目录
- 引入
- 2023年 真题
- 1001 A+B Format (20 分) 小数字相加再格式化输出
- 1002 A+B for Polynomials (25 分) 多项式相加
- 1003 Emergency 救援最短路径和最大救援部队
引入
2023睿抗 RoboCom机器人开发者大赛CAIP编程设计赛道编程技能赛
考察知识点
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lXp5axGqtSeA4eXrcU7vEA
往年真题:https://pintia.cn/market/tag/1447465711671738368
PAT甲级题解:https://blog.csdn.net/a617976080/article/details/89676670
2023年 真题
第一题 AC了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int g[5];
int gg[5];
int n;
int main(){
cin>>n;
int a,b;
while(n--){
cin>>a>>b;
if(a==0){
g[b]++;
}else gg[b]++;
}
int f = 0;
if((g[1]>gg[1])||(g[1]==gg[1]&&g[2]>gg[2])||(g[1]==gg[1]&&g[2]==gg[2]&&g[3]>gg[3])) f=1;
cout<<g[1]<<" "<<g[2]<<" "<<g[3]<<'\n';
cout<<gg[1]<<" "<<gg[2]<<" "<<gg[3]<<'\n';
if(f){
cout<<"The first win!";
}else{
cout<<"The second win!";
}
return 0;
}
第二题 就拿了8/15分
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
struct cu{
string s;
string den;
}cu[1010],en[1010];
int main(){
// string s1 = "Milk";
// string s2 = "Milk";
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 0; i <n; i++){
cin>>cu[i].s>>cu[i].den ;
}
int cnt = n;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n;i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < n;j++){
cu[cnt].s = cu[i].s + cu[j].s;
cu[cnt].den = cu[i].den + cu[j].den;
// cout<<i<<" "<<j<<" "<<cu[i].s<<" "<<cu[i].den <<" "<<cu[j].s<<" "<<cu[j].den <<endl;
// cout<<cu[cnt].s <<" "<<cu[cnt].den <<endl;
cnt++;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int f = 0;
cin>>en[i].s;
for(int j = 0; j < cnt; j++){
if(en[i].s==cu[j].s){
en[i].den = cu[j].den ; f=1;
}
}
if(f) f = 0;
else en[i].den = "D";
}
for(int i =0 ; i < m; i++){
cout<<en[i].den<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
三题略微变态
4、深搜 没搜出来 不想看了 0分
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
string a;
int sua;
string b;
int sub;
bool stu;
}tu[1010];
int n,cnt=0;
int ans[1010];
void dfs(int x){
//这一层的推论能前一层连上,但不和第一个互异
cnt++;
ans[cnt] = x;
if(tu[1].a == tu[x].b &&tu[1].sua != tu[x].sub){
for(int i = 1; i < cnt+1; i++){
cout<<tu[ans[i]].a<<" "<<tu[ans[i]].sua<<" "<<tu[ans[i]].b<<" "<<tu[ans[i]].sub<<" "<<"=";
}
cout<<tu[1].a<<" "<<tu[1].sua<<" "<<tu[cnt].b<<" "<<tu[cnt].sub<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i < n+1; i++){
if(tu[x+1].a == tu[x].b&&tu[x+1].sua==tu[x].sub&&tu[i].stu==0){
cnt++;
ans[cnt] = x; tu[i].stu=1;
dfs(x+1);
cnt--;
ans[cnt] = 0; tu[i].stu=0;
}
}
return;
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i = 1; i < n+1; i++) cin>>tu[i].a >>tu[i].sua >>tu[i].b >>tu[i].sub;
tu[1].stu =1;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
本科组
- 线性表:静态链表、堆栈、队列
- 树:遍历、搜索树、完全二叉树等
- 图:基本性质、最短距离、最大流/最小割,强连通分支、最近公共祖先、最小生成树、欧拉序列等
- 排序(贪心)+查找(二分、哈希)
- 经典算法(搜索剪枝、动态规划等)
- 具备较强的问题抽象和建模能力,能实现对复杂实际问题的模拟求解
1001 A+B Format (20 分) 小数字相加再格式化输出
Sample Input:
-1000000 9
Sample Output:
-999,991
题目大意:
计算a+b,−106 ≤a,b≤106,结果按照西方的那种写数字的方式输出,从三个数一个逗号那种。
考点:
格式控制输出
思路1:
首先考虑到的肯定是把a+b的结果通过取模和取余操作存入结果数组ans中,再格式化输出。这里面就涉及到特殊值的讨论问题,即“,”放置的位置和“-”。还好时OI可以通过多组数据的测试,不断完善分类判断的逻辑和范围准确性,但是其实浪费时间。
首先结果大于零,等于零和小于零,其次要判断数组长度,若n为1,输出时没有“,”,也不用0展位满3。结果数组的最有一位,也是没有逗号。
