零、文章目录
Vue2基础六、组件通信
1、组件通信
(1)组件通信是什么
-
组件通信, 就是指
组件与组件之间的数据传递。-
组件的数据是独立的,无法直接访问其他组件的数据。
-
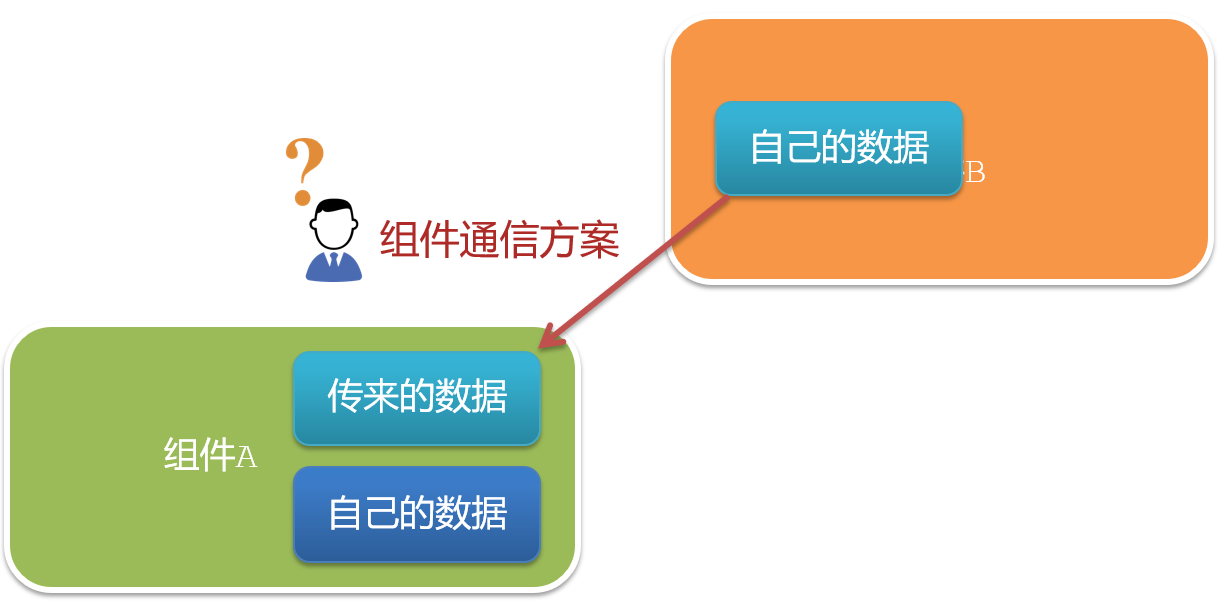
想使用其他组件的数据,就需要组件通信
-
(2)组件之间如何通信
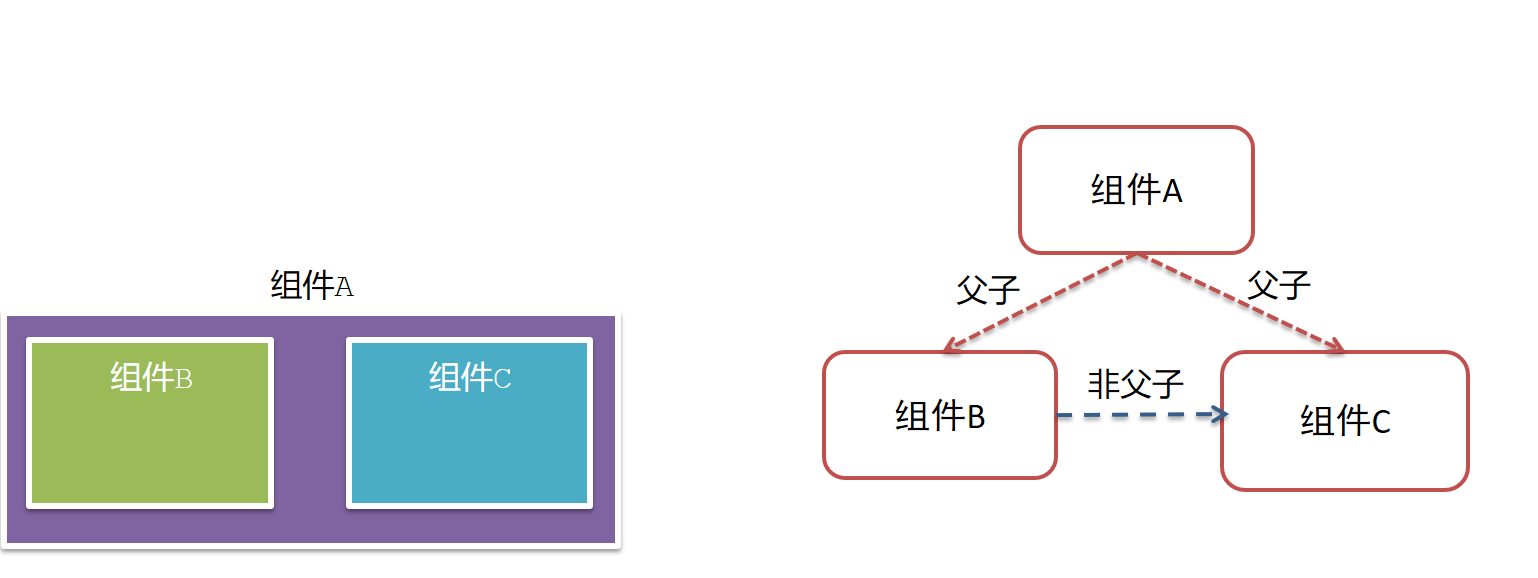
(3)组件关系分类
- 父子关系
- 非父子关系
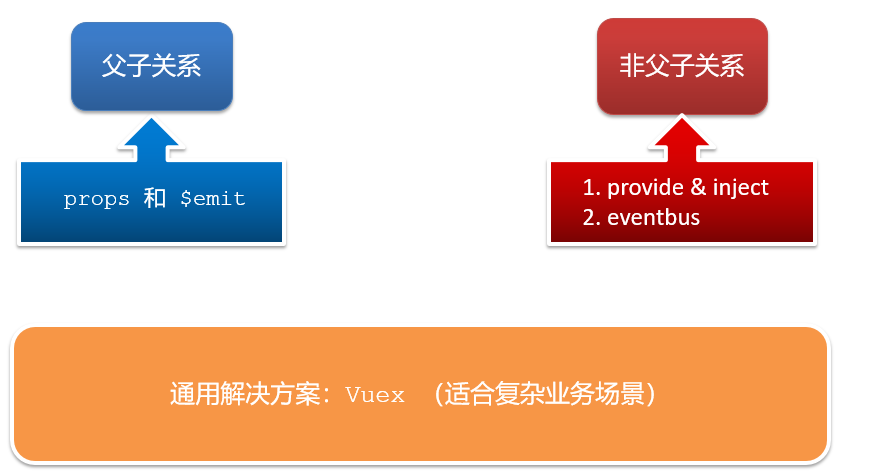
(4)通信解决方案
- 父子关系:props & $emit
- 非父子关系:provide & inject 或 eventbus
- 通用方案:vuex
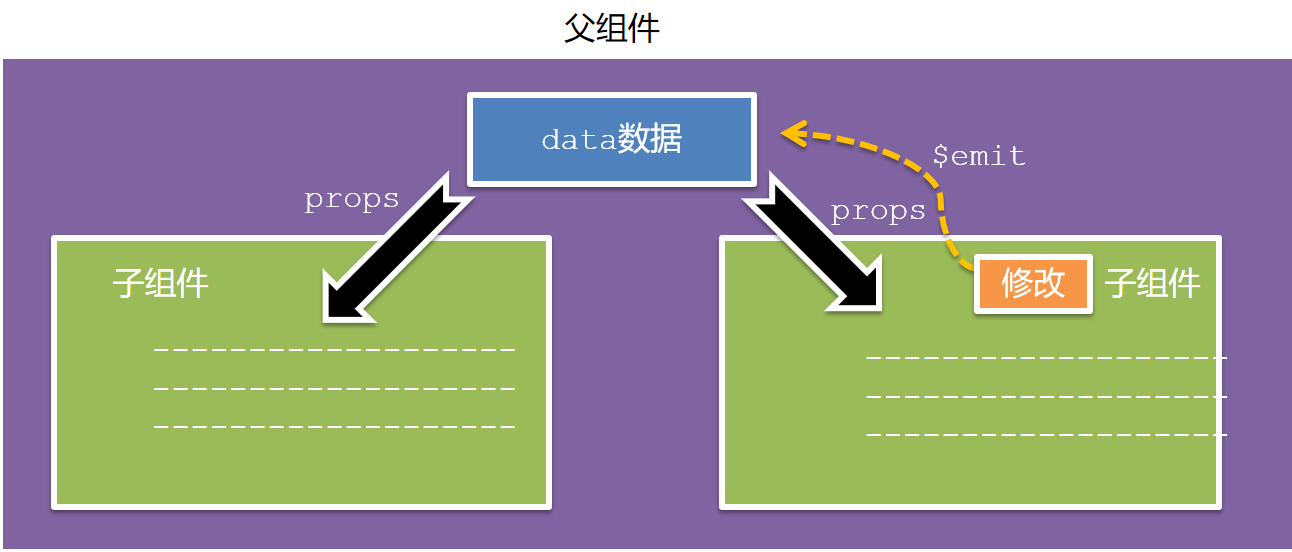
(5)父子通信流程
- 父组件通过 props 将数据传递给子组件
- 子组件利用 $emit 通知父组件修改更新
2、父组件传值子组件
(1)父向子传值步骤
- 父中给子添加属性传值
- 子组件内部通过
props接收 - 模板中直接使用props接收的值
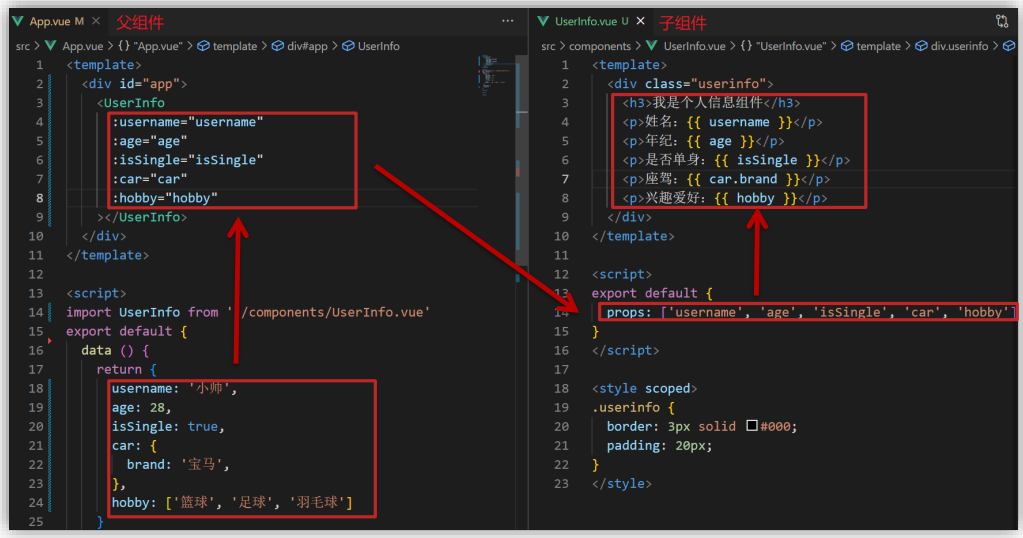
(2)代码实现
- 父组件
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app" style="border: 3px solid #000; margin: 10px">
我是APP组件
<!-- 1.给组件标签,添加属性方式 赋值 -->
<Son :title="myTitle"></Son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from './components/Son.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {
myTitle: '我是父组件传进来的值',
}
},
components: {
Son,
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- 子组件
Son.vue
<template>
<div class="son" style="border:3px solid #000;margin:10px">
<!-- 3.直接使用props的值 -->
我是Son组件--{{title}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Son-Child',
// 2.通过props来接受
props:['title']
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
3、子组件通知父组件更新
(1)子向父传值步骤
- 子组件
$emit触发事件,给父组件发送消息通知 - 父组件监听
$emit触发的事件 - 父组件提供处理函数
(2)代码实现
- 父组件
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app" style="border: 3px solid #000; margin: 10px">
我是APP组件
<!-- 2.父组件对子组件的消息进行监听 -->
<Son :title="myTitle" @changTitle="handleChange"></Son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from './components/Son.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {
myTitle: '我是父组件传进来的值',
}
},
components: {
Son,
},
methods: {
// 3.提供处理函数,提供逻辑
handleChange(newTitle) {
this.myTitle = newTitle
},
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- 子组件
Son.vue
<template>
<div class="son" style="border: 3px solid #000; margin: 10px">
我是Son组件 {{ title }}
<button @click="changeFn">修改title</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Son-Child',
props: ['title'],
methods: {
changeFn() {
// 通过this.$emit() 向父组件发送通知
this.$emit('changTitle','子组件通知父组件更新')
},
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
4、props详解
(1)prop是什么
-
定义:组件上 注册的一些 自定义属性
-
作用:向子组件传递数据
-
特点:
-
可以 传递 任意数量 的prop
-
可以 传递 任意类型 的prop
-
-
代码实现
- 父组件
App.vue
<template> <div class="app"> <UserInfo :username="username" :age="age" :isSingle="isSingle" :car="car" :hobby="hobby" ></UserInfo> </div> </template> <script> import UserInfo from './components/UserInfo.vue' export default { data() { return { username: '小帅', age: 28, isSingle: true, car: { brand: '宝马', }, hobby: ['篮球', '足球', '羽毛球'], } }, components: { UserInfo, }, } </script> <style> </style>- 子组件
UserInfo.vue
