1. 坐标系轴方向问题
3D数学基础中约定使用左手坐标系
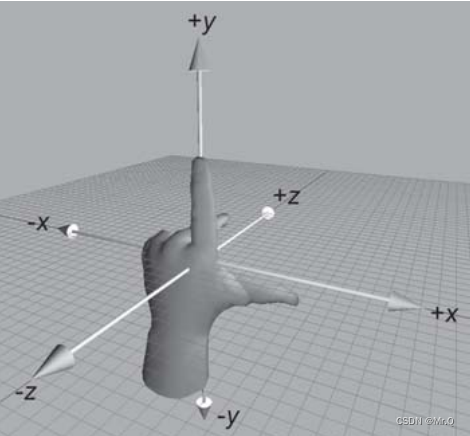
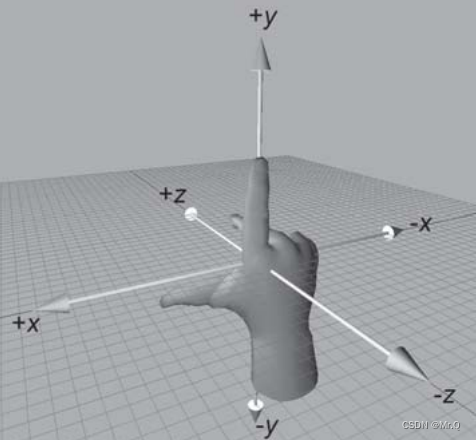
左手坐标系 右手坐标系
左手正方向:+x正向右平移,+y向上平移,+z向前平移.
右手正方向:+x正向左平移,+y向上平移,+z向前平移.
2. 常用的三种坐标系
2.1 世界坐标系
所关心的最大的坐标系,用来描述其他坐标系。


2.2 物体坐标系
以自身为原点,自身的坐标系,相机坐标系就属于物体坐标系。


 即z轴(前进方向)是向里的,其他很多书比如视觉SLAM是右手坐标系是,z轴是向外的。
即z轴(前进方向)是向里的,其他很多书比如视觉SLAM是右手坐标系是,z轴是向外的。
2.3 惯性坐标系
前面的世界坐标系和物体坐标系中间有个惯性坐标系。


