- 二进制文件的Python编写
- 这么基础的东西,必然用内置的就好
二进制文件的Python读写
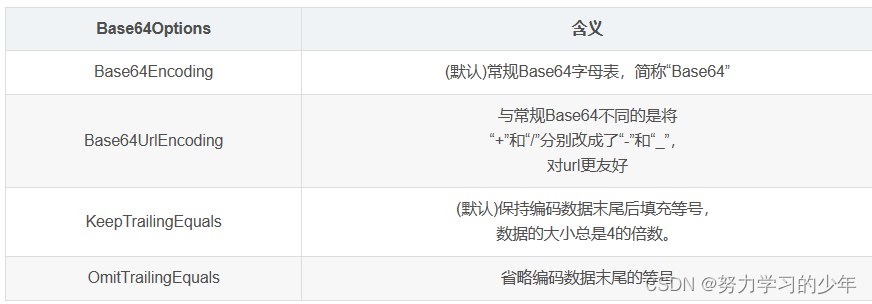
重要提示
- p.s. 1
>>> b'Hello World'.decode() == "Hello World"
True
>>>
example
import struct
with open('binary_file.bin', 'wb') as file:
data = b'\x48\x65\x6c\x6c\x6f\x20\x57\x6f\x72\x6c\x64' # 二进制数据
number = 42
packed_data = struct.pack('I', number)
file.write(data)
file.write(packed_data)
file.close()
with open('binary_file.bin', 'rb') as file:
data = file.read(len(data))
packed_data = file.read()
number = struct.unpack('I', packed_data)[0]
print(data.decode())
print(number)
file.close()
Hello World
42
>>>
文件打开函数
打开模式参数
- 'r':以只读模式打开文件。
- 文件指针将位于文件的开头。如果文件不存在,将引发 FileNotFoundError。
- 'w':以写入模式打开文件。
- 如果文件已存在,则其内容将被截断为空。
- 如果文件不存在,则创建新文件。
- 'x':以排他性创建模式打开文件。
- 如果文件已存在,则会引发 FileExistsError。
- 如果文件不存在,则创建新文件。
- 'a':以追加模式打开文件。
- 文件指针将位于文件的末尾。
- 如果文件不存在,则创建新文件。
- 'b':以二进制模式打开文件,例如 'rb' 或 'wb'。
- 't':以文本模式打开文件。
- 这是默认模式,适用于处理文本文件。可以与其他模式一起使用,例如 'rt' 或 'wt'
文件读取函数
read()
- 接受一个可选的参数,用于指定要读取的字节数
- 默认值为 -1,表示读取整个文件
- 上 example 已经可以清楚得说明了
- 在UTF-8编码中,一个字节可以表示一个ASCII字符
文件写入函数
write()
- 要写入文件的字节数据
- 在二进制模式下,数据以字节的形式写入文件,而不会进行任何字符编码或解码
string = "Hello, World!"
byte_string = b"Hello, World!"
print(type(string))
print(type(byte_string))
<class 'str'>
<class 'bytes'>
>>>
- 要将数字写入二进制文件,需要将其转换为字节数据
- 确保你选择的字节数 Bytes 能够容纳整数 number 的范围
- 如
example 02
number = 1200
Bytes = 4
byte_data = number.to_bytes(Bytes, 'big')
with open('binary_file.bin', 'wb') as file:
file.write(byte_data)
with open('binary_file.bin', 'rb') as file:
Number = file.read()
NUMBER = int.from_bytes(Number, 'big')
print(NUMBER)

- 最大值为 (2**(8*Bytes-1))-1
- Bytes = 4,4294967295
- Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\LX\Desktop\00.py", line 3, in <module>
byte_data = number.to_bytes(Bytes, 'big')
OverflowError: int too big to convert
seek()
- 在二进制文件中移动文件指针的位置
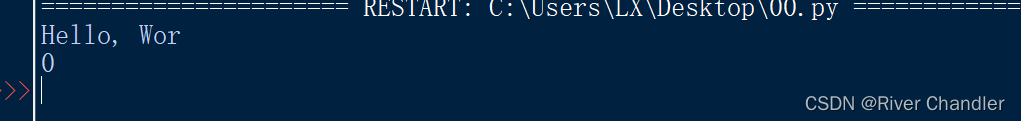
text_data = "Hello, World!"
number = 12345
with open('binary_file.bin', 'wb') as file:
file.write(text_data.encode())
file.seek(20)
byte_data = number.to_bytes(4, 'big')
file.write(byte_data)
with open('binary_file.bin', 'rb') as file:
text = file.read(10)
print(text.decode())
file.seek(20)
data = file.read()
print(int.from_bytes(data, 'big'))

tell()
- 函数可以获取当前文件指针的位置
- example
text_data = "Hello, World!"
number = 12345
with open('binary_file.bin', 'wb') as file:
file.write(text_data.encode())
position = file.tell()
byte_data = number.to_bytes(4, 'big')
file.write(byte_data)
with open('binary_file.bin', 'rb') as file:
text = file.read(10)
print(text.decode())
file.seek(20)
data = file.read()
print(int.from_bytes(data, 'big'))
文件格式
- 二进制文件:二进制文件是以字节为单位存储数据的文件。它们通常用于存储非文本数据,如图像、音频、视频等。
- 文本文件:文本文件是以字符形式存储数据的文件。它们通常用于存储文本数据,如普通文本文件、配置文件等。
- CSV文件:CSV(逗号分隔值)文件是一种常见的用途是存储表格数据的格式。它们使用逗号或其他分隔符来分隔不同的字段,并可以使用纯文本编辑器进行编辑。
- JSON文件:JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,常用于存储和传输结构化数据。