目录
Tower
Frozen Scoreboard
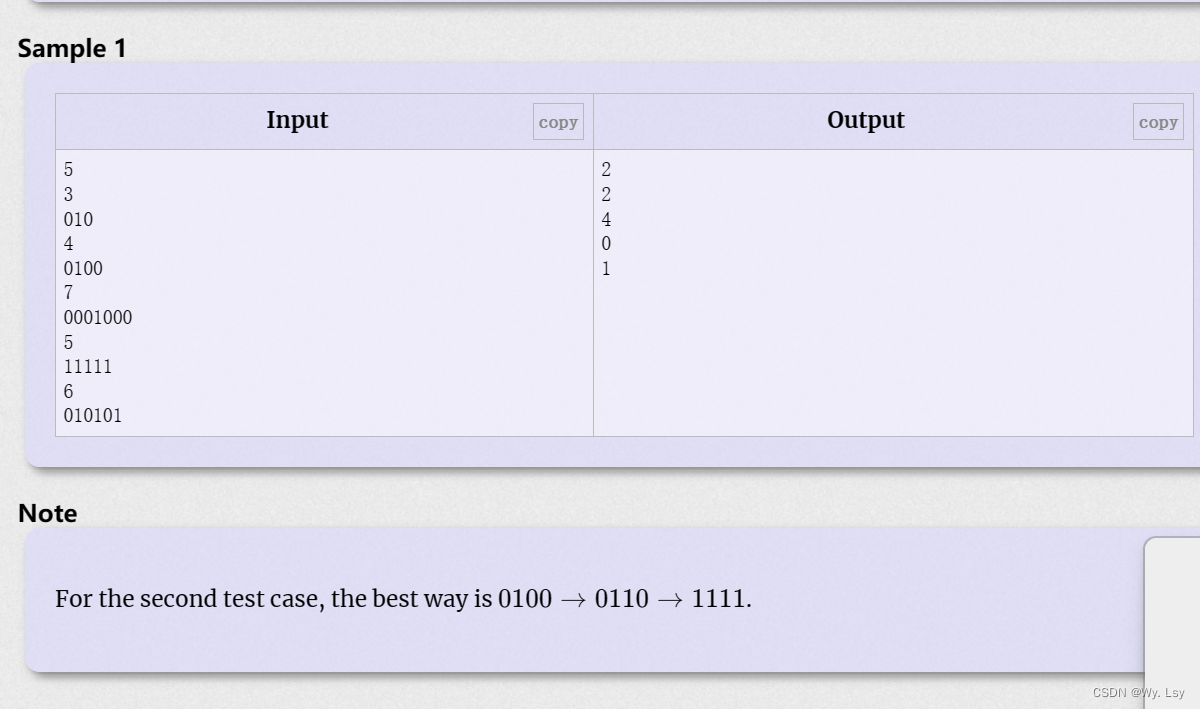
Identical Parity编辑
Best Carry Player
Stack Sort
Invoker
MUV LUV EXTRA
Forest Program
Angle Beats
Catch You Catch Me
Tower

思路:
提前进行/2的预处理操作,操作之后 ,在记录下要达到一样的步骤,由于可以可删除m座塔,所以此时,将步骤最多的删除,就是答案了
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 1e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
const ll hash_num = 3e9+9;
ll n,m,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
void solve()
{
map<ll,ll>mp,mmp;
cin >> n >> m;
rep(i,1,n)
{
ll x;
cin >> x;
arr[i] = x;
mp[x]++;
while(x)
{
mmp[x]++;
x>>=1;
}
}
ll ans = INF;
for(auto it:mmp)
{
rep(i,0,n)brr[i]=0;
ll ant = 0;
ll cnt = 0;
for(auto iit:mp)
{
if(iit.first==it.first)continue;
ll x=iit.first,y=iit.second;
ll res = 0;
if(x < it.first)
{
res += (it.first-x)*y;
ant += res;
while(y--)
{
brr[++cnt]=it.first-x;
}
continue;
}
while(x!=it.first)
{
if(x / 2 >= it.first)
{
x/=2;
res++;
}else{
res += min(x - it.first, 1 + it.first - x / 2);
x=it.first;
}
}
ant += res *y;
while(y--)brr[++cnt]=res;
}
sort(brr+1,brr+1+cnt);
per(j,cnt,cnt-m+1)
{
ant -=brr[j];
if(j==1)break;
}
ans=min(ans,ant);
}
cout <<ans<<endl;
}
int main()
{
IOS;
ll _;
_=1;
// scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>_;
ca=1;
while(_--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Frozen Scoreboard



