程中我们并没有看到依赖的引入(只是版本的锁定),真正的依赖是在我们引入场景启动器时引入的,我们点击spring-boot-starter-web场景启动器查看:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
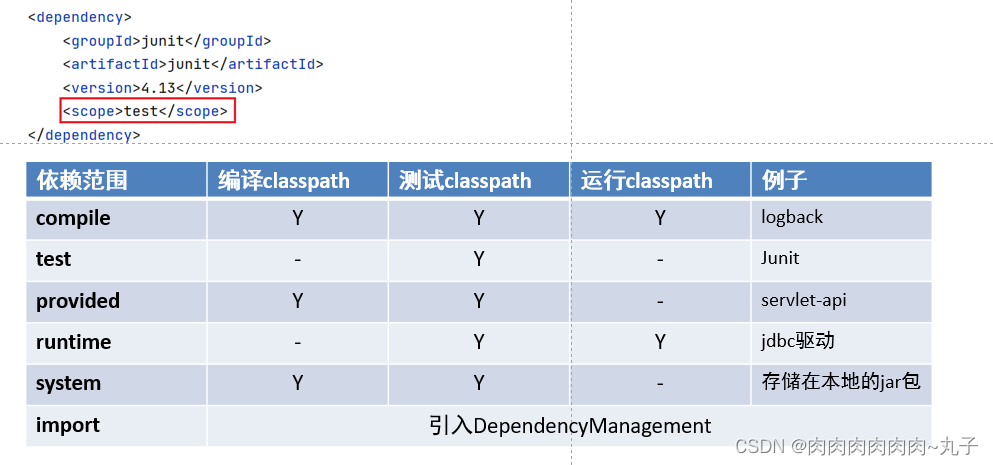
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.0.9.Final</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>我们发现在spring-boot-starter-web依赖中引入了大量web场景需要的依赖,如Spring-web、Spring-webmvc、json转换、tomcat等,SpringBoot中的场景启动器(starter)对场景的依赖进行"打包",这样以后我们的项目只需要引入对应场景的starter即可;
- 官方提供的场景命名规则为:spring-boot-starter-xxx
- 第三方提供场景命名规则为:xxx-spring-boot-starter
4.2 自动配置原理
我们在前面说到过,SpringBoot所有的配置基于约定理念,并不是不需要配置,而是SpringBoot在项目启动时帮我们配置了,所有的配置基于约定的参数已经配置好了;那么SpringBoot是如何做到"自动配置"的呢?
我们点击标注在引导类上的@SpringBootApplication注解:
@SpringBootApplication // 标注这是一个引导类
public class HelloApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class);
}
}4.2.1 @SpringBootApplication源码
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
...
}- 1)@Target({ElementType.TYPE}):元注解,标注这个注解只能在类上使用
- 2)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME):元注解,标注这个注解的生命周期是RUNTIME,可以在运行时解析到这个注解
- 3)@Documented:元注解,表明这个注解应该被 javadoc工具记录
- 4)@Inherited:元注解,标注在类上面时,该类的子类会自动继承此注解
4.2.2 @SpringBootConfiguration源码
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
}上面三个都是元注解
@Configuration:Spring提供的注解,表示这是一个配置类
也就是说标注了@SpringBootApplication、@SpringBootConfiguration等注解的类都可以当做一个配置类使用
4.2.3 @EnableAutoConfiguration源码
@EnableAutoConfiguration是SpringBoot自动配置的核心;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
}标注了两个注解:@AutoConfigurationPackage、@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
1)Registrar
- 1)@AutoConfigurationPackage:在该注解上标注了@Import注解,导入了一个Registrar导入器,开启包的自动导入配置,扫描注解标注类所在的包及其下面的子包
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}往容器中注册了一个Registrar,查看Registrar:
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 配置包注册(注册标注了AutoConfigurationPackage注解的类所在的全路径下面的所有类)
register(registry, new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName());
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImport(metadata));
}
}
SpringBoot应用的默认扫描规则是只扫描主程序所在包及其子包
也可以通过指定参数让SpringBoot来扫描其他包(主程序所在包就不会扫描了)
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "com.dfbz.controller")
public class HelloApplication {
}2)AutoConfigurationImportSelector
在@EnableAutoConfiguration还标注了一个@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class),导入了一个AutoConfigurationImportSelector类;
查看继承体系:

发现AutoConfigurationImportSelector实现接口ImportSelector,在导入时,一定会调用selectImports进行Bean配置;
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 给容器中导入一批组件(xxxAutoConfiguration)
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,
attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
// 过滤掉一些不生效的组件
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
// 其他全部导入到IOC容器给中
return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);
}
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations,
"No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}configurations值:

- SpringFactoriesLoader源码:
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
// META-INF/spring.factories
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
List<String> factoryClassNames = Arrays.asList(
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue()));
result.addAll((String) entry.getKey(), factoryClassNames);
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
4.2.4 @ComponentScan
@SpringBootApplication注解上除了标注了上面两个注解外,还标注了一个@ComponentScan注解,其内容如下:
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })添加了两个排除过滤器,分别是TypeExcludeFilter和AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter;两个排除过滤器都继承与TypeFilter接口,并且是一个函数式接口;IOC容器启动时,会将被扫描的Bean的元数据信息传递到该match,由该方法的返回值来决定是否要排除这个Bean;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface TypeFilter {
