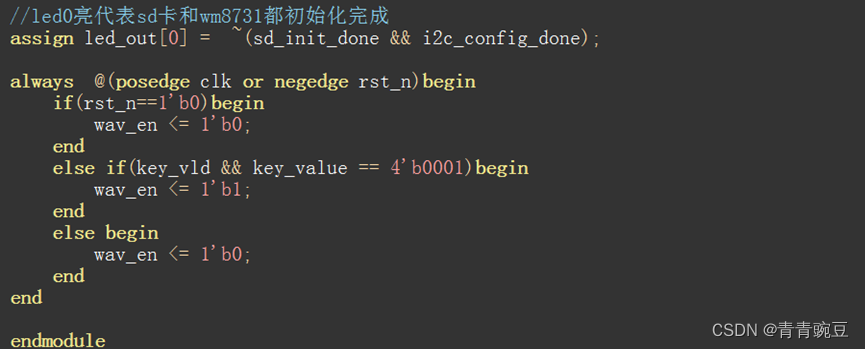
1. 方法
总共分为4类
- 基于欧式距离的聚类
- Supervoxel 聚类
- 深度(Depth) 聚类
- Scanline Run 聚类
1.1 基于欧氏距离的聚类
思路: 在点云上构造kd-tree, 然后在某个半径阈值(例如0.5m), 则分割为一个实例。
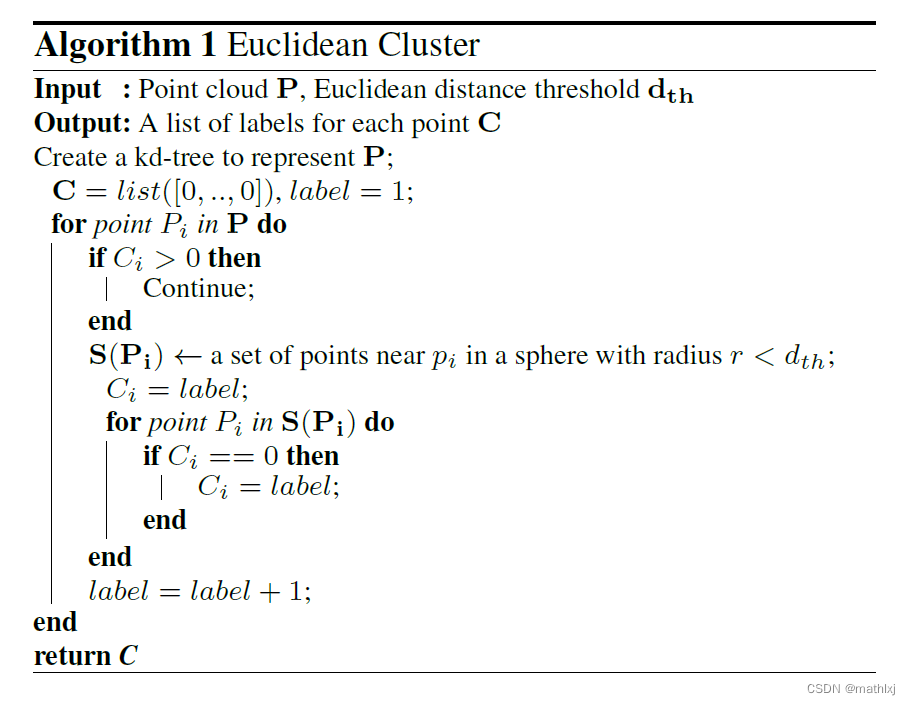
相似算法: RBNN (radially bounded nearest neighbor graph), 2008.


