文章目录
- HttpServlet
- 核心方法
- HttpServletRequest
- 核心方法
- HttpServletResponse
- 核心方法
Servlet中常用的API有以下三个:
HttpServletHttpServletRequestHttpServletResponse
HttpServlet
我们写 Servlet 代码的时候, 首先第一步就是先创建类, 继承自 HttpServlet, 并重写其中的某些方法.
核心方法
| 方法名称 | 调用时机 |
|---|---|
| init(初始化) | 在 HttpServlet 实例化之后被调用一次 |
| destory(销毁) | 在 HttpServlet 实例不再使用的时候调用一次 |
| service | 收到 HTTP 请求的时候调用 |
| doGet | 收到 GET 请求的时候调用(由 service 方法调用) |
| doPost | 收到 POST 请求的时候调用(由 service 方法调用) |
| doPut/doDelete/doOptions/… | 收到其他请求的时候调用(由 service 方法调用) |
说明:
init:tomcat首次收到和该类相关联的请求时触发.(类似于前面学的懒汉模式).例如:
tomcat收到 /hello 的路径请求,就会调用到HelloServlet进行实例化,于是就需要先对helloServlet进行实例化.(实例化只进行一次). 后续再收到 /hello,就不必重复实例化了,直接复用之前的HelloServlet实例即可.destroy:通过重写我们可以看到: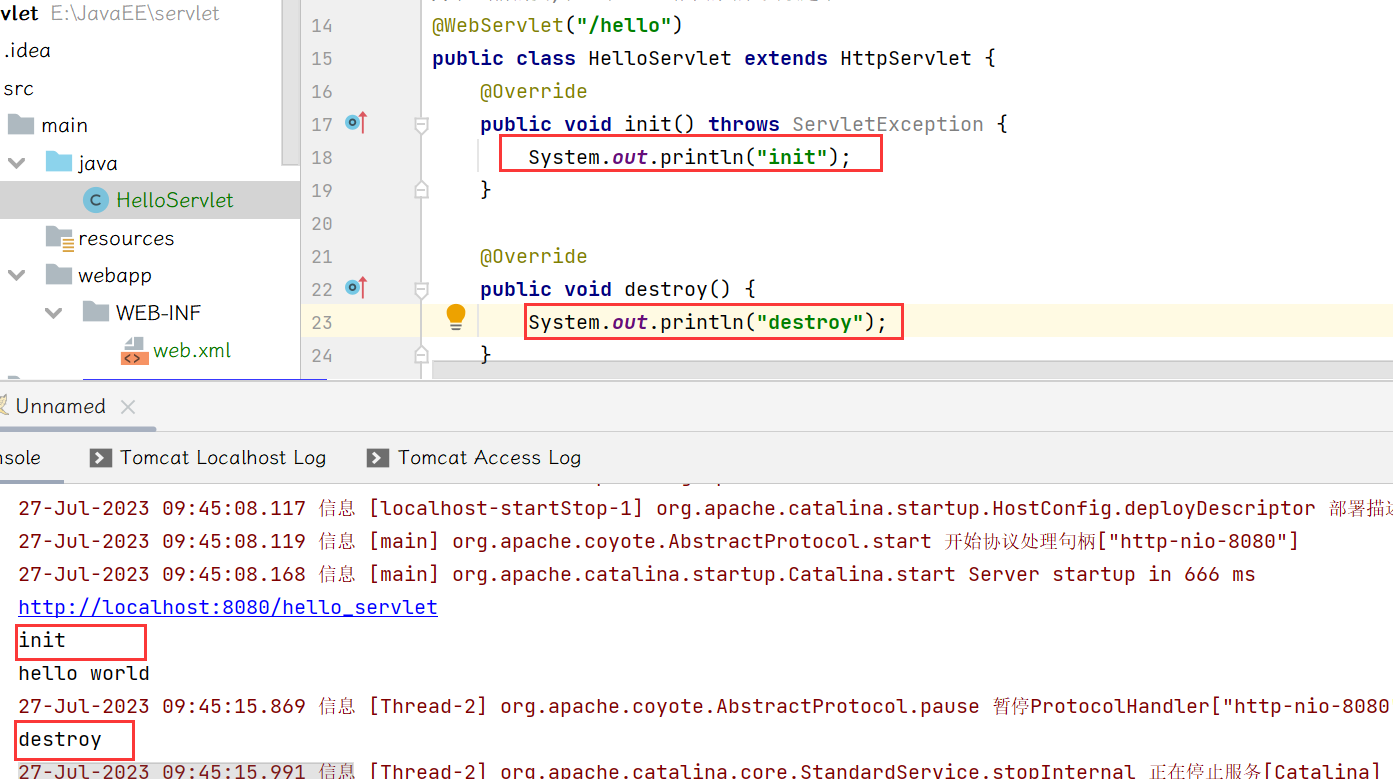
service:收到http请求就会触发(路径匹配请求).
以上三个方式是HTTPServlet最关键的三个方法.
面试题:Servlet的声明周期是什么?
- 开始的时候,执行init
- 每次收到请求的时候,执行service
- 销毁之前,执行destroy
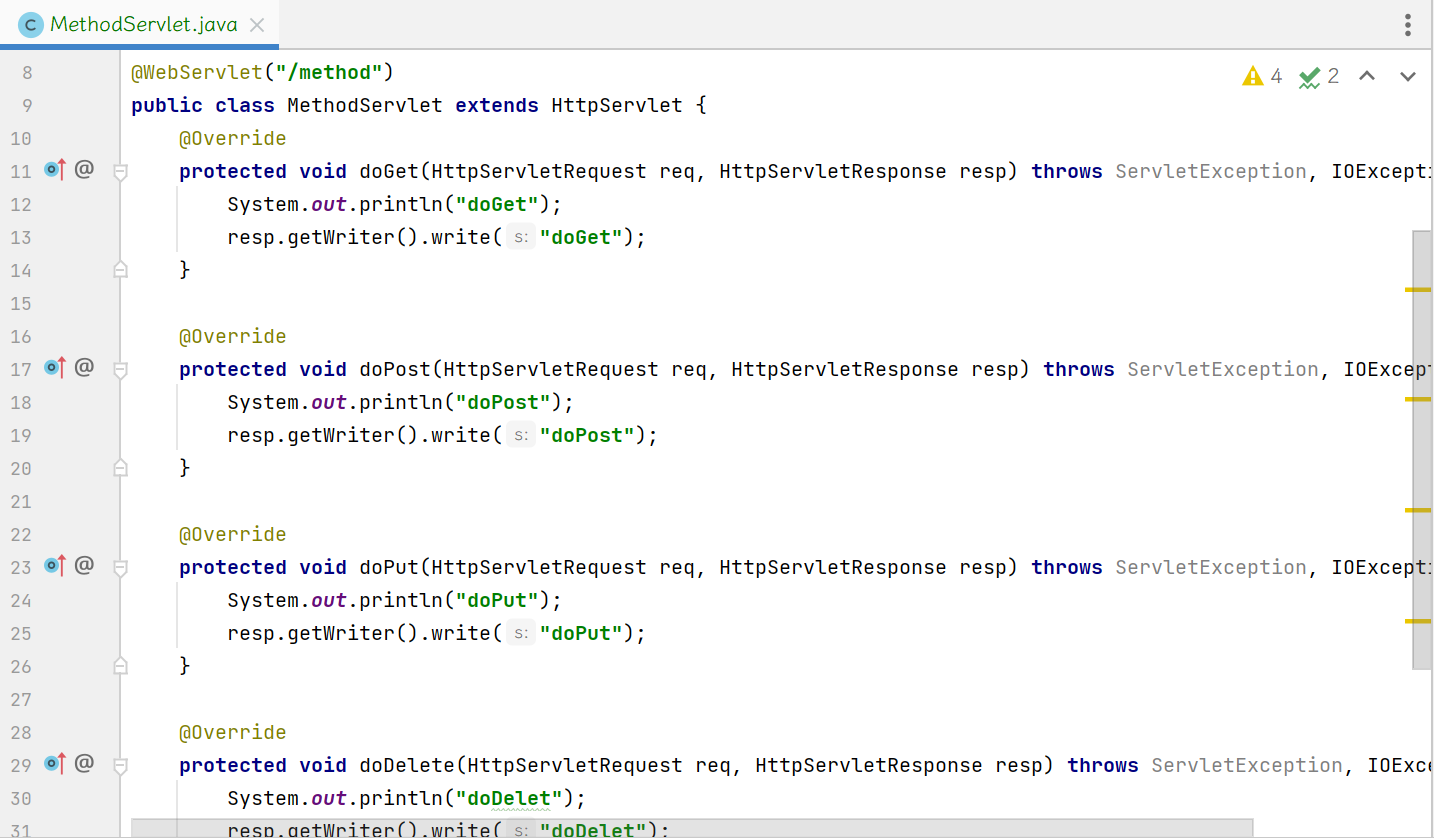
在浏览器中直接输入URL可以看到doGet请求:
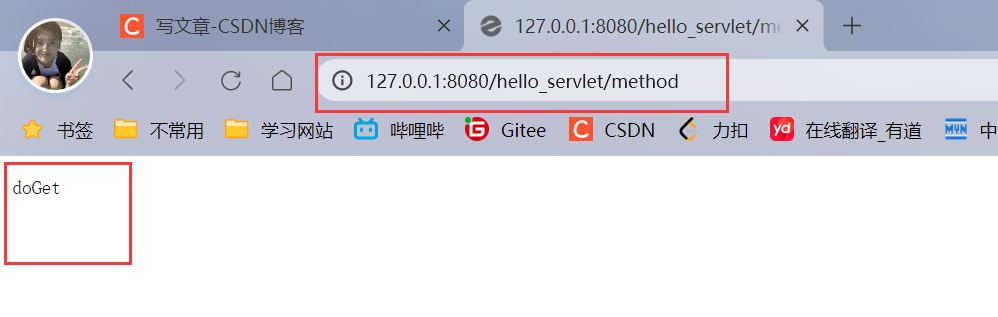
那么其他请求怎么构造呢?