<template> <div class="userinfo"> <h3>我是个人信息组件</h3> <div>姓名:{{username}}</div> <div>年龄:{{age}}</div> <div>是否单身:{{isSingle}}</div> <div>座驾:{{car.brand}}</div> <div>兴趣爱好:{{hobby.join('、')}}</div> </div> </template> <script> export default { props:['username','age','isSingle','car','hobby'] } </script> <style> .userinfo { width: 300px; border: 3px solid #000; padding: 20px; } .userinfo > div { margin: 20px 10px; } </style> - 父组件
(2)props 校验
-
**作用:**为组件的 prop 指定
验证要求,不符合要求,控制台就会有错误提示→ 帮助开发者,快速发现错误 -
语法:
-
类型校验
-
非空校验
-
默认值
-
自定义校验
-

-
注意:
-
default和required一般不同时写(因为当时必填项时,肯定是有值的)
-
default后面如果是简单类型的值,可以直接写默认。如果是复杂类型的值,则需要以函数的形式return一个默认值
-
-
代码实现:
- 父组件
App.vue
<template> <div class="app"> <BaseProgress :w="width"></BaseProgress> </div> </template> <script> import BaseProgress from './components/BaseProgress.vue' export default { data() { return { width: 30, } }, components: { BaseProgress, }, } </script> <style> </style>- 子组件
BaseProgress.vue
<template> <div class="base-progress"> <div class="inner" :style="{ width: w + '%' }"> <span>{{ w }}%</span> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { // 1.基础写法(类型校验) // props: { // w: Number, // }, // 2.完整写法(类型、默认值、非空、自定义校验) props: { w: { type: Number, required: true, default: 0, validator(val) { // console.log(val) if (val >= 100 || val <= 0) { console.error('传入的范围必须是0-100之间') return false } else { return true } }, }, }, } </script> <style scoped> .base-progress { height: 26px; width: 400px; border-radius: 15px; background-color: #272425; border: 3px solid #272425; box-sizing: border-box; margin-bottom: 30px; } .inner { position: relative; background: #379bff; border-radius: 15px; height: 25px; box-sizing: border-box; left: -3px; top: -2px; } .inner span { position: absolute; right: 0; top: 26px; } </style> - 父组件
(3)prop & data、单向数据流
-
**共同点:**都可以给组件提供数据
-
区别:
-
data 的数据是
自己的 → 随便改 -
prop 的数据是
外部的 → 不能直接改,要遵循单向数据流
-
-
**单向数据流:**父级props 的数据更新,会向下流动,影响子组件。这个数据流动是单向的。
-
代码实现:
- 父组件
App.vue
<template> <div class="app"> <BaseCount :count="count" @changeCount="handleChange"></BaseCount> </div> </template> <script> import BaseCount from './components/BaseCount.vue' export default { components:{ BaseCount }, data(){ return { count:100 } }, methods:{ handleChange(newVal){ // console.log(newVal); this.count = newVal } } } </script> <style> </style>- 子组件
BaseCount.vue
<template> <div class="base-count"> <button @click="handleSub">-</button> <span>{{ count }}</span> <button @click="handleAdd">+</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { // 1.自己的数据随便修改 (谁的数据 谁负责) // data () { // return { // count: 100, // } // }, // 2.外部传过来的数据 不能随便修改 props: { count: { type: Number, }, }, methods: { handleSub() { this.$emit('changeCount', this.count - 1) }, handleAdd() { this.$emit('changeCount', this.count + 1) }, }, } </script> <style> .base-count { margin: 20px; } </style> - 父组件
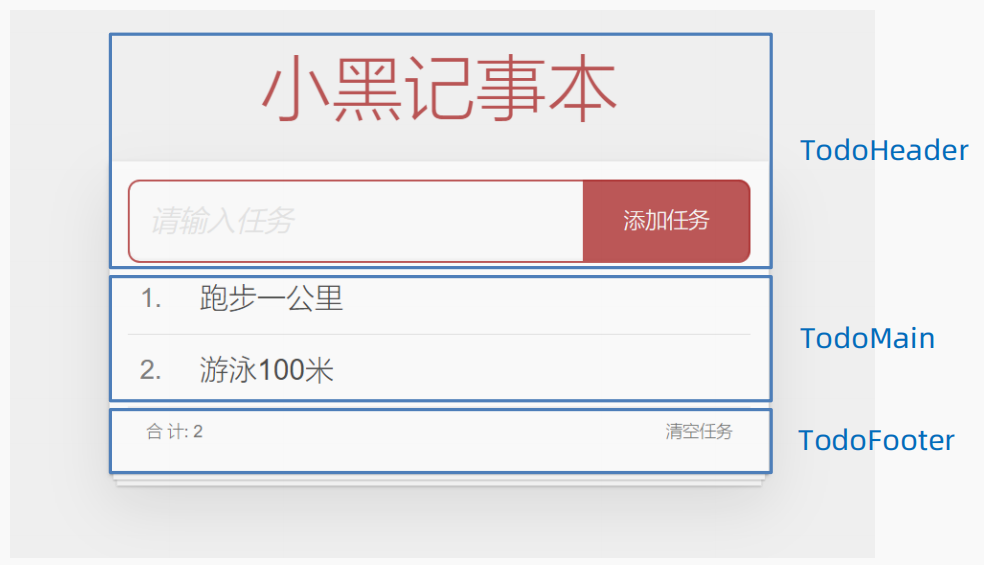
5、案例-小黑记事本
(1)需求说明
- 拆分基础组件
- 渲染待办任务
- 添加任务
- 删除任务
- 底部合计 和 清空功能
- 持久化存储
(2)核心步骤
- ① 拆分基础组件:新建组件 → 拆分存放结构 → 导入注册使用
- ② 渲染待办任务:提供数据(公共父组件) → 父传子传递 list → v-for 渲染
- ③ 添加任务:收集数据 v-model → 监听事件 → 子传父传递任务 → 父组件 unshift
- ④ 删除任务:监听删除携带 id → 子传父传递 id → 父组件 filter 删除
