论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.07148
代码地址:https://github.com/liuwei1206/LEBERT
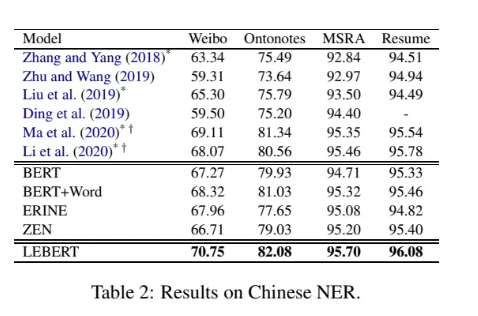
模型创新
- LEBRT采用句子中的词语对(论文中称为Char-Word Pair)的特征作为输入
- 作者设计Lexicon adapter,在BERT的中间某一层注入词汇特征
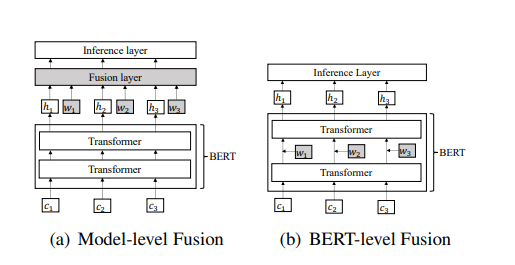
-
左图是在BERT之后的架构上面引入词汇信息
-
右图是在BERT底层时引入词汇信息
Char-Word Pair
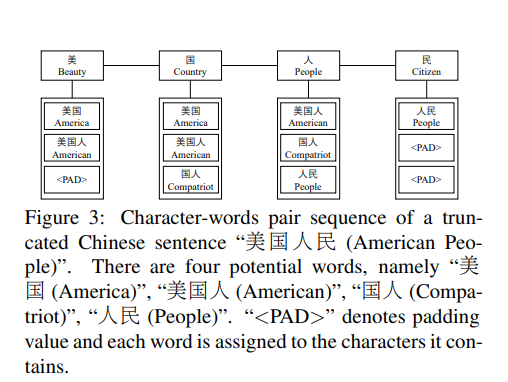
首先,对于给定的中文句子
s
c
=
{
c
1
,
c
2
,
.
.
.
,
c
n
}
c
i
代表句子中的第
i
个字符
s_c = \{c_1,c_2,...,c_n\}\quad c_i代表句子中的第i个字符
sc={c1,c2,...,cn}ci代表句子中的第i个字符
利用词典D匹配出句子中包含的潜在词汇(这里设定最多匹配出相关性最强的三个,不足三个则用PAD填充)。然后,每个字符和包含该字符的词汇组成词汇对,表示为
s
c
w
=
{
(
c
1
,
w
s
1
)
,
(
c
2
,
w
s
2
)
,
.
.
.
,
(
c
n
,
w
s
n
)
}
w
s
i
表示包含
c
i
词汇组成的集合
s_{cw} = \{(c_1,ws_1),(c_2,ws_2),...,(c_n,ws_n)\}\quad ws_i表示包含c_i词汇组成的集合
scw={(c1,ws1),(c2,ws2),...,(cn,wsn)}wsi表示包含ci词汇组成的集合
此时就构成了Char-Words Pair Sequence
Lexicon adapter
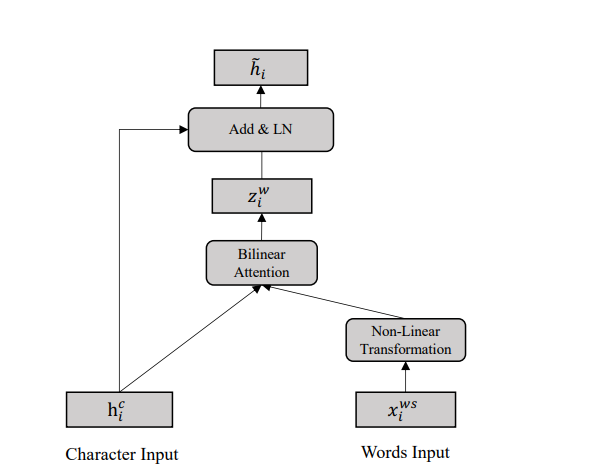
将输入数据构建成Char-Words Pair Sequence后,句子中的每个位置包含了字符特征和词汇特征,为了把词汇特征注入到BERT中,作者设计了Lexicon adapter
Char-Words Pair Sequence中的第i个位置char-words pair表示为 ( h i c , x i w s ) (h_i^c,x_i^{ws}) (hic,xiws)
- h i c h_i^c hic:第i个位置的字符特征,该特征是BERT的某个Transformer层的输出
- x i w s = { x i 1 w , x i 2 w , . . . , x i m w } x_i^{ws} = \{x_{i1}^w,x_{i2}^w,...,x_{im}^w\} xiws={xi1w,xi2w,...,ximw} :第i个位置字符对应m个词汇的词向量
对词向量使用非线性变换,以至于和字符向量进行维度对齐
v
i
j
w
=
W
2
(
t
a
n
h
(
W
1
x
i
j
w
+
b
1
)
)
+
b
2
j
=
1
,
.
