spring在开启事务的时候是去拿数据源的,今天我们详细分析一下,@Transactional 事务获取数据源的源码解析:
1、从业务代码声明式事务开始: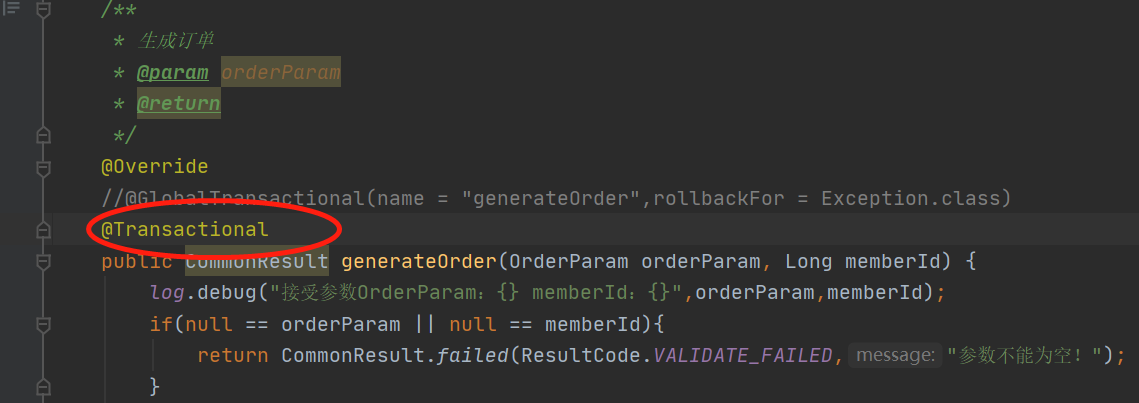
接口调用到这里,原理是生成了动态代理类,默认是通过cglib实现的类:
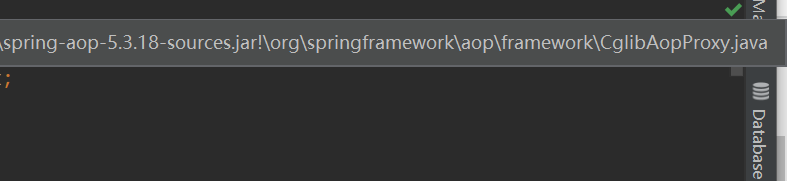
2、来到 class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable
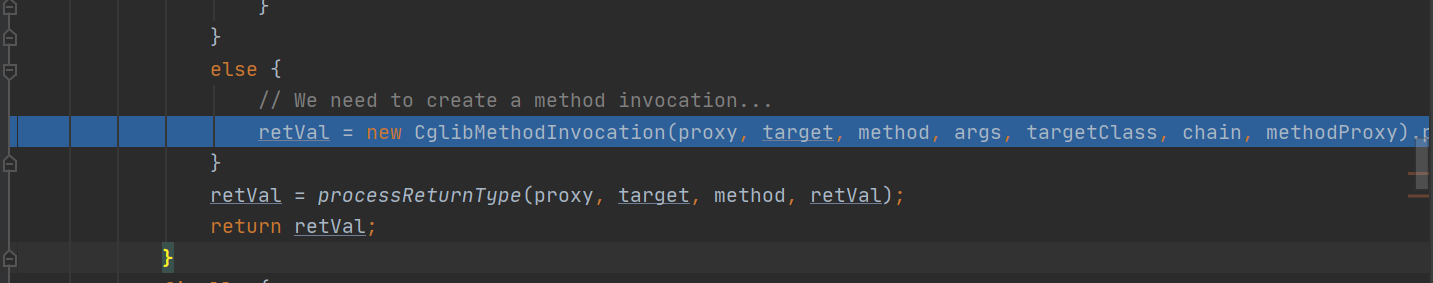
点进入:
public CglibMethodInvocation(Object proxy, @Nullable Object target, Method method,
Object[] arguments, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
List<Object> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers, MethodProxy methodProxy) {
super(proxy, target, method, arguments, targetClass, interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers);//进入父类
// Only use method proxy for public methods not derived from java.lang.Object
this.methodProxy = (isMethodProxyCompatible(method) ? methodProxy : null);
}3、来到:public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable
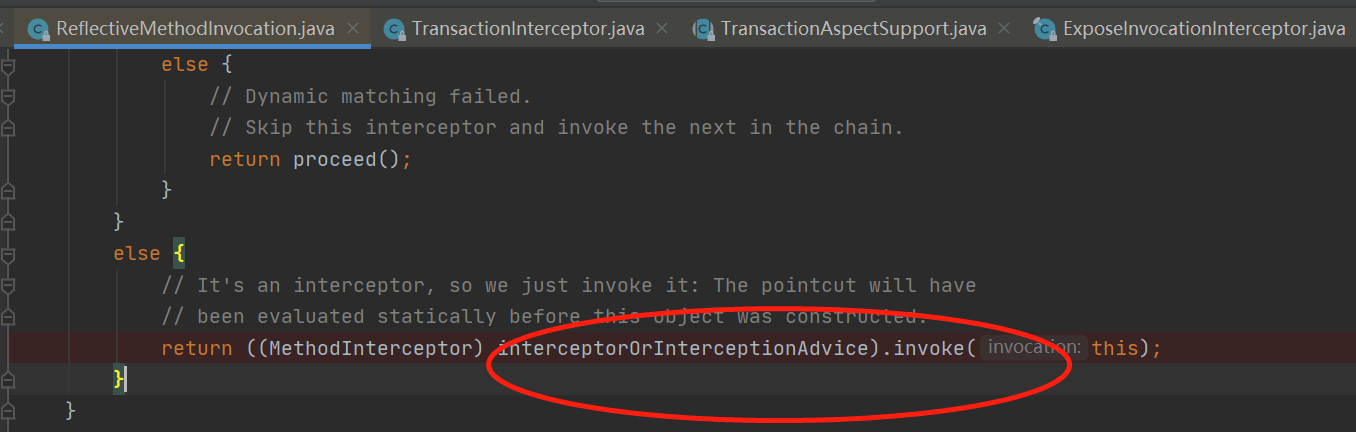
点击
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
try {
return mi.proceed();//进入事务相关的类
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}又进入父类
然后来到了事务的拦截器:
public class TransactionInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable
4、TransactionInterceptor 来到:
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
//进入父类 TransactionAspectSupport
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new CoroutinesInvocationCallback() {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();//接口实现,父类一会会调用
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
return invocation.getThis();//接口实现,父类一会会调用
}
@Override
public Object[] getArguments() {
return invocation.getArguments();//接口实现,父类一会会调用
}
});
}
5、来到:public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean
核心在这
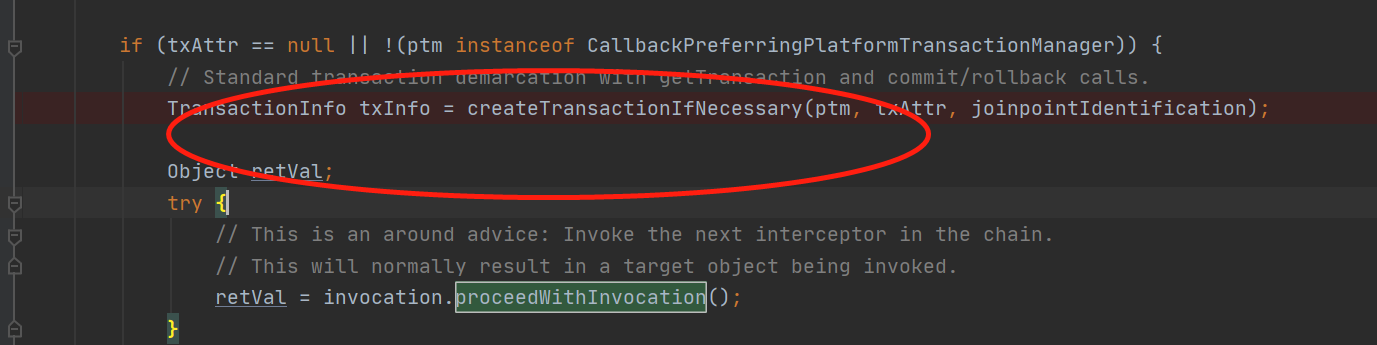
点击进入:
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
//PlatformTransactionManager tm 事务模板管理类,核心类
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);//点击进入
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
点击显然进入第一个抽象类
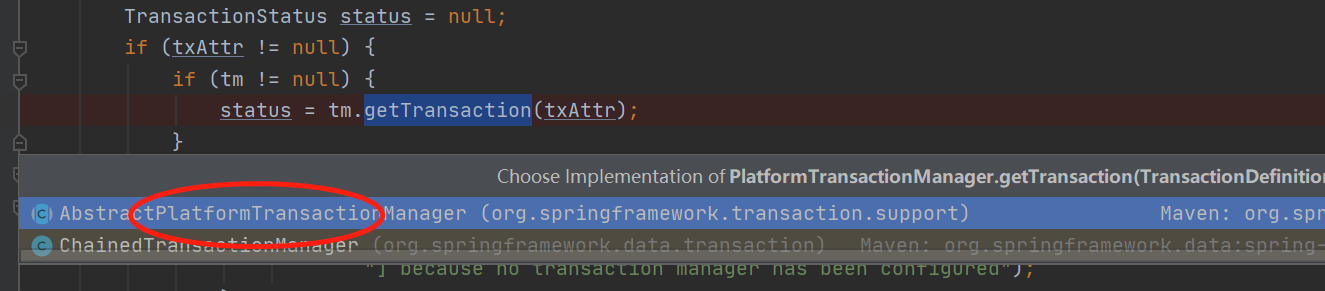
6、来到:public abstract class AbstractPlatformTransactionManager implements PlatformTransactionManager, Serializable
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
}
try {//核心处理,点击进入
return startTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}来到:
private TransactionStatus startTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction,
boolean debugEnabled, @Nullable SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources) {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
doBegin(transaction, definition);//开始获取
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}点击看到实现子类
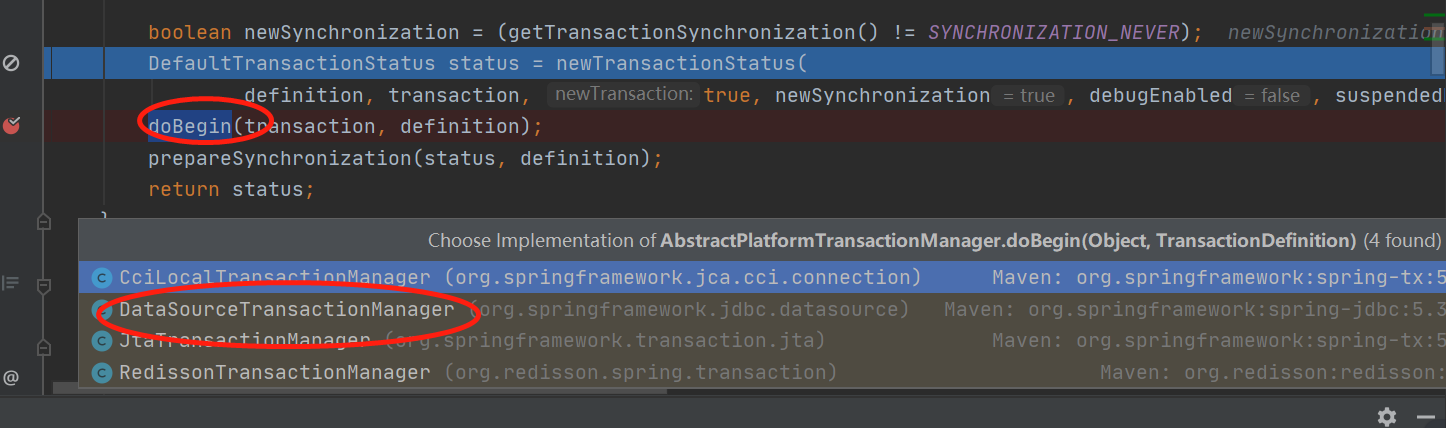
进入 public class DataSourceTransactionManager extends AbstractPlatformTransactionManager implements ResourceTransactionManager, InitializingBean
7、来到 DataSourceTransactionManager
@Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try {
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();//核心入口
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
}
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
txObject.setReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly());
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,
// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
// configured the connection pool to set it already).
if (con.getAutoCommit()) {
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
}
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
// Bind the connection holder to the thread.