- ⑤ 底部合计 和 清空功能
- 底部合计:父传子传递 list → 合计展示
- 清空功能:监听点击 → 子传父通知父组件 → 父组件清空
- ⑥ 持久化存储:watch监视数据变化,持久化到本地
(3)代码实现
- 子组件
TodoFooter.vue
<template>
<!-- 统计和清空 -->
<footer class="footer">
<!-- 统计 -->
<span class="todo-count"
>合 计:<strong> {{ list.length }} </strong></span
>
<!-- 清空 -->
<button class="clear-completed" @click="clear">清空任务</button>
</footer>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
list: {
type: Array,
},
},
methods:{
clear(){
this.$emit('clear')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- 子组件
TodoHeader.vue
<template>
<!-- 输入框 -->
<header class="header">
<h1>小黑记事本</h1>
<input placeholder="请输入任务" class="new-todo" v-model="todoName" @keyup.enter="handleAdd"/>
<button class="add" @click="handleAdd">添加任务</button>
</header>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return {
todoName:''
}
},
methods:{
handleAdd(){
// console.log(this.todoName)
this.$emit('add',this.todoName)
this.todoName = ''
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- 子组件
TodoMain.vue
<template>
<!-- 列表区域 -->
<section class="main">
<ul class="todo-list">
<li class="todo" v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id">
<div class="view">
<span class="index">{{ index + 1 }}.</span>
<label>{{ item.name }}</label>
<button class="destroy" @click="handleDel(item.id)"></button>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
list: {
type: Array,
},
},
methods: {
handleDel(id) {
this.$emit('del', id)
},
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- 父组件
App.vue
<template>
<!-- 主体区域 -->
<section id="app">
<TodoHeader @add="handleAdd"></TodoHeader>
<TodoMain :list="list" @del="handelDel"></TodoMain>
<TodoFooter :list="list" @clear="clear"></TodoFooter>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import TodoHeader from './components/TodoHeader.vue'
import TodoMain from './components/TodoMain.vue'
import TodoFooter from './components/TodoFooter.vue'
// 渲染功能:
// 1.提供数据: 提供在公共的父组件 App.vue
// 2.通过父传子,将数据传递给TodoMain
// 3.利用 v-for渲染
// 添加功能:
// 1.手机表单数据 v-model
// 2.监听事件(回车+点击都要添加)
// 3.子传父,讲任务名称传递给父组件 App.vue
// 4.进行添加 unshift(自己的数据自己负责)
// 5.清空文本框输入的内容
// 6.对输入的空数据 进行判断
// 删除功能
// 1.监听事件(监听删除的点击) 携带id
// 2.子传父,讲删除的id传递给父组件的App.vue
// 3.进行删除filter(自己的数据 自己负责)
// 底部合计:父传子 传list 渲染
// 清空功能:子传父 通知父组件 → 父组件进行更新
// 持久化存储:watch深度监视list的变化 -> 往本地存储 ->进入页面优先读取本地数据
export default {
data() {
return {
list: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('list')) || [
{ id: 1, name: '打篮球' },
{ id: 2, name: '看电影' },
{ id: 3, name: '逛街' },
],
}
},
components: {
TodoHeader,
TodoMain,
TodoFooter,
},
watch: {
list: {
deep: true,
handler(newVal) {
localStorage.setItem('list', JSON.stringify(newVal))
},
},
},
methods: {
handleAdd(todoName) {
// console.log(todoName)
this.list.unshift({
id: +new Date(),
name: todoName,
})
},
handelDel(id) {
// console.log(id);
this.list = this.list.filter((item) => item.id !== id)
},
clear() {
this.list = []
},
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- main.js引入样式