.
.
,
m
v_{ij}^w = W_2(tanh(W_1x_{ij}^w + b_1)) + b_2\quad\quad j=1,...,m
vijw=W2(tanh(W1xijw+b1))+b2j=1,...,m
- d c d_c dc:字符特征维度
- d w d_w dw:词向量维度
- W 1 ∈ R d c ∗ d w W_1\in R ^{d_c*d_w} W1∈Rdc∗dw
- W 2 ∈ R d c ∗ d c W_2\in R ^{d_c*d_c} W2∈Rdc∗dc
- v i j w ∈ R d c v_{ij}^w \in R^{d_c} vijw∈Rdc
此时,对于Char-Words Pair Sequence中的第i个位置,进行维度变换后的词向量集合为
V
i
=
(
v
i
1
w
,
.
.
.
,
v
i
m
w
)
∈
R
m
∗
d
c
V_i = (v_{i1}^w,...,v_{im}^w)\in R^{m*d_c}
Vi=(vi1w,...,vimw)∈Rm∗dc
此时,使用注意力机制对
V
i
V_i
Vi中的m个词向量进行融合
a
i
=
s
o
f
t
m
a
x
(
h
i
c
W
a
t
t
n
V
i
T
)
a_i = softmax(h_i^cW_{attn}V_i^T)
ai=softmax(hicWattnViT)
- h i c h_i^c hic:为query向量
- V i V_i Vi:为value
- a i a_i ai:使用双线性变换矩阵计算相似度得分得到
之后,再利用相似度得分对
V
i
V_i
Vi进行加权求和得到融合后词特征:
z
i
w
=
∑
j
=
1
m
a
i
j
v
i
j
w
z_i^w = \sum_{j=1}^m a_{ij}v_{ij}^w
ziw=j=1∑maijvijw
最后,再把字符特征和融合后的词特征相加得到:
h
^
i
=
h
i
c
+
z
i
w
\hat h_i^ = h_i^c + z_i^w
h^i=hic+ziw
Lexicon Enhanced BERT
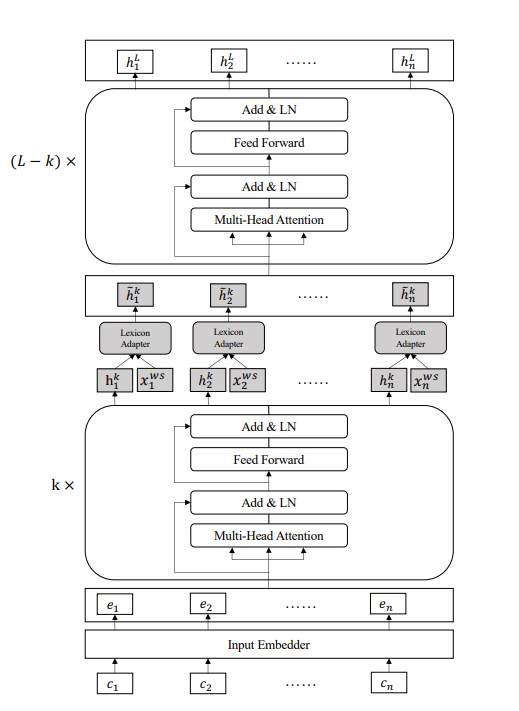
对于给定的中文句子
s
c
=
{
c
1
,
c
2
,
.
