这个简单的的案例展示了如何从
RecyclerView to ViewPager,以网上的公开图片为样例。
安卓开发中从RecyclerView 到 ViewPager
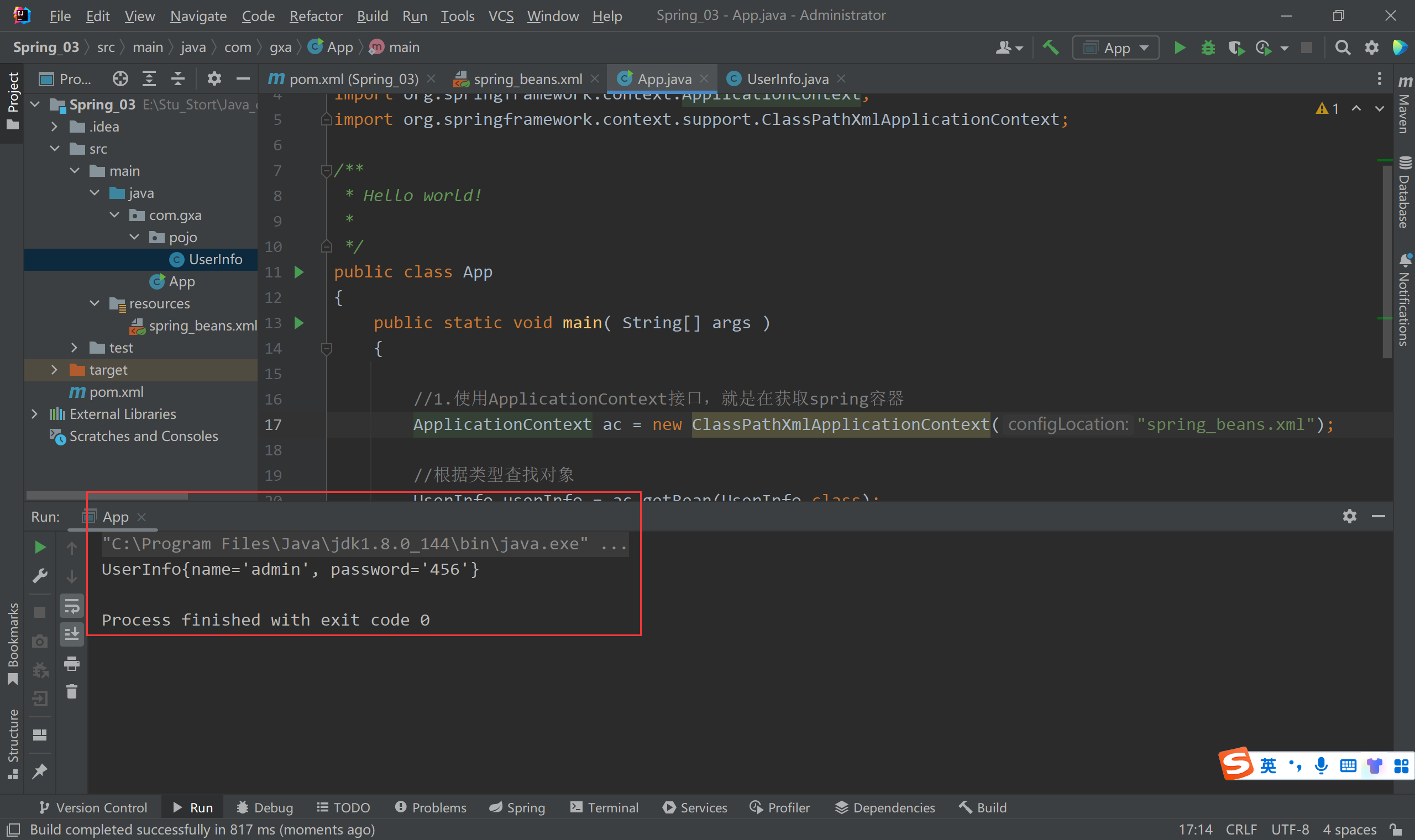
- demo运行结果
- demo项目工程目录结构
- 关键代码 MainActivity
- 关键代码GridFragment
- 关键代码ImageFragment
- 关键代码ImagePagerFragment
- 关键布局容器GridAdapter
- 关键代码ImagePagerAdapter
demo运行结果

demo项目工程目录结构

其中,需要特别说明的目录transition,这个资源目录包含了图片的淡入淡出动画和一些转场效果;adapter和fragment则是对应布局容器。
关键代码 MainActivity
给出MainActivity代码:
package com.test.samples.gridtopager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager;
import com.google.samples.gridtopager.fragment.GridFragment;
/**
* Grid to pager app's main activity.