1.2 Supervoxel Cluster
CVPR13 Voxel Cloud Connectivity Segmentation - Supervoxels for Point Clouds
3D is here: Point Cloud Library (PCL), 2011
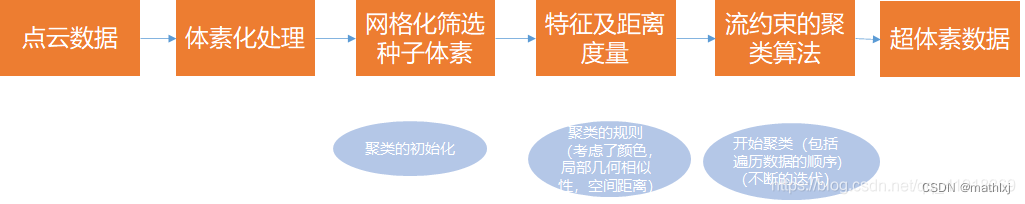

类似于K-Means
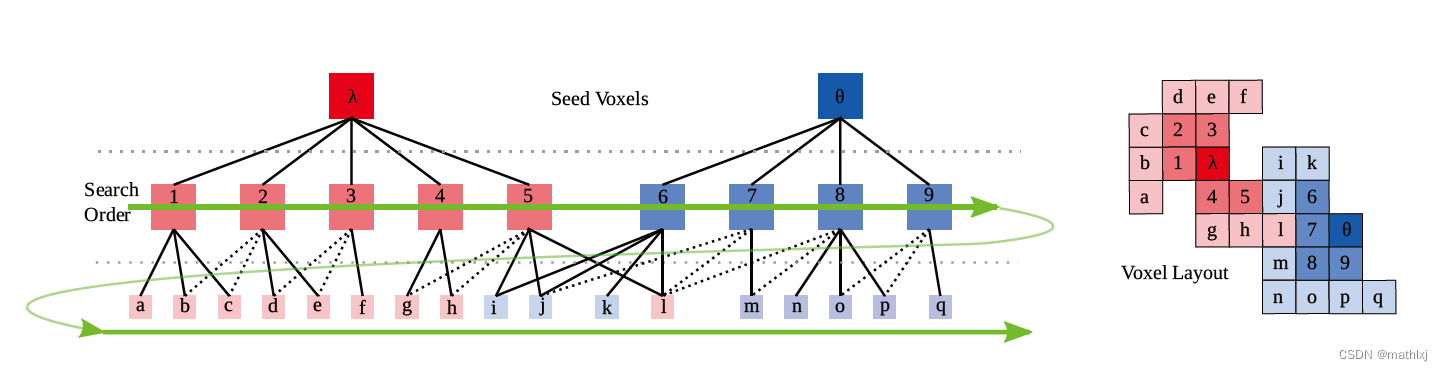
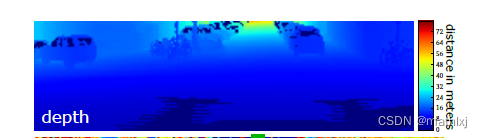
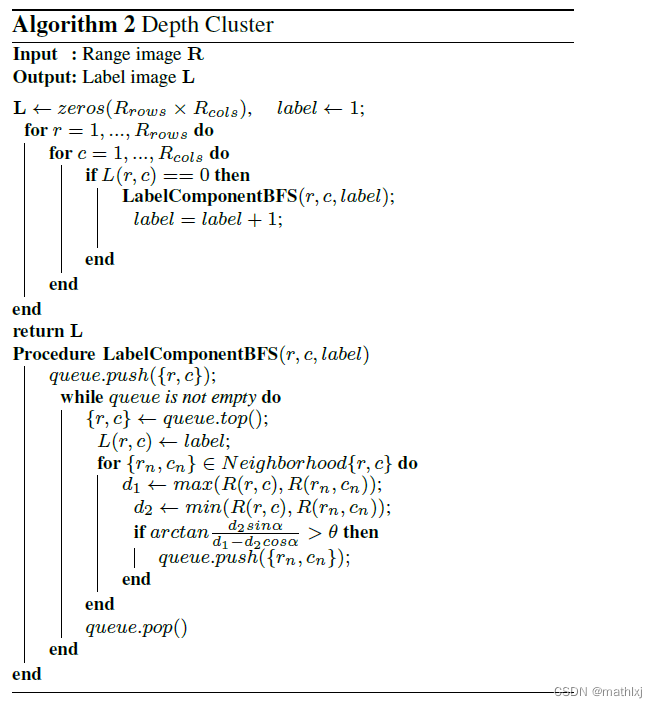
1.3 Depth Cluster
Fast range image-based segmentation of sparse 3D laser scans for online operation, 2016
首先,移除地面。
基于range image,优点是直接定义了邻居关系,使得分割更加简单;避免了3D点云的生成,速度更快.
-
行数: 垂直方向的线数, 即16,32或64
-
列: 旋转一周
-
像素点: 雷达到物体的距离
判断两个点是否属于同一个目标,可以使用angle-based measure.