.
.
,
c
n
}
s_c = \{c_1,c_2,...,c_n\}
sc={c1,c2,...,cn},将其构建成character-words pair sequence形式
s
c
w
=
{
(
c
1
,
w
s
1
)
,
(
c
2
,
w
s
2
)
,
.
.
.
,
(
c
n
,
w
s
n
)
}
s_{cw} = \{(c_1,ws_1),(c_2,ws_2),...,(c_n,ws_n)\}
scw={(c1,ws1),(c2,ws2),...,(cn,wsn)}
将
{
c
1
,
c
2
,
.
.
.
,
c
n
}
\{c_1,c_2,...,c_n\}
{c1,c2,...,cn}输入到BERT的Input Embedder当中,得到输出
E
=
{
e
1
,
e
2
,
.
.
.
,
e
n
}
E = \{e_1,e_2,...,e_n\}
E={e1,e2,...,en},之后将E($H^0 = E $)输入到BERT的Transformer encoder中,每个Transformer encoder表示为如下形式:
$$
G &= Layernormalization(H^{l-1 } + Multiheadattention(H^{l-1}))\
H &= Layernormalization(G + FFN(G))
$$
之后,通过Lexicon Adapter把词汇信息注入到第k层和第k+1层的Transformer层之间
第k层Transformer层的输出为
H
k
=
{
h
1
k
,
h
2
k
,
.
.
.
,
h
n
k
}
H^k = \{h_1^k,h_2^k,...,h_n^k\}
Hk={h1k,h2k,...,hnk}。将其中的每一个Char-Words Pair(
h
i
k
,
x
i
w
s
h_i^k,x_i^{ws}
hik,xiws)利用Lexicon Adapter进行转化得到:
h
^
k
=
L
A
(
h
i
k
,
x
i
w
s
)
\hat h^k = LA(h_i^k,x_i^{ws})
h^k=LA(hik,xiws)
代码讲解
词向量处理
加载词向量(load_word_embedding)
input
- word_embed_path:词向量的路径,这里选取腾讯的tencent-ailab-embedding-zh-d200-v0.2.0-s.txt
- 词的个数为2000000,向量维度为200
- max_scan_num:最多加载多少个词向量
output
- word_embed_dict:每个词对应的词向量 200000 * 200
- word_list:词集合,2000000
- word_embed_dim:词的维度,200
@classmethod
def build_trie_tree(cls, word_list, save_path):
"""
# todo 是否不将单字加入字典树中
构建字典树
:return:
"""
logger.info('building trie tree')
trie_tree = Trie()
for word in word_list:
trie_tree.insert(word)
write_pickle(trie_tree, save_path)
return trie_tree
def load_word_embedding(cls, word_embed_path, max_scan_num):
"""
todo 存在许多单字的,考虑是否去掉
"""
logger.info('loading word embedding from pretrain')
word_embed_dict = dict()
word_list = list()
with open(word_embed_path, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f:
for idx, line in tqdm(enumerate(f)):
# 只扫描前max_scan_num个词向量
if idx > max_scan_num:
break
items = line.strip().split()
if idx == 0:
assert len(items) == 2
num_embed, word_embed_dim = items
num_embed, word_embed_dim = int(num_embed), int(word_embed_dim)
else:
assert len(items) == word_embed_dim + 1
word = items[0]
embedding = np.empty([1, word_embed_dim])
embedding[:] = items[1:]
word_embed_dict[word] = embedding
word_list.append(word)
logger.info('word_embed_dim:{}'.format(word_embed_dim))
logger.info('size of word_embed_dict:{}'.format(len(word_embed_dict)))
logger.info('size of word_list:{}'.format(len(word_list)))
return word_embed_dict, word_list, word_embed_dim
构建字典树(build_trie_tree)
input
- word_list:word_list:词集合,2000000
- save_path:字典树的保存路径(方便复用)
output
- trie_tree:字典树
@classmethod
def build_trie_tree(cls, word_list, save_path):
"""
# todo 是否不将单字加入字典树中
"""
logger.info('building trie tree')
trie_tree = Trie()
for word in word_list:
trie_tree.insert(word)
write_pickle(trie_tree, save_path)
return trie_tree
def write_pickle(x, path):
with open(path, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(x, f)
找到数据集中的所有单词(get_words_from_corpus)
input
- files:训练、验证、测试的文件路径
- save_file:文件保存路径
- trie_tree:字典树
output
- all_matched_words:找到了所有跟我们训练、验证、测试数据有关的所有词
@classmethod
def get_words_from_corpus(cls, files, save_file, trie_tree):
"""
找出文件中所有匹配的单词
"""
logger.info('getting words from corpus')
all_matched_words = set()
for file in files:
with open(file, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for idx in trange(len(lines)):
line = lines[idx].strip()
data = json.loads(line)
text = data['text']
matched_words = cls.get_words_from_text(text, trie_tree)
_ = [all_matched_words.add(word) for word in matched_words]
all_matched_words = list(all_matched_words)