*/
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String KEY_CURRENT_POSITION = "com.test.samples.gridtopager.key.currentPosition";
public static int currentPosition;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 通过调用父类的 onCreate(savedInstanceState) 方法来执行必要的初始化工作
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 使用 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) 方法设置布局文件,将该 Activity 的内容显示在屏幕上。
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
if (savedInstanceState != null) {
// 通过检查 savedInstanceState 是否为 null,判断是否是应用程序发生配置变化(如屏幕旋转)而重新创建 Activity 的情况。
currentPosition = savedInstanceState.getInt(KEY_CURRENT_POSITION, 0);
// Return here to prevent adding additional GridFragments when changing orientation.
return;
}
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
fragmentManager.beginTransaction().add(R.id.fragment_container, new GridFragment(), GridFragment.class.getSimpleName()).commit();
}
/**
* 在 Activity 即将销毁前被调用。在这个方法中,你可以保存你想要在 Activity 重新创建时恢复的数据。
*
* @param outState Bundle in which to place your saved state.
*/
@Override
protected void onSaveInstanceState(@NonNull Bundle outState) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
// 它的作用是将 currentPosition 的值保存到 outState Bundle 对象中,以便在 Activity 重新创建时恢复该值。
outState.putInt(KEY_CURRENT_POSITION, currentPosition);
}
}
讲一下代码中的FragmentManager,这是一个Android开发中用于管理Fragment片段的类,是 Activity 类的一部分,用于添加、替换、移除和管理应用程序界面中的 Fragment 实例。
FragmentManager 提供了一系列方法来执行与 Fragment 相关的操作,包括:
- 添加 Fragment:可以使用
beginTransaction() 方法开始一个事务,并使用add() 方法将Fragment添加到指定的容器视图中。 - 替换 Fragment:使用
replace() 方法可以替换指定容器视图中的 Fragment,并将其显示在界面上。 - 移除 Fragment:使用
remove() 方法可以从界面上移除并销毁指定的 Fragment。 - 回退栈管理:FragmentManager 提供了回退栈(
BackStack)功能,允许用户返回上一个 Fragment 或回到之前的 Fragment 状态。 - 查找 Fragment:可以使用
findFragmentById() 或findFragmentByTag() 方法根据 ID 或标签查找已添加的 Fragment。 - 事务管理:
FragmentManager支持事务的提交和回滚,以确保多个 Fragment 操作能够按照预期顺序执行。
这段代码中的另一个关键点就是onSaveInstanceState的重写,它用于保存当前 Activity 的状态和数据。
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState):这一行调用父类的onSaveInstanceState() 方法,以确保默认的状态保存行为得到执行。outState.putInt(KEY_CURRENT_POSITION, currentPosition):这行代码将变量currentPosition的值保存到outState的Bundle对象中。putInt() 方法将一个整数值存储在 Bundle 中,并使用键名KEY_CURRENT_POSITION来标识该值。
关键代码GridFragment
给出GridFragment代码如下:
public class GridFragment extends Fragment {
private RecyclerView recyclerView;
/**
* 这个方法通过布局填充器(inflater)将指定的布局文件 R.layout.fragment_grid 填充到容器 container 中,并将返回的 View 对象强制转换为 RecyclerView 类型。
*
* @param inflater The LayoutInflater object that can be used to inflate
* any views in the fragment,
* @param container If non-null, this is the parent view that the fragment's
* UI should be attached to. The fragment should not add the view itself,
* but this can be used to generate the LayoutParams of the view.
* @param savedInstanceState If non-null, this fragment is being re-constructed
* from a previous saved state as given here.
* @return
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 通过布局填充器(inflater)将指定的布局文件 R.layout.fragment_grid 填充到容器 container 中,并将返回的 View 对象强制转换为 RecyclerView 类型
recyclerView = (RecyclerView) inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_grid, container, false);
// 同时设置适配器为 GridAdapter 的实例。
recyclerView.setAdapter(new GridAdapter(this));
// 调用 prepareTransitions() 方法来准备过渡效果(一般和共享元素动画有关)。
prepareTransitions();
// 调用 postponeEnterTransition() 方法来延迟进入过渡效果,一般是在使用共享元素动画时使用
postponeEnterTransition();
return recyclerView;
}
@Override
public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 在 onViewCreated() 方法中,首先调用父类的 onViewCreated() 方法进行基本的视图初始化操作,
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
// 然后调用 scrollToPosition() 方法来滚动到指定的位置。
scrollToPosition();
}
/**
* Scrolls the recycler view to show the last viewed item in the grid. This is important when
* navigating back from the grid.
* 滚动到指定位置的方法 scrollToPosition()。
* 它使用了 recyclerView 的布局监听器 addOnLayoutChangeListener() 来监听布局变化。当布局发生改变时,会执行 onLayoutChange() 方法。
*/
private void scrollToPosition() {
recyclerView.addOnLayoutChangeListener(new OnLayoutChangeListener() {
// 在 onLayoutChange() 方法中,首先移除当前的布局监听器,然后获取 recyclerView 的布局管理器 layoutManager。
// 接下来,通过 layoutManager.findViewByPosition() 方法找到当前位置对应的视图 viewAtPosition。
@Override
public void onLayoutChange(View v, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, int oldLeft, int oldTop, int oldRight, int oldBottom) {
// 在布局发生变化时,onLayoutChange方法被调用。
recyclerView.removeOnLayoutChangeListener(this);
// 通过recyclerView.removeOnLayoutChangeListener(this)将当前的OnLayoutChangeListener移除,以避免循环引用。
final RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager = recyclerView.getLayoutManager();
// 获取RecyclerView的布局管理器(LayoutManager)。
View viewAtPosition = layoutManager.findViewByPosition(MainActivity.currentPosition);
// Scroll to position if the view for the current position is null (not currently part of
// layout manager children), or it's not completely visible.
