目录
一、概述
二、构造函数
1.List()
2.List(IEnumerable)
3.List(Int32)
三、属性
1.Capacity
2.Count
3.Item[Int32]
四、方法
1.Add(T)
2.AddRange(IEnumerable)
3.AsReadOnly()
4.BinarySearch(T)
C# List 详解一
1.Add(T),2.AddRange(IEnumerable),3.AsReadOnly(),4.BinarySearch(T),
C# List 详解二
5.Clear(),6.Contains(T),7.ConvertAll(Converter),8.CopyTo(Int32, T[], Int32, Int32),9.CopyTo(T[]),10.CopyTo(T[], Int32)
C# List 详解三
11.Equals(Object),12.Exists(Predicate),13.Find(Predicate),14.FindAll(Predicate),15.FindIndex(Int32, Int32, Predicate),16.FindIndex(Int32, Predicate),17.FindIndex(Predicate)
C# List 详解四
18.FindLast(Predicate),19.FindLastIndex(Int32, Int32, Predicate),20.FindLastIndex(Int32, Predicate),21.FindLastIndex(Predicate),22.ForEach(Action),23.GetEnumerator(),24.GetHashCode(),25.GetRange(Int32, Int32)
C# List 详解五
26.GetType(),27.IndexOf(T),28.IndexOf(T, Int32),29.IndexOf(T, Int32, Int32),30.Insert(Int32, T),31.InsertRange(Int32, IEnumerable),32.LastIndexOf(T),33.LastIndexOf(T, Int32),34.LastIndexOf(T, Int32, Int32)
C# List 详解六
35.MemberwiseClone(),36.Remove(T),37.RemoveAll(Predicate),38.RemoveAt(Int32),39.RemoveRange(Int32, Int32),40.Reverse(),41.Reverse(Int32, Int32)
C# List 详解七
42.Sort(),43.ToArray(),44.ToString(),45.TrimExcess(),46.TrueForAll(Predicate)
C# List 详解二_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解三_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解四_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解五_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解六_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
C# List 详解七_熊思宇的博客-CSDN博客
一、概述
表示可通过索引访问的对象的强类型列表。 提供用于对列表进行搜索、排序和操作的方法,List是一个动态数组,它可以存储任意类型的对象,并且可以根据需要自动调整大小。
在 C# 的数据结构中,如果说谁用的最频繁,那么 List 这个数据结构绝对排第一,虽然用的多,在平时的开发中,大部分人只是重复的用几个固定的方法,比如 Add,Remove,Count,Clear 等。在一些初学者的代码中,假设要在 List 找出一个元素的下标,很多人直接写了一个 for 循环去判断,虽然我之前也是这么写的,其实 List 封装了很多很好用的方法,比如 FindIndex 这个方法就可以直接获取到 List 中某个元素的下标,根本不用自己写了一大堆代码去判断,我觉得对 List 这个类深入的去了解还是有必要的。
二、构造函数
1.List<T>()
初始化 List<T> 类的新实例,该实例为空并且具有默认初始容量。
public List ();常用的实例化方法,list 中不会有任何默认值
案例:
List<string> list = new List<string>();2.List<T>(IEnumerable<T>)
初始化 List<T> 类的新实例,该实例包含从指定集合复制的元素并且具有足够的容量来容纳所复制的元素。
public List (System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<T> collection);参数
collection
IEnumerable<T>
一个集合,其元素被复制到新列表中。
案例:
string[] input = { "a","b","c" };
List<string> list = new List<string>(input);3.List<T>(Int32)
初始化 List<T> 类的新实例,该实例为空并且具有指定的初始容量。
public List (int capacity);参数
capacity
Int32
新列表最初可以存储的元素数。
案例:
List<string> list = new List<string>(2);
Console.WriteLine(list.Count);这里并不会和数组一样,指定 length 的长度为2 会有两个空值
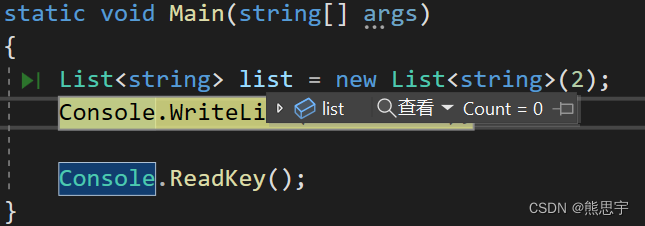
用 Count 获取这时候是0,但用 Capacity 属性来获取就有长度了,感觉这样做的意义感觉不大
