目录
事件系统
什么是事件
事件的使用方式
Event对象
事件分类
冒泡事件(bind)
非冒泡事件(catch)
事件类型
事件类型列表
事件携带参数
currentTarget 携带参数
mark 携带参数
条件渲染
wx:if
wx:else
wx:elif
列表渲染
基本使用
复杂数据
列表渲染_key属性
wx:key
列表渲染_应用
模板
定义模板
使用模板
模板应用
增加列表模板
页面应用模板
事件系统

什么是事件

事件的使用方式
在组件中绑定一个事件处理函数
<button type="primary" bindtap="tapName">Click me! </button>
<view bindtap="tapName"> Click me! </view>
// pages/event/event.js
Page({
tapName(){
console.log("点击");
}
})Event对象
在小程序中,也具有事件对象 event
Page({
tapName(e){
console.log(e);
}
})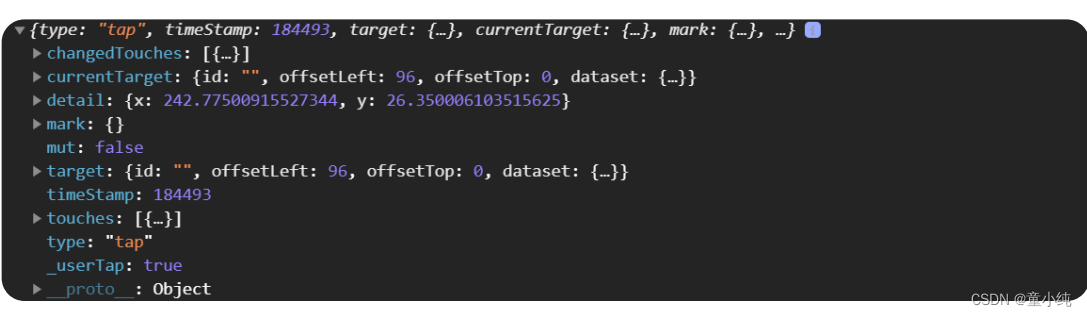
| 属性 | 类型 | 说明 |
| type | String | 事件类型 |
| timeStamp | Integer | 事件生成时的时间戳 |
| target | Object | 触发事件的组件的一些属性值集合 |
| currentTarget | Object | 当前组件的一些属性值集合 |
| mark | Object | 事件标记数据 |
| detail | Object | 事件标记数据 |
| touches | Array | 触摸事件,当前停留在屏幕中的触摸点信息的数组 |
| changedTouches | Array | 触摸事件,当前变化的触摸点信息的数组 |
1. 在微信小程序中, event 对象的属性 currentTarget 作用是:当前组件的一些属性值集合
事件分类

事件分为冒泡事件和非冒泡事件:

冒泡事件(bind)
当一个组件上的事件被触发后,该事件会向父节点传递
<view bindtap="bindParentHandle">
<button type="primary" bindtap="bindChildHandle">冒泡事件</button>
</view>// pages/event/event.js
Page({
bindParentHandle(){
console.log("父级事件");
},
bindChildHandle(){
console.log("子级事件");
}
})非冒泡事件(catch)
当一个组件上的事件被触发后,该事件不会向父节点传递
<view catchtap="catchParentHandle">
<button type="primary" catchtap="catchChildHandle">非冒泡事件</button>
</view>// pages/event/event.js
Page({
catchParentHandle(){
console.log("非冒泡父级事件");
},
catchChildHandle(){
console.log("非冒泡子级事件");
}
})1. 在微信小程序中,下列那个是冒泡事件:bind
事件类型

在微信小程序中,事件有很多中类型, 通过 bind 和 catch 与下面的类 型组合产生不同类型的事件
事件类型列表

<button type="primary" bindtouchstart="bindtouchStartHandle">touchstart bind</button>
<button type="primary" catchtouchstart="catchtouchStartHandle">touchstart catch</button>
<button type="primary" bindlongpress="bindlongpressHandle">longpress bind</button>
<button type="primary" catchlongpress="catchlongpressHandle">longpress catch</button>
// pages/event/event.js
Page({
bindtouchStartHandle(){
console.log("bind与touchStart组合");
},
catchtouchStartHandle(){
console.log("catch与touchStart组合");
},
bindlongpressHandle(){
console.log("bind与longpress组合");
},
catchlongpressHandle(){
console.log("catch与longpress组合");
}
})1. 在微信小程序中,下列那个是手指移动事件:touchmove
事件携带参数
事件在触发的过程中,我们可以携带参数
currentTarget 携带参数
在组件节点中可以附加一些自定义数据。这样,在事件中可以获取 这些自定义的节点数据,用于事件的逻辑处理。
<view data-id="1001" bindtap="bindViewTap">携带参数 </view>
// pages/event/event.js
Page({
bindViewTap(e){
console.log(e.currentTarget.dataset.id);
}
})温馨提示
在 wxml 中添加数据的时候,必须在自定义属性前添加 data-*
mark 携带参数
可以使用 mark 来识别具体触发事件的 target 节点。此外, mark 还可以用于承载一些自定义数据(类似于 dataset )。
当事件触发时,事件冒泡路径上所有的 mark 会被合并,并返回给事件回调函数。(即使事件不是冒泡事件,也会 mark 。)
<view mark:parentMark="父级" bindtap="bindMarkTap">
<button type="primary" mark:childMark="子级" bindtap="bindButtonTap">按钮</button>
</view>// pages/event/event.js
Page({
bindMarkTap(e){
console.log(e.mark);
},
bindButtonTap(e){
console.log(e.mark);
}
})1. 在微信小程序中,事件的 event 对象中,读取事件冒泡路径上所有的参数方案:mark
条件渲染


wx:if
在小程序中,使用 wx:if="" 来判断是否需要渲染该代码块
<view wx:if="{{ flag }}">我是孙悟空</view>Page({
data: {
flag:true
}
})wx:else
有 wx:if 匹配的同时还有 wx:else
<view wx:if="{{ flag }}">我是孙悟空</view>
<view wx:else="{{ flag }}">我是六耳猕猴</view>Page({
data: {
flag:false
}
})wx:elif
如同在 javascript 中,单纯的 if...else 是不够用的,所以引入了 elif
<view wx:if="{{length === 1}}"> 1 </view>
<view wx:elif="{{length === 2}}"> 2 </view>
<view wx:else>未知</view>Page({
data: {
length:1
}
})
hidden
hidden 与 wx:if 类似,同样可以来判断是否需要渲染该代码块
<view hidden="{{ hidden }}">果子熟了</view>
Page({
data: {
hidden:false
}
})wx:if vs hidden 区别
因为 wx:if 之中的模板也可能包含数据绑定,所以当 wx:if 的条件值切 换时,框架有一个局部渲染的过程,因为它会确保条件块在切换时 销毁或重新渲染。
同时 wx:if 也是惰性的,如果在初始渲染条件为 false ,框架什么也不 做,在条件第一次变成真的时候才开始局部渲染。
相比之下, hidden 就简单的多,组件始终会被渲染,只是简单的基 于CSS控制显示与隐藏。
一般来说, wx:if 有更高的切换消耗而 hidden 有更高的初始渲染消 耗。因此,如果需要频繁切换的情景下,用 hidden 更好,如果在运 行时条件不大可能改变则 wx:if 较好
列表渲染

在组件上使用 wx:for 控制属性绑定一个数组,即可使用数组中各项 的数据重复渲染该组件
基本使用
默认数组的当前项的下标变量名默认为 index ,数组当前项的变量名 默认为 item
<view>
<view wx:for="{{ users }}">{{ item }} </view>
</view>
Page({
data: {
users:["xiaotong","sxt"]
}
})使用 wx:for-item 可以指定数组当前元素的变量名
使用 wx:for-index 可以指定数组当前下标的变量名
<view>
<view
wx:for="{{ users }}"
wx:for-item="user"
wx:for-index="ids"
>
{{ user }}-{{ ids }}
</view>
</view>Page({
data: {
users:["xiaotong","sxt"]
}
})复杂数据
网络请求拿到的数据是 json 格式,相对比要复杂一些
<view>
<block wx:for="{{ result }}" wx:for-item="item">
<view>{{ item.name }}</view>
<image src="{{ item.pic }}"></image>
<view>{{ item.description }}</view>
<view>{{ item.price }}</view>
<view>{{ item.city }}</view>
</block>
</view>Page({
data: {
result: [{
"id": 1,
"name": "美食-甜豆干",
"pic": "http://iwenwiki.com:3002/images/goods/1.jpg",
"description": "津津卤汁豆腐干苏州特产豆干零食素食老字号食品豆制品小吃90g*10",
"price": "39.90",
"type": 0,
"buynum": "435",
"city": "北京"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "好欢螺螺蛳粉300g*6袋",
"pic": "http://iwenwiki.com:3002/images/goods/2.jpg",
"description": "好欢螺螺蛳粉300g*6袋柳州特产螺狮粉美食螺丝粉煮水方便面酸辣粉",
"price": "69.99",
"type": 0,
"buynum": "3333",
"city": "北京"
}
]
}
})1. 在微信小程序中, wx:for-item 属性的作用是:
使用 wx:for-item 可以指定数组当前元素的变量名
列表渲染_key属性

wx:key
如果列表中项目的位置会动态改变或者有新的项目添加到列表中, 并且希望列表中的项目保持自己的特征和状态,需要使用 wx:key 来 指定列表中项目的唯一的标识符
当数据改变触发渲染层重新渲染的时候,会校正带有 key 的组件, 框架会确保他们被重新排序,而不是重新创建,以确保使组件保持 自身的状态,并且提高列表渲染时的效率

<view wx:for="{{ news }}" wx:for-item="item" wx:key="id">
<view>{{ item.name }}</view>
</view>Page({
data: {
news:[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "美食-甜豆干"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "好欢螺螺蛳粉300g*6袋"
}
]
}
})当我们想数组中添加新的数据,并且放在首位的时候,在渲染的时 候, key 就起到了作用
<button type="primary" bindtap="clickHandle"> 增加数据</button>
<view wx:for="{{ news }}" wx:for-item="item" wx:key="id">
<view>{{ item.name }}</view>
</view>
Page({
data: {
news:[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "美食-甜豆干"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "好欢螺螺蛳粉300g*6袋"
}
]
},
clickHandle(){
this.setData({
news:this.data.news.concat({
"id":"3",
"name": "对夹"
})
})
}
})列表渲染_应用

列表渲染的应用场景,所有需要重复视图的地方都可以使用列表渲 染,例如: swiper
<swiper
indicator-dots
indicator-color="#fff"
indicator-active-color="#f00"
autoplay
>
<block wx:for="{{ swiperData }}" wx:foritem="item" wx:for-index="index" wx:key="index">
<swiper-item>
<image mode="widthFix" style="width: 100%;" src="{{ item }}"></image>
</swiper-item>
</block>
</swiper>Page({
data: {
swiperData:[
"../../images/1.png",
"../../images/2.jpg",
"../../images/3.jpg"
]
}
})
模板

WXML提供模板(template),可以在模板
<template name="customTemplate">
<view class="text">{{ test }}</view>
</template>中定义代码片段,然后 在不同的地方调用
定义模板
使用 name 属性,作为模板的名字。然后在<template/> 内定义代码片 段
使用模板
使用 is 属性,声明需要的使用的模板,然后将模板所需要的 data 传入
<import src="./list/list.wxml" />
<view>
<view>引用模板</view>
<template is="customTemplate" data="{{test }}"></template>
<template is="customTemplate" data="{{test }}"></template>
</view>Page({
data: {
test:"测试"
}
})
当然也需要引入样式,来丰富模板
.text{
color: red;
}
引入模板样式到页面
@import "./list/list.wxss";1. 在微信小程序中,模板引入到页面中是通过什么方式:
使用 import 属性,声明需要的使用的模板
模板应用

在微信小程序的项目中,同一个项目一般风格统一化,所以相同的页面效果也是常见的,此时模板的使用率就大大增多了。例如最常见的列表效果
增加列表模板
<template name="listTemplate" >
<view class="list">
<block wx:for="{{ foods }}" wx:for-item="item" wx:key="id">
<view class="item">
<image mode="widthFix" src="{{ item.pic }}"></image>
<text>{{ item.name }}</text>
</view>
</block>
</view>
</template>
.list{
width: 100%;
}
.item{
margin: 10px;
}
.list image{
width: 100px;
}页面应用模板
<import src="./lists/lists" />
<template is="listTemplate" data="{{ foods }}"></template>@import "./lists/lists.wxss";
Page({
data: {
foods: [{
"id": 1,
"name": "美食-甜豆干",
"pic": "http://iwenwiki.com:3002/images/goods/1.jpg"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "好欢螺螺蛳粉300g*6袋",
"pic": "http://iwenwiki.com:3002/images/goods/2.jpg"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "良品铺子-肉松饼380gx2袋",
"pic": "http://iwenwiki.com:3002/images/goods/3.webp"
}
]
}
})