// 该位置的View为null(当前不在布局管理器的子元素中),或者它没有完全可见
if (viewAtPosition == null || layoutManager.isViewPartiallyVisible(viewAtPosition, false, true)) {
// 使用recyclerView.post()方法在主线程中执行滚动到指定位置的操作。
recyclerView.post(() -> layoutManager.scrollToPosition(MainActivity.currentPosition));
}
}
});
}
/**
* Prepares the shared element transition to the pager fragment, as well as the other transitions
* that affect the flow.
* 该方法主要用于设置过渡效果(transition)和共享元素回调(shared element callback
*/
private void prepareTransitions() {
setExitTransition(TransitionInflater.from(getContext()).inflateTransition(R.transition.grid_exit_transition));
// A similar mapping is set at the ImagePagerFragment with a setEnterSharedElementCallback.
// 获取一个过渡效果的实例,并将其设置为退出过渡效果(exit transition)。
// 这个过渡效果可以在资源文件 R.transition.grid_exit_transition 中定义,用于指定界面切换时的动画效果。
// 设置了一个共享元素回调(SharedElementCallback)。共享元素回调是在共享元素动画期间被调用的一组方法,用于指定共享元素的映射关系。
setExitSharedElementCallback(new SharedElementCallback() {
@Override
public void onMapSharedElements(List<String> names, Map<String, View> sharedElements) {
// Locate the ViewHolder for the clicked position.
// 定位到当前点击位置的 ViewHolder。如果无法找到 ViewHolder,就直接返回。
RecyclerView.ViewHolder selectedViewHolder = recyclerView.findViewHolderForAdapterPosition(MainActivity.currentPosition);
if (selectedViewHolder == null) {
return;
}
// 将共享元素的名称与对应的视图放入 sharedElements 映射表中
// Map the first shared element name to the child ImageView.
sharedElements.put(names.get(0), selectedViewHolder.itemView.findViewById(R.id.card_image));
}
});
}
}
这段代码其实没什么好说,继承并重写Fragment的一些关键方法,然后就是onViewCreated,并在该方法内实现一个scrollToPosition滚动到指定位置。
这里多说一句关于onViewCreated和onCreateView,这是Fragment的两个生命周期方法,创建Fragment的时候起到了不同的作用,差异具体如下:
- onCreateView()
- 这个方法被调用用于创建 Fragment 的视图层次结构(
View Hierarchy) - 在该方法中,你需要使用布局填充器(
inflater)将指定的布局文件填充到容器中,并将返回的View对象作为创建的视图 - 通常,在这个方法中执行与视图相关的初始化操作,例如
查找视图元素、设置监听器等。 - 必须在此方法中返回
Fragment的根视图。
- onViewCreated():
- 这个方法是在
onCreateView() 方法完成后立即调用的。 - 它接收两个参数:
View view和Bundle savedInstanceState。 view参数表示通过onCreateView() 方法创建的Fragment视图。savedInstanceState参数是保存有关Fragment状态的数据的Bundle对象,可以在重新创建Fragment时使用- 这个方法通常用于配置和修改已经创建的视图。
关键代码ImageFragment
给出代码ImageFragment:
public class ImageFragment extends Fragment {
// 静态方法 newInstance(),用于创建一个新的 ImageFragment 实例,并传递一个图片资源的整型值作为参数
private static final String KEY_IMAGE_RES = "com.google.samples.gridtopager.key.imageRes";
// 在 newInstance() 方法中,首先创建一个新的 ImageFragment 实例
/**
* 这种设计模式称为静态工厂方法(Static Factory Method),
* 它提供了一种简单的方式来创建对象并传递参数。
* 在这个例子中,TODO:通过静态方法 newInstance() 创建 ImageFragment 实例,并将图片资源整型值作为参数传递给该实例。
* 这样做的好处是保证了创建实例时必须提供必要的参数,并且可以方便地在创建过程中传递其他需要的数据。
*
* @param drawableRes
* @return
*/
public static ImageFragment newInstance(@DrawableRes int drawableRes) {
ImageFragment fragment = new ImageFragment();
// 通过调用 fragment.setArguments(argument) 将参数 Bundle 设置给 ImageFragment 实例,并返回该实例
Bundle argument = new Bundle();
argument.putInt(KEY_IMAGE_RES, drawableRes);
fragment.setArguments(argument);
return fragment;
}
/**
* 这段代码是 ImageFragment 类中的 onCreateView() 方法的实现。
*
* @param inflater The LayoutInflater object that can be used to inflate
* any views in the fragment,
* @param container If non-null, this is the parent view that the fragment's
* UI should be attached to. The fragment should not add the view itself,
* but this can be used to generate the LayoutParams of the view.
