1. 概述
本篇文章会简略的介绍一下 Lambda 表达式,然后开启我们的正题 Java8 Stream 流,希望观众老爷们多多支持,并在评论区批评指正!
Java8 的 Stream 流使用的是函数式编程模式。它可以被用来对集合或数组进行链状流式的操作,可以更方便的让我们对集合或数组操作。
2. Stream流为什么操作集合便捷?
Stream流为什么操作集合便捷?我们通过一个小例子来演示一下:
首先我们创建一个类,准备一些数据用于演示:
public class StreamDemo {
private static List<Author> getAuthors() {
//数据初始化
Author author = new Author(1L,"蒙多",33,"一个从菜刀中明悟哲理的祖安人",null);
Author author2 = new Author(2L,"亚拉索",15,"狂风也追逐不上他的思考速度",null);
Author author3 = new Author(3L,"易",14,"是这个世界在限制他的思维",null);
Author author4 = new Author(3L,"易",14,"是这个世界在限制他的思维",null);
//书籍列表
List<Book> books1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Book> books2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Book> books3 = new ArrayList<>();
books1.add(new Book(1L,"刀的两侧是光明与黑暗","哲学,爱情",88,"用一把刀划分了爱恨"));
books1.add(new Book(2L,"一个人不能死在同一把刀下","个人成长,爱情",99,"讲述如何从失败中明悟真理"));
books2.add(new Book(3L,"那风吹不到的地方","哲学",85,"带你用思维去领略世界的尽头"));
books2.add(new Book(3L,"那风吹不到的地方","哲学",85,"带你用思维去领略世界的尽头"));
books2.add(new Book(4L,"吹或不吹","爱情,个人传记",56,"一个哲学家的恋爱观注定很难把他所在的时代理解"));
books3.add(new Book(5L,"你的剑就是我的剑","爱情",56,"无法想象一个武者能对他的伴侣这么的宽容"));
books3.add(new Book(6L,"风与剑","个人传记",100,"两个哲学家灵魂和肉体的碰撞会激起怎么样的火花呢?"));
books3.add(new Book(6L,"风与剑","个人传记",100,"两个哲学家灵魂和肉体的碰撞会激起怎么样的火花呢?"));
author.setBooks(books1);
author2.setBooks(books2);
author3.setBooks(books3);
author4.setBooks(books3);
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(author,author2,author3,author4));
return authorList;
}
}
复制代码假如我们对该作家列表进行操作,要求对作家列表进行去重,并过滤年龄小于18的作家,然后依次打印作者姓名和年龄。
我们不使用 Stream 流我们可以这样写:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
List<Author> fauthors = new ArrayList<>();
//进行去重
for (Author author : authors){
if (!fauthors.contains(author)){
fauthors.add(author);
}
}
authors.clear();
//筛选出年龄小于18的
for (Author author : fauthors){
if(author.getAge() < 18){
authors.add(author);
}
}
//输出姓名
for (Author author : authors){
System.out.println(author.getName() + " : " + author.getAge());
}
}
复制代码我们可以发现这种方式非常繁琐,且难懂。

