paper | code | project
总结:
- 任务是3D GAN Inversion,旨在找到给定图像的隐码/Tri-plane。
- 现有方法可分为Optimizaiton-based methods和encoder-based methods。前者旨在通过损失找到最优隐码,后者旨在学习给定图片和隐码的映射关系。前者通常效果更好,但速度较慢。
- 本文通过pSp得到粗tri-plane,通过TriplaneNet生成tri-plane残差,得到最终的精细化tri-plane。
目录
摘要
Related Work
3D Generative Models for Human Faces.
Inversion of 3D GANs
Applications of GAN encoders
方法
Preliminaries
GAN Inversion
EG3D
pSp
TriPlaneNet
Loss Functions
实验
Training procedure
Datasets
Results
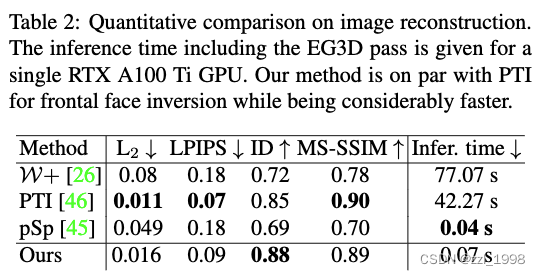
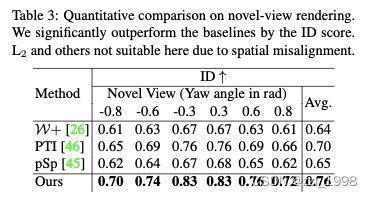
Comparison to the sota
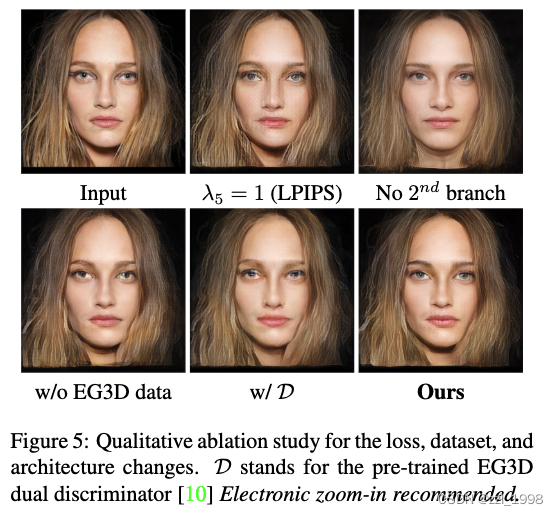
Ablation study
摘要
- NeRF-based GANs 有概率可对3D头像的新视角进行渲染;但实际应用时,inverse problem也很重要,该问题致力于再渲染或修改已有的图片或视频。(第一个是生成类任务,以EG3D为例,从高斯噪声中采样,即可得到一个3D头像,并能从不同视角对其渲染;第二个则是优化任务,给定一张照片,希望在EG3D的隐空间中找到和给定照片最像的3D头像。)
- 现有方法:1)2D GAN inversion(Optimizaiton-based inversion methods),这类方法不能很好应用于3D GANs,无法产生3D-consistent渲染;2)encoder-based techniques,多数是为StyleGAN发展,但这类方法在ID保留上效果不佳;前者效果通常优于后者,但后者更快。
- 本文方法:分为两步,第一步使用encoder-based方法,预测粗latent code;第二步用TriPlaneNet,预测tri-plane offsets;
- 实验:本文方法在渲染上和机遇优化的方法效果相近,但是在视角上提升显著。