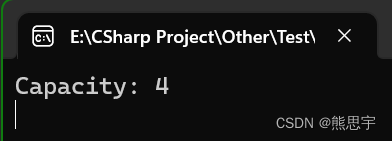
List<string> dinosaurs = new List<string>(4);
Console.WriteLine("Capacity: {0}", dinosaurs.Capacity);运行:
三、属性
1.Capacity
获取或设置该内部数据结构在不调整大小的情况下能够容纳的元素总数。
public int Capacity { get; set; }属性值
Int32
在需要调整大小之前 List<T> 可包含的元素数目。
案例:
List<string> dinosaurs = new List<string>(4);
Console.WriteLine("Capacity: {0}", dinosaurs.Capacity);2.Count
获取 List<T> 中包含的元素数。
public int Count { get; }属性值
Int32
List<T> 中包含的元素数。
案例:
List<int> list = new List<int>(2);
list.Add(1);
Console.WriteLine(list.Count);3.Item[Int32]
获取或设置指定索引处的元素。
public T this[int index] { get; set; }参数
index
Int32
要获取或设置的元素的从零开始的索引。
属性值
T
指定索引处的元素。
案例:
List<int> list = new List<int>(2);
list.Add(1);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(3);
list.Add(4);
int num = list[1];
Console.WriteLine(num);四、方法
1.Add(T)
将对象添加到 List<T> 的结尾处。
public void Add (T item);参数
item
T
要添加到 List<T> 末尾的对象。 对于引用类型,该值可以为 null。
案例:
List<int> list = new List<int>(2);
list.Add(1);2.AddRange(IEnumerable<T>)
将指定集合的元素添加到 List<T> 的末尾。
public void AddRange (System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<T> collection);参数
collection
IEnumerable<T>
应将其元素添加到 List<T> 的末尾的集合。 集合自身不能为 null,但它可以包含为 null 的元素(如果类型 T 为引用类型)。
案例:
List<int> list = new List<int>(2);
int[] arr = { 13, 3, 5, 67, 34 };
list.AddRange(arr);3.AsReadOnly()
返回当前集合的只读 ReadOnlyCollection<T> 包装器。
public System.Collections.ObjectModel.ReadOnlyCollection<T> AsReadOnly ();返回
ReadOnlyCollection<T>
一个对象,作为围绕当前 List<T> 的只读包装器。
案例:
下面代码的 AsReadOnly 用于获取包装原始列表的只读 IList<T> 泛型接口实现
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<string> dinosaurs = new List<string>(4);
dinosaurs.Add("Tyrannosaurus");
dinosaurs.Add("Amargasaurus");
dinosaurs.Add("Mamenchisaurus");
dinosaurs.Add("Deinonychus");
IList<string> roDinosaurs = dinosaurs.AsReadOnly();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}4.BinarySearch(T)
使用默认的比较器在整个已排序的 List<T> 中搜索元素,并返回该元素从零开始的索引。
public int BinarySearch (T item);参数
item
T
要定位的对象。 对于引用类型,该值可以为 null。
返回
Int32
如果找到 item,则为已排序的 List<T> 中 item 的从零开始的索引;否则为一个负数,该负数是大于 item 的下一个元素的索引的按位求补。如果没有更大的元素,则为 Count 的按位求补。
案例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ListTest
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<string> dinosaurs = new List<string>();
dinosaurs.Add("Pachycephalosaurus");
dinosaurs.Add("Parasauralophus");
dinosaurs.Add("Amargasaurus");
dinosaurs.Add("Galimimus");
dinosaurs.Add("Mamenchisaurus");
dinosaurs.Add("Deinonychus");
dinosaurs.Add("Oviraptor");
dinosaurs.Add("Tyrannosaurus");
int index = dinosaurs.BinarySearch("Tyrannosaurus");
Console.WriteLine(index);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}运行:

第 1 / 7 篇 End