如果我们使用 stream 流的话,代码就非常简单直观了。
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
//把集合转换成流,进行stream流操作
authors.stream()
.distinct() //去重
.filter(author -> author.getAge() < 18)//过滤
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName())); //打印年龄
}
}
复制代码3. 正式学习之前我们先学习一下Lambda表达式
Lambda 表达式是 JDK8中的一个语法糖。它可以对某些匿名内部类的写法进行简化。它是函数式编程思想的一个重要体现。让我们不用关注是什么对象,而关注于我们对数据进行了什么操作。
核心原则:可推导可省略
3.1. 基本格式
(参数列表)->代码
例1:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hi");
}
}).start();
}
}
复制代码public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("hi");
}).start();
}
}
复制代码例2:
现有方法定义如下,其中 InitBinaryOperator 是一个接口。先使用匿名内部类的写法调用该方法。
public class Test2 {
public static int calculateNum(IntBinaryOperator operator){
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
return operator.applyAsInt(a,b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = calculateNum(new IntBinaryOperator() {
@Override
public int applyAsInt(int left, int right) {
return left + right;
}
});
System.out.println(i);
}
}
复制代码使用 Lambda 表达式的写法:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//++++++++++++++lambda表达式写法+++++++++++++++
int i1 = calculateNum((int left, int right) -> {
return left + right;
});
System.out.println(i1);
}
}
复制代码例3:现有方法定义如下,其中 intPredicate 是一个接口。先使用匿名内部类的写法调用该方法。
public class Test3 {
/**
*
* @param predicate IntPredicate接口,实现接口方法 test用于判断数据满足条件
*/
public static void printNum(IntPredicate predicate){
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
for(int i: arr){
if(predicate.test(i)){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
printNum(new IntPredicate() {
@Override
public boolean test(int value) {
//判断当前参数是否是偶数
if(value%2 == 0) return true;
return false;
}
});
}
}
复制代码使用 Lambda 表达式的写法:
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("+++++++++++++lambda表达式写法++++++++++++++++");
//+++++++++++++lambda表达式写法++++++++++++++++
printNum((int value) ->{
return value%2 == 0;
});
}
}
复制代码例4:现有方法定义如下,其中 Function 是一个接口。先使用匿名内部类的写法调用该方法。
public class Test4 {
public static <R> R typeConver(Function<String, R> function){
String str = "1235";
R result = function.apply(str);
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer integer = typeConver(new Function<String, Integer>() {
//对字符串进行处理,返回结果
@Override
public Integer apply(String s) {
return s.length();
}
});
System.out.println(integer);
}
}
复制代码使用 Lambda 表达式写法:
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("+++++++++++++lambda表达式写法++++++++++++++++");
Integer integer1 = typeConver((String s) -> {
return s.length();
});
System.out.println(integer1);
}
}
复制代码例5:现有方法定义如下,其中 IntConsumer 是一个接口。先使用匿名内部类的写法调用该方法。
public class Test5 {
public static void foreachArr(IntConsumer consumer){
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
for (int i : arr){
consumer.accept(i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
foreachArr(new IntConsumer() {
//对数据进行处理
@Override
public void accept(int value) {
System.out.println(value*2);
}
});
}
}
复制代码使用 Lambda 表达式写法:
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("+++++++++++++lambda表达式写法++++++++++++++++");
foreachArr((int value) ->{
System.out.println(value * 2);
});
}
}
复制代码3.2. 省略规则
- 参数类型可以省略
- 方法体只有一句代码时大括号
{}、return以及一行代码后的;号可以省略 - 方法只有一个参数时小括号可以省略
如:
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
foreachArr(new IntConsumer() {
//对数据进行处理
@Override
public void accept(int value) {
System.out.println(value*2);
}
});
System.out.println("+++++++++++++lambda表达式写法++++++++++++++++");
foreachArr((int value) ->{
System.out.println(value * 2);
});
System.out.println("+++++++++++++lambda表达式省略写法++++++++++++++++");
foreachArr(value -> System.out.println(value * 2));
}
}
复制代码4. 常用操作
4.1. 创建流
单列集合:集合对象.stream()
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Stream<Author> stream = authors.stream();
复制代码数组:Arrays.stream(数组)或者使用 Steam.of(数组)来创建
Integer[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Stream<Integer> stream = Arrays.stream(arr);
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Steam.of(arr);
复制代码双列集合:转换成单列集合后再创建
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", 19);
map.put("2", 19);
map.put("3", 19);
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> stream = map.entrySet().stream();
复制代码4.2. 中间操作
filter()方法,可以对流中的元素进行条件过滤,符合过滤条件的才能继续留在流中。
public static void printAllAuthors(){
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream().filter(author -> author.getName().length() > 1)
.forEach(author -> {
System.out.println(author.getName());
});
}
复制代码map()方法,可以把流中元素进行计算或者转换,使其返回新的值(覆盖原先的值)。相当于一种映射操作。操作之后,返回改变后新的流元素。
public static void test4(){
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream().map(author -> author.getName())
.forEach(name -> {
System.out.println(name);
});
}
复制代码
distinct()方法,可以去除流中重复的元素
public static void test5(){
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.map(author -> author.getName())
.forEach(name -> System.out.println(name));
}
复制代码
注意:distinct() 方法是依赖 Objects 的 equals() 方法来判断对象是否相同。自定义对象实体类,注意重写 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法。
sorted方法,可以对流中的元素进行排序。
public static void test6(){
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.sorted((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge())
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getAge()));
}
复制代码
sorted() 方法传入一个比较器 Comparator,实现 compare() 方法,传入比较规则。
public static void test6(){
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.sorted(new Comparator<Author>() {
@Override
public int compare(Author o1, Author o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
})
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getAge()));
}
复制代码limit()方法,可以设置流的最大长度,超出的部分将被抛弃。
private static void test7() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.sorted((a1, a2) -> a2.getAge() - a1.getAge())
.limit(2)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
复制代码
对这个流分析图有些疑惑,为什么sorted 和 limit 中间操作的结果一致呢?
skip()方法,跳过流中的前n个元素,返回剩下的元素。
private static void test8() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.sorted((a1, a2) -> a2.getAge() - a1.getAge())
.skip(1)
.forEach(a -> System.out.println(a.getName()));
}
复制代码
flatMap()方法,map只能把一个对象转换成另一个对象来作为流中的元素。而flatMap可以把一个对象转换为多个对象作为流中的元素。
我们使用 map 来操作,发现不能进行去重,因为映射出来的是包含书籍列表的流。
private static void test9() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getBooks())
.forEach(books -> System.out.println(books));
}
复制代码
当我们使用 flatMap 进行操作时,会把映射出来的列表中的元素拿出来进行合并作为流对象进行操作。
private static void test9() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.forEach(book -> System.out.println(book));
}
复制代码
4.3. 终结操作
4.3.1. forEach、count、max/min、collect
forEach()方法,对流中的元素进行遍历操作,我们通过传入的参数去指定对遍历到的当前院所进行的是什么具体操作。
private static void test10() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
复制代码
count()方法,可以用来获取当前流中元素的个数。
private static void test11() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
long count = authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.count();
System.out.println("书籍总数量:" + count);
}
复制代码