* @param savedInstanceState If non-null, this fragment is being re-constructed
* from a previous saved state as given here.
* @return
*/
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 首先使用布局填充器(inflater)将指定的布局文件 R.layout.fragment_image 填充到容器中,并将得到的视图对象赋值给 view 变量。
final View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_image, container, false);
// 通过 getArguments() 获取传递给 ImageFragment 的参数数据。从参数中提取出图片资源的整型值,使用 arguments.getInt(KEY_IMAGE_RES),并将其赋值给 imageRes 变量。
Bundle arguments = getArguments();
@DrawableRes int imageRes = arguments.getInt(KEY_IMAGE_RES);
// Just like we do when binding views at the grid, we set the transition name to be the string
// value of the image res.
// 设置过渡名称(transition name)。这里使用图片资源整型值的字符串表示作为过渡名称。这样,在共享元素过渡动画期间,可以使用相同的过渡名称来匹配和映射共享元素
view.findViewById(R.id.image).setTransitionName(String.valueOf(imageRes));
// Load the image with Glide to prevent OOM error when the image drawables are very large.
/*
使用 Glide 库加载图片资源到 ImageView 视图中。通过 Glide.with(this).load(imageRes) 指定加载的图片资源,并设置一个监听器监听图片加载过程。
*/
Glide.with(this).load(imageRes).listener(new RequestListener<Drawable>() {
/**
* 如果图片加载失败(onLoadFailed()),则通过 getParentFragment().startPostponedEnterTransition() 通知父级 Fragment 开始延迟的共享元素过渡动画。
* @param e The maybe {@code null} exception containing information about why the request failed.
* @param model The model we were trying to load when the exception occurred.
* @param target The {@link Target} we were trying to load the image into.
* @param isFirstResource {@code true} if this exception is for the first resource to load.
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean onLoadFailed(@Nullable GlideException e, Object model, Target<Drawable> target, boolean isFirstResource) {
// The postponeEnterTransition is called on the parent ImagePagerFragment, so the
// startPostponedEnterTransition() should also be called on it to get the transition
// going in case of a failure.
getParentFragment().startPostponedEnterTransition();
return false;
}
/**
* 如果图片加载成功(onResourceReady()),同样调用 startPostponedEnterTransition() 来开始共享元素过渡动画。
* @param resource The resource that was loaded for the target.
* @param model The specific model that was used to load the image.
* @param target The target the model was loaded into.
* @param dataSource The {@link DataSource} the resource was loaded from.
* @param isFirstResource {@code true} if this is the first resource to in this load to be loaded
* into the target. For example when loading a thumbnail and a full-sized image, this will be
* {@code true} for the first image to load and {@code false} for the second.
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean onResourceReady(Drawable resource, Object model, Target<Drawable> target, DataSource dataSource, boolean isFirstResource) {
// The postponeEnterTransition is called on the parent ImagePagerFragment, so the
// startPostponedEnterTransition() should also be called on it to get the transition
// going when the image is ready.
// 当图片加载成功时,会调用 onResourceReady() 方法。
// 它接收一些参数,包括加载的图片资源 resource、模型对象 model、目标 target、数据源 dataSource 和一个标志 isFirstResource 表示是否为第一个资源。
//TODO: 通知父级 Fragment 开始延迟的共享元素过渡动画
getParentFragment().startPostponedEnterTransition();
return false;
}
// 使用 into((ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.image)) 将加载的图片设置到 ImageView 视图中。
}).into((ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.image));
// 返回填充好的视图 view 作为 Fragment 的根视图。
return view;
}
}
讲一下这段代码巧妙地设计思路,静态工厂方法,提供了一种简单的方式来创建对象并传递参数。在这个例子中,通过静态方法 newInstance() 创建 ImageFragment 实例,并将图片资源整型值作为参数传递给该实例。这样做的好处是保证了创建实例时必须提供必要的参数,并且可以方便地在创建过程中传递其他需要的数据。
然后就是Glide的库使用,加载图片资源到ImageView视图中,利用onResourceReady和onLoadFailed判定加载成功或者失败情况。
讲一下getParentFragment().startPostponedEnterTransition();这个方法就是调用父级的Fragment方法开始延迟的共享元素过渡动画。
在 Android 中,当使用共享元素进行 Fragment 之间的切换时,可以通过设置延迟开始的共享元素过渡动画。这样,在新的 Fragment 视图就绪后,可以手动触发共享元素过渡动画的开始,以获得平滑的过渡效果。
注意:
getParentFragment() 方法只在Fragment嵌套的情况下才会返回父级Fragment。如果没有父级 Fragment,则调用该方法可能会返回 null。因此,在使用此方法之前,需要确保有有效的父级Fragment存在。
关键代码ImagePagerFragment
给出代码ImagePagerFragment
public class ImagePagerFragment extends Fragment {
private ViewPager viewPager;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 首先使用布局解析器(inflater)将指定的布局文件 R.layout.fragment_pager 解析为一个 View 对象,并将其赋值给 viewPager 变量
viewPager = (ViewPager) inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_pager, container, false);
// 设置 ViewPager 的适配器,其中 ImagePagerAdapter 是自定义的适配器类。
viewPager.setAdapter(new ImagePagerAdapter(this));
// Set the current position and add a listener that will update the selection coordinator when
// paging the images.
