实验任务
(1) 掌握顺序查找算法的实现;
(2) 掌握二分查找算法的实现;
(3) 掌握两种查找算法的时间复杂度与适用场合。
实验内容
(1) 基于顺序查找表实现顺序查找和二分查找算法;
(2) 使用两个不同大小的查找表进行两次理论和实际性能对比;
(3) 根据实验环境调整两次查找表的大小,使得:
i.第1次查找表的长度 = ⌊ 第2次查找表长度 / 10 ⌋;
ii.第2次顺序查找的时间介于 [ 9000, 9999 ] ms之间。
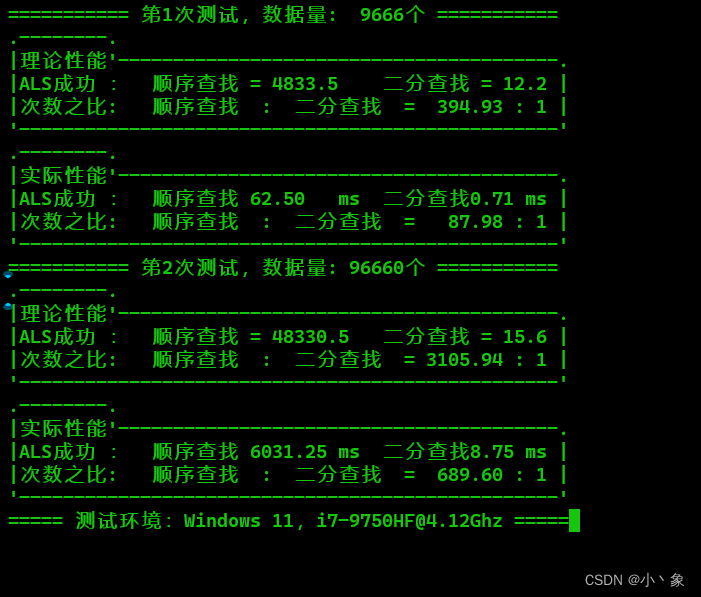
(4) 输出实验结果,结果应与如下图1所示尽可能相似。
实验源码
注意:由于编译器优化或电脑编程环境缓存等因素,实际运行和理论值可能有差距
//
// Created by Lenovo on 2022-05-27-上午 9:14.
// 作者:小象
// 版本:1.0
//
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <pthread_time.h>
#include <profileapi.h>
#define MAXSIZE 2147483 // int型0~21亿 顺序表可能达到的最大长度10位
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
// 数据元素类型定义
typedef struct {
int key; // 关键字域
int otherInfo; // 其他域
} ElemType;
// 顺序表定义
typedef struct {
ElemType *elem; // 存储空间的基地址
int length; // 当前长度
} SqSTable;
int InitTable(SqSTable *table); // 顺序表的初始化
int CreateTable(SqSTable *table, int length); // 顺序表的创建
double SearchSeq(SqSTable table, int key); // 顺序查找
double SearchSeq_Times(SqSTable table); // 顺序查找完 key 个关键字耗时
double SearchBin(SqSTable table, int key); // 二分查找
double SearchBin_Times(SqSTable table); // 二分查找完 key 个关键字耗时
void PrintResult(int data, double sequentialTimes, double binaryTimes); // 打印最终结果
/**
* <h2>二分查找 和 顺序查找算法 实验一</h2>
* <h3>实验要求:</h3>
* i.第1次查找表的长度 = 第2次查找表长度 / 10; <br>
* ii.第2次顺序查找的时间介于 [ 9000, 9999 ] ms之间。 <br>
* @return 0
*/
int main() {
SqSTable table;
if (!(InitTable(&table))) {
printf("空间申请失败!!!");
}
// 两种查找方式的所查找的数据量
int test_01_data = 9666;
int test_02_data = test_01_data * 10;
/*
* 第一次测试
*/
printf("=========== 第1次测试,数据量:%6d个 ===========\n", test_01_data);
// 创建顺序表
CreateTable(&table, test_01_data);
// 顺序查找
double sequentialTimes_01 = SearchSeq_Times(table);
// 二分查找
double binaryTimes_01 = SearchBin_Times(table);
// 查找结果
PrintResult(test_01_data, sequentialTimes_01, binaryTimes_01);
/*
* 第二次测试
*/
printf("=========== 第2次测试,数据量:%6d个 ===========\n", test_02_data);
// 创建顺序表
CreateTable(&table, test_02_data);
// 顺序查找
double sequentialTimes_02 = SearchSeq_Times(table);
// 二分查找
double binaryTimes_02 = SearchBin_Times(table);
// 查找结果
PrintResult(test_02_data, sequentialTimes_02, binaryTimes_02);
// 测试环境
printf("===== 测试环境:Windows 11,i7-9750HF@4.12Ghz =====");
getchar();
}
// 构造一个空的顺序表
int InitTable(SqSTable *table) {
table->elem = (ElemType *) malloc(sizeof(SqSTable) * MAXSIZE); // 动态方式需要先分配内存,而且
// 需要用到malloc函数申请,有可能申请不到,申请到后malloc()函数会把申请到的连续数据空间首地址返回
// 注意:这里申请到返回的地址是十六进制的地址,而elem只能存十进制的地址,所以需要强转为十进制地址后赋值
if (table->elem == NULL) { // 如果没有申请到地址,退出
return ERROR;
}
table->length = 0; // 空表长度为 0
return OK; // 初始化成功
}
// 顺序表的创建
int CreateTable(SqSTable *table, int length) {
for (int i = 1; i <= length; i++) { // 第一个数默认不使用
table->elem[i].key = i;
table->length++; // 表长加 1
}
return OK;
}
// 顺序查找
double SearchSeq(SqSTable table, int key) {