min()和max()方法,可以用来求流中的最值。

注意:使用 min 或者 max 方法需要传入一个比较器实现具体的排序规则,为什么要这样做呢?因为你操作的流是多个书籍对象,假如你要获取书籍评分最高的书籍对象,那么需要传入具体的比较规则,才能获取到最高评分的数据对象。
这与我们想象的不同,我们以为是对一组数取最大值,那样就不需要实现比较器。而stream 流为了实现统一,所以需要传入比较器规则。

min 和 max 方法相当于经过排序 sorted 和 limit 限制后的结果。
注意一旦做出终结操作,流自动关闭,那么该流对象就不能再进行操作了。

实战
注意:获取一组对象的最大值和最小值它们的比较规则应是相同的,而不是相反的。
private static void test12() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Integer> max = authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.map(book -> book.getScore())
.max((s1, s2) -> s1 - s2);
System.out.println("最大值:" + max.get());
Optional<Integer> min = authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.map(book -> book.getScore())
.min((s1, s2) -> s1 - s2);
System.out.println("最小值:" + min.get());
}
复制代码
collect()方法,把当前流转换成一个集合,收集。
collect() 方法需要传入一个参数,指定流转换集合的类型。
Collectors通过该工具类指定集合的类型
private static void test13() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
List<String> collect = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.map(author -> author.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
}
复制代码

private static void test14() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Set<String> collect = authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.map(book -> book.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(collect);
}
复制代码

private static void test15() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Map<String, List<Book>> collect = authors.stream()
.distinct()
//分别指定键和值的映射
.collect(Collectors.toMap(author -> author.getName(), author -> author.getBooks()));
System.out.println(collect);
}
复制代码