// 设置当前显示的页面位置,该位置由 MainActivity 类的 currentPosition 变量决定。
viewPager.setCurrentItem(MainActivity.currentPosition);
// 监听页面选中事件。当页面切换时,会更新 MainActivity 类的 currentPosition 变量的值。
viewPager.addOnPageChangeListener(new ViewPager.SimpleOnPageChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onPageSelected(int position) {
MainActivity.currentPosition = position;
}
});
// 进行共享元素转场的准备工作。
prepareSharedElementTransition();
// Avoid a postponeEnterTransition on orientation change, and postpone only of first creation.
// 在首次创建 Fragment 时,调用 postponeEnterTransition() 方法来延迟共享元素的过渡动画。
// 注意,这个方法只在首次创建 Fragment 时被调用。
if (savedInstanceState == null) {
postponeEnterTransition();
}
return viewPager;
}
/**
* Prepares the shared element transition from and back to the grid fragment.
*/
private void prepareSharedElementTransition() {
// 从上下文中获取 TransitionInflater 对象,并使用它来解析指定的过渡资源文件 image_shared_element_transition,返回对应的过渡动画对象 transition
Transition transition = TransitionInflater.from(getContext()).inflateTransition(R.transition.image_shared_element_transition);
//将 transition 设置为当前 Fragment 的进入共享元素过渡动画。
// TODO:这意味着当当前 Fragment 进入屏幕时,将使用该过渡动画。
setSharedElementEnterTransition(transition);
// A similar mapping is set at the GridFragment with a setExitSharedElementCallback.
setEnterSharedElementCallback(new SharedElementCallback() {
// TODO:在 onMapSharedElements() 方法中,你可以映射共享元素名称和对应的视图元素
/**
* names 参数是待映射的共享元素名称列表,sharedElements 参数是待映射的共享元素名称与对应视图元素的映射表。
* @param names The names of all shared elements transferred from the calling Activity
* or Fragment in the order they were provided.
* @param sharedElements The mapping of shared element names to Views. The best guess
* will be filled into sharedElements based on the transitionNames.
*/
@Override
public void onMapSharedElements(List<String> names, Map<String, View> sharedElements) {
// Locate the image view at the primary fragment (the ImageFragment that is currently
// visible). To locate the fragment, call instantiateItem with the selection position.
// At this stage, the method will simply return the fragment at the position and will
// not create a new one.
// 获取当前可见的 Fragment 对象。
// TODO:这里使用 instantiateItem() 方法,可以获取到已存在的 Fragment 而不是创建一个新的实例。
Fragment currentFragment = (Fragment) viewPager.getAdapter().instantiateItem(viewPager, MainActivity.currentPosition);
View view = currentFragment.getView();
if (view == null) {
return;
}
// TODO:通过 currentFragment.getView() 方法获取当前 Fragment 的视图对象 view。
// Map the first shared element name to the child ImageView.
sharedElements.put(names.get(0), view.findViewById(R.id.image));
}
});
}
}
这里讲一下Android开发中的LayoutInflater,用于将布局文件转换为视图层次结构View Hierarchy,使用 LayoutInflater 可以在代码中动态地创建视图对象,并将其添加到现有的视图层次结构中,或者作为 Fragment 的根视图返回。
常用的使用场景有:
- 在 Activity 或 Fragment 中创建布局文件对应的视图层次结构。
- 在自定义 View 中加载子视图。
- 在自定义适配器(如
ArrayAdapter或BaseAdapter)中为每个列表项创建视图。
关键布局容器GridAdapter
public class GridAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<ImageViewHolder> {
private final RequestManager requestManager;
private final ViewHolderListener viewHolderListener;
/**
* Constructs a new grid adapter for the given {@link Fragment}.
* 在适配器的构造函数中,传入了一个 Fragment 对象作为参数。
* 然后,在构造函数中使用 Glide.with(fragment) 创建一个 RequestManager 对象,并将其赋值给 requestManager 变量
*/
public GridAdapter(Fragment fragment) {
this.requestManager = Glide.with(fragment);
this.viewHolderListener = new ViewHolderListenerImpl(fragment);
}
/**
* 在 onCreateViewHolder() 方法中,
* 首先通过 LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()) 获取一个布局解析器(LayoutInflater)对象,
* 并调用其 inflate() 方法将 image_card 布局文件解析为一个视图对象。
*
* @param parent The ViewGroup into which the new View will be added after it is bound to
* an adapter position.