- 可以使用
Postman.
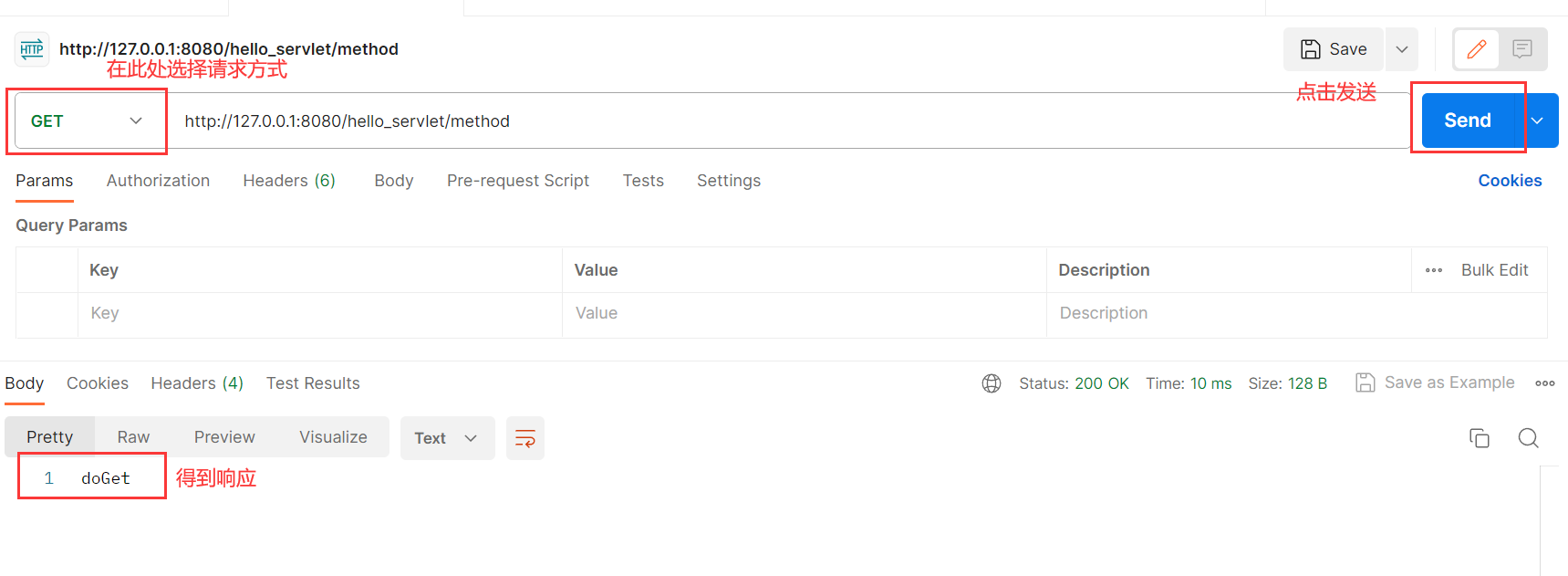
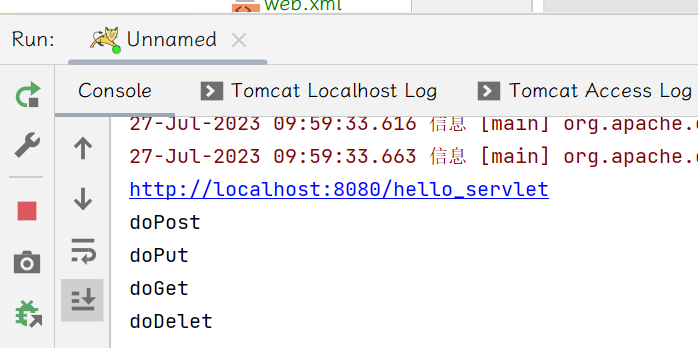
同时我们可以服务器处看到日志:
- 使用ajax构造请求
注意文件创建位置.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 构造ajax请求访问服务器 -->
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.3/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
$.ajax({
type:'get',
url:'method',
success:function(body,status){
console.log(body);
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
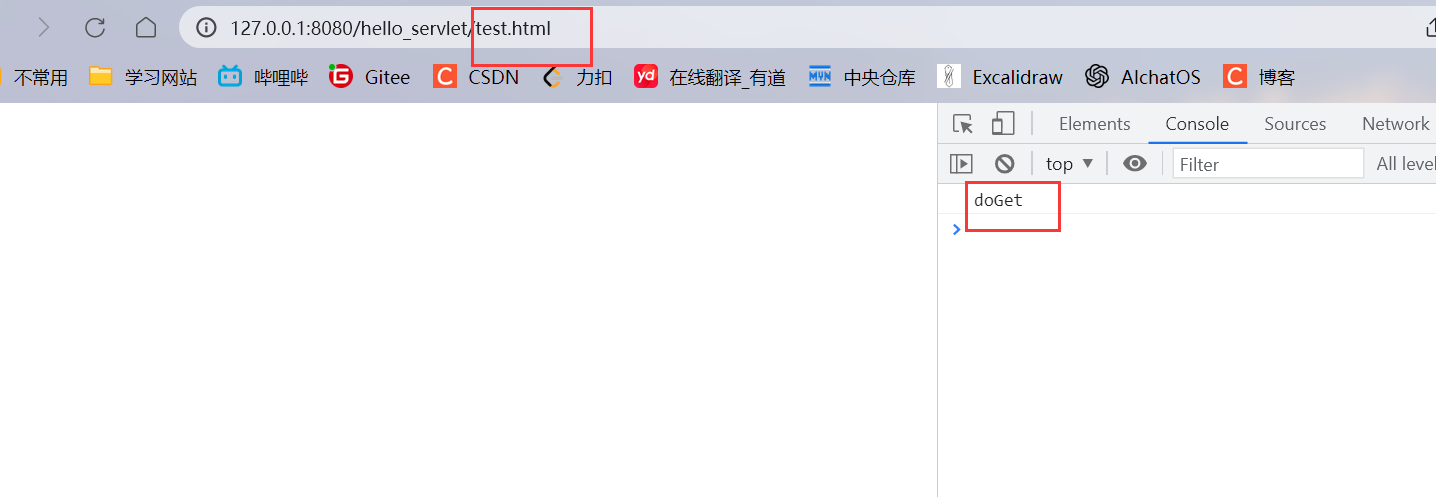
上述代码中url:'method'是相对路径.url:"/hello_servlet/method"是绝对路径.(浏览器中的要求) 注意两种路径的写法.还有在@WebServlet("/hello")这个注解中,这个路径必须/开头,但是并非表示绝对路径(Servlet中的要求)
HttpServletRequest
HttpServletRequest表示的是HTTP请求. 这个对象是Tomcat自动构造的.Tomcat会实现监听端口,接受连接,读取请求,构造请求对象等工作.