4.3.2. 查找与匹配
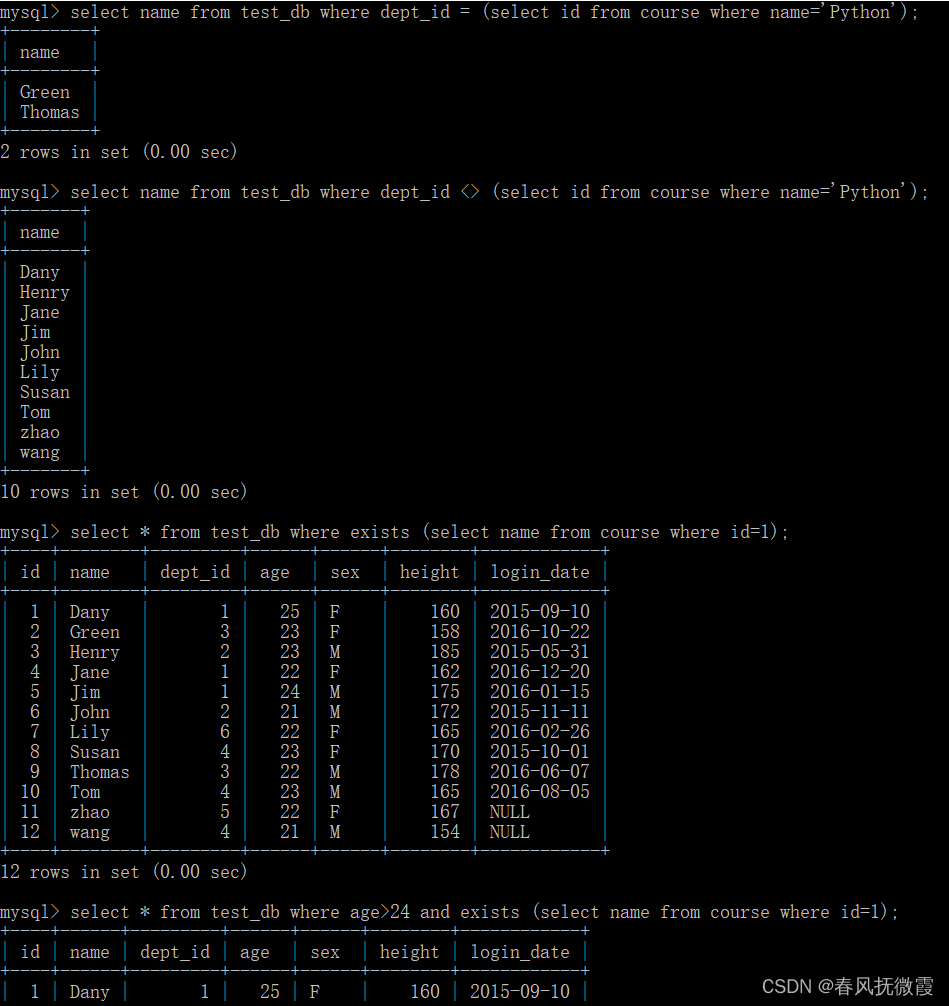
匹配,结果为 boolean 类型
anyMatch()方法,当流中至少有一个元素符合判断条件,就返回true。
需要传入一个判断条件,跟 filter方法的过滤条件类似。
private static void test16() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
boolean b = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.anyMatch(author -> author.getAge() > 29);
System.out.println(b ? "存在29岁以上作家" : "不存在");
}
复制代码

allMatch()方法,当流中所有元素都满足判断条件,就返回true。
private static void test17() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
boolean b = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.allMatch(author -> author.getAge() > 16);
System.out.println(b ? "作家年龄都大于16岁" : "不匹配");
}
复制代码

noneMatch()方法,当流中所有元素都不符合判断条件,返回true。
private static void test18() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
boolean b = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.noneMatch(author -> author.getAge() > 100);
System.out.println(b ? "作家年龄都不大于100岁" : "作家年龄都大于100岁");
}
复制代码