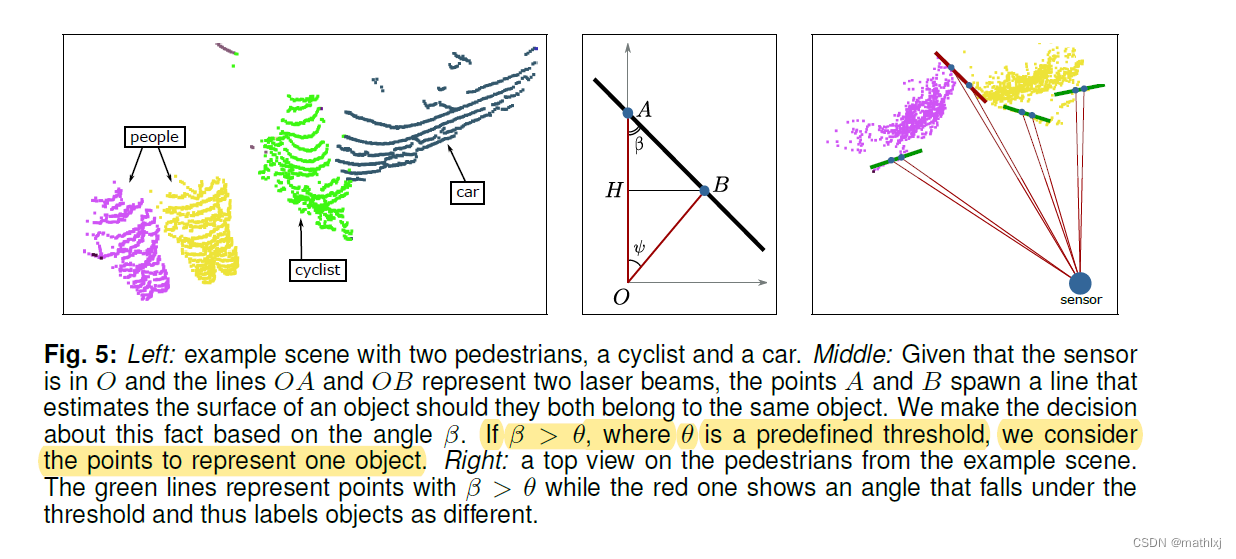
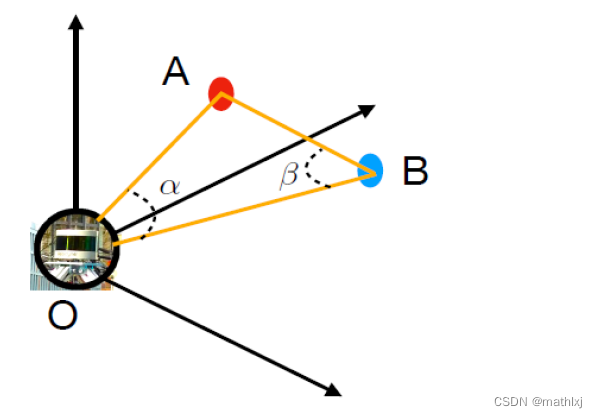
β \beta β的定义方法:- 激光雷达处于原点
- y轴选择两条线中更长的线
-
β
\beta
β定义为laser beam(较远的)和连接AB的线之间角度
在range image上视为邻居条件
-
if they are neighbours in a the range image (we use an N4 neighbourhood on the grid)
-
angle β \beta β between them is larger than θ = 10 \theta=10 θ=10度.
问题转换为 找利用range image的结构和 β \beta β的限制找连接的2D部分
从range image的左上角开始,遍历到右下角. 从左到右,从上到下。
广度优先,搜索上下左右四个点是否满足条件。
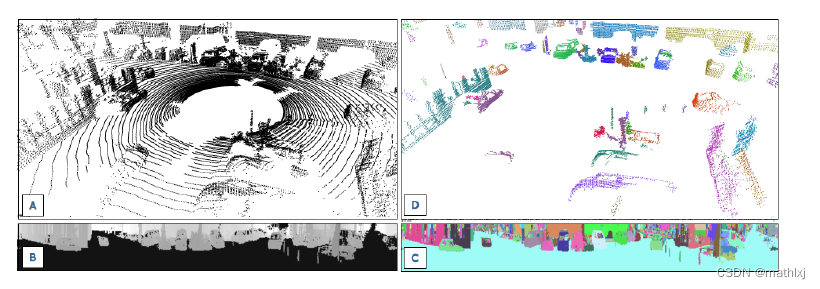
效果图
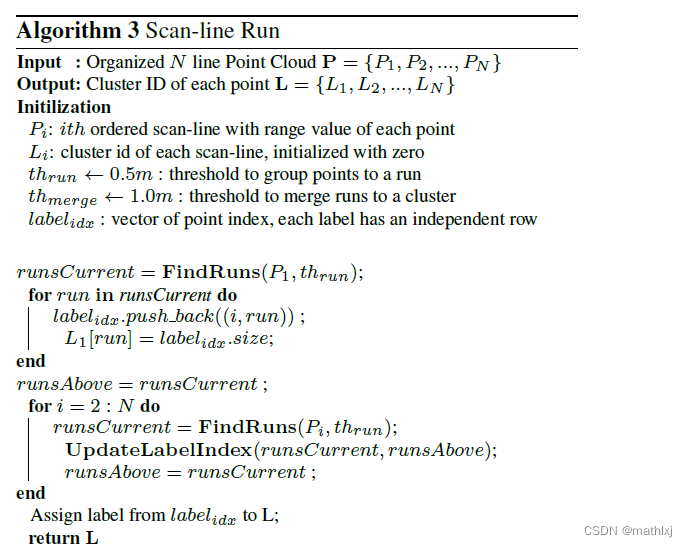
1.4 Scanline Run Cluster
Fast segmentation of 3D point clouds: A paradigm on LiDAR data for autonomous vehicle applications, 2017
需要实现去除地面。
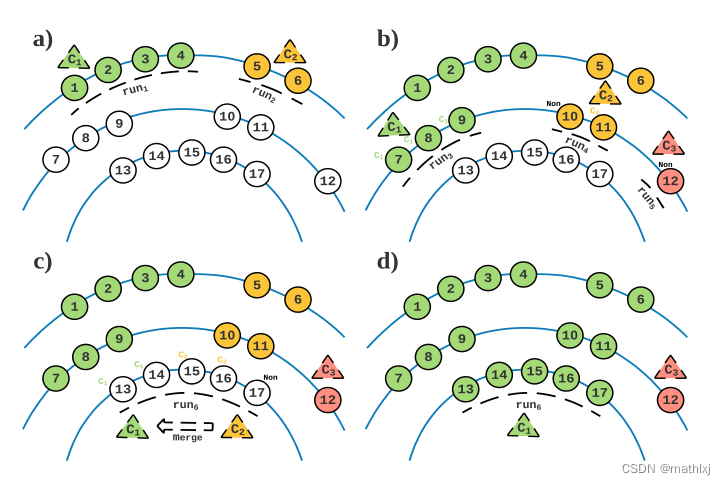
scan line: 在SLR中,所有相同(水平的角度)发散出的点被认为是一个scan-line.
run. :在单个scan line中,所有距离小于阈值的点会被分组在一起,成为一个run.
