网络连接一般包括最基本的五元组信息(源地址、目标地址、源端口、目标端口、协议号)再加上所属进程信息pid, exe, cmdline等。其中这两项数据大多可直接读取linux /proc目录下的网络状态连接文件/proc/net/tcp、/proc/net/udp), 进程状态目录(/proc/pid/xx)。
Linux 下的/proc/net子目录
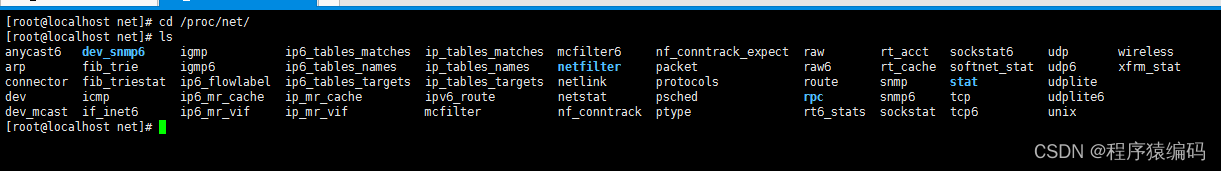
net该子目录包括多个 ASCII 格式的网络伪文件, 描述了网络 层的部分情况. 可以用 cat 来察看这些文件, 但标准的 netstat(8) 命令组更清晰地给出了这些文件的信息.
我们讲解下面的文件网络状态文件/proc/net/tcp、/proc/net/tcp6、/proc/net/udp、/proc/net/udp6
proc_net_tcp.txt介绍了/proc/net/tcp和/proc/net/tcp6接口。这些接口展示了tcp的连接信息。
它将首先列出所有侦听TCP套接字,然后列出所有已建立的TCP连接。/proc/net/tcp、/proc/net/tcp6的典型条目如下(由于行的长度,分为三部分):
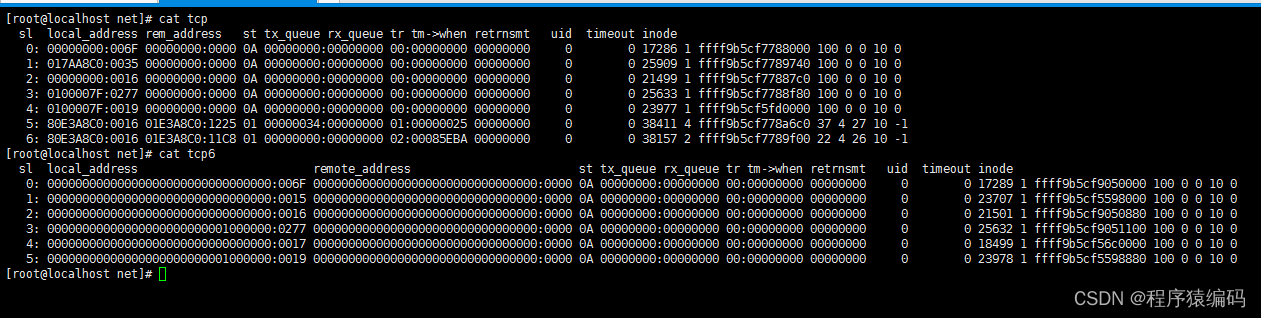
tcp该文件保存了 TCP 套接字表, 大部分信息除用于调试以外没有什么用.
"sl" 指出了套接字的内核散列槽号;
"local address" 包括本地地址和端口号;
"remote address" 包括远地地址和端口号(如果有连接的话);
'St' 是套接字的内 部状态;
'tx_queue' 和 'rx_queue' 是内核存储器使用意义上 的输入输出数据队列;
"tr", "tm->when" 和 "rexmits" 保存了内核套接字声明的内部信息, 只用于调试;
uid 是套接字创建者的有效 uid.