核心方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| String getProtocol() | 返回请求协议的名称和版本。 |
| String getMethod() | 返回请求的 HTTP 方法的名称,例如,GET、POST 或 PUT。 |
| String getRequestURI() | 从协议名称直到 HTTP 请求的第一行的查询字符串中,返回该请求的 URL 的一部分。 |
| String getContextPath() | 返回指示请求上下文的请求 URI 部分。 |
| String getQueryString() | 返回包含在路径后的请求 URL 中的查询字符串。 |
| Enumeration getParameterNames() | 返回一个 String 对象的枚举,包含在该请求中包含的参数的名称。 |
| String getParameter(Stringname) | 以字符串形式返回请求参数的值,或者如果参数不存在则返回null。 |
| String[] getParameterValues(Stringname) | 返回一个字符串对象的数组,包含所有给定的请求参数的值,如果参数不存在则返回 null。 |
| Enumeration getHeaderNames() | 返回一个枚举,包含在该请求中包含的所有的头名。 |
| String getHeader(Stringname) | 以字符串形式返回指定的请求头的值。 |
| String getCharacterEncoding() | 返回请求主体中使用的字符编码的名称。 |
| String getContentType() | 返回请求主体的 MIME 类型,如果不知道类型则返回 null。 |
| int getContentLength() | 以字节为单位返回请求主体的长度,并提供输入流,或者如果长度未知则返回 -1。 |
| InputStream getInputStream() | 用于读取请求的 body 内容. 返回一个 InputStream 对象 |
说明:
query String是键值对结构,使用getParameter就可以根据key获取到value.
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/showRequest")
public class ShowRequestServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html");
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append(req.getProtocol());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
stringBuilder.append(req.getMethod());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
stringBuilder.append(req.getRequestURI());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
stringBuilder.append(req.getContextPath());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
stringBuilder.append(req.getQueryString());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
resp.getWriter().write(stringBuilder.toString());
}
}
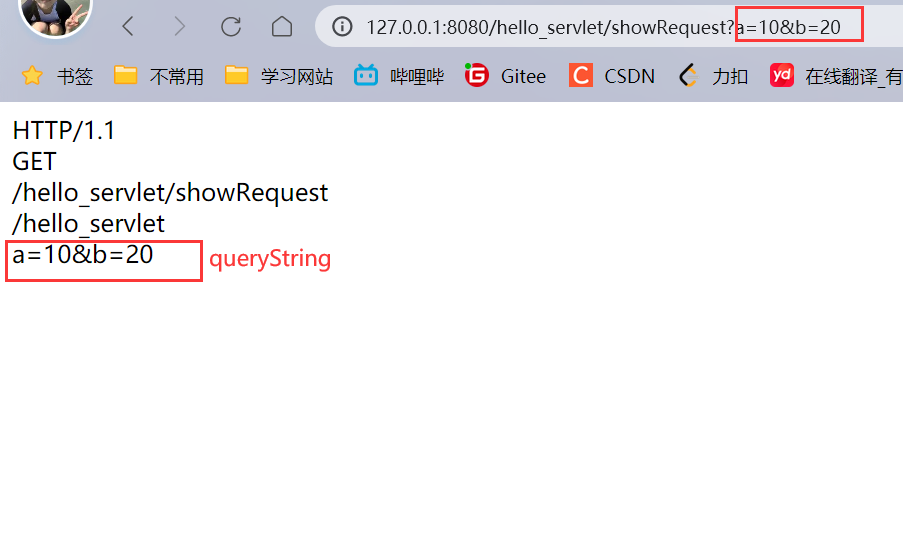

前端给后端传参的三种方式 :
- GET,queryString
- POST,from
- POST,json
- GET,queryString
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/getParameter")
public class GetParameterServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 预期浏览器会发一个形如 /getParameter?studentId=10&classId=20 请求.
// 借助 req 里的 getParameter 方法就能拿到 query string 中的键值对内容了.
// getParameter 得到的是 String 类型的结果.
String studentId = req.getParameter("studentId");
String classId = req.getParameter("classId");
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
// resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("学生id = " + studentId + " 班级id = " + classId);
}
}
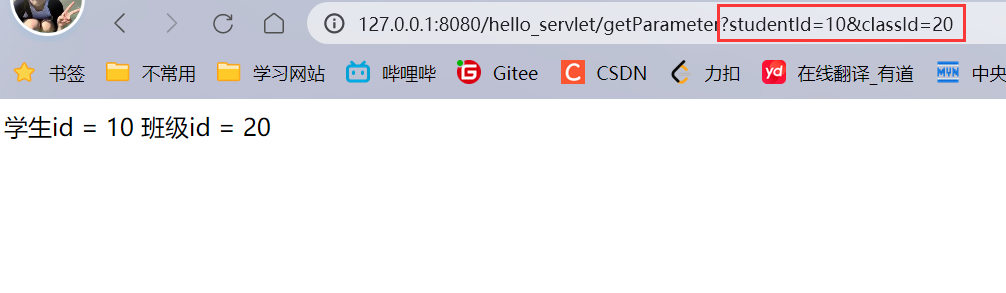
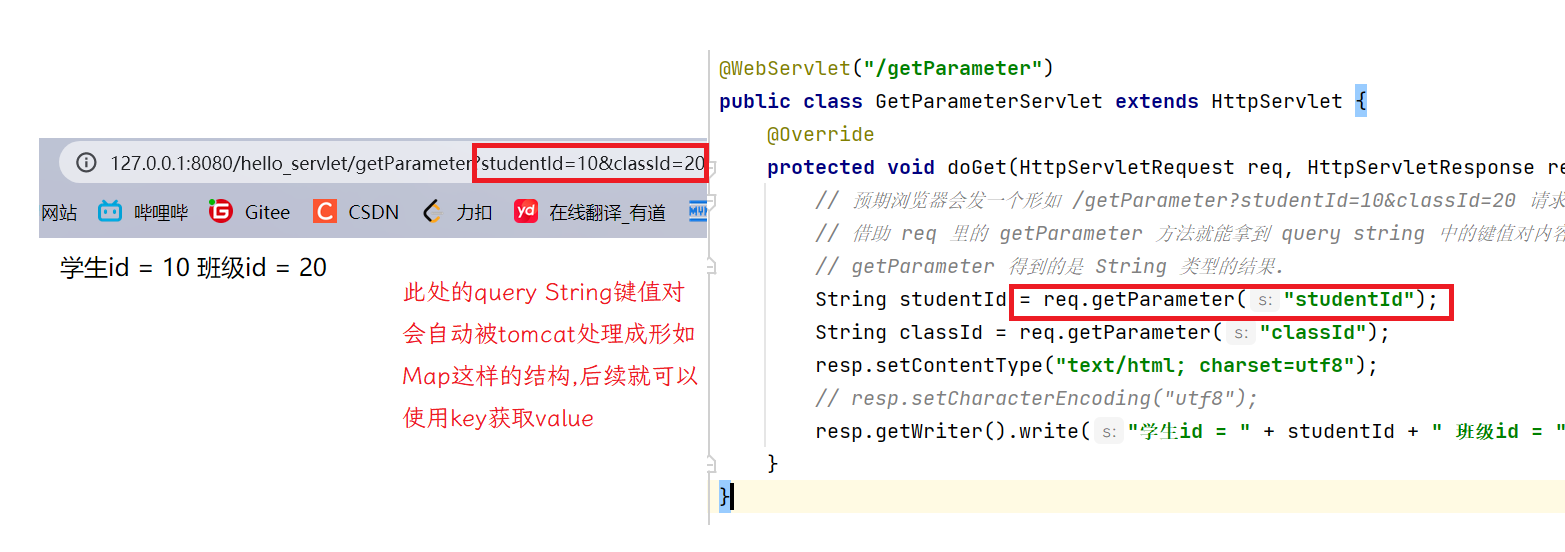
如果key在queryString中不存在,此时就返回null.