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
}
}
点击 obtainDataSource()
//获取JDK原生的dataSource
protected DataSource obtainDataSource() {
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();
Assert.state(dataSource != null, "No DataSource set");
return dataSource;
}点击:obtainDataSource().getConnection();
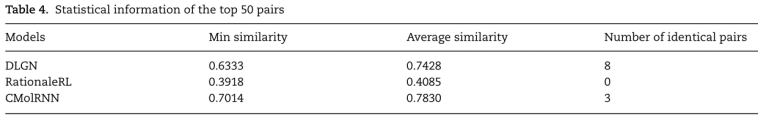
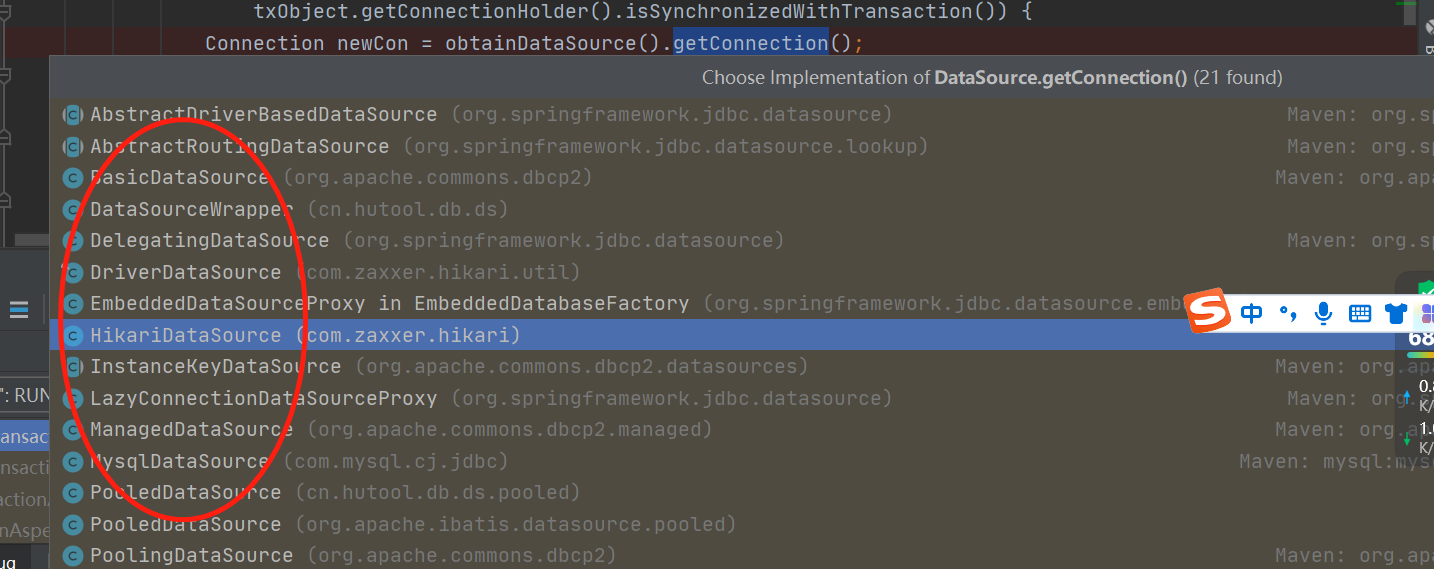 发现很多的实现类。具体进入哪个连接池实现类,就要参考我们的服务配置,spring.dataSource.type 配置的哪个类,如果不配置springboot高版本默认是HikariDatasource 连接池类,当然也可以是自定义的连接池,处理一些自定义的业务。
发现很多的实现类。具体进入哪个连接池实现类,就要参考我们的服务配置,spring.dataSource.type 配置的哪个类,如果不配置springboot高版本默认是HikariDatasource 连接池类,当然也可以是自定义的连接池,处理一些自定义的业务。
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计教务管理系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/365a0c1911df43a28e96fc1f1861adf1.png)