在Spring Boot中,可以通过多种方式实现多数据源的动态切换效果,本篇介绍第一种实现方案。
一 AbstractRoutingDataSource
Spring Boot提供了org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource 这个类,其中#determineCurrentLookupKey方法可以让用户根据自己定义的规则在某一个SQL执行之前动态地选择想要的数据源。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | /** * Determine the current lookup key. This will typically be * implemented to check a thread-bound transaction context. * <p>Allows for arbitrary keys. The returned key needs * to match the stored lookup key type, as resolved by the * {@link #resolveSpecifiedLookupKey} method. */ @Nullable protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey(); |
因此,我们的整体实现逻辑就很清晰了,具体分为以下几个步骤:
-
定义
DynamicRoutingDataSource类,继承AbstractRoutingDataSource类并实现#determineCurrentLookupKey方法(具体逻辑是从当前线程的ThreadLocal中获取我们在某一个SQL执行之前通过AOP切面动态指定的数据源名称); -
在
application.yml中配置多个数据源; -
解析在
application.yml中配置的多个数据源,然后生成DynamicRoutingDataSource实例,并设置默认数据源(defaultTargetDataSource)和其他数据源(targetDataSources); -
调用
AbstractRoutingDataSource的#getConnection的方法的时候,会先调用#determineTargetDataSource方法获取具体的数据源,而在这个方法中会进一步调用我们在DynamicRoutingDataSource类中自定义的#determineCurrentLookupKey方法,最后在返回DataSource后再进行#getConnection的调用。显然,剩下就是具体的SQL逻辑执行了。
二 具体实现
(1)测试使用的数据库
这里我们创建3个数据库,分别是:db01、db02、db03,然后这3个数据库都有一张名为user_info的表,表结构一样,只是数据不同。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | -- 建表语句 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user_info`; CREATE TABLE `user_info` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'ID', `name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名', `age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄', `addr_city` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '所在城市', `addr_district` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '所在区', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- db01中表「user_info」的数据 INSERT INTO `user_info` VALUES ('1', '张三', '20', '北京', '朝阳区'); INSERT INTO `user_info` VALUES ('2', '李四', '18', '北京', '东城区'); -- db02中表「user_info」的数据 INSERT INTO `user_info` VALUES ('1', '王五', '22', '上海', '普陀区'); INSERT INTO `user_info` VALUES ('2', '赵六', '24', '上海', '浦东新区'); -- db03中表「user_info」的数据 INSERT INTO `user_info` VALUES ('1', '孙七', '28', '成都', '武侯区'); INSERT INTO `user_info` VALUES ('2', '周八', '26', '成都', '天府新区'); |
(2)动态切换数据源的上下文
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; /** * 动态切换数据源的上下文 * */ @Slf4j public class DynamicDataSourceContext { /** * 所有配置过的数据源的KEY */ public static List<String> dataSourceKeys = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); /** * 默认数据源的KEY */ public static String defaultDataSourceKey; /** * 当前SQL执行之前,在{@link ThreadLocal}中设置的数据源的KEY */ private static final ThreadLocal<String> RESOURCE = new ThreadLocal<>(); /** * 获取「当前在{@link ThreadLocal}中设置的数据源的KEY」 */ public static String getRoutingDataSourceKey(){ return RESOURCE.get(); } /** * 获取「当前在{@link ThreadLocal}中设置的数据源的KEY」 */ public static void setRoutingDataSourceKey(String routingDataSourceKey){ log.debug("切换至「{}」数据源", routingDataSourceKey); RESOURCE.set(routingDataSourceKey); } /** * 动态路由完成之后,清空设置的数据源的KEY */ public static void clearRoutingDataSourceKey(){ RESOURCE.remove(); } /** * 添加配置过的数据源的KEY */ public static void addDataSourceKey(String dataSourceKey, boolean ifDefaultDataSourceKey){ dataSourceKeys.add(dataSourceKey); if(ifDefaultDataSourceKey){ defaultDataSourceKey = dataSourceKey; } } /** * 判断是否已经配置某个数据源 */ public static boolean containsDataSource(String dataSourceKey){ return dataSourceKeys.contains(dataSourceKey); } } |
(3)定义DynamicRoutingDataSource类
主要是继承AbstractRoutingDataSource类并实现#determineCurrentLookupKey方法,其具体逻辑是从当前线程的ThreadLocal中获取我们在某一个SQL执行之前通过AOP切面动态指定的数据源名称。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; /** * 动态数据源路由配置 * */ @Slf4j public class DynamicRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { //如果 currentDataSourceKey 为null,则调用方「#determineTargetDataSource」方法会在当前方法返回null之后自动使用默认数据源 String currentDataSourceKey = DynamicDataSourceContext.getRoutingDataSourceKey(); log.debug("当前使用的数据源是:「{}」(这里为null表示使用的是默认数据源)", currentDataSourceKey); return currentDataSourceKey; } } |
(4)新增application-datasource.yml配置文件