思路:
纯大模拟,写出来了是好题,写不出来,这什么lj题(气急败坏)
来自大佬的说法就是硬写,然后加上dfs
 这是佬码
这是佬码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll haoye=0;
struct vis{
ll t,s;
};
vis a[1005];
vector<string>d[1005];
vector<ll>q[1005];
vector<ll>h[1005];
ll st[15];
ll n,m;
ll check(ll x){
ll z=0,w=0;
ll ss=0;
for(int i=0;i<d[x].size();i++){
if(d[x][i]=="+"){
z++;
ss=ss+h[x][i]+(q[x][i]-1)*20;
}
else if(d[x][i]=="?"){
w++;
}
}
// cout<<z<<" "<<w<<" "<<st;
if(z>a[x].s)return 0;
if(z==a[x].s){
if(ss!=a[x].t)return 0;
else return 1;
}
if(z+w>=a[x].s){
return 2;
}
return 0;
}
void dfs(ll x,ll cnt,ll idx){
if(haoye==1)return ;
if(cnt==0){
vector<ll>md;
ll ssum=0;
ll hh=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
if(d[x][i]=="+"){
ssum=ssum+h[x][i]+(q[x][i]-1)*20;
}
else if(d[x][i]=="?"){
if(st[i]==1){
ssum=ssum+240+(h[x][i]-q[x][i])*20;
hh=hh+59+(q[x][i]-1)*20;
}
}
// cout<<i<<" "<<ssum<<" "<<hh<<"\n";
}
if(a[x].t>=ssum&&a[x].t<=ssum+hh) {
haoye=1;
cout<<"Yes\n";
ll tmp=a[x].t-ssum;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
if(d[x][i]=="."){
cout<<".\n";
continue;
}
else if(d[x][i]=="+"){
cout<<"+ ";
cout<<q[x][i]<<"/"<<h[x][i]<<"\n";
}
else if(d[x][i]=="-"){
cout<<"- "<<q[x][i]<<"\n";
}
else {
if(st[i]==0){
cout<<"- "<<h[x][i]<<"\n";
continue;
}
if(tmp==0){
cout<<"+ "<<h[x][i]-q[x][i]+1<<"/240\n";
}
else if(tmp<=59){
cout<<"+ "<<h[x][i]-q[x][i]+1<<"/"<<240+tmp<<"\n";
tmp=0;
}
else {
ll hh=h[x][i]-q[x][i]+1;
while(tmp>=20&&hh<h[x][i]){
tmp-=20;
hh++;
}
if(tmp<=59){
cout<<"+ "<<hh<<"/"<<240+tmp<<"\n";
tmp=0;
}
else {
cout<<"+ "<<hh<<"/299"<<"\n";
tmp-=59;
}
}
}
}
}
return ;
}
for(int i=idx;i<m;i++){
if(st[i]==0){
st[i]=1;
if(haoye==1)return ;
dfs(x,cnt-1,i+1);
st[i]=0;
if(haoye==1)return ;
}
}
}
void vision(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i].s>>a[i].t;
string op;
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
cin>>op;
if(op=="."){
d[i].push_back(op);
q[i].push_back(0);
h[i].push_back(0);
}
else if(op=="+"){
d[i].push_back(op);
string hh;
cin>>hh;
ll mm=0;
for(int k=0;k<hh.length();k++){
if(hh[k]!='/'){
mm=mm*10+hh[k]-'0';
}
else {
q[i].push_back(mm);
mm=0;
}
}
h[i].push_back(mm);
}
else if(op=="?"){
d[i].push_back(op);
ll caiq,caih;
cin>>caiq>>caih;
q[i].push_back(caiq);
h[i].push_back(caih);
}
else {
d[i].push_back(op);
ll cai;
cin>>cai;
q[i].push_back(cai);
h[i].push_back(0);
}
}
}
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
// for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
// cout<<d[i][j]<<" ";
// cout<<" "<<q[i][j]<<" "<<h[i][j]<<"\n";
// }
// }
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(check(i)==0){cout<<"No\n";continue;}
else if(check(i)==1){
cout<<"Yes\n";
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(d[i][j]=="."){
cout<<".\n";
continue;
}
else if(d[i][j]=="+"){
cout<<"+ ";
cout<<q[i][j]<<"/"<<h[i][j]<<"\n";
}
else if(d[i][j]=="-"){
cout<<"- "<<q[i][j]<<"\n";
}
else {
cout<<"- "<<h[i][j]<<"\n";
}
}
}
else {
ll cnt=0;
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(d[i][j]=="+"){st[j]=1;cnt++;}
else if(d[i][j]=="?")st[j]=0;
else
st[j]=1;
}
haoye=0;
// cout<<a[i].s-cnt<<" ";
dfs(i,a[i].s-cnt,0);
if(haoye==0)cout<<"No\n";
}
}
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ll t=1;
// cin>>t;
// scanf("%lld",&t);
while(t--)
vision();
return 0;
} Identical Parity
思路:

#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 1e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
const ll hash_num = 3e9+9;
ll n,m,ca;
ll arr[3000];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
unordered_map<ll,ll>mp;
ll Hash(ll x, ll y)
{
// if(x==0)y=abs(y);
// return x*233333333+y;
return x*hash_num+y;
}
ll gcdd(ll a, ll b)
{
// while(b^=a^=b^=a%=b);
// return a;
if(b==0)return a;
return gcdd(b,a%b);
}
struct noda
{
/* data */
ll x,y;
}noda[3000],q[3000];
void solve()
{
cin >> n>> m;
if(m%2==0)
{
yes;
}else
{
ll ant=(n+1)/2-(m+1)/2*(n/m);
ll cnt=n/2-m/2*(n/m);
if(ant>=0 && cnt>=0 && ant<=(m+1)/2 &&cnt<=m/2)
{
yes;
}else{
no;
}
}
}
int main()
{
IOS;
ll t;
t=1;
// scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Best Carry Player

思路:
签到题了属于;就进位+1就行
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 1e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
ll n,m,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
// ll get_len(ll x1,ll y1,ll x2 ,ll y2)
// {
// return abs(x1-x2)+abs(y1-y2);
// }
ll ss(ll a,ll b)
{
if(b>a)swap(a,b);
ll res =0;
int f =0;
while(a)
{
int x=a%10,y=b%10;
if(x+y+f>9)f=1;
else f =0;
res += f;
// f = 0;
a/=10,b/=10;
}
return res;
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
ll ans =0;
ll num =0;
rep(i,1,n)
{
ll x;
cin >> x;
ans += ss(x,num);
num += x;
}
cout << ans <<endl;
}
int main()
{
IOS;
ll t;
t=1;
// scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Stack Sort

思路:
记录,比当前大的有没有入栈,没入栈就ans++;
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 1e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
ll n,m,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
// ll get_len(ll x1,ll y1,ll x2 ,ll y2)
// {
// return abs(x1-x2)+abs(y1-y2);
// }
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
int flag = 0;
ll ans =0;
//memset(brr,0,sizeof(brr));
map<ll,ll>mp;
rep(i,1,n)
{
cin >> arr[i];
mp[arr[i]]++;
if(mp[arr[i]+1]==0)ans++;
}
//ll ans = cnt - ant + 1;
cout << ans<<endl;
}
int main()
{
IOS;
ll t;
t=1;
// scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Invoker

思路:
你和我说这是简单dp?????????
由于按键可以保留,那么尽量让本次的按键对下次技能的按键保留的最多。
但是由于技能之间的按键顺序可以任意,所以我们dp按键组合。
因为一个技能有三个键,所以可以产生六种排序方式(完全相同的也算上)。
dp[i][j]表示第i个技能使用第j种排序方式的按键数,这样我们可以得出方程dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],dp[i-1][k]+(第i-1个技能使用第j种排序方式和第i个技能使用第k种排序方式的差值))。
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 1e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
const ll hash_num = 3e9+9;
char d[10][6][4]={ //补全排序
{"QQQ","QQQ","QQQ","QQQ","QQQ","QQQ"},
{"QQW","QWQ","WQQ","WQQ","WQQ","WQQ"},
{"QQE","QEQ","EQQ","EQQ","EQQ","EQQ"},
{"WWW","WWW","WWW","WWW","WWW","WWW"},
{"QWW","WQW","WWQ","WWQ","WWQ","WWQ"},
{"WWE","WEW","EWW","EWW","EWW","EWW"},
{"EEE","EEE","EEE","EEE","EEE","EEE"},
{"QEE","EQE","EEQ","EEQ","EEQ","EEQ"},
{"WEE","EWE","EEW","EEW","EEW","EEW"},
{"QWE","QEW","EQW","EWQ","WEQ","WQE"},
};
map<char,ll>m;
char ch[100010];
ll p[1000100],dp[1000100][6];
ll check(ll a,ll b,ll x,ll y){
if(d[a][x][0]==d[b][y][0]&&d[a][x][1]==d[b][y][1]&&d[a][x][2]==d[b][y][2])
return 0;
else if(d[a][x][1]==d[b][y][0]&&d[a][x][2]==d[b][y][1])
return 1;
else if(d[a][x][2]==d[b][y][0])
return 2;
else
return 3;
}
int main()
{
m['X']=0;m['V']=1;m['G']=2;
m['C']=3;m['X']=4;m['Z']=5;
m['T']=6;m['F']=7;m['D']=8;m['B']=9;
ll ans=0,sum=0;
while(cin>>ch){
int l=strlen(ch);
ans=0,sum=0;
p[sum++]=m[ch[0]];
for(int i=1;i<l;i++){
if(m[ch[i]]==p[sum-1])
ans++;
else
p[sum++]=m[ch[i]];
}
ans+=sum;
memset(dp,0x3f,sizeof(dp));
dp[0][0]=3;dp[0][1]=3;dp[0][2]=3;dp[0][3]=3;dp[0][4]=3;dp[0][5]=3;
for(int i=1;i<sum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<6;j++){
for(int k=0;k<6;k++){
dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],dp[i-1][k]+check(p[i-1],p[i],k,j));
}
}
}
ll mi=dp[sum-1][0];
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
mi=min(mi,dp[sum-1][i]);
cout<<ans+mi<<endl;;
}
return 0;
}
MUV LUV EXTRA