物体坐标系到世界坐标系转换的意义:比如手机在你前面3米处(以你为中心的物体坐标系描述),那这个手机在这个房间哪个位置呢?(这个房间就是世界坐标系)
那如何表示旋转呢?下面介绍的三种表示方式:矩阵,欧拉角,四元数。
3. 矩阵
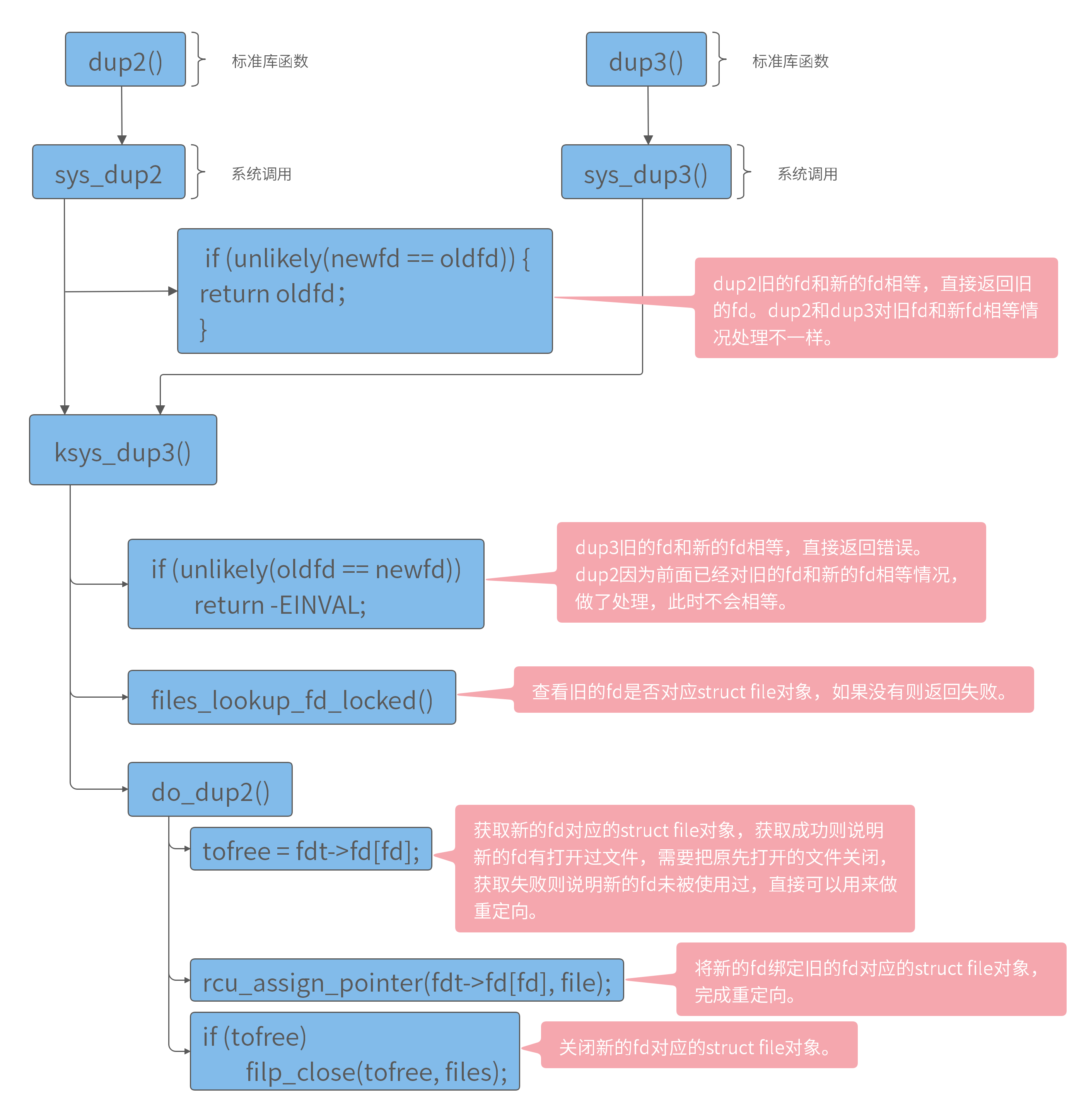
一个矩阵用来把一个向量从一个坐标系转换到另一个坐标系中进行描述,则该旋转矩阵描述这两个坐标系之间的相对位移。4x4矩阵包含3x3旋转部分和1x3平移部分。

因为最后一列总是[0,0,0,1]^T,所以去掉,变成4x3矩阵,此矩阵具有旋转和平移功能。
4. 欧拉角
欧拉角表示旋转是把旋转拆分成绕任意三个相互垂直的轴旋转。哪三个轴,什么顺序都可以,但常用的如下。
| 朝向 | 倾斜 | 翻滚 | |
| 3D Math Foundation | heading | pitch | bank |
| Vision SLAM 14 | yaw | pitch | roll |
| 绕物体坐标系旋转轴 | y | x | z |