- POST,from
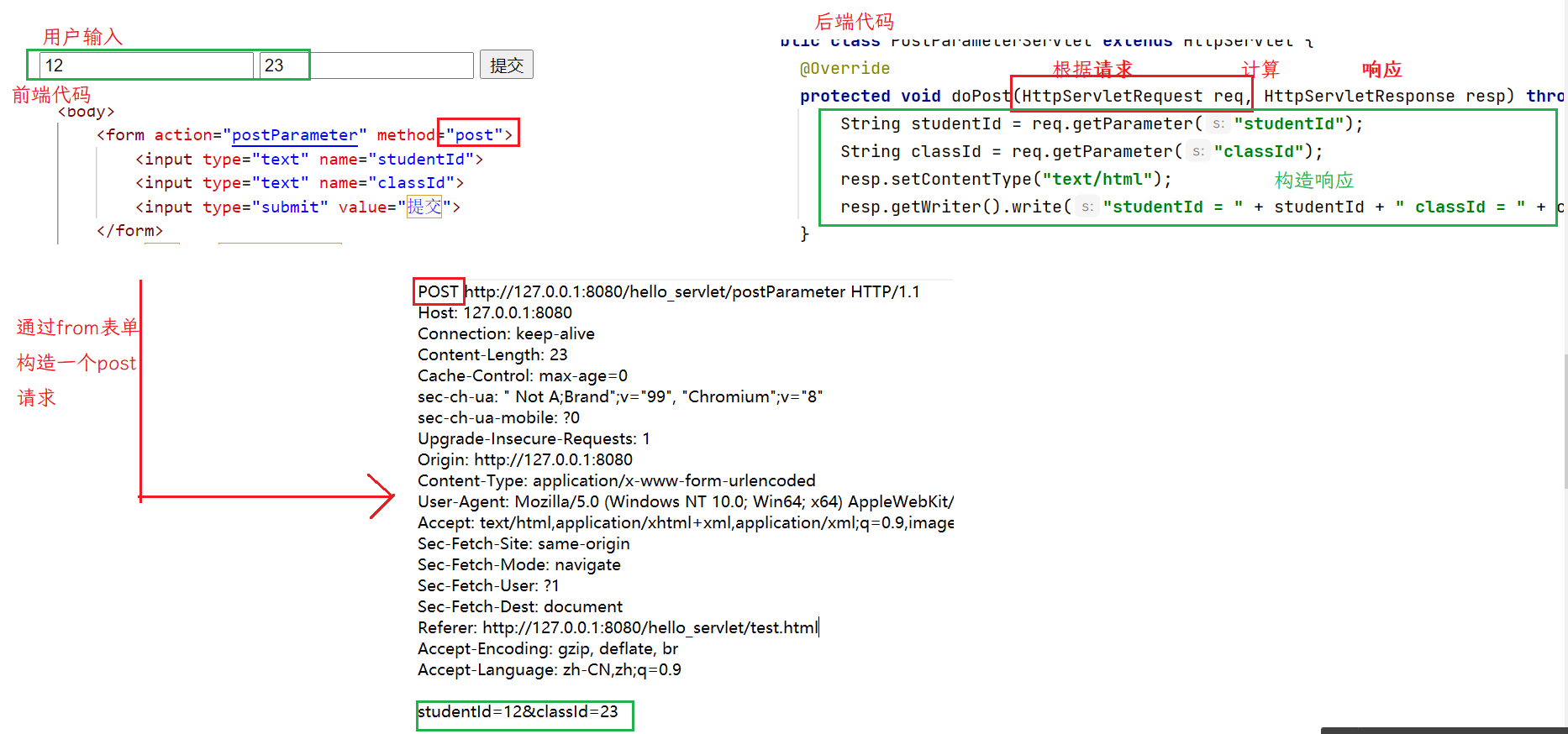
对于前端from表单这样的数据结构,后端还是使用GetParameter来获取.注意,from表单也是键值对,和queryString的格式一样,只是这部分内容在body中
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="postParameter" method="post">
<input type="text" name="studentId">
<input type="text" name="classId">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<!-- 构造ajax请求访问服务器 -->
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.4/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
// $.ajax({
// type:'get',
// url:'method',
// success:function(body,status){
// console.log(body);
// }
// })
</script>
</body>
</html>
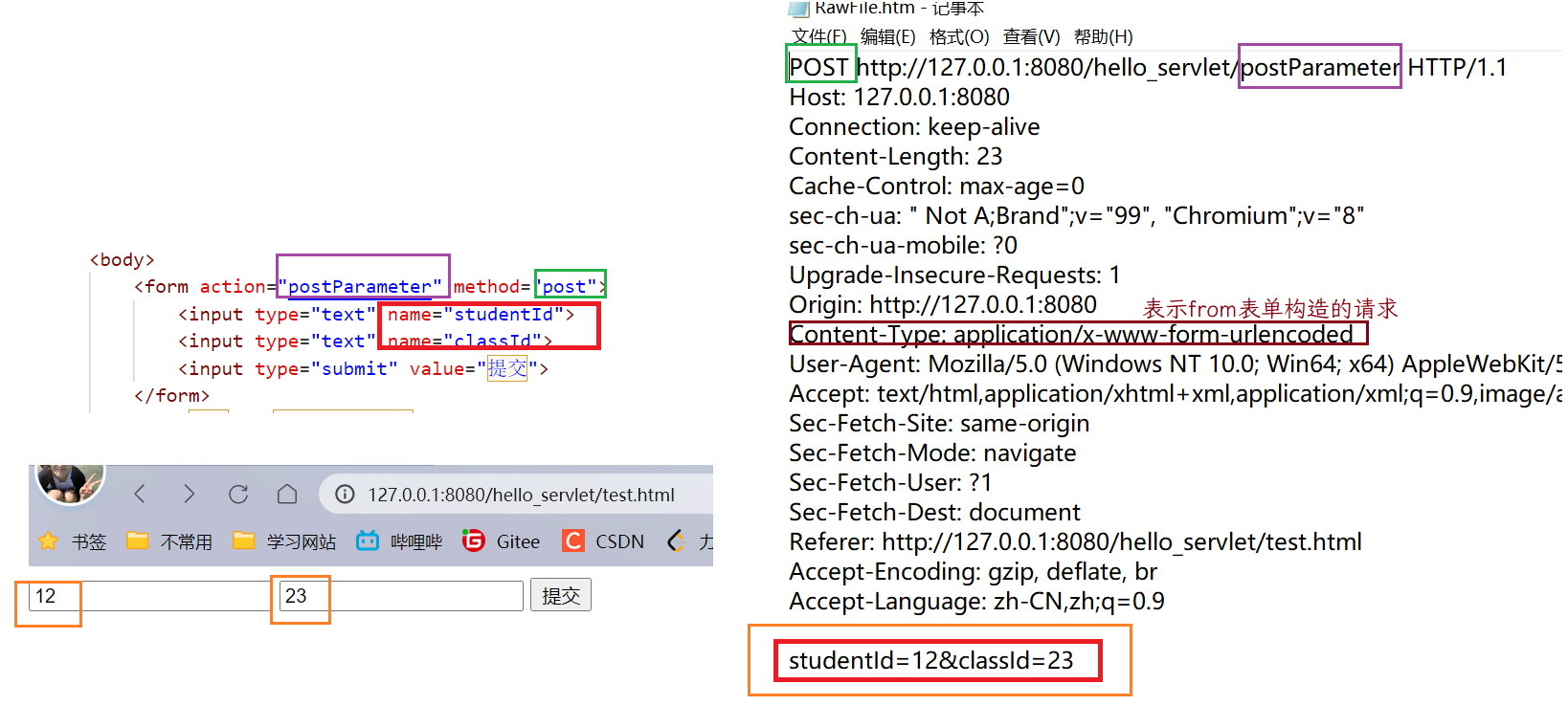
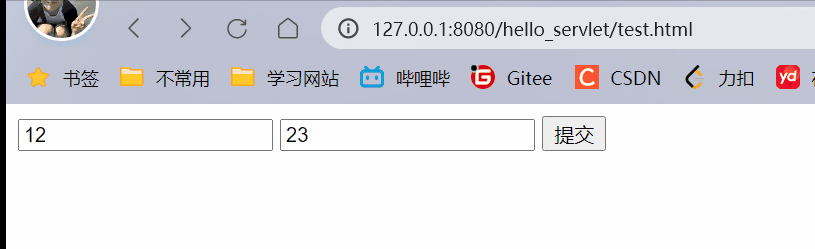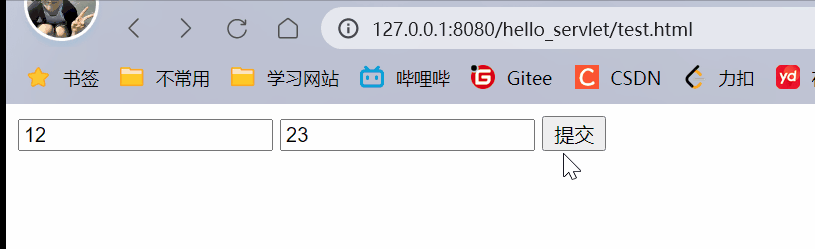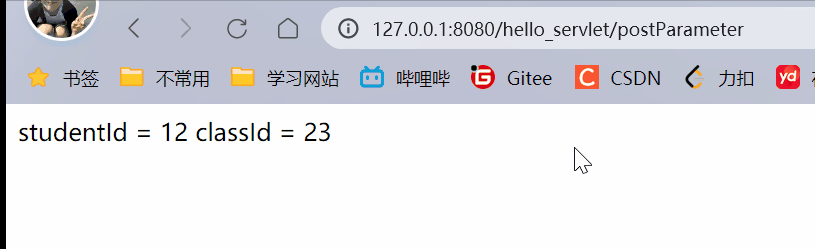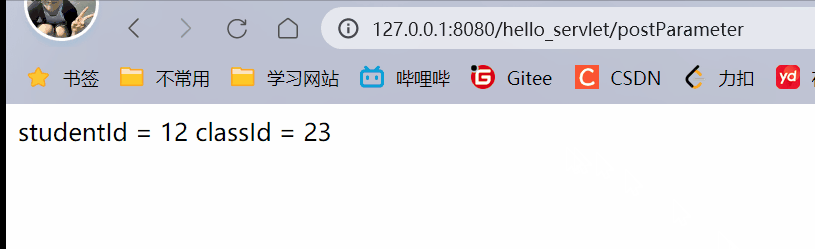
使用getparameter既可以获取到queryString键值对,也可以获取到form表单构造的body中的键值对.
