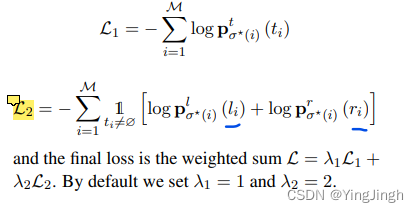文章目录
- 关系抽取——OD-RTE: A One-Stage Object Detection Framework for Relational Triple Extraction
- 目标函数1——object 四个顶点概率
- 目标函数2——span的概率
- 总目标函数
- Revisiting Relation Extraction in the era of Large Language Models
- Can NLI Provide Proper Indirect Supervision for Low-resource Biomedical Relation Extraction?
- Continual Contrastive Finetuning Improves Low-Resource Relation Extraction
- Coarse-to-fine Few-shot Learning for Named Entity Recognition
- PromptNER: Prompt Locating and Typing for Named Entity Recognition
- 损失函数
关系抽取——OD-RTE: A One-Stage Object Detection Framework for Relational Triple Extraction
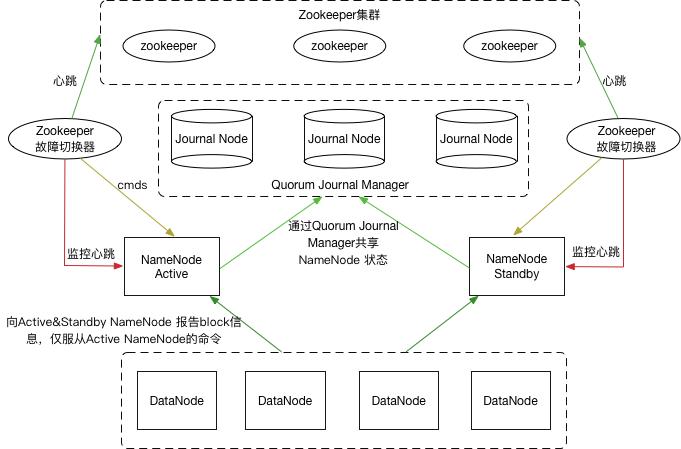
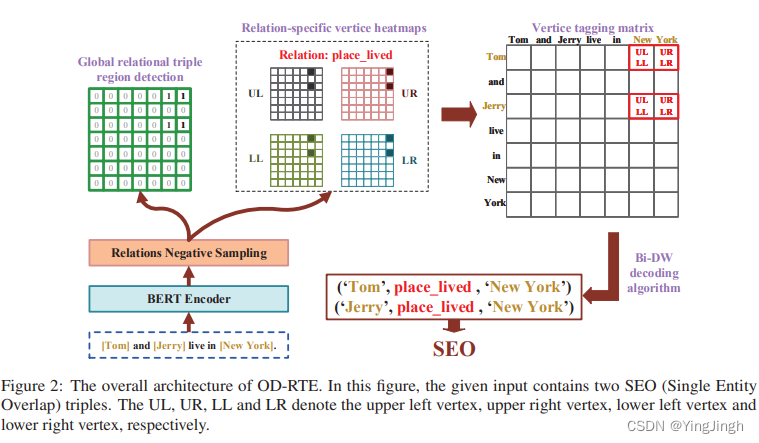
关系抽取使用object detection的方式,得到三元组。
每个token作为一个pixel,然后物体检测,在这个grid中,找到object的上下左右四个角。
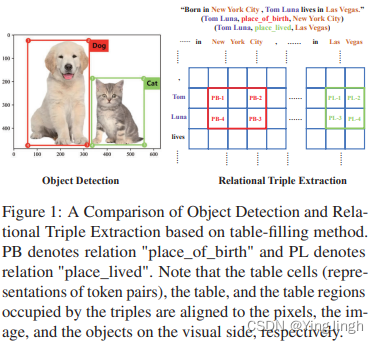
object的四个角分别为:UL、UR、LR、LL,分别表示:
UL is the upper left vertex of the object region
UR is the upper right vertex of the object region
LR is the lower right vertex of the object region
LL is the lower left vertex of the object region
计算每个token是object四个角的概率:
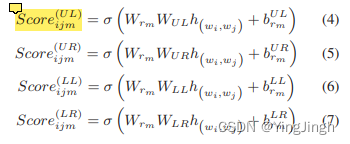
目标函数1——object 四个顶点概率
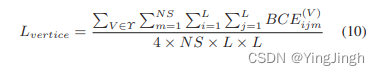
目标函数2——span的概率
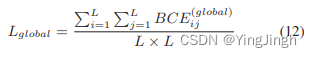
总目标函数
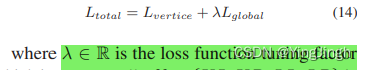
模型结构图:
Revisiting Relation Extraction in the era of Large Language Models
核心: 大语言模型在relation extraction 任务中的表现。
不足:
- we did not consider corpora containing n-ary relations between entities 没有考虑n为关系
- 没有在过长的文本和包含过多关系的文本中run experiments。(such as DocRED)
Can NLI Provide Proper Indirect Supervision for Low-resource Biomedical Relation Extraction?