查找
findAny()方法,获取流中任意一个元素,该方法不能保证获取的一定是流中第一个元素。
private static void test19() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Author> any = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.filter(author -> author.getAge() > 16)
.findAny();
System.out.println(any.get());
}
复制代码

findFirst()方法,获取流中的第一个元素。
private static void test20() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Author> first = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.sorted((a1, a2) -> a1.getAge() - a2.getAge())
.findFirst();
first.ifPresent(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
复制代码

4.3.3. reduce归并
reduce 归并,对流中的数据按照指定的计算方式计算出一个结果(缩减操作)。
reduce 的作用就是把 stream 流中的元素组合起来,我们可以传入一个初始值,它会按照我们的计算方式依次拿流中的元素和初始值进行计算后返回结果,结果再和后面的元素计算(累加)。
reduce()方法有三种重载,如下图。

第一种重载,其内部的计算方式如下:
T result = identity;
for(T element : this.stream){
result = accumulator.apply(result, element);
}
return result;
复制代码其中 identity 就是我们可以通过方法参数传入的初始值, accumulator的 apply() 方法,具体进行扫描计算也是通过我们传入的方法参数来确定的。
第二种重载,其内部的计算方式如下:
boolean foundAny = false;
T result = null;
for (T element : this stream) {
if (!foundAny) {
foundAny = true;
result = element;
}
else
result = accumulator.apply(result, element);
}
return foundAny ? Optional.of(result) : Optional.empty();
复制代码第二种重载方式,由于没有初始值,其内部会在第一次循环时,对 foundAny 进行判断,满足将stream 流中的第一个元素,赋值给初始值,然后进行循环计算。这种方式适用于与自身进行一些运算。
举例
- 使用
reduce求所有作者年龄的和
private static void test21() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Integer reduce = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce(0, (result, age) -> result + age);
System.out.println(reduce);
}
复制代码
这种方式计算所有作者年龄的和,reduce() 方法需要传入两个参数,第一个传入初始值(指定 result 初始值);第二个传入计算规则:result代表结果, age 代表下一个需要累加的值,累加完毕后返回结果给 result ,然后重新累加。
- 使用
reduce求所有作者中年龄的最大值
private static void test22() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Integer max = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce(Integer.MIN_VALUE, (result, age) -> result < age ? age : result);
System.out.println(max);
}
复制代码
- 使用
reduce求所有作者中年龄的最小值
private static void test23() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Integer min = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce(Integer.MAX_VALUE, (result, age) -> result > age ? age : result);
System.out.println(min);
}
复制代码
- 通过
reduce第二种重载,求所有作者中年龄的最小值
private static void test24() {
Optional<Integer> minOptional = getAuthors().stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce((result, age) -> result < age ? result : age);
minOptional.ifPresent(min -> System.out.println(min.intValue()));
}
复制代码
5. 注意事项
- 不要惰性求值(如果没有终结操作,中间操作是不会得到执行的)
- 流是一次性的(一旦一个流对象经过一个终结操作后,这个流就不能再被使用)
- 不会影响原数据(我们在流中可以对数据做很多处理,不会对原数据有影响)


![[论文阅读] 颜色迁移-梯度保护颜色迁移](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1a70eda52f5a40c4bfc952c3d8f7e9fe.png)
![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM基于农产品交易系统(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/37e991aeccf147c5afe41e97f6690000.png)


![[论文阅读] 颜色迁移-Illuminant Aware Gamut-Based](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4ea3ae4df7604ed881378f2511577e88.png)