46: 010310AC:9C4C 030310AC:1770 01
| | | | | |--> connection state(套接字状态)
| | | | |------> remote TCP port number(远端端口,主机字节序)
| | | |-------------> remote IPv4 address(远端IP,网络字节序)
| | |--------------------> local TCP port number(本地端口,主机字节序)
| |---------------------------> local IPv4 address(本地IP,网络字节序)
|----------------------------------> number of entry
00000150:00000000 01:00000019 00000000
| | | | |--> number of unrecovered RTO timeouts(超时重传次数)
| | | |----------> number of jiffies until timer expires(超时时间,单位是jiffies)
| | |----------------> timer_active (定时器类型,see below)
| |----------------------> receive-queue(根据状态不同有不同表示,see below)
|-------------------------------> transmit-queue(发送队列中数据长度)
1000 0 54165785 4 cd1e6040 25 4 27 3 -1
| | | | | | | | | |--> slow start size threshold,
or -1 if the threshold is >=0xFFFF
| | | | | | | | | (如果慢启动阈值大于等于0xFFFF则显示-1,否则表示慢启动阈值)
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |----> sending congestion window(当前拥塞窗口大小)
| | | | | | | |-------> (ack.quick<<1)|ack.pingpong
(快速确认数和是否启用的标志位的或运算结果)
| | | | | | |---------> Predicted tick of soft clock (delayed ACK control data)
(用来计算延时确认的估值)
| | | | | |
| | | | | |------------> retransmit timeout()(RTO,单位是clock_t)
| | | | |------------------> location of socket in memory(socket实例的地址)
| | | |-----------------------> socket reference count(socket结构体的引用数)
| | |-----------------------------> inode(套接字对应的inode)
| |----------------------------------> unanswered 0-window probes(see below)
|---------------------------------------------> uid(用户id)
connection state(套接字状态),不同的数值代表不同的状态,参照如下:
“01″: “ESTABLISHED”,
“02″: “SYN_SENT”,
“03″: “SYN_RECV”,
“04″: “FIN_WAIT1″,
“05″: “FIN_WAIT2″,
“06″: “TIME_WAIT”,
“07″: “CLOSE”,
“08″: “CLOSE_WAIT”,
“09″: “LAST_ACK”,
“0A”: “LISTEN”,
“0B”: “CLOSING”
receive-queue:当状态是ESTABLISHED,表示接收队列中数据长度;状态是LISTEN,表示已经完成连接队列的长度。
timer_active:
0 no timer is pending //没有启动定时器
1 retransmit-timer is pending //重传定时器
2 another timer (e.g. delayed ack or keepalive) is pending //连接定时器、FIN_WAIT_2定时器或TCP保活定时器
3 this is a socket in TIME_WAIT state. Not all fields will contain data (or even exist) //TIME_WAIT定时器
4 zero window probe timer is pending //持续定时器
unanswered 0-window probes:持续定时器或保活定时器周期性发送出去但未被确认的TCP段数目,在收到ACK之后清零

udp该文件保存了 UDP 套接字表, 大部分信息除用于调试以外没有什么用。
"sl" 指出了套接字的内核散列槽号;
"local address" 包括本地地址和端口号;
"remote address" 包括远地地址和端口号(如果有连接的话);
"St" 是套接字的内 部状态;
"tx_queue" 和 "rx_queue" 是内核存储器使用意义上 的输入输出数据队列;
UDP 没有使用 "tr","tm->when" 和"rexmits";
uid 是套接字创建者的有效 uid
Linux下实现类似netstat命令
...
void checkProc(struct ProcNet *Net, int len, int flag, const char protocol[])
{
char path[1000], buf2[256], link[64], tmp[10], inode[15], p_name[512];
int ret;
//ino_t inode;
ssize_t link_size;
//printf("flag: %d\n", flag);
if ((proc = opendir("/proc")) == NULL)
{
perror("Cannot open /proc directory\n");
exit(1);
}
while ((procent = readdir(proc)) != NULL)
{
if (!isdigit(*(procent->d_name)))
continue;
sprintf(buf2, "/proc/%s/fd", procent->d_name);
//printf("%s\n", buf2);
if ((fd = opendir(buf2)) == NULL)
continue;
while((fdent = readdir(fd)) != NULL)
{
struct stat st;
sprintf(buf2, "/proc/%s/fd/%s", procent->d_name, fdent->d_name);
if (stat(buf2, &st) < 0)
continue;
if (!S_ISSOCK(st.st_mode))
continue;
ret = checkInode(Net, st.st_ino, len);
if (ret >= 0)
{
if (flag)
{
if (read_program_name_args_filter(procent))
{
display_at(Net, ret, protocol);
printf("%s/", procent->d_name);
read_program_name_args(procent);
}
}
else
{
display_at(Net, ret, protocol);
printf("%s/", procent->d_name);
read_program_name_args(procent);
//printf("%s", p_name);
}
}
}
closedir(fd);
}
//printf("here\n");
closedir(proc);
}
...
static const char *state2str(unsigned state)
{
switch(state){
case 0x1: return "ESTABLISHED";
case 0x2: return "SYN_SENT";
case 0x3: return "SYN_RECV";
case 0x4: return "FIN_WAIT1";
case 0x5: return "FIN_WAIT2";
case 0x6: return "TIME_WAIT";
case 0x7: return "CLOSE";
case 0x8: return "CLOSE_WAIT";
case 0x9: return "LAST_ACK";
case 0xA: return "LISTEN";
case 0xB: return "CLOSING";
default: return "UNKNOWN";
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
...