** 任务形式:** 生物学中的关系分类问题 ,给出两个实体,判断实体之间的关系类型。
NBR 将输入视为前提,同时将每个关系标签口头化为基于模板的自然语言假设,从而将 RE 重构为 NLI。NBR 学会根据蕴涵得分对关系进行排序,这样正确关系的假设得分应高于错误关系的假设得分。
实施方式上:
将sentence中entity mention做mask,然后将entity type 填充在每个relation的template中,用于relation classification。
每个relation填充后得到的template,做NLI任务,可分为三类:中立、矛盾和蕴含。
具体来说,我们设计了以下几种模板(详情和性能见附录§D),每种模板都包含两种类型的实体掩码:
1. 简单模板用 "is-a "短语口头表达两个实体之间的关系。
2. 描述性模板提供关系的上下文描述。
3. 示范模板包括一个随机抽样的具有相同关系的训练集示例。
4. 描述+演示模板结合了描述性说明和抽样示例。
5. 学习提示模板(Yeh 等人,2022 年)为描述学习最佳离散标记。
Continual Contrastive Finetuning Improves Low-Resource Relation Extraction
任务形式: 文件级别的关系分类模型。
pretraining the entity pair embedding by RE-based objective and finetuning on labeled data by classification-based objective.
方法实施:
1.预训练阶段:
使用(未标记的)文档语料库,基于我们改进的匹配空白训练目标(MTB;Baldini Soares 等人,2019 年)对实体对嵌入进行预训练,其中 LM 学会判断两个实体对嵌入是否对应于实体对,并通过对比学习加强表征学习
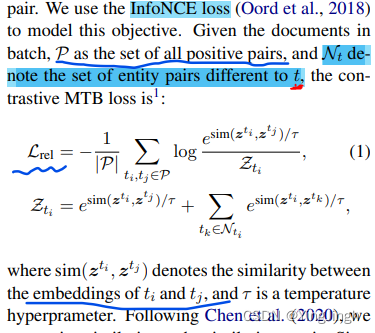
这个对比学习损失函数中,是把来自同一个文件的entity pairs作为positive pair,把不同的entity pairs作为negative pairs.
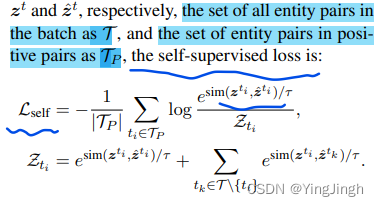
这个对比损失函数中,是把同一个entity pair,但不同mask rate下的entity pair作为positive pairs。
总损失函数:
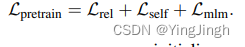
2.微调阶段:
首先,我们建议通过对比学习来不断微调预训练的嵌入,从而鼓励与相同关系对应的实体对嵌入相似。 多中心对比损失 (MCCL),它鼓励实体对只与同一关系的实体对子集相似,从而允许一种关系形成多个聚类.
在entity pair embedding上,加一个classifier做分类任务。
多聚类中心的分类任务: 带权重的Loss函数

其次,我们使用k-nearest neighbors (kNN; Khandelwal et al. arXiv:2212.10823v3 [cs.CL] 31 May 2023 2020, 2021) 在推理中,根据最相似的实例进行预测。
Coarse-to-fine Few-shot Learning for Named Entity Recognition
PromptNER: Prompt Locating and Typing for Named Entity Recognition
核心:设计了双槽模板,一个slot表示position slot,一个slot表示type slot。
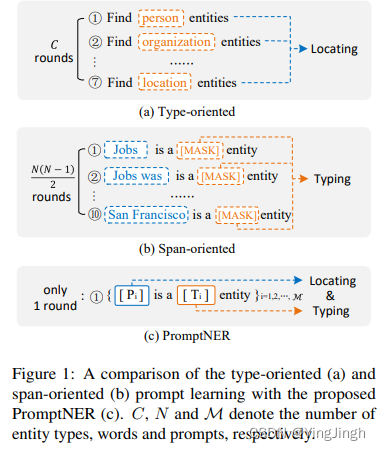
举个例子如下:
a sentence X =“Jobs was born in San Francisco”, the default dual-slot multi-prompt input sequence can be represented as:

损失函数
损失函数包括实体的type分类和实体location的定位。
实体有左右边界,left和right。