* @param viewType The view type of the new View.
* @return
*/
@NonNull
@Override
public ImageViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()).inflate(R.layout.image_card, parent, false);
return new ImageViewHolder(view, requestManager, viewHolderListener);
}
/**
* onBindViewHolder() 方法是 RecyclerView 的适配器(Adapter)中的一个回调方法,用于绑定数据到 ViewHolder 并更新视图
*
* @param holder The ViewHolder which should be updated to represent the contents of the
* item at the given position in the data set.
* @param position The position of the item within the adapter's data set.
*/
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(ImageViewHolder holder, int position) {
/*
onBind() 是一个自定义的方法,属于 ImageViewHolder 类(或其父类)的方法。这个方法的实现将根据给定的 position 参数获取对应位置的数据,
并将数据绑定到 ViewHolder 的视图中。这样,在 RecyclerView 中显示的每个列表项都会调用一次 onBindViewHolder() 方法来更新数据和视图。
*/
holder.onBind();
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return IMAGE_DRAWABLES.length;
}
/**
* A listener that is attached to all ViewHolders to handle image loading events and clicks.
*/
private interface ViewHolderListener {
void onLoadCompleted(ImageView view, int adapterPosition);
void onItemClicked(View view, int adapterPosition);
}
/**
* Default {@link ViewHolderListener} implementation.
* ViewHolderListenerImpl 是一个实现了 ViewHolderListener 接口的私有静态内部类。
*/
private static class ViewHolderListenerImpl implements ViewHolderListener {
// 一个 Fragment 对象,用于处理视图回调事件。
private Fragment fragment;
// enterTransitionStarted:一个 AtomicBoolean 对象,用于标记是否已经开始过过渡动画。
private AtomicBoolean enterTransitionStarted;
ViewHolderListenerImpl(Fragment fragment) {
this.fragment = fragment;
this.enterTransitionStarted = new AtomicBoolean();
}
/**
* onLoadCompleted() 方法实现了 ViewHolderListener 接口的方法,它在图片加载完成时进行回调。
* 在这个方法中,首先判断当前的图片位置是否与 MainActivity.currentPosition 相同,若不相同则直接返回。
* 然后使用 enterTransitionStarted.getAndSet(true) 检查并设置过渡动画状态,只有在过渡动画未开始时才会执行后续操作。
* 最后,通过调用 fragment.startPostponedEnterTransition() 方法通知 Fragment 开始延迟的进入过渡动画。
*
* @param view
* @param position
*/
@Override
public void onLoadCompleted(ImageView view, int position) {
// Call startPostponedEnterTransition only when the 'selected' image loading is completed.
if (MainActivity.currentPosition != position) {
return;
}
if (enterTransitionStarted.getAndSet(true)) {
return;
}
fragment.startPostponedEnterTransition();
}
/**
* onItemClicked() 方法实现了 ViewHolderListener 接口的方法,它处理视图的点击事件。
* 在这个方法中,首先更新 MainActivity.currentPosition 的值为传入的位置参数。
* 然后,将点击的卡片视图排除在退出过渡动画之外,以防止其与其他视图同时淡出。接下来,获取到点击视图中的 ImageView 对象作为共享元素,使用 fragment.getFragmentManager() 开启事务,并通过 addSharedElement() 方法设置共享元素的过渡动画。
* 最后,用新的 ImagePagerFragment 替换当前的 Fragment,并将事务添加到返回栈中。
* <p>
* Handles a view click by setting the current position to the given {@code position} and
* starting a {@link ImagePagerFragment} which displays the image at the position.
*
* @param view the clicked {@link ImageView} (the shared element view will be re-mapped at the
* GridFragment's SharedElementCallback)
* @param position the selected view position
*/
@Override
public void onItemClicked(View view, int position) {
// 更新 MainActivity.currentPosition 的值为传入的位置参数,表示当前选中的位置。
// Update the position.
MainActivity.currentPosition = position;
// Exclude the clicked card from the exit transition (e.g. the card will disappear immediately
// instead of fading out with the rest to prevent an overlapping animation of fade and move).
// 将点击的卡片视图排除在退出过渡动画之外,以防止其与其他视图同时淡出。
// 这是通过将点击的视图 view 作为目标视图,并设置 excludeTarget(view, true) 来实现的。
((TransitionSet) fragment.getExitTransition()).excludeTarget(view, true);
ImageView transitioningView = view.findViewById(R.id.card_image);
// 调用 setReorderingAllowed(true) 方法来优化共享元素过渡动画的效果。
// 使用 addSharedElement() 方法设置共享元素过渡动画,传入 transitioningView 和其过渡名称作为参数。
// 使用 replace() 方法将当前容器中的 Fragment 替换为新的 ImagePagerFragment。
// 使用 addToBackStack(null) 方法将事务添加到返回栈中,以便可以通过返回按钮返回到前一个 Fragment。
fragment.getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().setReorderingAllowed(true) // Optimize for shared element transition
.addSharedElement(transitioningView, transitioningView.getTransitionName()).replace(R.id.fragment_container, new ImagePagerFragment(), ImagePagerFragment.class.getSimpleName()).addToBackStack(null).commit();
}
}
/**
* ViewHolder for the grid's images.