all_matched_words = sorted(all_matched_words)
write_lines(all_matched_words, save_file)
return all_matched_words
@classmethod
def get_words_from_text(cls, text, trie_tree):
"""
找出text中所有的单词
"""
length = len(text)
matched_words_set = set() # 存储匹配到的单词
for idx in range(length):
sub_text = text[idx:idx + trie_tree.max_depth]
words = trie_tree.enumerateMatch(sub_text)
_ = [matched_words_set.add(word) for word in words]
matched_words_set = list(matched_words_set)
matched_words_set = sorted(matched_words_set)
return matched_words_set
def write_lines(lines, path, encoding='utf8'):
with open(path, 'w', encoding=encoding) as f:
for line in lines:
f.writelines('{}\n'.format(line))
初始化模型的词向量(init_model_word_embedding)
input
- corpus_words:所有跟我们训练、验证、测试数据有关的所有词
- word_embed_dict:每个词对应的词向量 200000 * 200
- save_embed_path:词向量的保存路径
- save_word_vocab_path:词表的保存保存
output
- model_word_embedding:模型的嵌入向量 --> 20857 * 200
- word_vocab:模型的词表 --> 20857
- embed_dim:嵌入维度 --> 200
def init_model_word_embedding(self, corpus_words, word_embed_dict, save_embed_path, save_word_vocab_path):
logger.info('initializing model word embedding')
# 构建单词和id的映射
word_vocab = Vocabulary(corpus_words, vocab_type='word')
# embed_dim = len(word_embed_dict.items()[1].size)
embed_dim = next(iter(word_embed_dict.values())).size
scale = np.sqrt(3.0 / embed_dim)
model_word_embedding = np.empty([word_vocab.size, embed_dim])
matched = 0
not_matched = 0
for idx, word in enumerate(word_vocab.idx2token):
if word in word_embed_dict:
model_word_embedding[idx, :] = word_embed_dict[word]
matched += 1
else:
model_word_embedding[idx, :] = np.random.uniform(-scale, scale, [1, embed_dim])
not_matched += 1
logger.info('num of match:{}, num of not_match:{}'.format(matched, not_matched))
write_pickle(model_word_embedding, save_embed_path)
write_pickle(word_vocab, save_word_vocab_path)
return model_word_embedding, word_vocab, embed_dim
数据加载格式
每个汉字对应的单词列表(get_char2words)
input:
- text:文本
output:
- char_index2words:文本中每个汉字所对应的词
def get_char2words(self, text):
"""
获取每个汉字,对应的单词列表
"""
text_len = len(text)
char_index2words = [[] for _ in range(text_len)]
for idx in range(text_len):
sub_sent = text[idx:idx + self.trie_tree.max_depth] # speed using max depth
words = self.trie_tree.enumerateMatch(sub_sent) # 找到以text[idx]开头的所有单词
for word in words:
start_pos = idx
end_pos = idx + len(word)
for i in range(start_pos, end_pos):
char_index2words[i].append(word)
return char_index2words
数据加载格式(collate)
output
- 特征输入为:
'text': text,
'input_ids': input_ids,
'attention_mask': input_mask,
'token_type_ids': token_type_ids,
'word_ids': word_ids,
'word_mask': word_mask,
'label_ids': label_ids
def get_input_data(self, file):
lines = load_lines(file)
features = []
cls_token_id = self.tokenizer.cls_token_id
sep_token_id = self.tokenizer.sep_token_id
pad_token_id = self.tokenizer.pad_token_id
o_label_id = self.label_vocab.convert_token_to_id('O')
pad_label_id = self.label_vocab.convert_token_to_id('[PAD]')
for line in tqdm(lines):
data = json.loads(line)
text = data['text']
labels = data['label']
char_index2words = self.get_char2words(text)
# 在开头与结尾分别添加[CLS]与[SEP]
input_ids = [cls_token_id] + self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(text) + [sep_token_id]
label_ids = [o_label_id] + self.label_vocab.convert_tokens_to_ids(labels) + [o_label_id]
word_ids_list = []
word_pad_id = self.word_vocab.convert_token_to_id('[PAD]')
for words in char_index2words:
words = words[:self.max_word_num]
word_ids = self.word_vocab.convert_tokens_to_ids(words)