/**
* 根据match方法的返回值来决定当前Bean是否要注册到IOC容器
* @param metadataReader: 这个注解标注的目标类的元数据读取器
* @param metadataReaderFactory: 获取元数据读取器的工厂
*/
boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory)
throws IOException;
}1)AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter
- AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter:
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter;
/**
* A {@link TypeFilter} implementation that matches registered auto-configuration classes.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 1.5.0
*/
public class AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter implements TypeFilter, BeanClassLoaderAware {
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
private volatile List<String> autoConfigurations;
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
}
// 作用: 当前这个类不能是一个配置类 并且 也不能是一个自动配置类(不能写在META-INF/spring.factroies文件中)
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader,
MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
return isConfiguration(metadataReader) && isAutoConfiguration(metadataReader);
}
// 当前这个类上是否标注了Configuration注解
private boolean isConfiguration(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
return metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata()
.isAnnotated(Configuration.class.getName());
}
// 当前这个类是否是一个自动配置类
private boolean isAutoConfiguration(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
return getAutoConfigurations()
.contains(metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName());
}
protected List<String> getAutoConfigurations() {
if (this.autoConfigurations == null) {
this.autoConfigurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
EnableAutoConfiguration.class, this.beanClassLoader);
}
return this.autoConfigurations;
}
}说明:因为自动配置类是SpringBoot规定的加载规则,默认规则为加载每个jar包下的/META-INF/spring.factories文件中的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration指定的自动配置类;
如果我们自己想要自定义自动配置类让其生效,有两种方法:
- 1)在类上只标注一个@Configuration注解,没有写在/META-INF/spring.factories文件中,不会被排除,但也被默认的规则扫描到了(Registrar导入器);
- 2)在类上只标注一个@Configuration注解,写在/META-INF/spring.factories文件中,被排除(但被SpringBoot扫描到了),这是SpringBoot推荐的写法,标准的自动配置类
Tips:自动配置类和普通的配置类的作用都是一模一样的,只不过自动配置类一般用于加载某些场景,而且是写在/META-INF/spring.factories中的;
2)TypeExcludeFilter
- TypeExcludeFilter:
package org.springframework.boot.context;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter;
public class TypeExcludeFilter implements TypeFilter, BeanFactoryAware {
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
// 作用: 获取IOC容器中,所有有关于TypeExcludeFilter的后代类,然后执行这些后代类的match方法
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader,
MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory
&& getClass() == TypeExcludeFilter.class) {
// 从IOC容器中获取有关于TypeExcludeFilter的所有Bean(包括后代类)
Collection<TypeExcludeFilter> delegates = ((ListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory)
.getBeansOfType(TypeExcludeFilter.class).values();
for (TypeExcludeFilter delegate : delegates) {
// 调用TypeExcludeFilter后代类的所有match方法
if (delegate.match(metadataReader, metadataReaderFactory)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"TypeExcludeFilter " + getClass() + " has not implemented equals");
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"TypeExcludeFilter " + getClass() + " has not implemented hashCode");
}
}TypeExcludeFilter过滤器是SpringBoot提供给我们用的排除过滤器,我们可以根据一些条件来决定是否要过滤某些Bean;
3)自定义排除器
- 自定义排除器:
package com.dfbz;
import com.dfbz.controller.HelloController;
import org.springframework.boot.context.TypeExcludeFilter;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro:
*/
//@Component // 不能用这种方式注册到IOC容器,因为排除器在容器扫描之前就要生效
public class MyTypeExcludeFilter extends TypeExcludeFilter {
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
// 排除HelloController
return metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName().equals(HelloController.class.getName());
}
}排除器(MyTypeExcludeFilter)需要注册到IOC容器中才会生效,但不能使用@Component 注册,因为排除器在容器扫描之前就要生效
- 编写初始化器:
package com.dfbz;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro:
*/
public class MyApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 往IOC容器中注册一个单例Bean(在IOC容器初始化后,@ComponentScan组件扫描之前执行)
applicationContext.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("myTypeExcludeFilter",new MyTypeExcludeFilter());
}
}- 让初始化器生效:
在resources目录下编写META-INF/spring.factories,内容如下:
# Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
com.dfbz.MyApplicationContextInitializer4.3 自动配置类
4.3.1 自动配置类说明
通过刚刚的自动配置原理我们发现,SpringBoot在启动时,就加载了非常多的一些配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration),这些配置类中配置了非常多的信息,包括根据条件导入一些Bean、配置一些属性、绑定一些配置;
我们之所以能够启动SpringBoot环境就配置好了大量的环境(SpringMVC环境/MyBatis环境/JPA环境等)都是因为这些自动配置类在SpringBoot启动时帮我们在IOC容器里注册了大量的Bean;
Tips:配置类的地址在META-INF/spring.factories文件中org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfigurationkey所指定的内容;
以DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration配置类举例:
// 配置顺序(数字越小,越优先加载,负数也可以)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
// 标注这是一个配置类
@Configuration
// 如果是web环境才配置此类
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
// 如果系统中有DispatcherServlet类才配置此类(导入了这个依赖就配置这个类)
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class)
// 在ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration类加载之后再加载此类
@AutoConfigureAfter(ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class)
// 开启属性配置
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
public class DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration {
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServlet";
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServletRegistration";
// 标注这是一个配置类
@Configuration
// 满足DefaultDispatcherServletCondition的matches方法时配置该类
@Conditional(DefaultDispatcherServletCondition.class)
// 容器中有ServletRegistration类时配置该类
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
// 开启配置属性
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
private final WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties;
public DispatcherServletConfiguration(WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
this.webMvcProperties = webMvcProperties;
}
// 往IOC容器中配置一个DispatcherServlet类
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet() {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(
this.webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(
this.webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(
this.webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
return dispatcherServlet;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
}
@Configuration
@Conditional(DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
@Import(DispatcherServletConfiguration.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
private final WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties;
private final MultipartConfigElement multipartConfig;
public DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration(
ServerProperties serverProperties, WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties,
ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfigProvider) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
this.webMvcProperties = webMvcProperties;
this.multipartConfig = multipartConfigProvider.getIfAvailable();
}
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public ServletRegistrationBean<DispatcherServlet> dispatcherServletRegistration(
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) {
ServletRegistrationBean<DispatcherServlet> registration = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(
dispatcherServlet,
this.serverProperties.getServlet().getServletMapping());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(
this.webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
if (this.multipartConfig != null) {
registration.setMultipartConfig(this.multipartConfig);
}
return registration;
}
}
}4.3.2 @Conditional派生注解
我们已经知道了自动配置类的加载规则,只要配置在META-INF/spring.factories文件的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfigurationkey中的全类名,该配置类即可被加载,但有些时候我们并不希望这些配置类能够被立即加载,而是需要符合某些条件时这些配置类才会被加载;
SpringBoot内置了非常多的条件判断注解,这些注解可以帮助我们在符合条件的清空下,该配置类/方法才会生效;这些注解我们统一称为派生注解;为@ConditionalXxx;
- @Conditional表格:
| @Conditional扩展注解 | 作用(判断是否满足当前指定条件) |
| @ConditionalOnJava | 系统的java版本是否符合要求 |
| @ConditionalOnBean | 容器中存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | 容器中不存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnExpression | 满足SpEL表达式指定 |
| @ConditionalOnClass | 系统中有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnMissingClass | 系统中没有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate | 容器中只有一个指定的Bean,或者这个Bean是首选Bean |
| @ConditionalOnProperty | 系统中指定的属性是否有指定的值 |
| @ConditionalOnResource | 类路径下是否存在指定资源文件 |
| @ConditionalOnWebApplication | 当前是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication | 当前不是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnJndi | JNDI存在指定项 |
4.3.3 自定义自动配置类
- 自动配置类的加载说明:
- 1)必须是一个配置类
- 2)必须配置在META-INF/spring.factories中的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfigurationkey中;
- 3)可能还会包含一些派生注解(@ConditionalXxx)
package com.dfbz.config;
import com.dfbz.controller.HelloController;
import com.dfbz.entity.City;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnJava;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnResource;
import org.springframework.boot.system.JavaVersion;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro:
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnJava(JavaVersion.EIGHT) // Java版本必须是1.8
@ConditionalOnBean(HelloController.class) // IOC容器中必须存在HelloController这个对象
@ConditionalOnResource(resources = "application.properties") // 类路径下必须存在application.properties
public class MyAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public City city() {
return new City();
}
}4.4 属性配置类
4.4.1 属性配置类说明
自动配置类中通常会绑定(通过EnableConfigurationProperties开启)一些属性配置类(xxxProperties.class),这些属性配置类通过@ConfigurationProperties注解标识;
在自动配置类中根据条件配置了大量的Bean,而这些Bean上面大都开启(@EnableConfigurationProperties)了属性配置类(xxxProperties.class),这些属性配置类是SpringBoot"基于约定配置"的保障;
查看ServerProperties:
- @ConfigurationProperties:与application.yml/properties配置文件进行绑定;
// 与配置文件进行绑定
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true)
public class ServerProperties {
private Integer port;
private InetAddress address;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final ErrorProperties error = new ErrorProperties();
private Boolean useForwardHeaders;
private String serverHeader;
}4.4.2 自定义属性配置类
- 自定义属性配置类:
package com.dfbz.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro:
*/
@Data // 提供get/set/toString...