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import './style/index.css'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
- index.css样式
html,
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
background: #fff;
}
button {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border: 0;
background: none;
font-size: 100%;
vertical-align: baseline;
font-family: inherit;
font-weight: inherit;
color: inherit;
-webkit-appearance: none;
appearance: none;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
}
body {
font: 14px 'Helvetica Neue', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.4em;
background: #f5f5f5;
color: #4d4d4d;
min-width: 230px;
max-width: 550px;
margin: 0 auto;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
font-weight: 300;
}
:focus {
outline: 0;
}
.hidden {
display: none;
}
#app {
background: #fff;
margin: 180px 0 40px 0;
padding: 15px;
position: relative;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2), 0 25px 50px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
#app .header input {
border: 2px solid rgba(175, 47, 47, 0.8);
border-radius: 10px;
}
#app .add {
position: absolute;
right: 15px;
top: 15px;
height: 68px;
width: 140px;
text-align: center;
background-color: rgba(175, 47, 47, 0.8);
color: #fff;
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 18px;
border-radius: 0 10px 10px 0;
}
#app input::-webkit-input-placeholder {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: 300;
color: #e6e6e6;
}
#app input::-moz-placeholder {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: 300;
color: #e6e6e6;
}
#app input::input-placeholder {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: 300;
color: gray;
}
#app h1 {
position: absolute;
top: -120px;
width: 100%;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
font-size: 60px;
font-weight: 100;
text-align: center;
color: rgba(175, 47, 47, 0.8);
-webkit-text-rendering: optimizeLegibility;
-moz-text-rendering: optimizeLegibility;
text-rendering: optimizeLegibility;
}
.new-todo,
.edit {
position: relative;
margin: 0;
width: 100%;
font-size: 24px;
font-family: inherit;
font-weight: inherit;
line-height: 1.4em;
border: 0;
color: inherit;
padding: 6px;
box-shadow: inset 0 -1px 5px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
box-sizing: border-box;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
}
.new-todo {
padding: 16px;
border: none;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.003);
box-shadow: inset 0 -2px 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.03);
}
.main {
position: relative;
z-index: 2;
}
.todo-list {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
overflow: hidden;
}
.todo-list li {
position: relative;
font-size: 24px;
height: 60px;
box-sizing: border-box;
border-bottom: 1px solid #e6e6e6;
}
.todo-list li:last-child {
border-bottom: none;
}
.todo-list .view .index {
position: absolute;
color: gray;
left: 10px;
top: 20px;