static struct option long_options[] = {
{"tcp", optional_argument, 0, 't'},
{"udp", optional_argument, 0, 'u'},
{0, 0, 0, 0}
};
int long_index = 0;
while((opt = getopt_long(argc, argv, ":tu", long_options, &long_index)) != -1)
{
//printf("%d,", long_index);
switch(opt)
{
case 't':
tcp = 1;
udp = 0;
if (opt_flag)
udp = 1;
++opt_flag;
break;
case 'u':
udp = 1;
tcp = 0;
if (opt_flag)
tcp = 1;
++opt_flag;
break;
case '?':
printf("Usage: ./my_netstat [-t|--tcp][-u|--udp] [filter-string | \"regular expression\"]\n");
exit(1);
}
}
if (optind < argc)
{
filter_string = argv[optind];
filter = 1;
//printf("filter string: %s ", filter_string);
/* Compile regular expression */
reti = regcomp(®ex, filter_string, 0);
if( reti ){ fprintf(stderr, "Could not compile regex\n"); exit(1); }
}
//printf("\ntcp: %d, udp: %d\n", tcp, udp);
int num_tcp, num_udp;
if (tcp)
{
printf("\n\nList of TCP connections::: \n");
printf("Proto \tLocal Address \t\t\tForeign Address \t\tstate \t\tPID/Program name and arguments \n");
printf("---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
num_tcp = checkTCP();
num_tcp++;
//display(TCPdata, num_tcp);
//printf("\n Number of TCP: %d\n", num_tcp);
checkProc(TCPdata, num_tcp, filter, "tcp");
}
if (udp)
{
printf("\nList of UDP connections::: \n");
printf("Proto \tLocal Address \t\t\tForeign Address \t\tstate \t\tPID/Program name and arguments \n");
printf("---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
num_udp = checkUDP();
num_udp++;
checkProc(UDPdata, num_udp, filter, "udp");
}
return 0;
}
If you need the complete source code of my_netstat, please add WeChat number (c17865354792)
编译运行:

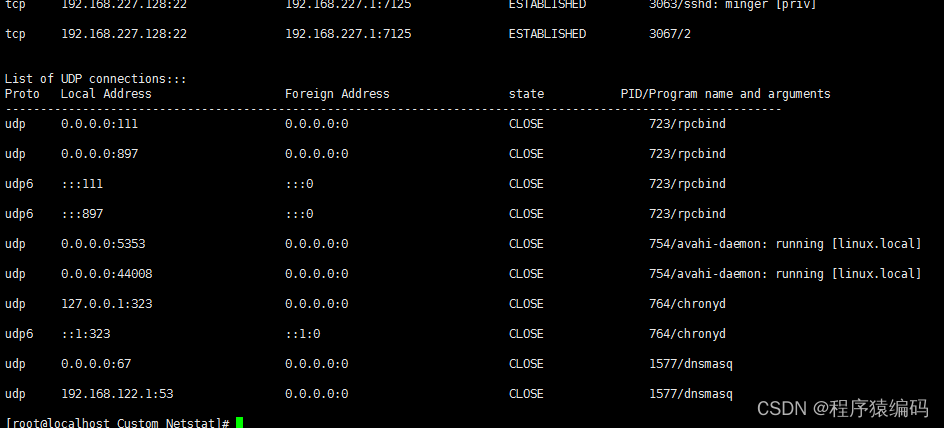
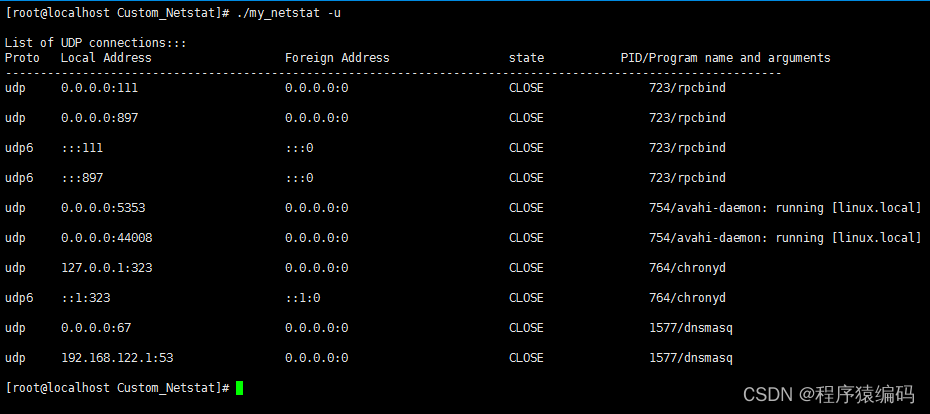
./my_netstat -u
 ./my_netstat -t
./my_netstat -t

总结
这是一个简单的netstat(类似netstat)。该程序列出了所有现有的TCP和UDP连接。对于每个已标识的连接(套接字描述符),查找相应的进程名称及其创建连接的命令行(套接字描述符)。
Welcome to follow WeChat official account【程序猿编码】
参考:https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/v5.8/networking/proc_net_tcp.html