上述过程,是前后端交互的过程.
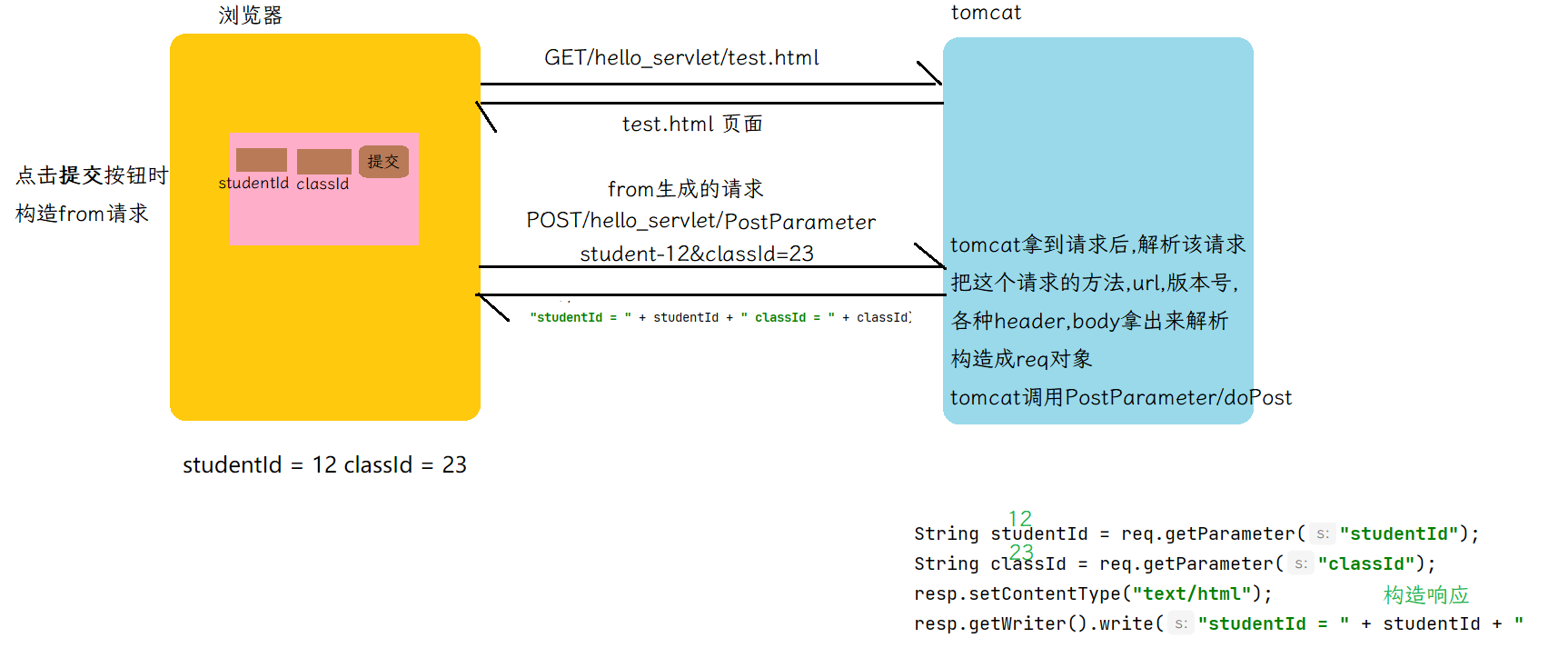
3. POST,json
json是一种非常主流的数据结构,也是键值对结构
使用Postman构造POST:
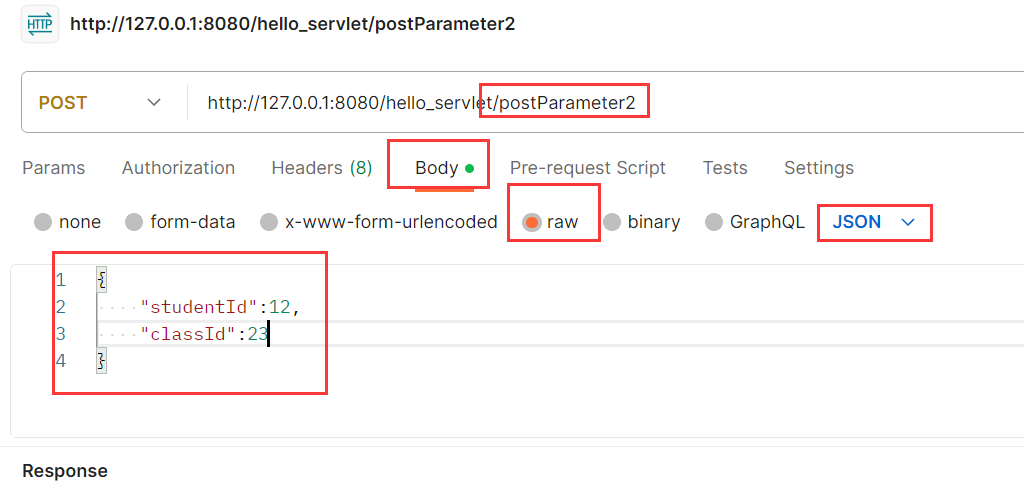
下面写PostParameter2服务器代码:
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
@WebServlet("/postParameter2")
public class PostParameter2Servlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 通过这个方法来处理 body 为 json 格式的数据.
// 直接把 req 对象里 body 完整的读取出来.
// getInputStream
// 在流对象中读多少个字节? 取决于 Content-Length
int length = req.getContentLength();
byte[] buffer = new byte[length];
InputStream inputStream = req.getInputStream();
inputStream.read(buffer);
// 把这个字节数组构造成 String, 打印出来.