int i;
table.elem[0].key = key; // 第一个数的作用来了 -> 设置 “哨兵”
for (i = table.length; table.elem[i].key != key; i--); // 从后往前找
}
// 顺序查找测时
double SearchSeq_Times(SqSTable table) {
/*
* 时间测试方式二:
* 所用精度:纳秒级
*/
struct timespec start;
struct timespec end;
// 开始时间
clock_gettime(CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID, &start);
for (int i = 1; i <= table.length; i++) { // 所有数都查找一遍
SearchSeq(table, i);
}
// 结束时间
clock_gettime(CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID, &end);
// 总耗时
// 转化为 ms 为单位(但是精度可以直接到 ns 级别)
double start_ms = start.tv_sec * 1000.0 + start.tv_nsec / 1000000.0;
double end_ms = end.tv_sec * 1000.0 + end.tv_nsec / 1000000.0;
return end_ms - start_ms;
}
// 在有序表table中折半查找其关键字等于key的数据元素。若找到,则函数值为该元素在表中的位置,否则为0
double SearchBin(SqSTable table, int key) {
// 置 查找区间 初值
int leftIndex = 1; // 第一个数默认不使用
int rightIndex = table.length;
while (leftIndex <= rightIndex) { // 循环限制条件:查找过程中如果没有找到的情况,会造成栈溢出
int minIndex = (leftIndex + rightIndex) / 2; // 二分查找的精髓:先找到中间那个数
if (key == table.elem[minIndex].key) {
// 如果需要查找的数等于中间那个数,则直接输出中间那个数(即需要查找的数的)下标
return minIndex; // 找到待查元素
} else if (key < table.elem[minIndex].key) {
// 如果需要查找的数小于中间那个数,说明需要从中间那个数的左边第一个数继续进行二分查找,其他不变
rightIndex = minIndex - 1;
} else {
// 如果需要查找的数大于中间那个数,说明需要从中间那个数的右边第一个数继续进行二分查找,其他不变
leftIndex = minIndex + 1;
}
}
return -1; // 如果没有找到返回-1
}
// 二分查找测时
double SearchBin_Times(SqSTable table) {
/*
* 时间测试方式二:
* 所用精度:微秒级
*/
union _LARGE_INTEGER time_start; // 开始时间
union _LARGE_INTEGER time_over; // 结束时间
LARGE_INTEGER f; // 计时器频率
QueryPerformanceFrequency(&f);
double dqFreq = (double) f.QuadPart; // 计时器频率
QueryPerformanceCounter(&time_start); // 计时开始
for (int i = 1; i <= table.length; i++) { // 所有数都查找一遍
SearchBin(table, i);
}
QueryPerformanceCounter(&time_over); // 计时结束
// 乘以1000000把单位由秒化为微秒,精度为1000 000/(cpu主频)微秒
double run_time = 1000000.0 * (time_over.QuadPart - time_start.QuadPart) / dqFreq;
return run_time / 1000.0;
}
void PrintResult(int data, double sequentialTimes, double binaryTimes) {
// 理论ASL
double sequentialASL = (data + 1) / 2.0;
double binaryASL = log2(data + 1) - 1;
printf(".--------.\n");
printf("|理论性能'----------------------------------------.\n");
printf("|ALS成功 : 顺序查找 = %-7.1f 二分查找 = %-4.1f |\n", sequentialASL, binaryASL);
printf("|次数之比: 顺序查找 : 二分查找 = %7.2f : 1 |\n", sequentialASL / binaryASL);
printf("'-------------------------------------------------'\n");
printf(".--------.\n");
printf("|实际性能'----------------------------------------.\n");
printf("|ALS成功 : 顺序查找 %-7.2f ms 二分查找%-4.2f ms |\n", sequentialTimes, binaryTimes);
printf("|次数之比: 顺序查找 : 二分查找 = %7.2f : 1 |\n", sequentialTimes / binaryTimes);
printf("'-------------------------------------------------'\n");
}
实验结果