Related Work
3D Generative Models for Human Faces.
- NeRF的改进方法:
- [6] Fully Controllable Neural 3D Portrait
- [16] Dynamic Neural Radiance Fields for Monocular 4F facial avatar reconstruction
- [42] Nerfies: Deformable Neural Radiance Fields.
- NeRF-based GAN:
- [8] Generative Neural Articulated Radiance Fields
- [21] A real-time Nerf-based parametric head model
- 这些方法支持对渲染人脸表情和外观的显式控制
Inversion of 3D GANs
- PTI(fix找到的latent code,用给定图片fine-tune生成器)是一个通用方法,但是PTI找到的latent code,在新视角下效果不佳。针对这个问题,[29]引入多视角一致性约束(multi-view consistency regularizers),[57]训练时用surrogate mirrored images进行增强,[28]使用深度信息
Applications of GAN encoders
- 可以作为语义分割[7]、face recognition[49]和generic prior[58, 40].
方法
Preliminaries
GAN Inversion
给定一张图片,GAN inversion的任务是找到让重建损失最小的隐码,可形式化表达如下,其中损失常用L2或LPIPS:
![]()
该式子可以通过两种优化或encoder-based approaches来解决。
Encoder-based方法使用encoder network E,将真实图像映射为隐码。encoder网络的训练需要大量数据集:
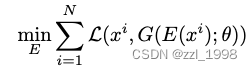
在推理阶段,输入图片送入encoder网络得到隐码。
EG3D
latent code (z = 512), camera parametrs (c = 25) -- mapping network --> pivotal latent code (w = 14 x 512);
w -- StyleGAN2 CNN generator G(.) -> Tri-plane (T = H x W x 32 x 3)
T -- neural decoder -- volume rendering --> feature image
feature image -- super-resoltion --> image (512 x 512 x 3)
通常,将neural decoder、volume rendering和super-resoltion合称为rendering block R(.)
pSp
real images -- encoder --> W+
具体来说,encoder将图片处理为具有三层特征的特征金字塔,特征经过map2style网络,提取风格向量,风格向量送入生成网络,产生图片。上述过程可形式化表达如下:![]()
其中,G(.)是生成器,E(.)是encoder,hat(w)是预训练生成器的平均风格向量。
TriPlaneNet
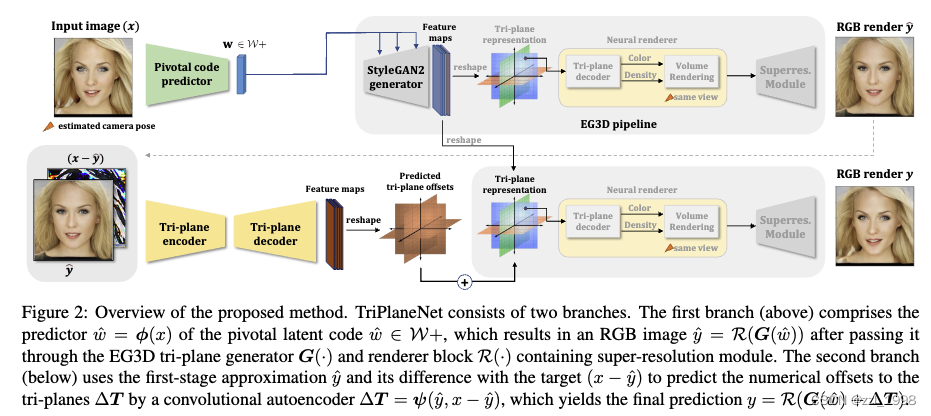
包含两个阶段,第一阶段用pSp encdoer将图片编码到EG3D的pivotal latent code空间:
![]()
将pSp输出,送入EG3D生成器,得到初始tri-plane features T,送入渲染模块后,产生初始重建图像:
![]()
第二阶段,TriplaneNet是一个autoencoder。该网络的输入是初始重建和重建残差,输出是tri-plane特征的残差。残差tri-plane和初始tri-plane相加得到最终的tri-plane,并得到最终的重建图像:
![]()
autoencoder使用经典U-Net结构,整体结构和RUNet很像。encoder是预训练IR-SE-50结构,deocder是subpixel convolutional layers,用于将提取特征高效上采样。
Loss Functions
包含两阶段损失:
![]()
![]()
![]()
实验
Training procedure
Datasets
- 训练集:使用FFHQ数据集和100,000预训练EG3D中生成的图片;
- 测试集:2824张CelebA-HQ
Results
Comparison to the sota

Ablation study









![[Linux] CentOS7 中 pip3 install 可能出现的 ssl 问题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/29c830d4f53c9cf7208604914d0e34a2.png)