- Step1: SLR对第一个line, 获取第一个line的runs. 每个run有不同的label
- Step2: SLR对第二个line, 重复run segmenting,检查是否新的run满足由新的阈值定义的merging条件. 如果满足merge条件,则merge. 如果没有merge,则新的run获取新的label, 直到将所有的line都扫一遍.

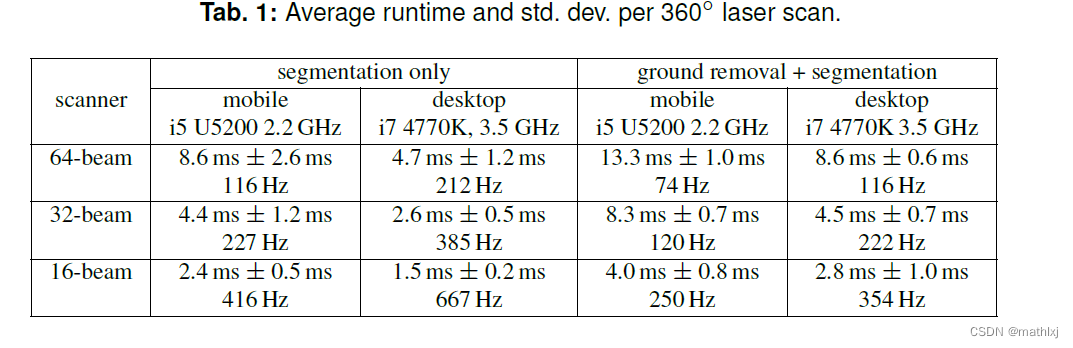
2. 测速和实现
ICCV21, A Technical Survey and Evaluation of Traditional Point Cloud Clustering
Methods for LiDAR Panoptic Segmentation
github,C++ and Python
思路: 使用Cylinder3D(CVPR2021)做语义分割,获得所有点的类别,再使用以上方法做聚类,得到实例分割结果。
数据集: SemanticKITTI
PQ (panoptic quality)

Cylinder3D速度: 文章没提,github说10HZ, python代码,不知显卡类型。
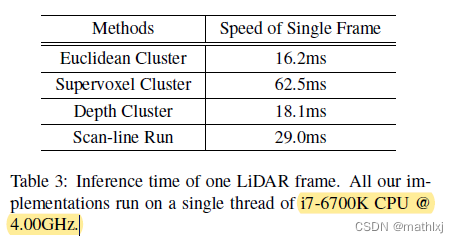
速度

![[Java EE初阶] 进程调度的基本过程](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3fe0f4e75b224ad6a872df911f3b7d46.png)

![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM基于的智慧校园安防综合管理系统(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f0497cd276534b64a07acad68025c3fb.png)