* 给定的代码是一个静态内部类 ImageViewHolder,它继承自 RecyclerView.ViewHolder 并实现了 View.OnClickListener 接口。
*/
static class ImageViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder implements View.OnClickListener {
// image:一个 ImageView 对象,用于显示图片
private final ImageView image;
// requestManager:一个 RequestManager 对象,用于加载和处理图片
private final RequestManager requestManager;
// viewHolderListener:一个 ViewHolderListener 对象,用于处理视图的回调事件。
private final ViewHolderListener viewHolderListener;
// 在构造函数中,通过传入的参数初始化成员变量,并为 itemView 中的 card_view 设置点击监听器为当前对象(this)。
ImageViewHolder(View itemView, RequestManager requestManager, ViewHolderListener viewHolderListener) {
super(itemView);
this.image = itemView.findViewById(R.id.card_image);
this.requestManager = requestManager;
this.viewHolderListener = viewHolderListener;
itemView.findViewById(R.id.card_view).setOnClickListener(this);
}
/**
* Binds this view holder to the given adapter position.
* <p>
* The binding will load the image into the image view, as well as set its transition name for
* later.
* <p>
* TODO:onBind() 方法用于将数据绑定到 ViewHolder,它首先获取当前列表项的位置(adapterPosition),
* 然后使用 setImage() 方法设置对应位置的图片。
* 同时,设置图片的过渡名称(transition name)为 IMAGE_DRAWABLES[adapterPosition]。
*/
void onBind() {
int adapterPosition = getAdapterPosition();
setImage(adapterPosition);
// Set the string value of the image resource as the unique transition name for the view.
image.setTransitionName(String.valueOf(IMAGE_DRAWABLES[adapterPosition]));
}
/**
* setImage() 方法用于加载图片并设置到 ImageView。
* 它使用 Glide 图片加载库的 requestManager 对象加载指定位置的图片资源,并设置一个请求监听器。
* 当加载成功或失败时,通过 viewHolderListener 调用 onLoadCompleted() 方法。
*
* @param adapterPosition
*/
void setImage(final int adapterPosition) {
// Load the image with Glide to prevent OOM error when the image drawables are very large.
requestManager.load(IMAGE_DRAWABLES[adapterPosition]).listener(new RequestListener<Drawable>() {
/**
* 在该方法的实现中,通过调用 viewHolderListener 的 onLoadCompleted() 方法,
* 将加载失败的图片视图 image 和对应的适配器位置 adapterPosition 传递给监听器。然后返回 false,表示加载失败事件未被完全处理。
*
* @param e The maybe {@code null} exception containing information about why the request failed.
* @param model The model we were trying to load when the exception occurred.
* @param target The {@link Target} we were trying to load the image into.
* @param isFirstResource {@code true} if this exception is for the first resource to load.
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean onLoadFailed(@Nullable GlideException e, Object model, Target<Drawable> target, boolean isFirstResource) {
viewHolderListener.onLoadCompleted(image, adapterPosition);
return false;
}
/**
* 在该方法的实现中,通过调用 viewHolderListener 的 onLoadCompleted() 方法,将加载成功的图片视图 image 和对应的适配器位置 adapterPosition 传递给监听器。
* 然后返回 false,表示加载成功事件未被完全处理。
* <p>
* 通过实现这个方法,可以在图片加载成功后进行相应的处理操作。例如,可以通知用户加载完成、执行动画效果等。
*
* @param resource The resource that was loaded for the target.
* @param model The specific model that was used to load the image.
* @param target The target the model was loaded into.
* @param dataSource The {@link DataSource} the resource was loaded from.
* @param isFirstResource {@code true} if this is the first resource to in this load to be loaded
* into the target. For example when loading a thumbnail and a full-sized image, this will be
* {@code true} for the first image to load and {@code false} for the second.
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean onResourceReady(Drawable resource, Object model, Target<Drawable> target, DataSource dataSource, boolean isFirstResource) {
viewHolderListener.onLoadCompleted(image, adapterPosition);
return false;
}
}).into(image);
}
/**
* onClick() 方法实现了点击事件的处理,通过 viewHolderListener 调用 onItemClicked() 方法,通知监听器用户点击了列表中的某个项。
*
* @param view The view that was clicked.