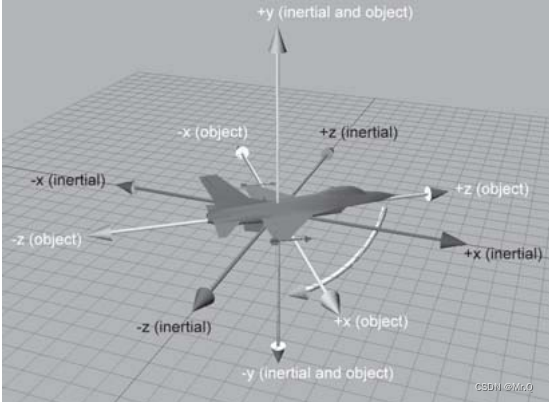
heading是绕物体坐标系y轴旋转量 pitch是绕绕物体坐标系x旋转量
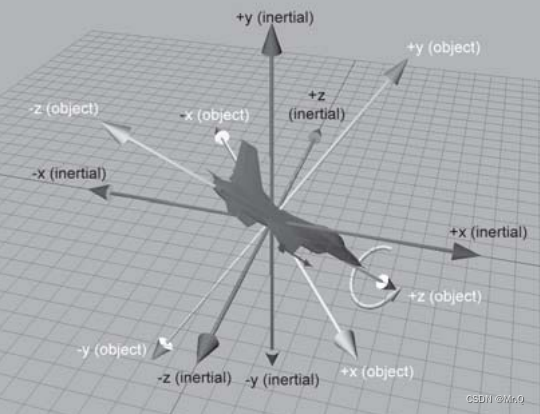
bank是绕绕物体坐标系z轴旋转量
比如,马路上的汽车只有绕物体坐标系的y轴旋转,即只有heading。
5. 四元数
四元数包含一个标量w和一个3D向量v,表示形式为:
[w, v] 或者
[w, (x,y,z)]
举个例子,四元数

/
//
// 3D Math Primer for Games and Graphics Development
//
// EulerAngles.h - Declarations for class EulerAngles
//
// Visit gamemath.com for the latest version of this file.
//
// For more details, see EulerAngles.cpp
//
/
#ifndef __EULERANGLES_H_INCLUDED__
#define __EULERANGLES_H_INCLUDED__
// Forward declarations 预声明
class Quaternion;
class Matrix4x3;
class RotationMatrix;
// 以欧拉角形式保存方位
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// class EulerAngles
//
// This class represents a heading-pitch-bank Euler angle triple.
class EulerAngles {
public:
// Public data
// Straightforward representation. 直接的表示方式
// Store the three angles, in radians 弧度表示
float heading; // heading,pitch,bank (朝向,倾斜,翻滚)
float pitch;
float bank;
// Public operations
// 1,Default constructor does nothing
EulerAngles() {}
// Construct from three values
EulerAngles(float h, float p, float b) :
heading(h), pitch(p), bank(b) {}
// Set to identity triple (all zeros)
//2,单位欧拉角
void identity() { heading = pitch = bank = 0.0f; }
// Determine "canonical" Euler angle triple
//3,声明限制的欧拉角:pitch倾斜限制在-90,90之间
void canonize();
// Convert the quaternion to Euler angle format.
// The input quaternion is assumed to perform the rotation from object-to-inertial
// or inertial-to-object, as indicated.
// 3, 两个函数功能:四元数转欧拉角形式
void fromObjectToInertialQuaternion(const Quaternion &q); // 输入四元数参数作用:物体坐标转惯性坐标
void fromInertialToObjectQuaternion(const Quaternion &q); //
// Convert the transform matrix to Euler angle format.
// The input matrix is assumed to perform the transformation from object-to-world,
// or world-to-object, as indicated.
// The translation portion of the matrix is ignored. The matrix is assumed to be orthogonal(正交矩阵).
// 4,两个函数功能:转换矩阵转欧拉角形式
void fromObjectToWorldMatrix(const Matrix4x3 &m); // 输入四元数参数作用:物体坐标转世界坐标
void fromWorldToObjectMatrix(const Matrix4x3 &m);
// Convert a rotation matrix to Euler Angle form.
// 5,函数功能:旋转矩阵转欧拉角形式
void fromRotationMatrix(const RotationMatrix &m);
};
// A global "identity" Euler angle constant
// 全局单位欧拉角常量
extern const EulerAngles kEulerAnglesIdentity;
/
#endif // #ifndef __EULERANGLES_H_INCLUDED__
待续。。。