实验五 分支限界法
01背包问题的分治限界法的实现
剪枝函数
限界函数
1.实验目的
1、理解分支限界法的剪枝搜索策略,掌握分支限界法的算法框架
2、设计并实现问题,掌握分支限界算法。
2.实验环境
java
3.问题描述
给定n种物品和一背包。物品i的重量是wi,其价值为vi,背包的容量为C。问应如何选择装入背包的物品,使得装入背包中物品的总价值最大?
4.复杂度
算法整体的时间复杂度主要由回溯操作的时间复杂度决定,在最坏情况下为O(2^n)。然而,在实际应用中,由于剪枝操作的存在,实际的分支数会远远小于2^n,因此算法的执行时间通常会有所缩减。
5.算法实现
package shiyan5;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Item {
int weight;
int value;
double density; // 物品的单位价值(价值重量比)
public Item(int weight, int value) {
this.weight = weight;
this.value = value;
this.density = (double) value / weight;
}
}
public class BranchAndBound {
static List<Item> items;
static int capacity;
static int maxTotalValue;
static List<Item> selectedItems;
public static void main(String[] args) {
readInputData("input.txt");
branchAndBound();
writeOutputData("output.txt");
}
private static void readInputData(String filename) {
try {
File file = new File(filename);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
capacity = scanner.nextInt();
items = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int weight = scanner.nextInt();
int value = scanner.nextInt();
items.add(new Item(weight, value));
}
scanner.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void branchAndBound() {
Collections.sort(items, (a, b) -> Double.compare(b.density, a.density)); // 按单位价值从大到小排序
maxTotalValue = 0;
selectedItems = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(0, 0, 0);
// 按照物品的原始顺序排序
Collections.sort(selectedItems, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(items.indexOf(a), items.indexOf(b)));
}
private static void backtrack(int level, int currentWeight, int currentValue) {
if (level == items.size() || currentWeight == capacity) {
if (currentValue > maxTotalValue) {
maxTotalValue = currentValue;
selectedItems.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
if (items.indexOf(items.get(i)) != -1) {
selectedItems.add(items.get(i));
}
}
}
return;
}
if (currentWeight + items.get(level).weight <= capacity) {
currentWeight += items.get(level).weight;
currentValue += items.get(level).value;
backtrack(level + 1, currentWeight, currentValue);
currentWeight -= items.get(level).weight;
currentValue -= items.get(level).value;
}
if (bound(level + 1, currentWeight, currentValue) > maxTotalValue) {
backtrack(level + 1, currentWeight, currentValue);
}
}
private static double bound(int level, int currentWeight, int currentValue) {
double maxBound = currentValue;
int currentLevel = level;
int currentWeightSum = currentWeight;
while (currentWeightSum < capacity && currentLevel < items.size()) {
if (currentWeightSum + items.get(currentLevel).weight <= capacity) {
currentWeightSum += items.get(currentLevel).weight;
maxBound += items.get(currentLevel).value;
} else {
double remainingWeight = capacity - currentWeightSum;
maxBound += (remainingWeight / items.get(currentLevel).weight) * items.get(currentLevel).value;
break;
}
currentLevel++;
}
return maxBound;
}
private static void writeOutputData(String filename) {
try {
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(filename);
writer.write("背包中物品的总价值: " + maxTotalValue);
writer.write("\n\n已选物品列表:\n");
for (Item item : selectedItems) {
writer.write("重量: " + item.weight + ", 价值: " + item.value);
writer.write("\n");
}
writer.close();
System.out.println("输出成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输入
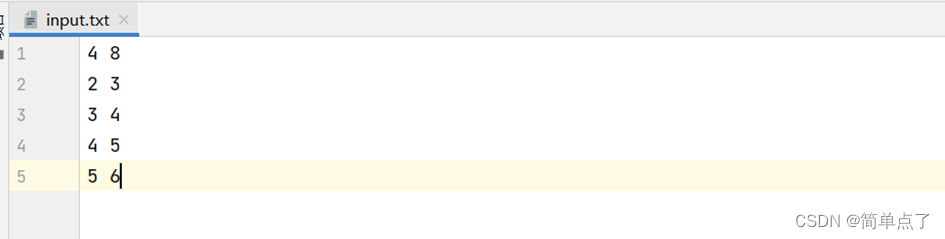
运行
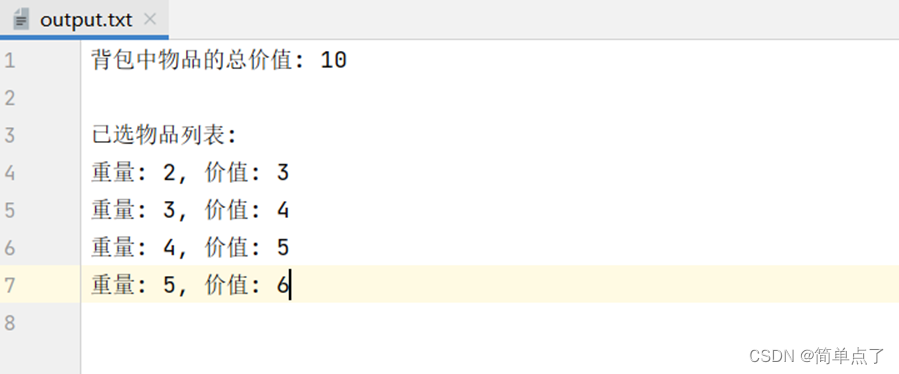
输出






![[数学建模] [2019年A 模拟练习][层次分析法、熵值法、多目标优化、主成分分析法] 4. 深圳居民健康水平评估与测控模型研究](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/45b69d3ab4964bafa99bbb8122c93785.png#pic_center)