VOC数据格式与YOLO数据格式互转
1.VOC数据格式

VOC(Visual Object Classes)是一个常用的计算机视觉数据集,它主要用于对象检测、分类和分割任务。VOC的标注格式,也被许多其他的数据集采用,因此理解这个数据格式是很重要的。下面是一个详细的介绍:
一个典型的VOC数据集主要包括以下两个主要组成部分:
- JPEGImages:这个文件夹包含所有的图片文件,通常都是jpg格式。
- Annotations:这个文件夹包含每张图片对应的标注文件。每个标注文件都是xml格式的,其中包含了图片中每个对象的信息,如类别、位置等。
格式如下:
<annotation>
<folder>图像文件所在文件夹名称</folder>
<filename>图像文件名</filename>
<source>...省略...</source>
<size>
<width>图像宽度</width>
<height>图像高度</height>
<depth>图像深度,例如RGB图像深度为3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>省略...</segmented>
<object>
<name>物体类别名称</name>
<pose>省略...</pose>
<truncated>是否被截断(0表示未被截断,1表示被截断)</truncated>
<difficult>是否难以识别(0表示容易识别,1表示难以识别)</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>物体边界框左上角的x坐标</xmin>
<ymin>物体边界框左上角的y坐标</ymin>
<xmax>物体边界框右下角的x坐标</xmax>
<ymax>物体边界框右下角的y坐标</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
...其他物体的标注信息...
</annotation>在标注文件中,可以包含多个<object>标签,每个标签都表示图片中的一个物体。每个物体的类别名称和位置信息都包含在这个标签中。位置信息通过一个矩形边界框来表示,该框由左上角和右下角的坐标确定。
2.YOLO数据格式
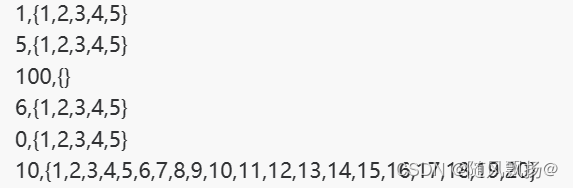
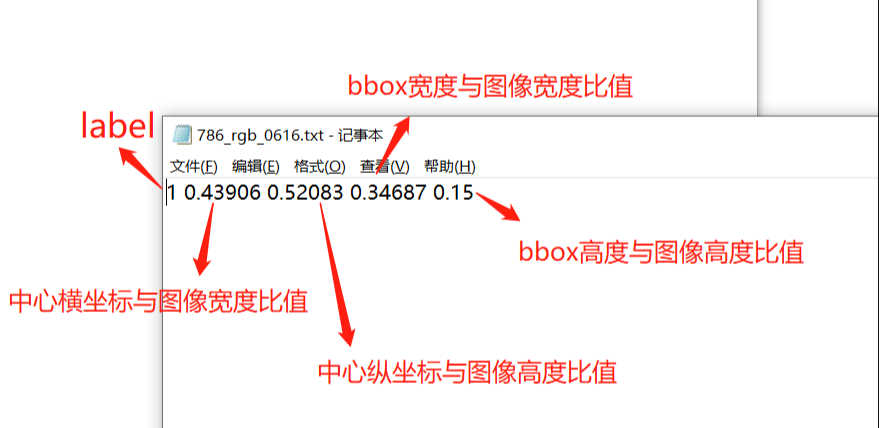
数据格式:label_index,cx, cy,w,h
label_index :为标签名称在标签数组中的索引,下标从 0 开始。
cx:标记框中心点的 x 坐标,数值是原始中心点 x 坐标除以 图宽 后的结果。
cy:标记框中心点的 y 坐标,数值是原始中心点 y 坐标除以 图高 后的结果。
w:标记框的 宽,数值为 原始标记框的 宽 除以 图宽 后的结果。
h:标记框的 高,数值为 原始标记框的 高 除以 图高 后的结果。
xml转txt
import os
import glob
import argparse
import random
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
def get_all_classes(xml_path):
xml_fns = glob.glob(os.path.join(xml_path, '*.xml'))
class_names = []
for xml_fn in xml_fns:
tree = ET.parse(xml_fn)
root = tree.getroot()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
cls = obj.find('name').text
class_names.append(cls)
return sorted(list(set(class_names)))
def convert_annotation(img_path, xml_path, class_names, out_path):
output = []
im_fns = glob.glob(os.path.join(img_path, '*.jpg'))
for im_fn in tqdm(im_fns):
if os.path.getsize(im_fn) == 0:
continue
xml_fn = os.path.join(xml_path, os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(im_fn))[0] + '.xml')
if not os.path.exists(xml_fn):
continue
img = Image.open(im_fn)
height, width = img.height, img.width
tree = ET.parse(xml_fn)
root = tree.getroot()
anno = []
xml_height = int(root.find('size').find('height').text)
xml_width = int(root.find('size').find('width').text)
if height != xml_height or width != xml_width:
print((height, width), (xml_height, xml_width), im_fn)
continue
for obj in root.iter('object'):
cls = obj.find('name').text
cls_id = class_names.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
xmin = int(xmlbox.find('xmin').text)
ymin = int(xmlbox.find('ymin').text)
xmax = int(xmlbox.find('xmax').text)
ymax = int(xmlbox.find('ymax').text)
cx = (xmax + xmin) / 2.0 / width
cy = (ymax + ymin) / 2.0 / height
bw = (xmax - xmin) * 1.0 / width
bh = (ymax - ymin) * 1.0 / height
anno.append('{} {} {} {} {}'.format(cls_id, cx, cy, bw, bh))
if len(anno) > 0:
output.append(im_fn)
with open(im_fn.replace('.jpg', '.txt'), 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(anno))
random.shuffle(output)
train_num = int(len(output) * 0.9)
with open(os.path.join(out_path, 'train.txt'), 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(output[:train_num]))
with open(os.path.join(out_path, 'val.txt'), 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(output[train_num:]))
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('generate annotation')