新建这个用于测试的配置文件,主要配置了接下来需要用到的多个数据源,其关键配置如下:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | spring: datasource: master: type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db01?autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&failOverReadOnly=false&useSSL=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai username: root password: root # HikariCP 连接池配置 hikari: pool-name: db01_HikariCP minimum-idle: 5 #最小空闲连接数量 idle-timeout: 30000 #空闲连接存活最大时间,默认600000(10分钟) maximum-pool-size: 20 #连接池最大连接数,默认是10 auto-commit: true #此属性控制从池返回的连接的默认自动提交行为,默认值:true max-lifetime: 1800000 #此属性控制池中连接的最长生命周期,值0表示无限生命周期,默认1800000即30分钟 connection-timeout: 30000 #数据库连接超时时间,默认30秒,即30000 cluster: - key: db02 type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db02?autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&failOverReadOnly=false&useSSL=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai username: root password: root # HikariCP 连接池配置 hikari: pool-name: db02_HikariCP minimum-idle: 5 #最小空闲连接数量 idle-timeout: 30000 #空闲连接存活最大时间,默认600000(10分钟) maximum-pool-size: 20 #连接池最大连接数,默认是10 auto-commit: true #此属性控制从池返回的连接的默认自动提交行为,默认值:true max-lifetime: 1800000 #此属性控制池中连接的最长生命周期,值0表示无限生命周期,默认1800000即30分钟 connection-timeout: 30000 #数据库连接超时时间,默认30秒,即30000 - key: db03 type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db03?autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&failOverReadOnly=false&useSSL=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai username: root password: root # HikariCP 连接池配置 hikari: pool-name: db03_HikariCP minimum-idle: 5 #最小空闲连接数量 idle-timeout: 30000 #空闲连接存活最大时间,默认600000(10分钟) maximum-pool-size: 20 #连接池最大连接数,默认是10 auto-commit: true #此属性控制从池返回的连接的默认自动提交行为,默认值:true max-lifetime: 1800000 #此属性控制池中连接的最长生命周期,值0表示无限生命周期,默认1800000即30分钟 connection-timeout: 30000 #数据库连接超时时间,默认30秒,即30000 |
(5)解析在application-datasource.yml中配置的多个数据源
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource; import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.GenericBeanDefinition; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.Bindable; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.Binder; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.source.ConfigurationPropertyName; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.source.ConfigurationPropertyNameAliases; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.source.MapConfigurationPropertySource; import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; /** * 动态数据源注册 * <p>实现{@link [email protected]�</p> * <p>实现{@link EnvironmentAware}目的是读取 application-datasource.yml 配置</p> * */ @Slf4j public class DynamicDataSourceRegister implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, EnvironmentAware { /** * 别名 */ private final static ConfigurationPropertyNameAliases ALIASES = new ConfigurationPropertyNameAliases(); //由于部分数据源配置不同,所以在此处添加别名,避免切换数据源出现某些参数无法注入的情况 static { ALIASES.addAliases("url", "jdbc-url"); ALIASES.addAliases("username", "user"); }
/** * 参数绑定工具 */ private Binder binder; @Override public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) { this.binder = Binder.get(environment); } @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { log.info("开始注册多个数据源"); //1. 注册默认数据源 //1.1 获取默认数据源参数 Map defaultDataSourceProperties = this.binder.bind("spring.datasource.master", Map.class).get(); //1.2 获取默认数据源类型 String defaultDataSourceType = defaultDataSourceProperties.get("type").toString(); Class<? extends DataSource> defaultDataSourceClazz = this.getDataSourceType(defaultDataSourceType); //1.3 绑定默认数据源参数 DataSource defaultDataSource = this.bind(defaultDataSourceClazz, defaultDataSourceProperties); //1.4 将其添加到「动态切换数据源的上下文」中 DynamicDataSourceContext.addDataSourceKey("master", true); log.info("注册默认数据源「master」成功"); //2. 注册其他数据源 Map<String, DataSource> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>(); List<Map> slaveDataSourcePropertiesList = this.binder.bind("spring.datasource.cluster", Bindable.listOf(Map.class)).get(); if(slaveDataSourcePropertiesList != null && slaveDataSourcePropertiesList.size() > 0){ //2.1 获取某一数据源参数 for(Map dataSourceProperties : slaveDataSourcePropertiesList){ //2.2 获取数据源类型 String dataSourceType = dataSourceProperties.get("type").toString(); Class<? extends DataSource> dataSourceClazz = this.getDataSourceType(dataSourceType); //2.3 绑定数据源参数 DataSource dataSource = this.bind(dataSourceClazz, dataSourceProperties); //2.4 获取数据源的KEY,并将其添加到「动态切换数据源的上下文」和「targetDataSources」中 String dataSourceKey = dataSourceProperties.get("key").toString(); DynamicDataSourceContext.addDataSourceKey(dataSourceKey, false); targetDataSources.put(dataSourceKey, dataSource); log.info("注册数据源「{}」成功", dataSourceKey); } } //3. 