、
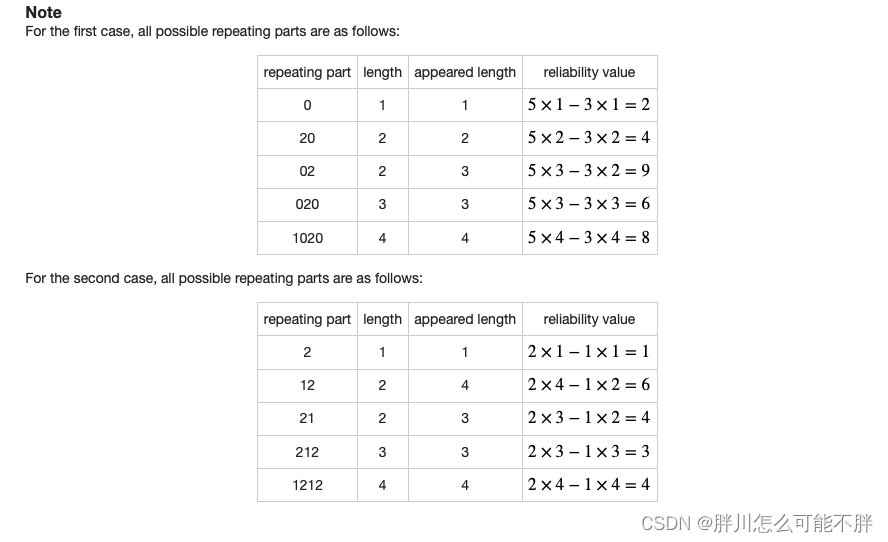
思路:
先反转一下,对于每一个位置,我们要求出这个位置开始的最短循环节。这个 K M P KMP KMP一下即可。
例如 a b a a b a a b abaabaab abaabaab, f a i l [ 8 ] fail[8] fail[8](最后一位后面)指向 6 6 6( a b a a b abaab abaab后面),那么说明这两段相同。这个又说明 a b , a b a a b ab,abaab ab,abaab也匹配,所以 f a i l fail fail跳跃的数量就是最短的可行循环节。
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 1e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
const ll hash_num = 3e9+9;
ll n,m,ca, k, p;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
//string s;
char s[N];
char x[N];
ll ant[N];
void KMP(){
ant[0]=-1,ant[1]=0;
ll len=strlen(x);
ll i=1,j=0;
while(i<len&&j<len){
if(j==-1||x[i]==x[j])ant[++i]=++j;
else j=ant[j];
}
}
void solve()
{
scanf("%lld %lld%s",&n,&m,s);
// scanf("%s",s);
ll tlen=strlen(s);
ll len=0;
per(i,tlen-1,0){
if(s[i]=='.')break;
x[len++]=s[i];
}
KMP();
ll ans=n-m;
rep(i,1,len-1){
ans=max(ans,n*(i+1)-m*(i+1-ant[i+1]));
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
int main()
{
//IOS;
ll _;
_=1;
// scanf("%d",&t);
//cin>>_;
ca=1;
while(_--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Forest Program