font-size: 22px;
}
.todo-list li .toggle {
text-align: center;
width: 40px;
/* auto, since non-WebKit browsers doesn't support input styling */
height: auto;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
margin: auto 0;
border: none; /* Mobile Safari */
-webkit-appearance: none;
appearance: none;
}
.todo-list li .toggle {
opacity: 0;
}
.todo-list li .toggle + label {
/*
Firefox requires `#` to be escaped - https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=922433
IE and Edge requires *everything* to be escaped to render, so we do that instead of just the `#` - https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-edge/platform/issues/7157459/
*/
background-image: url('data:image/svg+xml;utf8,%3Csvg%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A//www.w3.org/2000/svg%22%20width%3D%2240%22%20height%3D%2240%22%20viewBox%3D%22-10%20-18%20100%20135%22%3E%3Ccircle%20cx%3D%2250%22%20cy%3D%2250%22%20r%3D%2250%22%20fill%3D%22none%22%20stroke%3D%22%23ededed%22%20stroke-width%3D%223%22/%3E%3C/svg%3E');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: center left;
}
.todo-list li .toggle:checked + label {
background-image: url('data:image/svg+xml;utf8,%3Csvg%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A//www.w3.org/2000/svg%22%20width%3D%2240%22%20height%3D%2240%22%20viewBox%3D%22-10%20-18%20100%20135%22%3E%3Ccircle%20cx%3D%2250%22%20cy%3D%2250%22%20r%3D%2250%22%20fill%3D%22none%22%20stroke%3D%22%23bddad5%22%20stroke-width%3D%223%22/%3E%3Cpath%20fill%3D%22%235dc2af%22%20d%3D%22M72%2025L42%2071%2027%2056l-4%204%2020%2020%2034-52z%22/%3E%3C/svg%3E');
}
.todo-list li label {
word-break: break-all;
padding: 15px 15px 15px 60px;
display: block;
line-height: 1.2;
transition: color 0.4s;
}
.todo-list li.completed label {
color: #d9d9d9;
text-decoration: line-through;
}
.todo-list li .destroy {
display: none;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 10px;
bottom: 0;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
margin: auto 0;
font-size: 30px;
color: #cc9a9a;
margin-bottom: 11px;
transition: color 0.2s ease-out;
}
.todo-list li .destroy:hover {
color: #af5b5e;
}
.todo-list li .destroy:after {
content: '×';
}
.todo-list li:hover .destroy {
display: block;
}
.todo-list li .edit {
display: none;
}
.todo-list li.editing:last-child {
margin-bottom: -1px;
}
.footer {
color: #777;
padding: 10px 15px;
height: 20px;
text-align: center;
border-top: 1px solid #e6e6e6;
}
.footer:before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
height: 50px;
overflow: hidden;
box-shadow: 0 1px 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2), 0 8px 0 -3px #f6f6f6,
0 9px 1px -3px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2), 0 16px 0 -6px #f6f6f6,
0 17px 2px -6px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
}
.todo-count {
float: left;
text-align: left;
}
.todo-count strong {
font-weight: 300;
}
.filters {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
left: 0;
}