实例化 DynamicRoutingDataSource Bean //3.1 bean定义 GenericBeanDefinition definition = new GenericBeanDefinition(); definition.setBeanClass(DynamicRoutingDataSource.class); //3.2 注入需要的参数 MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = definition.getPropertyValues(); propertyValues.add("defaultTargetDataSource", defaultDataSource); propertyValues.add("targetDataSources", targetDataSources); //3.3 将该bean注册为datasource,不使用springboot自动生成的datasource registry.registerBeanDefinition("datasource", definition); log.info("注册数据源成功,一共注册「{}」个数据源", targetDataSources.keySet().size() + 1); } /** * 通过数据源字符串获取数据源Class对象 */ private Class<? extends DataSource> getDataSourceType(String dataSourceType){ Class<? extends DataSource> type; try { if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(dataSourceType)){ //如果字符串不为空,则通过反射获取class对象 type = (Class<? extends DataSource>) Class.forName(dataSourceType); }else { //否则设置为默认的 HikariCP 连接池 type = HikariDataSource.class; } return type; } catch (Exception e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("can not resolve class with type: " + dataSourceType); } } /** * 通过类型绑定参数并获得实例对象 */ private <T extends DataSource> T bind(Class<T> clazz, Map properties){ MapConfigurationPropertySource propertySource = new MapConfigurationPropertySource(properties); Binder binder = new Binder(propertySource.withAliases(ALIASES)); //通过类型绑定参数并获得实例对象 return binder.bind(ConfigurationPropertyName.EMPTY, Bindable.of(clazz)).get(); } } |
(6)通过AOP+注解实现数据源的动态切换
i)在pom.xml文件中添加切面需要的依赖:
| 1 2 3 4 | <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency> |
ii)新增一个用于切换数据源的注解:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource; import java.lang.annotation.*; /** * 用于动态切换数据源的注解(优先级:方法级别 > 类级别) */ @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface DataSource { String value() default "master"; } |
iii)定义一个AOP的通知类:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /** * 基于注解拦截后的通知 * */ @Slf4j public class AnnotationInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { /** * 缓存方法对应的注解值 */ private Map<Method, DataSource> methodCacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable { try { String dataSource = this.determineDataSource(methodInvocation); if(dataSource == null || !DynamicDataSourceContext.containsDataSource(dataSource)){ String defaultDataSource = DynamicDataSourceContext.defaultDataSourceKey; log.error("数据源「{}」不存在,即将使用默认数据源「{}」。", dataSource, defaultDataSource); dataSource = defaultDataSource; } DynamicDataSourceContext.setRoutingDataSourceKey(dataSource); return methodInvocation.proceed(); }finally { DynamicDataSourceContext.clearRoutingDataSourceKey(); } } /** * 获取用于动态切换数据源的注解 */ private String determineDataSource(MethodInvocation invocation){ Method method = invocation.getMethod(); if(this.methodCacheMap.containsKey(method)){ return this.methodCacheMap.get(method).value(); }else{ DataSource dataSource = method.isAnnotationPresent(DataSource.class) ? //从当前方法获取 DataSource 注解 method.getAnnotation(DataSource.class) : //如果获取不到,则尝试从当前方法所在类或者接口级别获取 AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method.getDeclaringClass(), DataSource.class); this.methodCacheMap.put(method, dataSource); return (dataSource != null) ? dataSource.value() : null; } } } |
iv)定义一个Advisor,将通知注入到指定的切点:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource; import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice; import org.springframework.aop.Pointcut; import org.springframework.aop.support.AbstractPointcutAdvisor; import org.springframework.aop.support.ComposablePointcut; import org.springframework.aop.support.annotation.AnnotationMatchingPointcut; /** * 将通知注入到指定的切点 * */ public class AnnotationAdvisor extends AbstractPointcutAdvisor { private Advice advice; private Pointcut pointcut; public AnnotationAdvisor(AnnotationInterceptor annotationInterceptor) { this.advice = annotationInterceptor; this.pointcut = this.buildPointcut(); } @Override public Advice getAdvice() { return this.advice; } @Override public Pointcut getPointcut() { return this.pointcut; } /** * 定义AOP的切点范围 */ private Pointcut buildPointcut(){ //类注解,包括超类和接口 Pointcut classPointcut = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(DataSource.class, true); //方法注解 Pointcut methodPointcut = AnnotationMatchingPointcut.forMethodAnnotation(DataSource.class); return new ComposablePointcut(classPointcut).union(methodPointcut); } } |
