##promise解析
*啥是异步?
//异步执行
let count = 1
let timer = setTimeout(function () {
count++
console.log('in', count);
}, 1000);
console.log('out');
// out=>1000=>in
//循环执行
let count = 1
let timer = setInterval(function () {
count++
console.log('in', count);
}, 1000);
console.log('out');
setTimeout(function () {
clearInterval(timer)
console.log('clear');//第5秒后清空循环器
}, 5000);
//看不见的队列,存放着需要默默执行的命令###1.进程&线程
####a.概念 & 区别
####b.面试题
*映射到前端-浏览器
chrome新开一个窗口,是进程还是线程(可以理解为互相协作,相互之间独立)?=>进程(可以理解为完整的独立体系)
*发散
方向一:窗口(进程间)通信?=>storage | cookie=>多种存储的区别=>应用场景=>结合简历项目
方向二:浏览器原理(中高级岗位面试居多)
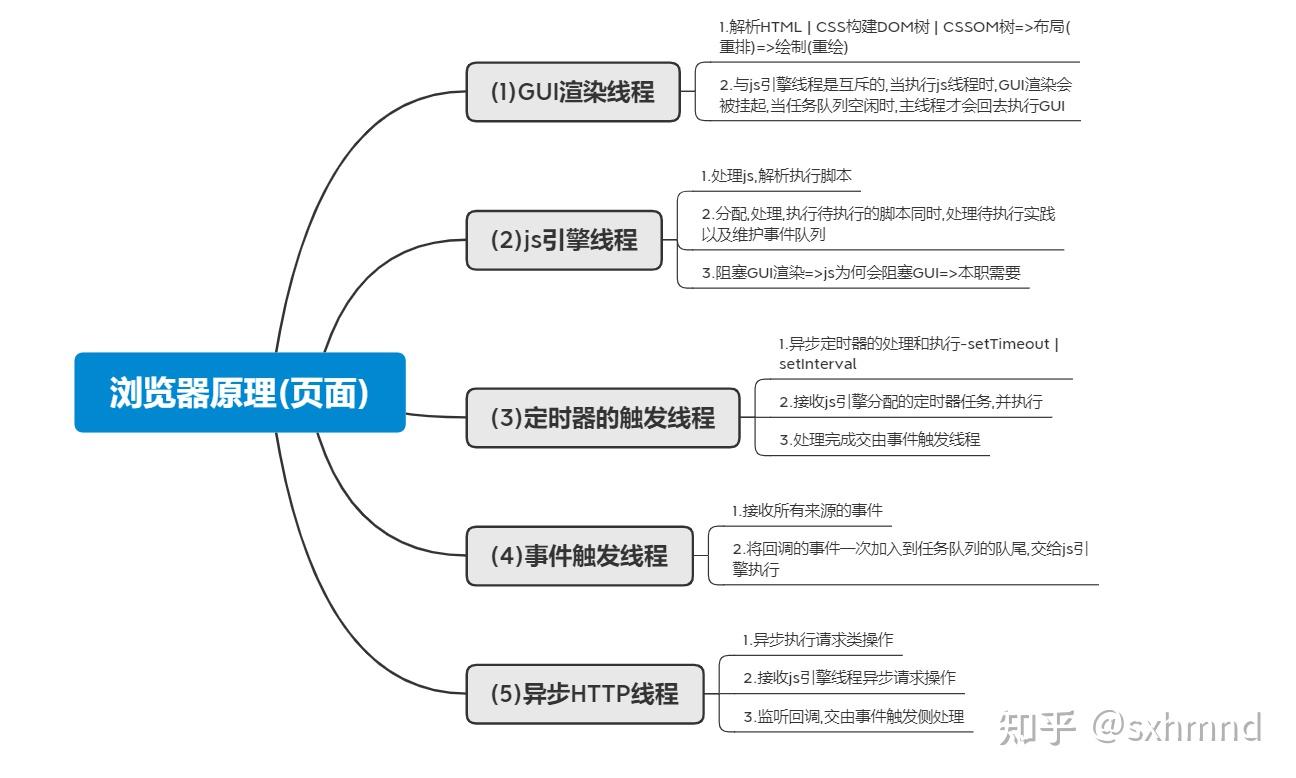
###2.EVENT-LOOP
####a.执行栈
*js单线程语言,单步执行
function func2() {
throw new Error('please check your call stack');
}
function func1() {
func2()
}
function func() {
func1()
}
func()####b.面试题

// 执行顺序
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('count');//5.宏任务2
}, 0);
new Promise(resolve => {
console.log('new Promise');//1.属于同步进入主线程 宏任务1
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('Promise then');//3.微任务1
}).then(() => {
console.log('Promise then then');//4.微任务2
})
console.log('hi');//2.同步+宏任务1
//任务拆分 : macro | micro
//同步 | 异步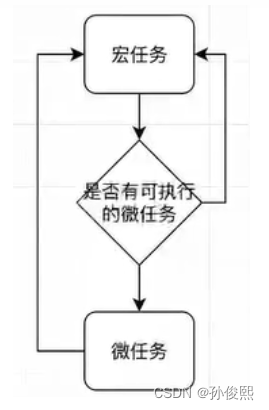
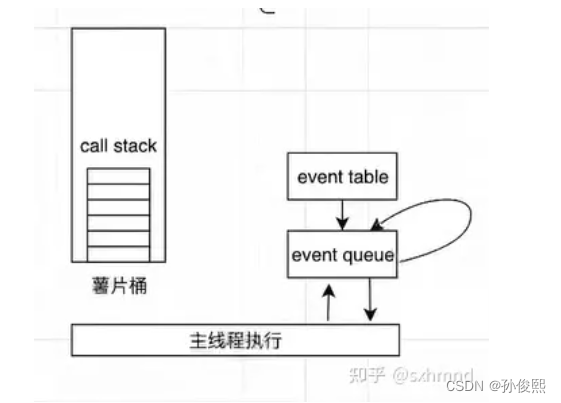
event-table:可以.理解为异步待执行
event queue:异步队列
同步的走同步的执行栈,异步的走异步的事件队列.
###promise化=>链式化
####a.理论-回调地狱
request.onreadystatechange = () => {
//回调后处理
}
//加时延
setTimeout(() => {
request.onreadystatechange = () => {
//回调后处理
setTimeout(() => {
//处理
request.onreadystatechange = () => {
//......
}
});
}
});
//promise化
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('ok')
});
}).then(res => {
request()
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err);
})多个异步顺序执行=>复合链式调用
function wait500(input) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(input + 500)
}, 500);
})
}
function wait1000(input) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(input + 1000)
}, 1000);
})
}
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(1)
})
p.then(wait500)
.then(wait1000)
.then(wait500)
.then(wait1000)
.then(res => {
console.log('end', res);
})
//全部执行完成回调
Promise.all([wait500, wait1000]).then(res => {