word_pad_num = self.max_word_num - len(words)
word_ids = word_ids + [word_pad_id] * word_pad_num
word_ids_list.append(word_ids)
# 开头和结尾进行padding
word_ids_list = [[word_pad_id]*self.max_word_num] + word_ids_list + [[word_pad_id]*self.max_word_num]
if len(input_ids) > self.max_seq_len:
input_ids = input_ids[: self.max_seq_len]
label_ids = label_ids[: self.max_seq_len]
word_ids_list = word_ids_list[: self.max_seq_len]
input_mask = [1] * len(input_ids)
token_type_ids = [0] * len(input_ids)
assert len(input_ids) == len(label_ids) == len(word_ids_list)
# padding
padding_length = self.max_seq_len - len(input_ids)
input_ids += [pad_token_id] * padding_length
input_mask += [0] * padding_length
token_type_ids += [0] * padding_length
label_ids += [pad_label_id] * padding_length
word_ids_list += [[word_pad_id]*self.max_word_num] * padding_length
text = ''.join(text)
input_ids = torch.LongTensor(input_ids)
label_ids = torch.LongTensor(label_ids)
input_mask = torch.LongTensor(input_mask)
token_type_ids = torch.LongTensor(token_type_ids)
word_ids = torch.LongTensor(word_ids_list)
word_mask = (word_ids != word_pad_id).long()
feature = {
'text': text, 'input_ids': input_ids, 'attention_mask': input_mask, 'token_type_ids': token_type_ids,
'word_ids': word_ids, 'word_mask': word_mask, 'label_ids': label_ids
}
features.append(feature)
return features
模型运行
模型初步加载
- config.word_vocab_size:20857
- config.word_embed_dim:200
- LEBertModel:对其中的BertEncoder模块进行改造,后续会详细介绍
class LEBertSoftmaxForNer(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config):
super(LEBertSoftmaxForNer, self).__init__(config)
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.word_vocab_size, config.word_embed_dim)
self.num_labels = config.num_labels
self.bert = LEBertModel(config)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_labels)
self.loss_type = config.loss_type
self.init_weights()
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids, word_ids, word_mask, ignore_index, labels=None):
word_embeddings = self.word_embeddings(word_ids)
outputs = self.bert(
input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
word_embeddings=word_embeddings, word_mask=word_mask
)
sequence_output = outputs[0]
sequence_output = self.dropout(sequence_output)
logits = self.classifier(sequence_output)
outputs = (logits,) + outputs[2:] # add hidden states and attention if they are here
if labels is not None:
assert self.loss_type in ['lsr', 'focal', 'ce']
if self.loss_type == 'lsr':
loss_fct = LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy(ignore_index=ignore_index)
elif self.loss_type == 'focal':
loss_fct = FocalLoss(ignore_index=ignore_index)
else:
loss_fct = CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=ignore_index)
# Only keep active parts of the loss
if attention_mask is not None:
active_loss = attention_mask.contiguous().view(-1) == 1
active_logits = logits.contiguous().view(-1, self.num_labels)[active_loss]
active_labels = labels.contiguous().view(-1)[active_loss]
loss = loss_fct(active_logits, active_labels)
else:
loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1, self.num_labels), labels.view(-1))
outputs = (loss,) + outputs
return outputs # (loss), scores, (hidden_states), (attentions)
model.word_embeddings.weight.data.copy_(torch.from_numpy(processor.word_embedding))
- 把词向量的word_embedding赋给LEBertSoftmaxForNer
简要概述
class LEBertModel(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config):
self.encoder = BertEncoder(config)
class BertEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.layer = nn.ModuleList([BertLayer(config) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)])
self.word_embedding_adapter = WordEmbeddingAdapter(config)
def forward():
# 在第i层之后,进行融合
if i == self.config.add_layer:
hidden_states = self.word_embedding_adapter(hidden_states, word_embeddings, word_mask)
核心代码
class WordEmbeddingAdapter(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(WordEmbeddingAdapter, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
self.tanh = nn.Tanh()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(config.word_embed_dim, config.hidden_size)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size)
attn_W = torch.zeros(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size)
self.attn_W = nn.Parameter(attn_W)
self.attn_W.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=config.initializer_range)
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
def forward(self, layer_output, word_embeddings, word_mask):
"""
:param layer_output:bert layer的输出,[b_size, len_input, d_model]
:param word_embeddings:每个汉字对应的词向量集合,[b_size, len_input, num_word, d_word]
:param word_mask:每个汉字对应的词向量集合的attention mask, [b_size, len_input, num_word]
"""
# transform
# 将词向量,与字符向量进行维度对齐
word_outputs = self.linear1(word_embeddings)
word_outputs = self.tanh(word_outputs)
word_outputs = self.linear2(word_outputs)
word_outputs = self.dropout(word_outputs) # word_outputs:[b_size, len_input, num_word, d_model]
# 计算每个字符向量,与其对应的所有词向量的注意力权重,然后加权求和。采用双线性映射计算注意力权重
# layer_output = layer_output.unsqueeze(2) # layer_output:[b_size, len_input, 1, d_model]
socres = torch.matmul(layer_output.unsqueeze(2), self.attn_W) # [b_size, len_input, 1, d_model]
socres = torch.matmul(socres, torch.transpose(word_outputs, 2, 3)) # [b_size, len_input, 1, num_word]
socres = socres.squeeze(2) # [b_size, len_input, num_word]
socres.masked_fill_(word_mask, -1e9) # 将pad的注意力设为很小的数
socres = F.softmax(socres, dim=-1) # [b_size, len_input, num_word]
attn = socres.unsqueeze(-1) # [b_size, len_input, num_word, 1]
weighted_word_embedding = torch.sum(word_outputs * attn, dim=2) # [N, L, D] # 加权求和,得到每个汉字对应的词向量集合的表示
layer_output = layer_output + weighted_word_embedding
layer_output = self.dropout(layer_output)
layer_output = self.layer_norm(layer_output)
return layer_output
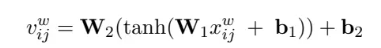
# transform
# 将词向量,与字符向量进行维度对齐
word_outputs = self.linear1(word_embeddings)
word_outputs = self.tanh(word_outputs)
word_outputs = self.linear2(word_outputs)
word_outputs = self.dropout(word_outputs) # word_outputs:[b_size, len_input, num_word, d_model]
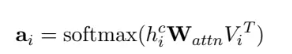
# 计算每个字符向量,与其对应的所有词向量的注意力权重,然后加权求和。采用双线性映射计算注意力权重
# layer_output = layer_output.unsqueeze(2) # layer_output:[b_size, len_input, 1, d_model]
socres = torch.matmul(layer_output.unsqueeze(2), self.attn_W) # [b_size, len_input, 1, d_model]
socres = torch.matmul(socres, torch.transpose(word_outputs, 2, 3)) # [b_size, len_input, 1, num_word]
socres = socres.squeeze(2) # [b_size, len_input, num_word]
socres.masked_fill_(word_mask, -1e9) # 将pad的注意力设为很小的数
socres = F.softmax(socres, dim=-1) # [b_size, len_input, num_word]
attn = socres.unsqueeze(-1) # [b_size, len_input, num_word, 1]
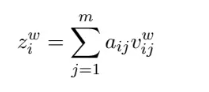
weighted_word_embedding = torch.sum(word_outputs * attn, dim=2)
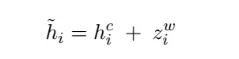
layer_output = layer_output + weighted_word_embedding
参照资料
论文解说:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/374720213
复现代码:https://github.com/yangjianxin1/LEBERT-NER-Chinese