.filters li {
display: inline;
}
.filters li a {
color: inherit;
margin: 3px;
padding: 3px 7px;
text-decoration: none;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 3px;
}
.filters li a:hover {
border-color: rgba(175, 47, 47, 0.1);
}
.filters li a.selected {
border-color: rgba(175, 47, 47, 0.2);
}
.clear-completed,
html .clear-completed:active {
float: right;
position: relative;
line-height: 20px;
text-decoration: none;
cursor: pointer;
}
.clear-completed:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
.info {
margin: 50px auto 0;
color: #bfbfbf;
font-size: 15px;
text-shadow: 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.5);
text-align: center;
}
.info p {
line-height: 1;
}
.info a {
color: inherit;
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: 400;
}
.info a:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
/*
Hack to remove background from Mobile Safari.
Can't use it globally since it destroys checkboxes in Firefox
*/
@media screen and (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 0) {
.toggle-all,
.todo-list li .toggle {
background: none;
}
.todo-list li .toggle {
height: 40px;
}
}
@media (max-width: 430px) {
.footer {
height: 50px;
}
.filters {
bottom: 10px;
}
}
6、非父子通信
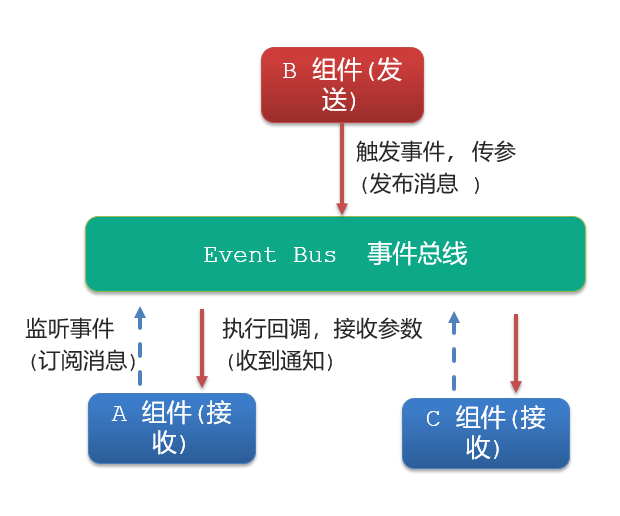
(1)event bus 事件总线
- **作用:**非父子组件之间,进行简易消息传递。(复杂场景 → Vuex)
-
代码实现:
- 创建一个都能访问到的事件总线 (空 Vue 实例) →
utils/EventBus.js
import Vue from 'vue' const Bus = new Vue() export default Bus- A 组件
BaseA.vue(接收方),监听Bus 实例的事件
<template> <div class="base-a"> 我是A组件(接受方) <p>{{msg}}</p> </div> </template> <script> import Bus from '../utils/EventBus' export default { data() { return { msg: '', } }, created() { Bus.$on('sendMsg', (msg) => { // console.log(msg) this.msg = msg }) }, } </script> <style scoped> .base-a { width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 3px solid #000; border-radius: 3px; margin: 10px; } </style>- C 组件
BaseC.vue(接收方),监听Bus 实例的事件
<template> <div class="base-c"> 我是C组件(接受方) <p>{{msg}}</p> </div> </template> <script> import Bus from '../utils/EventBus' export default { data() { return { msg: '', } }, created() { Bus.$on('sendMsg', (msg) => { // console.log(msg) this.msg = msg }) }, } </script> <style scoped> .base-c { width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 3px solid #000; border-radius: 3px; margin: 10px; } </style>- B 组件
BaseB.vue(发送方),触发Bus 实例的事件
<template> <div class="base-b"> <div>我是B组件(发布方)</div> <button @click="sendMsgFn">发送消息</button> </div> </template> <script> import Bus from '../utils/EventBus' export default { methods: { sendMsgFn() { Bus.$emit('sendMsg', '今天天气不错,适合旅游') }, }, } </script> <style scoped> .base-b { width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 3px solid #000; border-radius: 3px; margin: 10px; } </style>- 父组件
App.vue引入三个子组件
<template> <div class="app"> <BaseA></BaseA> <BaseB></BaseB> <BaseC></BaseC> </div> </template> <script> import BaseA from './components/BaseA.vue' import BaseB from './components/BaseB.vue' import BaseC from './components/BaseC.vue' export default { components:{ BaseA, BaseB, BaseC } } </script> <style> </style> - 创建一个都能访问到的事件总线 (空 Vue 实例) →
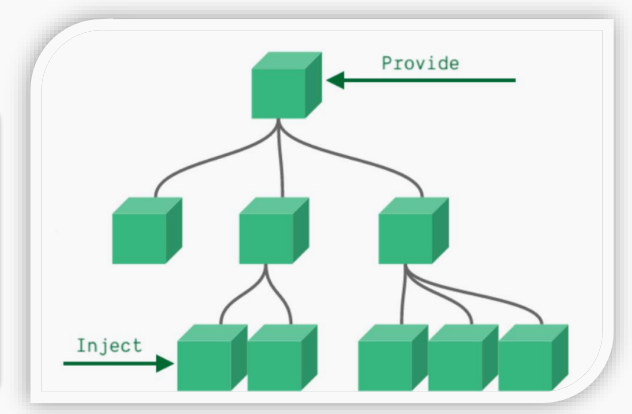
(2)provide & inject
- **作用:**跨层级共享数据。
-
代码实现:
-
父组件
App.vue用provide提供数据
<template>
<div class="app">
我是APP组件
<button @click="change">修改数据</button>
<SonA></SonA>
<SonB></SonB>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import SonA from './components/SonA.vue'
import SonB from './components/SonB.vue'
export default {
provide() {
return {
// 简单类型 是非响应式的
color: this.color,
// 复杂类型 是响应式的
userInfo: this.userInfo,
}
},
data() {
return {
color: 'pink',
userInfo: {
name: 'zs',
age: 18,
},
}
},
methods: {
change() {
this.color = 'red'
this.userInfo.name = 'ls'
},
},
components: {
SonA,
SonB,
},
}
</script>
<style>
.app {
border: 3px solid #000;
border-radius: 6px;
margin: 10px;
}
</style>
- 子组件
SonA.vue
<template>
<div class="SonA">我是SonA组件
<GrandSon></GrandSon>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import GrandSon from '../components/GrandSon.vue'
export default {
components:{
GrandSon
}
}
</script>
<style>
.SonA {
border: 3px solid #000;
border-radius: 6px;
margin: 10px;
height: 200px;
}
</style>
- 子组件
SonB.vue
<template>
<div class="SonB">
我是SonB组件
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
.SonB {
border: 3px solid #000;
border-radius: 6px;
margin: 10px;
height: 200px;
}
</style>
- 孙组件
GrandSon.vue用inject取值使用
<template>
<div class="grandSon">
我是GrandSon
{{ color }} -{{ userInfo.name }} -{{ userInfo.age }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
inject: ['color', 'userInfo'],
}
</script>
<style>
.grandSon {
border: 3px solid #000;
border-radius: 6px;
margin: 10px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>
7、表单组件封装
(1)v-model原理
- 作用: 给
表单元素使用,双向数据绑定→ 可以快速获取 或 设置表单元素内容- 数据变化 → 视图自动更新
- 视图变化 → 数据自动更新
- 语法: v-model = ‘变量’
<input type="text" v-model="username">
- **原理:**v-model本质上是一个语法糖。例如应用在输入框上,就是value属性 和input事件的合写。
<!-- v-model的底层其实就是:value和 @input的简写 -->
<input type="text" :value="username" @input="$event.target.value" />
- **v-model使用在其他表单元素上的原理:**不同的表单元素, v-model在底层的处理机制是不一样的。比如给checkbox使用v-model,底层处理的是 checked属性和change事件。
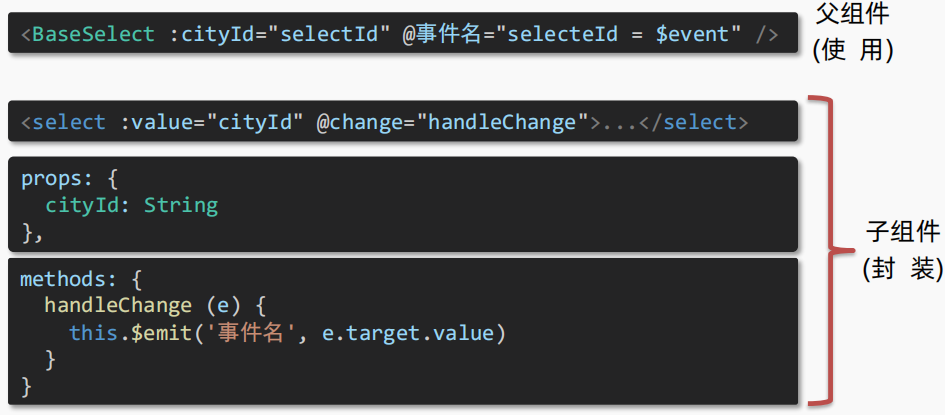
(2)表单组件封装
- **目标:**实现子组件和父组件数据的
双向绑定父传子:数据 应该是父组件props传递 过来的,拆解 v-model绑定数据子传父:监听输入,子传父传值给父组件修改
-
代码实现:
- 父组件
App.vue
<template> <div class="app"> <BaseSelect :selectId="selectId" @changeCity="selectId = $event" ></BaseSelect> </div> </template> <script> import BaseSelect from './components/BaseSelect.vue' export default { data() { return { selectId: '102', } }, components: { BaseSelect, }, } </script> <style> </style>- 子组件
BaseSelect.vue
<template> <div> <select :value="selectId" @change="selectCity"> <option value="101">北京</option> <option value="102">上海</option> <option value="103">武汉</option> <option value="104">广州</option> <option value="105">深圳</option> </select> </div> </template> <script> export default { props: { selectId: String, }, methods: { selectCity(e) { this.$emit('changeCity', e.target.value) }, }, } </script> <style> </style> - 父组件
