基于飞桨paddle的极简方案构建手写数字识别模型测试代码
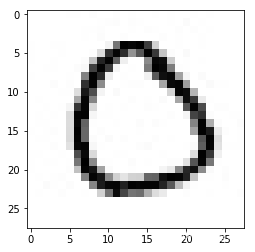
原始测试图片为255X252的图片
因为是极简方案采用的是线性回归模型,所以预测结果数字不一致
本次预测的数字是 [[3]]
测试结果:
PS E:\project\python> & D:/Python39/python.exe e:/project/python/MNIST.py
10.0.0
2.4.2
图像数据形状和对应数据为: (28, 28)
图像标签形状和对应数据为: (1,) [5]
打印第一个batch的第一个图像,对应标签数字为[5]
epoch_id: 0, batch_id: 0, loss is: [34.4626]
epoch_id: 0, batch_id: 1000, loss is: [7.599941]
epoch_id: 0, batch_id: 2000, loss is: [4.583123]
epoch_id: 0, batch_id: 3000, loss is: [2.8974648]
epoch_id: 1, batch_id: 0, loss is: [3.610869]
epoch_id: 1, batch_id: 1000, loss is: [5.6290216]
epoch_id: 1, batch_id: 2000, loss is: [1.9465038]
epoch_id: 1, batch_id: 3000, loss is: [2.1046467]
epoch_id: 7, batch_id: 2000, loss is: [4.63013]
epoch_id: 7, batch_id: 3000, loss is: [4.4638147]
epoch_id: 8, batch_id: 0, loss is: [3.0043283]
epoch_id: 8, batch_id: 1000, loss is: [1.633965]
epoch_id: 8, batch_id: 2000, loss is: [3.1906333]
epoch_id: 8, batch_id: 3000, loss is: [2.4461133]
epoch_id: 9, batch_id: 0, loss is: [3.9595613]
epoch_id: 9, batch_id: 1000, loss is: [1.3417265]
epoch_id: 9, batch_id: 2000, loss is: [2.3505783]
epoch_id: 9, batch_id: 3000, loss is: [2.0194921]
原始图像shape: (252, 255)
采样后图片shape: (28, 28)
result Tensor(shape=[1, 1], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=False,
[[3.94108272]])
本次预测的数字是 [[3]]
PS E:\project\python>
测试代码如下所示:
#加载飞桨和相关类库
import paddle
from paddle.nn import Linear
import paddle.nn.functional as F
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 导入图像读取第三方库
from PIL import Image,ImageFilter
print(Image.__version__) #10.0.0
#原来是在pillow的10.0.0版本中,ANTIALIAS方法被删除了,使用新的方法即可Image.LANCZOS
#或降级版本为9.5.0,安装pip install Pillow==9.5.0
print(paddle.__version__) #2.4.2
#飞桨提供了多个封装好的数据集API,涵盖计算机视觉、自然语言处理、推荐系统等多个领域,
# 帮助读者快速完成深度学习任务。
# 如在手写数字识别任务中,
# 通过paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST可以直接获取处理好的MNIST训练集、测试集,
# 飞桨API支持如下常见的学术数据集:
'''
mnist
cifar
Conll05
imdb
imikolov
movielens
sentiment
uci_housing
wmt14
wmt16
'''
#数据处理
# 设置数据读取器,API自动读取MNIST数据训练集
train_dataset = paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST(mode='train')
train_data0 = np.array(train_dataset[0][0])
train_label_0 = np.array(train_dataset[0][1])
# 显示第一batch的第一个图像
'''
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure("Image") # 图像窗口名称
plt.figure(figsize=(2,2))
plt.imshow(train_data0, cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.axis('on') # 关掉坐标轴为 off
plt.title('image') # 图像题目
plt.show()
'''
print("图像数据形状和对应数据为:", train_data0.shape) #(28, 28)
print("图像标签形状和对应数据为:", train_label_0.shape, train_label_0) #(1,) [5]
print("\n打印第一个batch的第一个图像,对应标签数字为{}".format(train_label_0)) # [5]
#飞桨将维度是28×28的手写数字图像转成向量形式存储,
# 因此使用飞桨数据加载器读取到的手写数字图像是长度为784(28×28)的向量。
#模型设计
#模型的输入为784维(28×28)数据,输出为1维数据,
# 定义mnist数据识别网络结构,同房价预测网络
#===========================================
class MNIST(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(MNIST, self).__init__()
# 定义一层全连接层,输出维度是1
self.fc = paddle.nn.Linear(in_features=784, out_features=1)
# 定义网络结构的前向计算过程
def forward(self, inputs):
outputs = self.fc(inputs)
return outputs
#===========================================
#训练配置
# 声明网络结构
model = MNIST()
def train(model):
# 启动训练模式
model.train()
# 加载训练集 batch_size 设为 16
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST(mode='train'),
batch_size=16,
shuffle=True)
# 定义优化器,使用随机梯度下降SGD优化器,学习率设置为0.001
opt = paddle.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001, parameters=model.parameters())
#===========================================
# 图像归一化函数,将数据范围为[0, 255]的图像归一化到[0, 1]
def norm_img(img):
# 验证传入数据格式是否正确,img的shape为[batch_size, 28, 28]
assert len(img.shape) == 3
batch_size, img_h, img_w = img.shape[0], img.shape[1], img.shape[2]
# 归一化图像数据
img = img / 255
# 将图像形式reshape为[batch_size, 784]
img = paddle.reshape(img, [batch_size, img_h*img_w])
return img
#===========================================
import paddle
# 确保从paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST中加载的图像数据是np.ndarray类型
paddle.vision.set_image_backend('cv2')
# 声明网络结构
model = MNIST()
#===========================================
def run(model):
# 启动训练模式
model.train()
# 加载训练集 batch_size 设为 16
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST(mode='train'),
batch_size=16,
shuffle=True)
# 定义优化器,使用随机梯度下降SGD优化器,学习率设置为0.001
opt = paddle.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001, parameters=model.parameters())
EPOCH_NUM = 10
for epoch in range(EPOCH_NUM):
for batch_id, data in enumerate(train_loader()):
images = norm_img(data[0]).astype('float32')
labels = data[1].astype('float32')
#前向计算的过程
predicts = model(images)
# 计算损失
loss = F.square_error_cost(predicts, labels)
avg_loss = paddle.mean(loss)
#每训练了1000批次的数据,打印下当前Loss的情况
if batch_id % 1000 == 0:
print("epoch_id: {}, batch_id: {}, loss is: {}".format(epoch, batch_id, avg_loss.numpy()))
#后向传播,更新参数的过程
avg_loss.backward()
opt.step()
opt.clear_grad()
#===========================================
#调用训练
run(model)
paddle.save(model.state_dict(), './mnist.pdparams')
#模型测试
#===========================================
def showImage(im):
#img_path = 'example_0.jpg'
# 读取原始图像并显示
#im = Image.open('example_0.jpg')
plt.imshow(im)
plt.show()
# 将原始图像转为灰度图
im = im.convert('L')
print('原始图像shape: ', np.array(im).shape)
# 使用Image.ANTIALIAS方式采样原始图片
im = im.resize((28, 28), Image.LANCZOS)
plt.imshow(im)
plt.show()
print("采样后图片shape: ", np.array(im).shape)
#===========================================
im = Image.open('example_0.jpg')
showImage(im)
# 读取一张本地的样例图片,转变成模型输入的格式
#===========================================
def load_image(img_path):
# 从img_path中读取图像,并转为灰度图
im = Image.open(img_path).convert('L')
# print(np.array(im))
im = im.resize((28, 28), Image.LANCZOS)
im = np.array(im).reshape(1, -1).astype(np.float32)
# 图像归一化,保持和数据集的数据范围一致
im = 1 - im / 255
return im
#===========================================
# 定义预测过程
def test():
model = MNIST()
params_file_path = 'mnist.pdparams'
img_path = 'example_0.jpg'
# 加载模型参数
param_dict = paddle.load(params_file_path)
model.load_dict(param_dict)
# 灌入数据
model.eval()
tensor_img = load_image(img_path)
result = model(paddle.to_tensor(tensor_img))
print('result',result)
# 预测输出取整,即为预测的数字,打印结果
print("本次预测的数字是", result.numpy().astype('int32'))
#===========================================
test();


![解决[Vue Router warn]: No match found for location with path “/day“问题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d2e9732ac14e4d1a819d4efa1ccafba3.png)