v)导入上面的数据源配置,以及启动切面:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.config; import cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource.AnnotationAdvisor; import cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource.AnnotationInterceptor; import cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource.DynamicDataSourceRegister; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; /** * 动态切换数据源配置 * */ @Import(DynamicDataSourceRegister.class) @Configuration public class DynamicDataSourceConfig { @Bean public AnnotationAdvisor annotationAdvisor(){ return new AnnotationAdvisor(new AnnotationInterceptor()); } } |
三 效果测试
(1)新建两个测试使用的Mapper
UserInfoMapper为插件自动生成,没有添加我们自定义的@DataSource注解,用于测试不添加注解的情况下默认使用的数据源。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.mapper; import cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.model.UserInfo; public interface UserInfoMapper { int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer id); int insert(UserInfo record); int insertSelective(UserInfo record); UserInfo selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id); int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(UserInfo record); int updateByPrimaryKey(UserInfo record); } |
UserInfoDynamicMapper为手动新建的几个方法,用于测试数据源的动态切换效果。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.mapper; import cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource.DataSource; import cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.model.UserInfo; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; @DataSource("db02") public interface UserInfoDynamicMapper { /** * 通过默认数据源查询,方法级别的注解优先级更高 */ @DataSource UserInfo selectByDefaultDataSource(Integer id); /** * 方法级别没有添加注解,则使用接口级别的注解,通过 db02 数据源查询 */ UserInfo selectByDB02DataSource(Integer id); /** * 通过 db03 数据源查询 */ @DataSource("db03") UserInfo selectByDB03DataSource(Integer id); /** * 测试事务是否回滚(数据插入 db02 数据源) */ @DataSource("db02") int addToDB02(UserInfo record); /** * 测试事务是否回滚(数据插入 db03 数据源) */ @DataSource("db03") int addToDB03(UserInfo record); /** * 从 db03 数据源删除数据 */ @DataSource("db03") int deleteFromDB03ByName(@Param("name") String name); } |
其对应的UserInfoDynamicMapper.xml文件是:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.mapper.UserInfoDynamicMapper"> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.model.UserInfo"> <id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id" /> <result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name" /> <result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age" /> <result column="addr_city" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="addrCity" /> <result column="addr_district" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="addrDistrict" /> </resultMap> <sql id="Base_Column_List"> id, `name`, age, addr_city, addr_district </sql> <select id="selectByDefaultDataSource" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap"> select <include refid="Base_Column_List" /> from user_info where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER} </select> <select id="selectByDB02DataSource" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap"> select <include refid="Base_Column_List" /> from user_info where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER} </select> <select id="selectByDB03DataSource" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap"> select <include refid="Base_Column_List" /> from user_info where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER} </select> <insert id="addToDB02" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" parameterType="cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.model.UserInfo" useGeneratedKeys="true"> insert