String body = new String(buffer, 0, length, "utf8");
System.out.println("body = " + body);
}
}
打开Postman发送请求,在日志可以看到:
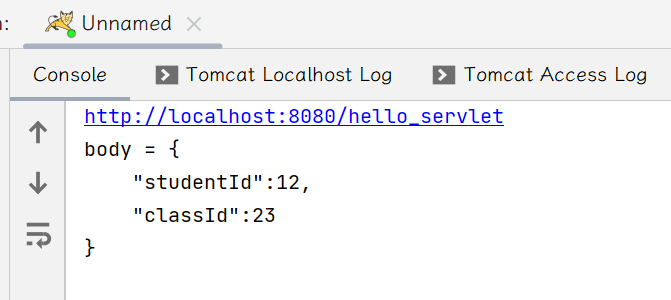
打开fiddler抓包可以看到:
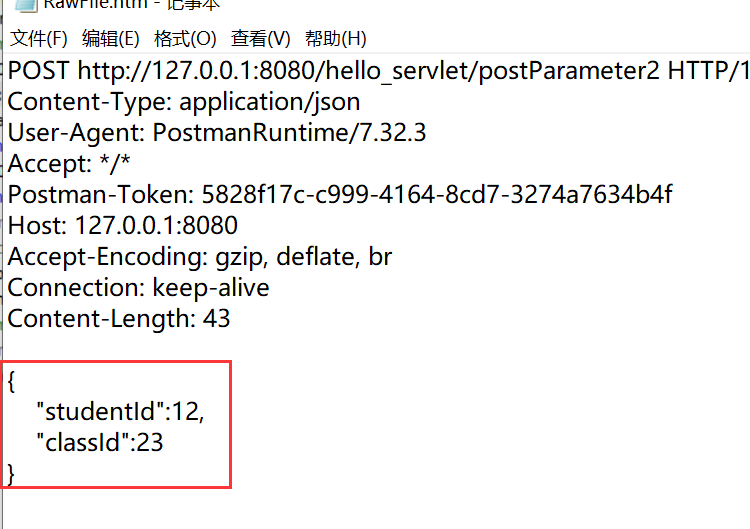
小结:
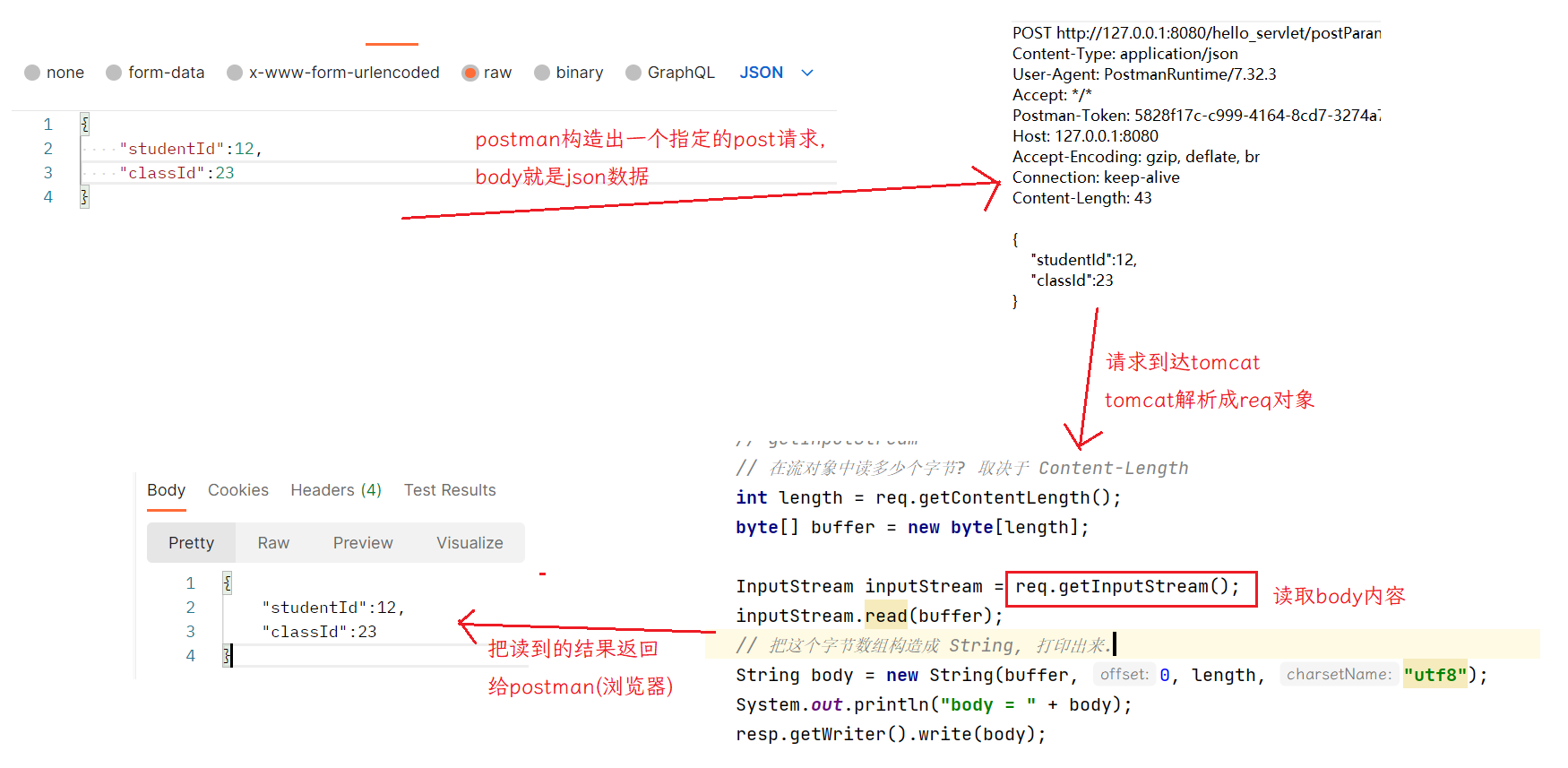
当前通过json传递数据,但是服务器这边只是把整个body读取进来,并没有按照键值对的方式来处理(还不能根据key获取value),此时可以使用第三方库来解决这个问题.
打开maven中央仓库:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
class Student {
public int studentId;
public int classId;
}
@WebServlet("/postParameter2")
public class PostParameter2Servlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
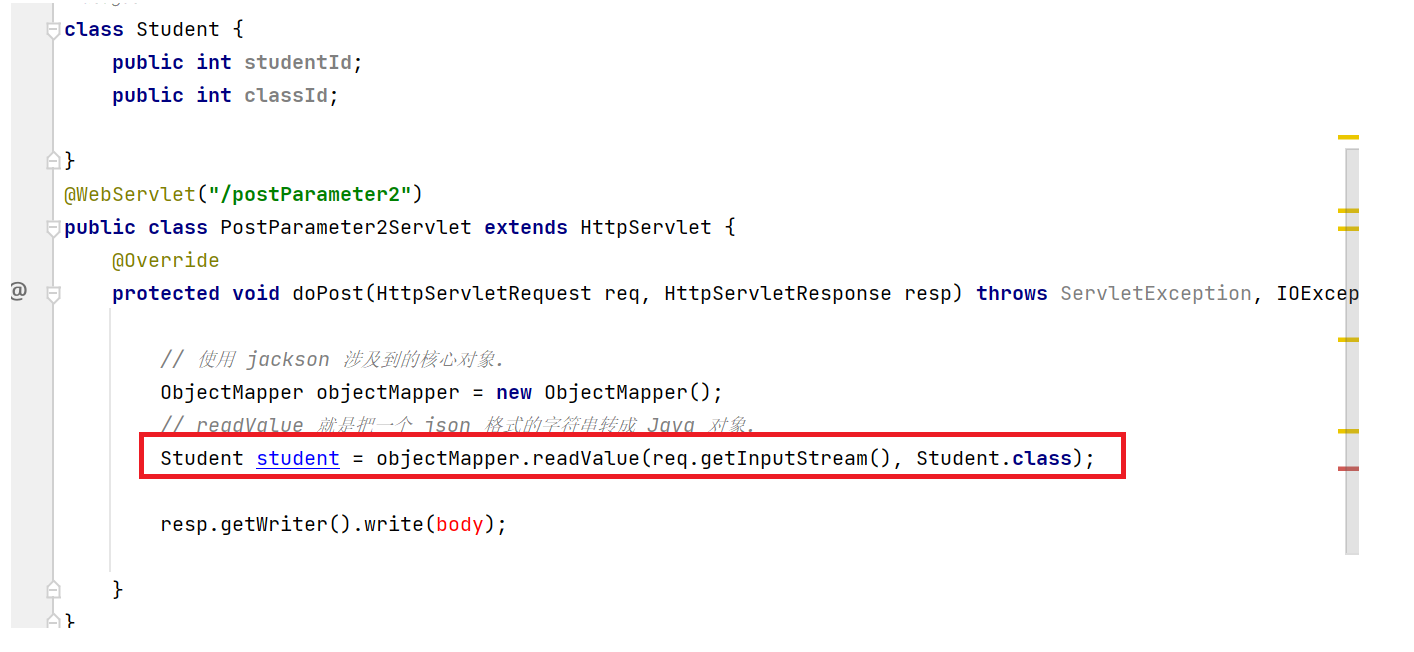
// 使用 jackson 涉及到的核心对象.