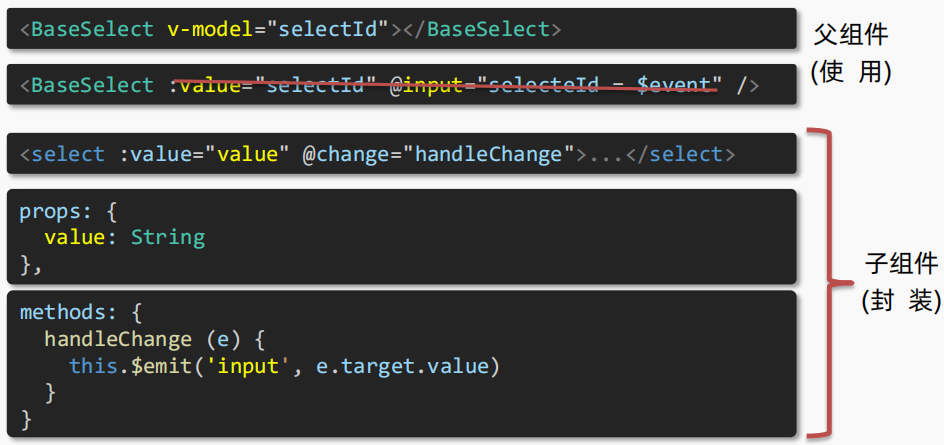
(3)v-model简化代码
- 父组件
v-model 简化代码,实现 子组件 和 父组件数据 双向绑定父组件中:v-model 给组件直接绑数据( :value + @input )子组件中:props 通过value接收,事件触发input
-
代码实现:
- 父组件
App.vue
<template> <div class="app"> <BaseSelect v-model="selectId" ></BaseSelect> </div> </template> <script> import BaseSelect from './components/BaseSelect.vue' export default { data() { return { selectId: '102', } }, components: { BaseSelect, }, } </script> <style> </style>- 子组件
BaseSelect.vue
<template> <div> <select :value="value" @change="selectCity"> <option value="101">北京</option> <option value="102">上海</option> <option value="103">武汉</option> <option value="104">广州</option> <option value="105">深圳</option> </select> </div> </template> <script> export default { props: { value: String, }, methods: { selectCity(e) { this.$emit('input', e.target.value) }, }, } </script> <style> </style> - 父组件
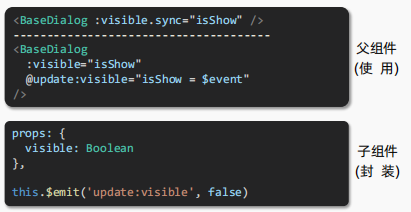
8、.sync修饰符
-
作用:
-
可以实现
子组件与父组件数据的双向绑定,简化代码- 简单理解:
子组件可以修改父组件传过来的props值
- 简单理解:
-
-
**特点:**prop属性名,可以自定义,非固定为 value
-
**场景:**封装弹框类的基础组件,
visible属性true显示 false隐藏 -
本质:.sync修饰符 就是
:属性名和@update:属性名合写 -
语法:
-
代码实现:
- 父组件
App.vue
<template> <div class="app"> <button @click="openDialog">退出按钮</button> <!-- isShow.sync => :isShow="isShow" @update:isShow="isShow=$event" --> <BaseDialog :isShow.sync="isShow"></BaseDialog> </div> </template> <script> import BaseDialog from './components/BaseDialog.vue' export default { data() { return { isShow: false, } }, methods: { openDialog() { this.isShow = true // console.log(document.querySelectorAll('.box')); }, }, components: { BaseDialog, }, } </script> <style> </style>- 子组件
BaseDialog.vue
<template> <div class="base-dialog-wrap" v-show="isShow"> <div class="base-dialog"> <div class="title"> <h3>温馨提示:</h3> <button class="close" @click="closeDialog">x</button> </div> <div class="content"> <p>你确认要退出本系统么?</p> </div> <div class="footer"> <button>确认</button> <button>取消</button> </div> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { props: { isShow: Boolean, }, methods:{ closeDialog(){ this.$emit('update:isShow',false) } } } </script> <style scoped> .base-dialog-wrap { width: 300px; height: 200px; box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px 2px #ccc; position: fixed; left: 50%; top: 50%; transform: translate(-50%, -50%); padding: 0 10px; } .base-dialog .title { display: flex; justify-content: space-between; align-items: center; border-bottom: 2px solid #000; } .base-dialog .content { margin-top: 38px; } .base-dialog .title .close { width: 20px; height: 20px; cursor: pointer; line-height: 10px; } .footer { display: flex; justify-content: flex-end; margin-top: 26px; } .footer button { width: 80px; height: 40px; } .footer button:nth-child(1) { margin-right: 10px; cursor: pointer; } </style> - 父组件