into user_info (`name`, age, addr_city, addr_district) values (#{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{age,jdbcType=INTEGER}, #{addrCity,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{addrDistrict,jdbcType=VARCHAR}) </insert> <insert id="addToDB03" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" parameterType="cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.model.UserInfo" useGeneratedKeys="true"> insert into user_info (`name`, age, addr_city, addr_district) values (#{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{age,jdbcType=INTEGER}, #{addrCity,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{addrDistrict,jdbcType=VARCHAR}) </insert> <delete id="deleteFromDB03ByName" parameterType="java.lang.String"> delete from user_info where name = #{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </delete> </mapper> |
(2)使用单元测试测试「动态切换数据源」的效果
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 | package cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.dataSource; import cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.mapper.UserInfoDynamicMapper; import cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.mapper.UserInfoMapper; import cn.zifangsky.example.webexercise.model.UserInfo; import org.junit.jupiter.api.*; import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * 测试动态切换数据源 * */ @DisplayName("测试动态切换数据源") @TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class) @ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class) @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) public class DynamicDataSourceTest { @Autowired private UserInfoMapper userInfoMapper; @Autowired private UserInfoDynamicMapper userInfoDynamicMapper; @Test @Order(1) @DisplayName("普通方法——使用默认数据源") public void testCommonMethod(){ UserInfo userInfo = userInfoMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1); Assertions.assertNotNull(userInfo); Assertions.assertEquals("张三", userInfo.getName()); } @Test @Order(2) @DisplayName("通过默认数据源查询,方法级别的注解优先级更高") public void testSelectByDefaultDataSource(){ UserInfo userInfo = userInfoDynamicMapper.selectByDefaultDataSource(1); Assertions.assertNotNull(userInfo); Assertions.assertEquals("张三", userInfo.getName()); } @Test @Order(3) @DisplayName("方法级别没有添加注解,则使用接口级别的注解,通过 db02 数据源查询") public void testSelectByDB02DataSource(){ UserInfo userInfo = userInfoDynamicMapper.selectByDB02DataSource(1); Assertions.assertNotNull(userInfo); Assertions.assertEquals("王五", userInfo.getName()); } @Test @Order(4) @DisplayName("方法级别添加注解,手动指定通过 db03 数据源查询") public void testSelectByDB03DataSource(){ UserInfo userInfo = userInfoDynamicMapper.selectByDB03DataSource(1); Assertions.assertNotNull(userInfo); Assertions.assertEquals("孙七", userInfo.getName()); } @Test @Order(5) @DisplayName("在一个方法执行过程中嵌套操作多个数据源的情况") public void testNestedMultiDataSource(){ //1. 从 db02 查询一条数据 UserInfo userInfo = userInfoDynamicMapper.selectByDB02DataSource(1); //2. 插入到 db03 userInfo.setId(null); userInfoDynamicMapper.addToDB03(userInfo); } @Test @Order(6) @DisplayName("从 db03 数据源删除数据") public void testDeleteFromDB03ByName(){ userInfoDynamicMapper.deleteFromDB03ByName("王五"); } @Test @Order(7) @DisplayName("嵌套多个数据源的事务回滚情况") @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) public void testTransaction() throws SQLException { //1. 从 db01 查询一条数据 UserInfo userInfo = userInfoDynamicMapper.selectByDefaultDataSource(1); //2. 分别插入到 db02 和 db03 userInfo.setId(null); userInfoDynamicMapper.addToDB02(userInfo); userInfoDynamicMapper.addToDB03(userInfo); //3. 手动抛出一个异常,测试事务回滚效果 throw new SQLException("SQL执行过程中发生某些未知异常"); } } |
注:以上测试代码基于Junit5 测试框架编写,需要的依赖如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
运行单元测试后,测试效果如下:
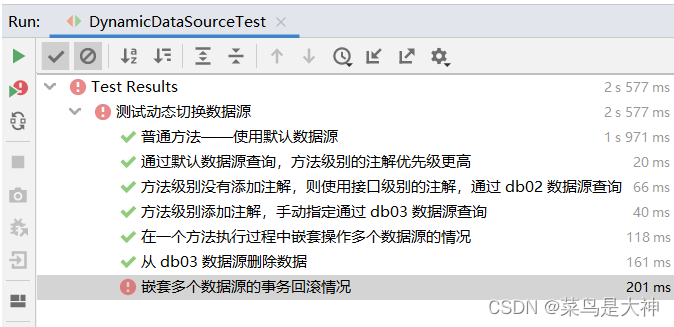
可以发现,除了最后手动抛出一个异常的方法,其他几个方法都测试通过了。然后,通过查询数据库中的数据还可以发现,事务做了我们预期效果的回滚,因此本篇文章介绍的「多数据源动态切换」方案是可行的。





![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Djangoospringboot作业管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8a78827d55934b51a1678112870d5095.png)



![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计医疗器械销售电子商城(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f7532c2fbe324aab9293f275647982f8.png)