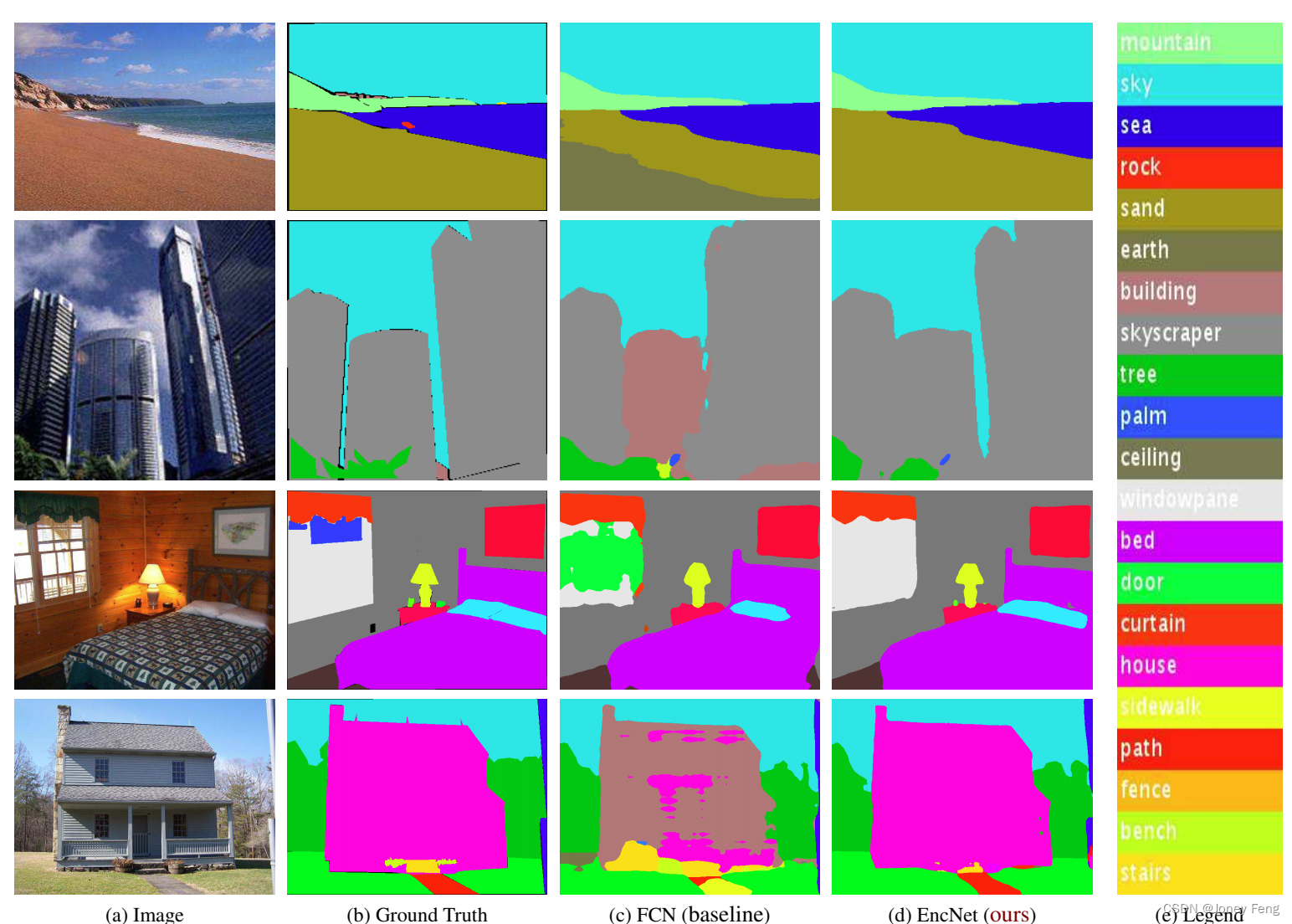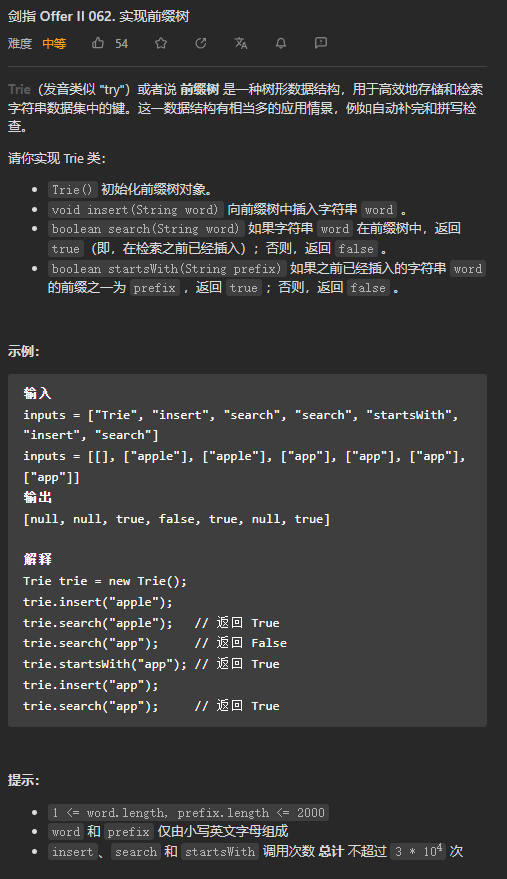
Trie,又称前缀树或字典树,是一棵有根树,其每个节点包含以下字段:
- 指向子节点的指针数组children,对于本题而言,数组长度为26,即小写英文字母的数量。此时children[0]对应着小写字母a,children[1]对应着小写字母b,…,children[25]对应小写字母z
- 布尔字段isEnd,表示该节点是否为字符串的结尾
插入字符串
从字典树的根开始,插入字符串。对于当前字符对应的子节点,有两种情况:
- 子节点存在。沿着指针移动到子节点,继续处理下一个字符
- 子节点不存在。创建一个新的子节点,记录在children数组的对应的位置上,然后沿着指针移动到子节点,继续搜索下一个字符。
重复以上步骤,直到处理字符串的最后一个字符,然后将当前节点标记为字符串的结尾
查找前缀
从字典树的根开始,查找前缀。对于当前字符对应的子节点,有两种情况:
- 子节点存在。沿着指针移动到子节点,继续搜索下一个字符
- 子节点不存在。说明字典树中不包含该前缀,返回空指针
重复以上步骤,直到返回空指针或搜索完前缀的最后一个字符
若搜索到了前缀的末尾,就说明字典树中存在该前缀。此外,若前缀末尾对应的节点的isEnd为真,则说明字典树中存在该字符串
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
class Trie {
private Trie[] children;
private boolean isEnd;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public Trie() {
children = new Trie[26];
isEnd = false;
}
/**
* Inserts a word into the trie.
*/
public void insert(String word) {
Trie node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
int index = c - 'a';
if (node.children[index] == null) {
node.children[index] = new Trie();
}
node = node.children[index];
}
node.isEnd = true;
}
/**
* Returns if the word is in the trie.
*/
public boolean search(String word) {
Trie node = searchPrefix(word);
return node != null && node.isEnd;
}
/**
* Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix.
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return searchPrefix(prefix) != null;
}
private Trie searchPrefix(String prefix) {
Trie node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
int index = c - 'a';
if (node.children[index] == null) {
return null;
}
node = node.children[index];
}
return node;
}
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
* boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix);
*/
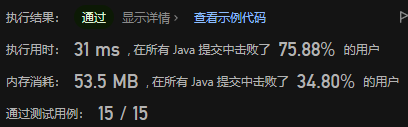
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:初始化为O(1),其余操作为O(|S|),其中|S|是每次插入或查询的字符串的长度
- 空间复杂度:O( ∣ T ∣ ⋅ ∑ |T|\cdot\sum ∣T∣⋅∑),其中|T|为所有插入字符串的长度之和, ∑ \sum ∑为字符集大小,本题 ∑ = 26 \sum=26 ∑=26。