@AllArgsConstructor // 有参构造
@NoArgsConstructor // 无参构造
@Component // 必须要放入IOC容器才能使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "com.dfbz.book") // 绑定的前缀为: com.dfbz.book
public class Book {
private String name;
private Double price;
}- application.yml:
com:
dfbz:
book:
name: 《Java入门到精通》
price: 38.8- DemoController:
package com.dfbz.controller;
import com.dfbz.entity.Book;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro:
*/
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private Book book;
@GetMapping("/getBook")
@ResponseBody
public Book getBook() {
return book;
}
}访问:http://localhost:8080/getBook:
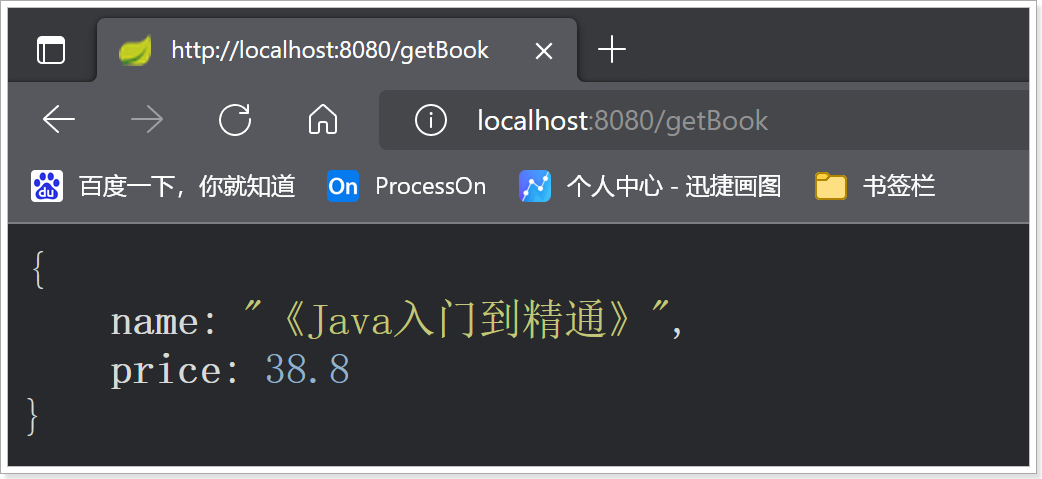
也可以使用@EnableConfigurationProperties注解来指定要开启某个类上面的属性配置;该类会自动被加载到IOC容器
package com.dfbz;
import com.dfbz.entity.Book;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Book.class) // 开启Book类的属性配置功能
public class HelloApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class);
}
}注释Book类中的@Component注解;
重启服务器,再次访问:http://localhost:8080/getBook发现配置依旧可以;
4.5 自定义场景启动器
4.5.1 场景启动器包含内容
1)自动配置类;
xxxAutoConfiguration
2)开启属性配置,并绑定属性配置类;
xxxProperties
3)加入到META-INF/spring.factories中;
4.5.2 搭建自动配置工程
自动配置场景启动器名称规范:{name}-springboot-starter-autoconfigurer
4.5.2.1 依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.dfbz</groupId>
<artifactId>02-mystarter-springboot-starter-autoconfigurer</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!--springboot的启动器,包含所有starter的基本配置-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>4.5.2.2 自动配置类
package com.mystarter.autoconfig;
import com.mystarter.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro: 自动配置类
*/
// 标注这是一个配置类
@Configuration
// 如果是web环境才配置此类
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
// 开启配置属性
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MyStarterProperties.class)
public class MyStarterAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public HelloService helloService(){
return new HelloService();
}
}4.5.2.3 属性配置类
package com.mystarter.properties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro: 属性配置类,绑定配置文件,指定前缀
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mystarter")
public class MyStarterProperties {
private String text;
public String getText() {
return text;
}
public void setText(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
}4.5.2.4 具体配置的类
package com.mystarter.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro:
*/
public class HelloService {
@Autowired
private MyStarterProperties properties;
public String sayHello() {
return properties.getText();
}
}4.5.2.5 spring.factories
在/MATA-INF/目录下新建spring.factories文件;
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.mystarter.autoconfig.MyStarterAutoConfiguration4.5.3 搭建测试工程
4.5.3.1 依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>03-MyStarterTest</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!--导入我们自定义的starter-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dfbz</groupId>
<artifactId>02-mystarter-springboot-starter-autoconfigurer</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!--web场景的starter-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>4.5.2.2 Controller
package com.dfbz.controller;
import com.mystarter.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro:
*/
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String hello() {
return helloService.sayHello();
}
}4.5.2.3 application.yml
mystarter:
text: hello~4.5.2.4 引导类
package com.dfbz;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @author lscl
* @version 1.0
* @intro:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
}

![uniapp小程序警告:[sitemap 索引情况提示]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7a9f542c59214cbf9317a0bc26229fa1.png)