思路:
一个博弈论,也就是看奇偶路径情况
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 1e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
const ll hash_num = 3e9+9;
ll n,m,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
vector<ll>ve[n+1],vve[n+1];
rep(i,1,n)
{
arr[i]=0,brr[i]=0;
}
rep(i,2,n)
{
cin >> arr[i];
brr[arr[i]]++;
}
ll flag=0;
rep(i,1,n)
{
if(brr[i]==0)
{
ll ant=i,res=0;
while(brr[ant]<2)
{
res++;
if(ant==1)break;
ant=arr[ant];
}
if(res&1){flag=1;break;}
}
}
if(flag)
{
cout<<"Takeru"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"Meiya"<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
IOS;
ll _;
_=1;
// scanf("%d",&t);
cin>>_;
ca=1;
while(_--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Angle Beats

思路:
运用离线处理的方法,要不然会t,直角三角形去考虑斜率的问题,斜率相乘-1都是垂直
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 1e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
const ll hash_num = 3e9+9;
ll n,m,ca;
ll arr[3000];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
unordered_map<ll,ll>mp;
ll Hash(ll x, ll y)
{
// if(x==0)y=abs(y);
// return x*233333333+y;
return x*hash_num+y;
}
ll gcdd(ll a, ll b)
{
// while(b^=a^=b^=a%=b);
// return a;
if(b==0)return a;
return gcdd(b,a%b);
}
struct noda
{
/* data */
ll x,y;
}noda[3000],q[3000];
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
rep(i,1,n)cin >> noda[i].x >> noda[i].y;
rep(i,1,m)cin >> q[i].x >> q[i].y;
rep(i,1,m)
{
mp.clear();
rep(j,1,n)
{
ll xx = q[i].x - noda[j].x;
ll yy = q[i].y - noda[j].y;
ll ant = gcdd(xx,yy);
xx /= ant,yy /= ant;
ll num = Hash(xx,yy);
mp[num]++;
}
rep(j,1,n)
{
ll xx = q[i].x - noda[j].x;
ll yy = q[i].y - noda[j].y;
ll ant = gcdd(xx,yy);
xx /= ant,yy /= ant;
arr[i] += mp[Hash(yy,-xx)];
arr[i] += mp[Hash(-yy,xx)];
}
arr[i] /= 2;
}
rep(i,1,n)
{
mp.clear();
rep(j,1,n)
{
if(i != j)
{
ll xx = noda[i].x-noda[j].x;
ll yy = noda[i].y-noda[j].y;
ll ant = gcdd(xx,yy);
xx/=ant,yy/=ant;
ll num = Hash(xx,yy);
mp[num]++;
}
}
rep(j,1,m)
{
ll xx = noda[i].x-q[j].x;
ll yy = noda[i].y-q[j].y;
ll ant = gcdd(xx,yy);
xx/=ant,yy/=ant;
arr[j]+=mp[Hash(yy,-xx)];
arr[j]+=mp[Hash(-yy,xx)];
}
}
rep(i,1,m)
{
cout<<arr[i]<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
IOS;
ll t;
t=1;
// scanf("%d",&t);
// cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
Catch You Catch Me


思路:
思维题,只要在1节点下面的节点等着就行了
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
// int get_len(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
// {
// return (x2-x1)*(x2-x1) + (y2-y1)*(y2-y1);
// }
const ll N = 1e6+ 10;
const ll mod =1000000007;
ll n,m,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
// int h[N],ne[N],e[N],w[N],idx;
// ll get_len(ll x1,ll y1,ll x2 ,ll y2)
// {
// return abs(x1-x2)+abs(y1-y2);
// }
vector<ll>ve[N];
ll ant ,cnt,ans;
ll dep[N];
ll depth(ll ant,ll cnt)
{
dep[ant] = dep[cnt] + 1;
ll res = dep[ant];
for (auto it : ve[ant])
{
if (it != cnt)
{
ll d = depth(it,ant);
res = max(res, d);
if (ant == 1) ans += d - 1;
}
}
return res;
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
rep(i,1,n-1)
{
ll x,y;
cin >> x >> y;
ve[x].push_back(y);
ve[y].push_back(x);
}
// ll ans = 0;
// ans += ve[1].size();
// //cout << ans<<endl;
// for(int i =0;i< ve[1].size();i++)
// {
// ant =0,res =0;
// depth(ve[1][i],res);
// ans += ant;
// }
depth(1,0);
cout << ans;
}
int main()
{
IOS;
ll t;
t=1;
// scanf("%d",&t);
//cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
总结就是:我还是太菜了啊