优化:其实大于零,小于零,等于零可以一个判断就行了,只要判断是否小于零,小于零就多输出一个“-”。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long a,b,c,res;
long long ans[10]={0};
int main(){
cin>>a>>b;
c = a + b;
res = c;
int n;
// cout<<"c: "<<c<<'\n';
if(c>0){
//存结果
for(n = 0; res != 0; n++){
ans[n]= res%1000;
res = res/1000;
}
//输出
for(int i = n-1;i >= 0;i--){
if(i==n-1&&n==1) printf("%d",ans[n-1]);
else if(i==n-1&&n!=1) printf("%d,",ans[n-1]);
else if(i==0&&n!=1)printf("%03d",ans[i]);
else printf("%03d,",ans[i]);
}
}else if (c<0){
res = -c;
for( n = 0; res != 0; n++){
ans[n]= res%1000;
res = res/1000;
}
cout<<"-";
for(int i = n-1;i >= 0;i--){
if(i==n-1&&n==1) printf("%d",ans[n-1]);
else if(i==n-1&&n!=1) printf("%d,",ans[n-1]);
else if(i==0&&n!=1)printf("%03d",ans[i]);
else printf("%03d,",ans[i]);
}
}else cout<<0;
return 0;
}
思路2:
数据范围不大,可以先计算一下边界值[-2000000,2000000],然后得到一个很通用的输出方式:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
long long sum = n+m;
if(sum<0){
cout<<"-"; sum *= -1;
}
if(sum<1000){
cout<<sum;
}else if(sum>=1000&&sum<1000000) {
printf("%d,%03d",sum/1000,sum%1000);
}else if(sum>=1000000){
printf("%d,%03d,%03d",sum/1000000,(sum%1000000)/1000,sum%1000);
}
return 0;
}
思路3:
字符串的长度来判断,什么时候需要输出“,”。把值当正数看待(也可以不,前面加一位,不影响),从前往后输出,当数到的数和整体长度对3取模的值相等,就该输出“,”了,同时要注意排除末尾不用输出“,”。
优势:代码量少,熟练了以后会加快编码速度。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long a,b,c;
int main(){
cin>>a>>b;
c = a + b;
if(c<0){ c = -c; cout<<"-"; }
string s = to_string(c);
int len = s.size();
//cout<<"s: "<<len<<endl;
int t = len %3;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
cout<<s[i];
if((i+1)%3==t&&i!=len-1) cout<<",";
}
return 0;
}
注:一题多解,思路门儿清。
用三种存储方式都(int,数组,string)
%md:m为指定的输出字段的宽度。如果数据的位数小于m,则左端补以空格,若大于m,则按实际位数输出。
%0md 用0来补空格
1002 A+B for Polynomials (25 分) 多项式相加
Sample Input:
2 1 2.4 0 3.2
2 2 1.5 1 0.5
Sample Output:
3 2 1.5 1 2.9 0 3.2
题目大意:
两个多项式相加,每一行第一个数表示多项式的非零项个数,后面跟着非零项,第一个是阶数,第二个是系数。最后以相同的格式输出相加后的多项式,保留小数点后1位。
思路:
首先吐槽!这题的数据范围给的乱七八糟,导致我最开始数组开小了,段错误。
小细节,也蛮费时间的:
1、输入的时候可能会被吞。
2、数据类型问题会导致答案不正确
3、数组范围
4、结果保留一位小数。浮点数的保留一位小数!!!
思路就是数组模拟多项式的加法,记录求得的多项式的项数和最高次幂就行。读入的时候,将系数存到对应幂上,便于两多项式相加。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
double a[1005],b[1005]; //系数
int ea[1005],eb[1005];//幂
double ans[1005];
int main(){
int na,nb,k;
cin>>na;
for(int i = 0; i <na ;i++){
cin>>ea[i];
int t = ea[i];
cin>>a[t]; //按照对应幂去存系数
}
scanf("%d",&nb);
for(int i = 0; i < nb; i++){
cin>>eb[i];
int t = eb[i];
cin>>b[t]; //按照对应幂去存系数
}
k = ea[0] > eb[0] ? ea[0]:eb[0];//最高次幂
int n = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= k; i++){
ans[i] = a[i] + b[i];
//cout<<"i: "<<i<<" "<<a[i]<<" "<<b[i]<<" "<<ans[i]<<endl;
if(ans[i]!=0) n++;
}
cout<<n;
for(int i = k; i >= 0; i--){
if(ans[i]) printf(" %d %.1f",i,ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}
1003 Emergency 救援最短路径和最大救援部队
首先来一张最短路算法,知识结构图。
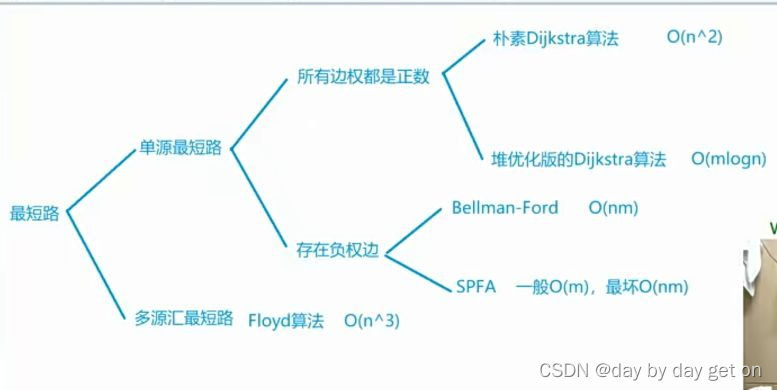
稠密图用邻接矩阵存图,稀疏图一般用邻接表存图,节约空间。稠密图用朴素迪杰斯特拉,稀疏图图用堆优化迪杰斯特拉。多源,指要求多个起点到终点的最短路。
我们这个题,显然是单源。求一个点到另一个点的最短路,可以是用求一个点到其他所有点的最短路来找出 s 到 t 的最短路。
![线程栈溢出异常,程序崩溃在汇编代码test dword ptr [eax],eax上的问题排查](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/936e39ca9b404af99a7166a621d44fe7.png)