console.log('all end', res);
})
//有执行完成的立刻操作
Promise.race()([wait500, wait1000]).then(res => {
console.log('all end', res);
})####b.面试-promise
*1.promise状态 - pedding | fulfilled | rejected
executor(执行器):new Promise的时候立即执行,接收两个参数,resolve | rejected
*2.promise默认状态?状态是如何流转的?-默认是pedding,状态流转:pedding=>fulfilled | pedding=>rejected
内部维护成功value:underfined | thenable | promise
内部维护失败原因resaon
*3.promise返回值?-then方法:接收onFulfilled和onRejected
如果then时,promise已经成功,执行onFulfilled,参数value
如果then时,promise已经失败,执行onRejected,参数resaon
如果then中有异常,执行onRejected
*追问:手写?
const PENDING = 'PENDING'
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED'
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED'
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
//1.默认状态-PENDING
this.status = 'PENDING'
//2.内部维护的变量值
this.value = undefined
this.reason = undefined
//成功的回调
let resolve = value => {
//状态流转
this.status = FULFILLED
this.value = value
}
//失败的回调
let reason = reason => {
//状态流转
this.status = REJECTED
this.reason = reason
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
onFulfilled(this.reason)
}
}
}
//异步怎么办?
const PENDING = 'PENDING'
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED'
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED'
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
//1.默认状态-PENDING
this.status = 'PENDING'
//2.内部维护的变量值
this.value = undefined
this.reason = undefined
//存放回调
this.onResolvedCallbacks = []
this.onRejectedCallbacks = []
//成功的回调
let resolve = value => {
//状态流转
this.status = FULFILLED
this.value = value
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn())
}
//失败的回调
let reason = reason => {
//状态流转
this.status = REJECTED
this.reason = reason
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn())
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
onFulfilled(this.reason)
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
//存放队列
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
onFulfilled(this.value)
})
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
onFulfilled(this.reason)
})
}
}
}
![[JVM] 1. 初步认识JVM](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fe3f6df33e5344cabc15b0ddb8d4a921.png)