*/
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// Let the listener start the ImagePagerFragment.
viewHolderListener.onItemClicked(view, getAdapterPosition());
}
}
}
首先讲一下GridAdapter 是一个公共类,它扩展自 RecyclerView.Adapter,并指定了泛型参数为 ImageViewHolder。
其中GridAdapter 是一个用于在 RecyclerView 中显示网格布局的适配器。它负责管理和提供数据项,并协调视图的创建、绑定和回收等操作。
需要实现的几个关键方法如下:
onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType):用于创建ViewHolder对象,在这个方法中通常会创建并返回一个ImageViewHolder实例。onBindViewHolder(ImageViewHolder holder, int position):用于将数据绑定到ViewHolder并更新视图,根据给定的位置参数,可以获取对应位置的数据,并将其绑定到相应的ViewHolder上。getItemCount():返回数据项的数量,即列表中要显示的项数。
再来说一下代码中的fragment.startPostponedEnterTransition();,这个方法用来启动延迟的进入过度动画。
在 Android 中,当使用共享元素过渡动画时,通常需要在 Activity 或 Fragment 的进入转场中共享元素准备完成后才能开始过渡动画。为了实现这个效果,引入了 PostponeEnterTransition 的概念。
具体的流程如下:
- 在启动 Activity 或切换 Fragment 时,首先创建或获取目标 Fragment 实例。
- 调用
fragment.postponeEnterTransition() 方法来暂停进入过渡动画。 - 在共享元素准备就绪时,例如在加载图片完成后,调用
fragment.startPostponedEnterTransition() 方法来开始延迟的进入过渡动画。 - 进入过渡动画会根据设置的共享元素进行相应的动画效果,实现平滑的过渡效果。
通过使用 startPostponedEnterTransition() 方法,可以确保在所需的时机启动进入过渡动画,从而提升用户体验,并确保共享元素过渡的顺利执行。
另一个需要注意的点就是AtomicBoolean的使用,在这行代码private AtomicBoolean enterTransitionStarted;,AtomicBoolean是Java中的一个类,它提供了对布尔值进行原子操作的功能。原子操作是线程安全的,确保在多线程环境下访问或修改变量时不会受到其他线程的干扰。
其中,关于AtomicBoolean关键字:
- 原子性:
AtomicBoolean提供了原子操作,确保对布尔值的读取和修改是原子的,即不会发生半写的情况。这可以保证在多线程环境下正确地处理共享布尔状态。 - 可见性:
AtomicBoolean使用了内存屏障(memory barriers)和volatile语义,确保在一个线程中修改了布尔值后,其他线程能够立即看到最新的值。这解决了多线程间的数据同步问题。 - 线程安全:由于
AtomicBoolean提供了原子操作和可见性保证,它适用于高并发的多线程环境。多个线程可以同时访问和修改AtomicBoolean实例,而无需额外的同步机制。 - 原子条件更新:
AtomicBoolean还提供了一些便捷的原子条件更新方法,如compareAndSet(),通过比较当前值与期望值,并在相等时原子地进行更新。这在某些场景下可以用来实现特定的业务逻辑。
具体的关键字应用代码:
@Override
public void onLoadCompleted(ImageView view, int position) {
// 当ImageView加载完成时,会调用onLoadCompleted 方法。
// 通过比较MainActivity.currentPosition 和position 变量的值来判断是否执行后续操作。如果它们不相等,则返回(即不执行后续代码)。
if (MainActivity.currentPosition != position) {
return;
}
// 使用enterTransitionStarted.getAndSet(true) 来检查并设置enterTransitionStarted 的值
if (enterTransitionStarted.getAndSet(true)) {
return;
}
// 如果以上条件都满足,调用fragment.startPostponedEnterTransition() 方法来开始延迟的进入过渡效果。
fragment.startPostponedEnterTransition();
}
目的是在特定条件下启动延迟的进入过渡效果,确保只有在满足条件且尚未启动过渡效果的情况下才执行启动过渡的操作。
关键代码ImagePagerAdapter
代码如下:
public class ImagePagerAdapter extends FragmentStatePagerAdapter {
/**
* 它接收一个父级 Fragment,并使用该父级 Fragment 的子级 Fragment 管理器(getChildFragmentManager())进行初始化。
*
* @param fragment
*/
public ImagePagerAdapter(Fragment fragment) {
// Note: Initialize with the child fragment manager.
super(fragment.getChildFragmentManager(), BEHAVIOR_RESUME_ONLY_CURRENT_FRAGMENT);
}
/**
* getCount() 方法返回图片数组 IMAGE_DRAWABLES 的长度,即要展示的图片数量。
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getCount() {
return IMAGE_DRAWABLES.length;
}
/**
* getItem() 方法根据传入的位置参数创建并返回一个 ImageFragment 实例。
* 每个 ImageFragment 对应一个图片资源,通过调用 ImageFragment.newInstance(IMAGE_DRAWABLES[position]) 来创建对应位置的 ImageFragment。
*
* @param position
* @return
*/
@NonNull
@Override
public Fragment getItem(int position) {
return ImageFragment.newInstance(IMAGE_DRAWABLES[position]);
}
}







![[QT编程系列-12]:QT快速学习 - 0 - 主要内容](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a02435c12eb1425d8e79f4222dc07929.png)