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// readValue 就是把一个 json 格式的字符串转成 Java 对象.
Student student = objectMapper.readValue(req.getInputStream(), Student.class);
System.out.println(student.studentId + ", " + student.classId);
//resp.getWriter().write(body);
}
}
- 会从body中读取json格式的字符串
- 根据第二个参数类对象,创建Student实例
- 解析上述json格式的字符串,处理成map键值对结构
- 遍历所有键值对,看键的名字和student实例中那个属性名字匹配,就把对应的value设置到该属性中.
- 返回该Student实例
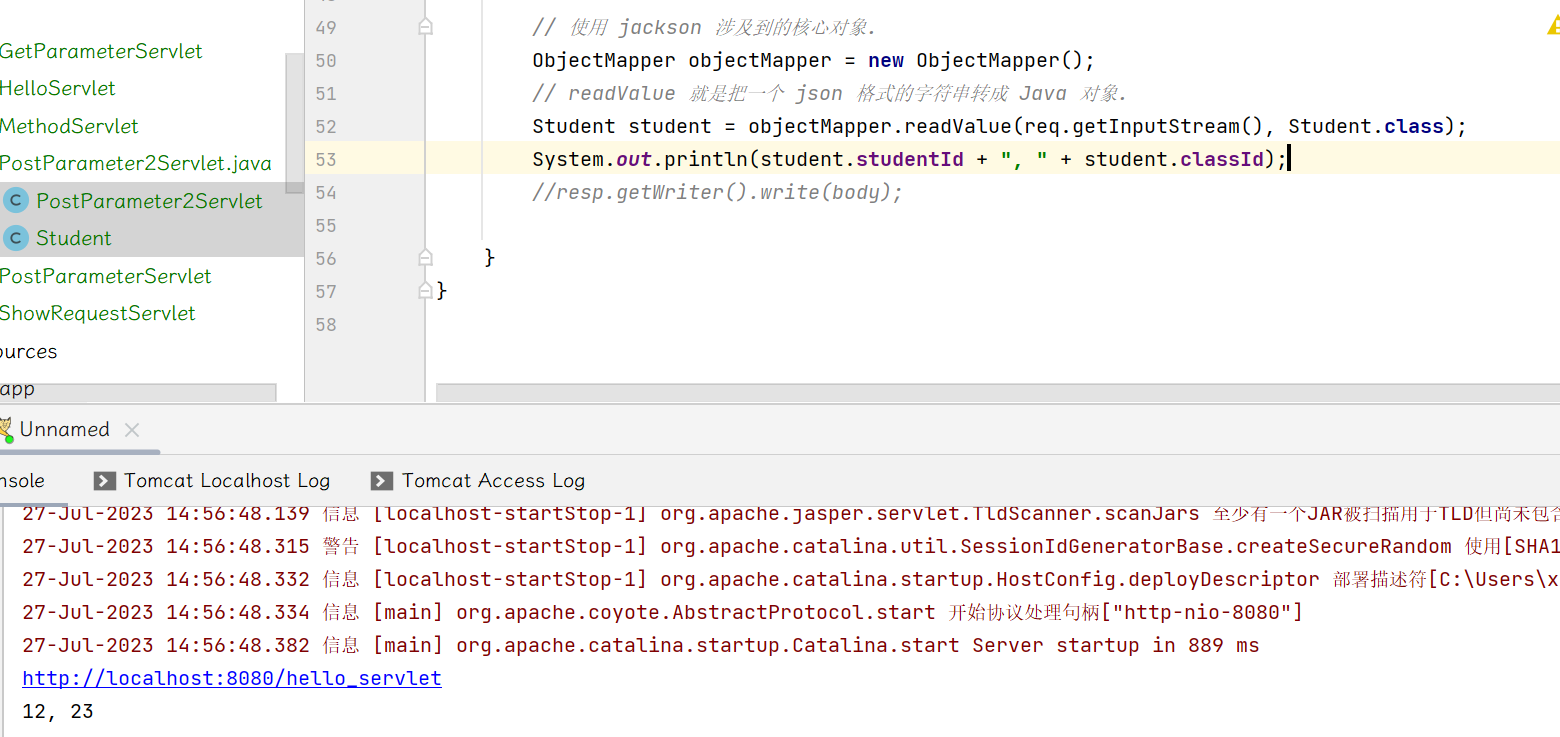
如果请求中多一个参数,Student中没有,则会出现500 服务器内部错误.
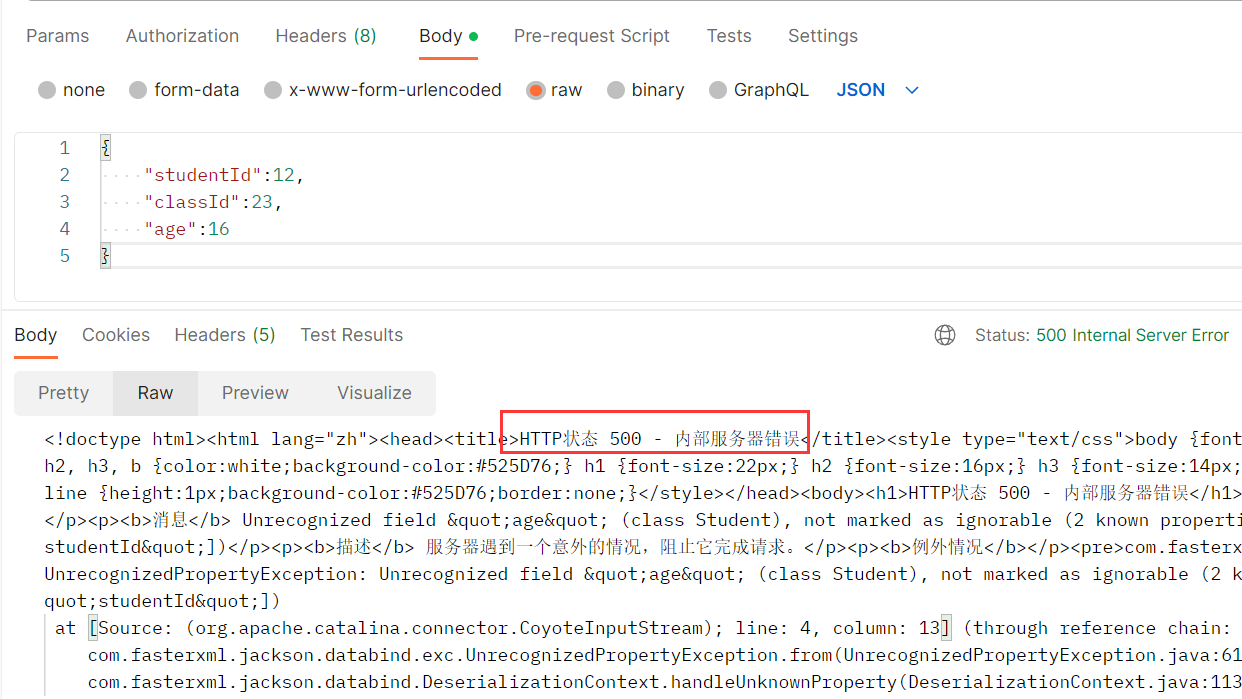
如果请求中少一个参数,Student中有这个参数,则会返回默认值.
HttpServletResponse
Servlet 中的 doXXX 方法的目的就是根据请求计算得到相应, 然后把响应的数据设置到
HttpServletResponse 对象中.
然后 Tomcat 就会把这个 HttpServletResponse 对象按照 HTTP 协议的格式, 转成一个字符串, 并通过Socket 写回给浏览器.
核心方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| void setStatus(int sc) | 为该响应设置状态码。 |
| void setHeader(String name,String value) | 设置一个带有给定的名称和值的 header. 如果 name 已经存在,则覆盖旧的值. |
| void addHeader(Stringname, String value) | 添加一个带有给定的名称和值的 header. 如果 name 已经存在,不覆盖旧的值, 并列添加新的键值对 |
| void setContentType(String type) | 设置被发送到客户端的响应的内容类型。 |
| void setCharacterEncoding(String charset) | 设置被发送到客户端的响应的字符编码(MIME 字符集)例如,UTF-8。 |
| void sendRedirect(String location) | 使用指定的重定向位置 URL 发送临时重定向响应到客户端。 |
| PrintWriter getWriter() | 用于往 body 中写入文本格式数据. |
| OutputStream getOutputStream() | 用于往 body 中写入二进制格式数据. |
说明:
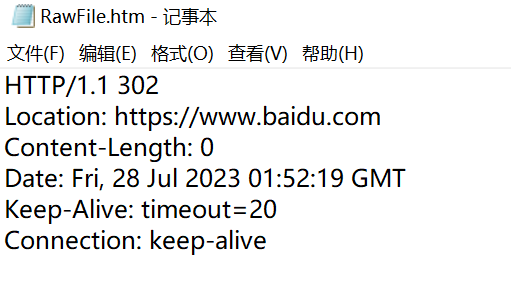
sendRedirect重定向.