parser.add_argument('--img_path', type=str, help='input image directory',default= "data/jpg/")
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', type=str, help='input xml directory',default= "data/xml/")
parser.add_argument('--out_path', type=str, help='output directory',default= "data/dataset/")
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = parse_args()
class_names = get_all_classes(args.xml_path)
print(class_names)
convert_annotation(args.img_path, args.xml_path, class_names, args.out_path)
txt转xml
from xml.dom.minidom import Document
import os
import cv2
def makexml(picPath, txtPath, xmlPath): # txt所在文件夹路径,xml文件保存路径,图片所在文件夹路径
dic = {'0': "ship", # 创建字典用来对类型进行转换
'1': "car_trucks", # 此处的字典要与自己的classes.txt文件中的类对应,且顺序要一致
'2' :'person',
'3': 'stacking_area',
'4': 'car_forklift',
'5': 'unload_car',
'6': 'load_car',
'7': 'car_private',
}
files = os.listdir(txtPath)
for i, name in enumerate(files):
xmlBuilder = Document()
annotation = xmlBuilder.createElement("annotation") # 创建annotation标签
xmlBuilder.appendChild(annotation)
txtFile = open(txtPath + name)
print(txtFile)
txtList = txtFile.readlines()
img = cv2.imread(picPath + name[0:-4] + ".png")
Pheight, Pwidth, Pdepth = img.shape
folder = xmlBuilder.createElement("folder") # folder标签
foldercontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("driving_annotation_dataset")
folder.appendChild(foldercontent)
annotation.appendChild(folder) # folder标签结束
filename = xmlBuilder.createElement("filename") # filename标签
filenamecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(name[0:-4] + ".png")
filename.appendChild(filenamecontent)
annotation.appendChild(filename) # filename标签结束
size = xmlBuilder.createElement("size") # size标签
width = xmlBuilder.createElement("width") # size子标签width
widthcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pwidth))
width.appendChild(widthcontent)
size.appendChild(width) # size子标签width结束
height = xmlBuilder.createElement("height") # size子标签height
heightcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pheight))
height.appendChild(heightcontent)
size.appendChild(height) # size子标签height结束
depth = xmlBuilder.createElement("depth") # size子标签depth
depthcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pdepth))
depth.appendChild(depthcontent)
size.appendChild(depth) # size子标签depth结束
annotation.appendChild(size) # size标签结束
for j in txtList:
oneline = j.strip().split(" ")
object = xmlBuilder.createElement("object") # object 标签
picname = xmlBuilder.createElement("name") # name标签
namecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(dic[oneline[0]])
picname.appendChild(namecontent)
object.appendChild(picname) # name标签结束
pose = xmlBuilder.createElement("pose") # pose标签
posecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("Unspecified")
pose.appendChild(posecontent)
object.appendChild(pose) # pose标签结束
truncated = xmlBuilder.createElement("truncated") # truncated标签
truncatedContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
truncated.appendChild(truncatedContent)
object.appendChild(truncated) # truncated标签结束
difficult = xmlBuilder.createElement("difficult") # difficult标签
difficultcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
difficult.appendChild(difficultcontent)
object.appendChild(difficult) # difficult标签结束
bndbox = xmlBuilder.createElement("bndbox") # bndbox标签
xmin = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmin") # xmin标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[1])) * Pwidth + 1) - (float(oneline[3])) * 0.5 * Pwidth)
xminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
xmin.appendChild(xminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmin) # xmin标签结束
ymin = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymin") # ymin标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[2])) * Pheight + 1) - (float(oneline[4])) * 0.5 * Pheight)
yminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
ymin.appendChild(yminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymin) # ymin标签结束
xmax = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmax") # xmax标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[1])) * Pwidth + 1) + (float(oneline[3])) * 0.5 * Pwidth)
xmaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
xmax.appendChild(xmaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmax) # xmax标签结束
ymax = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymax") # ymax标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[2])) * Pheight + 1) + (float(oneline[4])) * 0.5 * Pheight)
ymaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
ymax.appendChild(ymaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymax) # ymax标签结束
object.appendChild(bndbox) # bndbox标签结束
annotation.appendChild(object) # object标签结束
f = open(xmlPath + name[0:-4] + ".xml", 'w')
xmlBuilder.writexml(f, indent='\t', newl='\n', addindent='\t', encoding='utf-8')
f.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
picPath = "data/images/" # 图片所在文件夹路径,后面的/一定要带上
txtPath = "data/labels/" # txt所在文件夹路径,后面的/一定要带上
xmlPath = "data/xml/" # xml文件保存路径,后面的/一定要带上
makexml(picPath, txtPath, xmlPath)
json转txt
import os
import numpy as np
import json
from glob import glob
import cv2
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from os import getcwd
classes = ["0","1","2"]
# 1.标签路径
labelme_path = r"dataset/"
isUseTest = False # 是否创建test集
# 3.获取待处理文件
files = glob(labelme_path + "*.json")
files = [i.replace("\\", "/").split("/")[-1].split(".json")[0] for i in files]
# print(files)
if isUseTest:
trainval_files, test_files = train_test_split(files, test_size=0.1, random_state=55)
else:
trainval_files = files
train_files = files
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
wd = getcwd()
# print(wd)
def ChangeToYolo5(files, txt_Name):
if not os.path.exists('tmp/'):
os.makedirs('tmp/')
list_file = open('tmp/%s.txt' % (txt_Name), 'w')
for json_file_ in files:
print(json_file_)
json_filename = labelme_path + json_file_ + ".json"
imagePath = labelme_path + json_file_ + ".png"
list_file.write('%s/%s\n' % (wd, imagePath))
out_file = open('%s/%s.txt' % (labelme_path, json_file_), 'w')
json_file = json.load(open(json_filename, "r", encoding="utf-8"))
height, width, channels = cv2.imread(labelme_path + json_file_ + ".png").shape
for multi in json_file["shapes"]:
points = np.array(multi["points"])
xmin = min(points[:, 0]) if min(points[:, 0]) > 0 else 0
xmax = max(points[:, 0]) if max(points[:, 0]) > 0 else 0
ymin = min(points[:, 1]) if min(points[:, 1]) > 0 else 0
ymax = max(points[:, 1]) if max(points[:, 1]) > 0 else 0
label = multi["label"]
if xmax <= xmin:
pass
elif ymax <= ymin:
pass
else:
cls_id = classes.index(label)
b = (float(xmin), float(xmax), float(ymin), float(ymax))
bb = convert((width, height), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
print(json_filename, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, cls_id)
ChangeToYolo5(train_files, "train")