给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:n = 4, k = 2
输出:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
示例 2:
输入:n = 1, k = 1
输出:[[1]]
提示:
1 <= n <= 20
1 <= k <= n
解题思路:
1.每个元素有选与不选两种情况,
2.回溯能将选与不选这两种情况都包含
3.递归刚好能满足这个需求
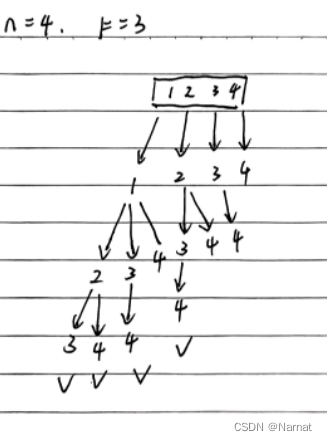
dfs + 回溯代码:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> end = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> mb = new ArrayList<>();
addmbzh(1, k, end, mb, n);
return end;
}
public static void addmbzh(int x, int k, List<List<Integer>> end, List<Integer> none, int n) {
if(x > n + 1) return;
if(none.size() == k) {
end.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(none));
return;
}
none.add(x);
addmbzh(x + 1, k, end, none, n);
none.remove(none.size() - 1);
addmbzh(x + 1, k, end, none, n);
}
}

可以出上述递归树,有很多没有用的分支,可以加入特定判断条件将无用分支剪切掉
if(none.size() + n - x + 1 < k) return;//即剩下元素不足,直接退出
dfs + 回溯 + 剪枝:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> end = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> mb = new ArrayList<>();
addmbzh(1, k, end, mb, n);
return end;
}
public static void addmbzh(int x, int k, List<List<Integer>> end, List<Integer> none, int n) {
if(none.size() + n - x + 1 < k) return;//退出条件
if(none.size() == k) {
end.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(none));
return;
}
none.add(x);//选
addmbzh(x + 1, k, end, none, n);
none.remove(none.size() - 1);//回溯(不选)
addmbzh(x + 1, k, end, none, n);
}
}

不难看出爆搜会超时的主要原因是一些无用枝节耗费了大量时间
本代码也可以用全局变量来写,反而更简洁
代码:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> nums = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> num = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
dfs(1, n, k);
return nums;
}
public void dfs(int i, int n, int k) {
if(num.size() + n - i + 1 < k) return;//剪枝
if(num.size() == k) {
nums.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(num));
return;
}//重要的事情最先做
num.add(i);//装
dfs(i + 1, n, k);
num.remove(num.size() - 1);//回溯(不装)
dfs(i + 1, n, k);
}
}