两种写法:
@WebServlet("/redirect")
public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.sendRedirect("https://www.baidu.com");
}
}
@WebServlet("/redirect")
public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setStatus(302);
resp.setHeader("Location","https://www.baidu.com");
}
}
启动服务器,在地址栏中输入http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello_servlet/redirect可以看到网页跳转至百度页面:
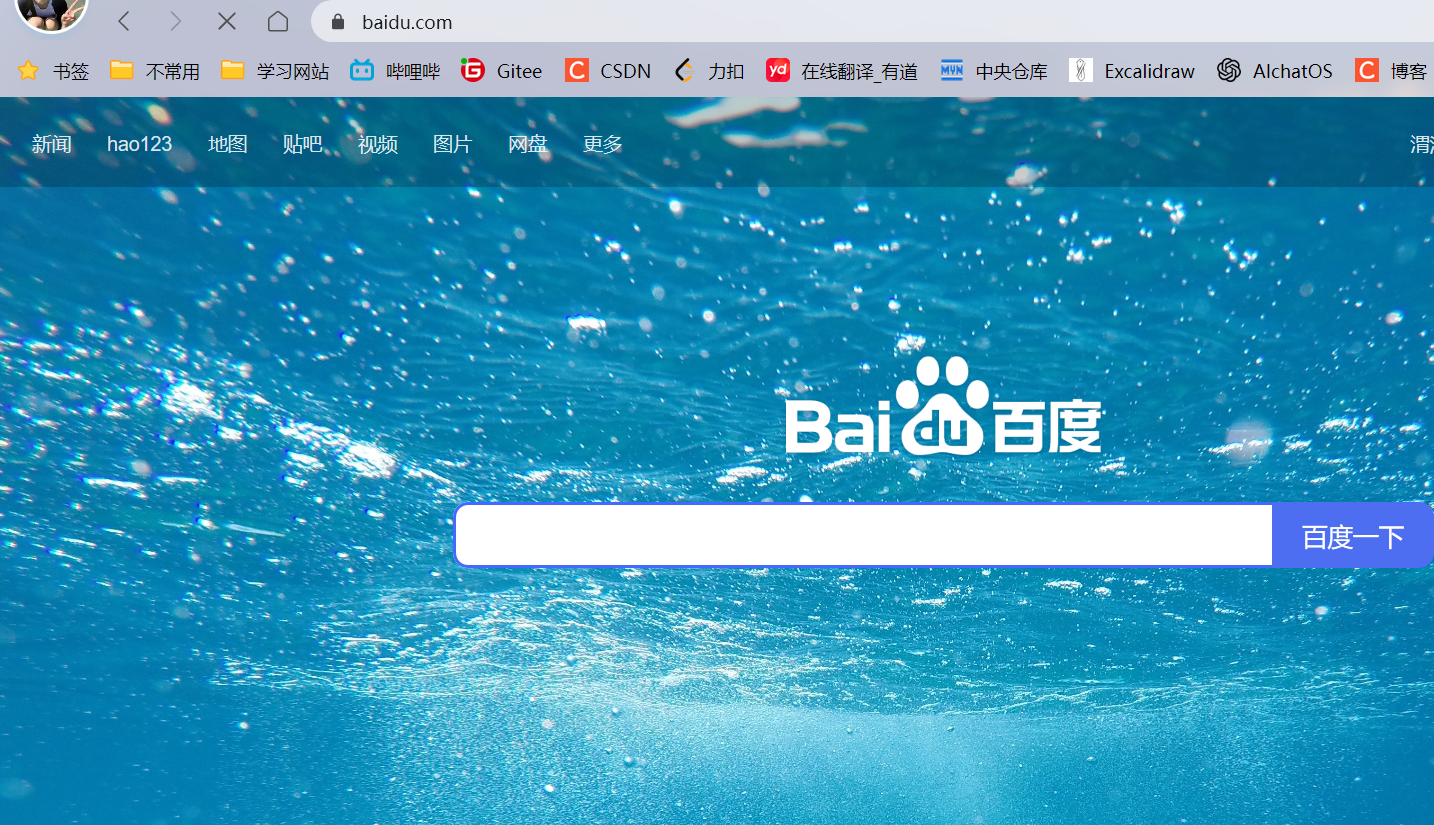
使用fiddler可以看到:
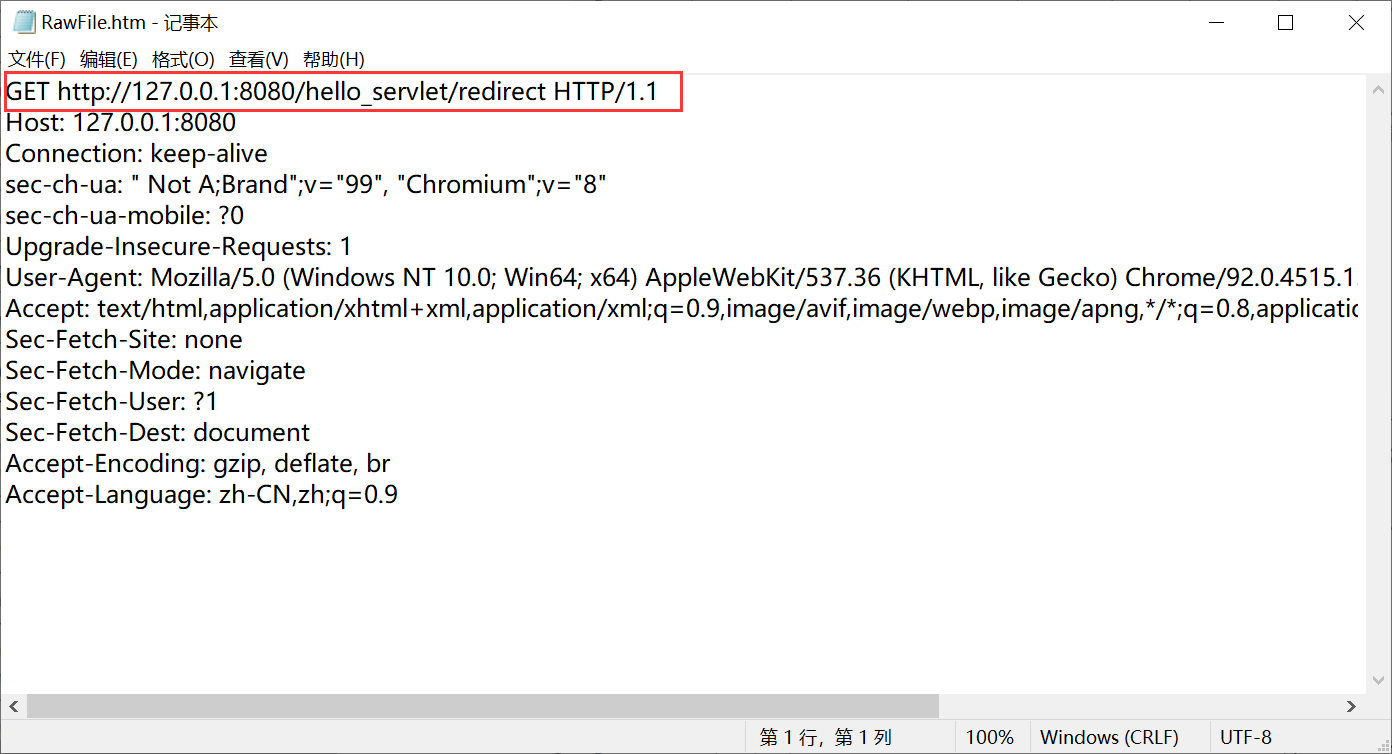
上述GET请求触发resp.sendRedirect("https://www.baidu.com");代码,从而得到响应: