1. nuScenes Dataloader
对nuScenes数据集处理的了解,大体上的核心还是getitem函数、prepare_data函数,以及collate_batch函数三个部分的处理。其中prepare_data函数和collate_batch函数是在Dataset这个父类实现的,基本的处理流程基本不变,这里记录data_dict的数据处理部分。
1.1 NuScenesDataset初始化
在初始化的步骤中,进行了两个重要的操作,一个是加载了在create_nuscenes_infos 函数处理后的pkl文件,另外一个就是对类别不平衡进行了重采样的操作。
ps:如果构建出这个pkl文件在后续会介绍到
class NuScenesDataset(DatasetTemplate):
def __init__(self, dataset_cfg, class_names, training=True, root_path=None, logger=None):
root_path = (root_path if root_path is not None else Path(dataset_cfg.DATA_PATH)) / dataset_cfg.VERSION
super().__init__(
dataset_cfg=dataset_cfg, class_names=class_names, training=training, root_path=root_path, logger=logger
)
self.infos = []
.....
self.include_nuscenes_data(self.mode)
if self.training and self.dataset_cfg.get('BALANCED_RESAMPLING', False): # train time
self.infos = self.balanced_infos_resampling(self.infos)
这里是对[‘nuscenes_infos_10sweeps_train.pkl’]文件的加载,其加载的结果如下:

每个列表是一个scense场景,每个scenes场景还有对应了多帧sweep场景,对于每个scense是一个字典结构,包含了14个key,详细如下所示:

随后会执行类别不均衡函数,这个处理是统计每个sences场景中的gt,然后按照gt的类别进行划分,此时构架的样本是重复的,因为一个sensces一般是包含了多个类别的gt,那么这个scenes会被同时存放在这些类别gt的对应列表结构中。

在进行了按类别的scense存储之后,再按照每个gt的数量从列表中进行随机采样,重新构建出一个scense列表结构。此时的列表数量要比原始的多,也包含了重复的样本,但总体上各类别的gt样本会均衡一点。
def balanced_infos_resampling(self, infos):
"""
Class-balanced sampling of nuScenes dataset from https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.09492
"""
if self.class_names is None:
return infos
# 每个场景包含了某个类别都进行存储
cls_infos = {name: [] for name in self.class_names}
for info in infos:
for name in set(info['gt_names']):
if name in self.class_names:
cls_infos[name].append(info)
duplicated_samples = sum([len(v) for _, v in cls_infos.items()]) # 1639
cls_dist = {k: len(v) / duplicated_samples for k, v in cls_infos.items()} # 类别样本在每个scene中的分布占比
sampled_infos = []
frac = 1.0 / len(self.class_names) # 0.1
ratios = [frac / v for v in cls_dist.values()] # 分布占比越大权重越小
# 从每个类别的样本中按权重进行随机采样,每个类别采样的数量是:len(cur_cls_infos) * ratio,采样后的数据构建成一个列表存储
for cur_cls_infos, ratio in zip(list(cls_infos.values()), ratios):
sampled_infos += np.random.choice(
cur_cls_infos, int(len(cur_cls_infos) * ratio)
).tolist()
self.logger.info('Total samples after balanced resampling: %s' % (len(sampled_infos))) # 1630
# 对类别不平衡采样后重新组织类别数据
cls_infos_new = {name: [] for name in self.class_names}
for info in sampled_infos:
for name in set(info['gt_names']):
if name in self.class_names:
cls_infos_new[name].append(info)
cls_dist_new = {k: len(v) / len(sampled_infos) for k, v in cls_infos_new.items()}
# 返回的是重新采样后的数据,此时样本量会扩充
return sampled_infos
此时的采样数据中更改如下:

可以看出,从原来的nuscenes_infos_10sweeps_train.pkl文件只有300+的样本,此时采样数量更改到了1600+个样本,里面的很多scenes都是重复的。getitem函数每次也是从这里随机采样一个场景来进行处理,也可以理解为重复对类别gt较少的样本进行重复处理,来减少长尾分布带来的性能影响。这个是从数据层面的上采样实现,简单来说就是对类别gt较少的样本进行重复多遍实现的数据上采样。

1.2 getitem函数对单场景处理
在上述提到,在初始化中进行了对样本的重采样,从而实现对样本数量的扩充,对一些类别数目较少的类别gt场景进行重复的处理。
info = copy.deepcopy(self.infos[index])
points = self.get_lidar_with_sweeps(index, max_sweeps=self.dataset_cfg.MAX_SWEEPS) # 整合sweep点数据
随机获取了一个scenes数据,随后就是根据对应的路径读取点云数据,此外还包含了对个sweep数据的补充,这里会将多个sweep点云场景与scenes场景进行拼接操作。
def get_sweep(self, sweep_info):
def remove_ego_points(points, center_radius=1.0):
mask = ~((np.abs(points[:, 0]) < center_radius) & (np.abs(points[:, 1]) < center_radius)) # ~取反
return points[mask]
lidar_path = self.root_path / sweep_info['lidar_path']
points_sweep = np.fromfile(str(lidar_path), dtype=np.float32, count=-1).reshape([-1, 5])[:, :4]
points_sweep = remove_ego_points(points_sweep).T # 删除中间范围内-1~1的点
if sweep_info['transform_matrix'] is not None:
num_points = points_sweep.shape[1] # 26182
points_sweep[:3, :] = sweep_info['transform_matrix'].dot(
np.vstack((points_sweep[:3, :], np.ones(num_points))))[:3, :] # 提取xyz信息并添加1行‘1’元素进行矩阵点乘实现转换
cur_times = sweep_info['time_lag'] * np.ones((1, points_sweep.shape[1])) # (1, 26182)
return points_sweep.T, cur_times.T
def get_lidar_with_sweeps(self, index, max_sweeps=1):
info = self.infos[index]
lidar_path = self.root_path / info['lidar_path']
# 提取scene点:(x,y,z,intensity,ring index)
points = np.fromfile(str(lidar_path), dtype=np.float32, count=-1).reshape([-1, 5])[:, :4]
sweep_points_list = [points]
sweep_times_list = [np.zeros((points.shape[0], 1))] # scene场景的时间戳设置为0
# 提取sweep点:从当前的sweep数量中最多提取max_sweeps-1个
for k in np.random.choice(len(info['sweeps']), max_sweeps - 1, replace=False):
points_sweep, times_sweep = self.get_sweep(info['sweeps'][k]) # 获取每个sweep场景的点信息与时间戳信息
sweep_points_list.append(points_sweep)
sweep_times_list.append(times_sweep)
# 将单帧的scene场景和多帧的sweep场景点云进行拼接
points = np.concatenate(sweep_points_list, axis=0)
times = np.concatenate(sweep_times_list, axis=0).astype(points.dtype)
points = np.concatenate((points, times), axis=1) # 拼接 (270396, 5)
return points
然后开始构建data_dict的字典。这里对于少于1个点的gt进行筛选,从事构建gt和gt的类别信息到data_dict中:
# 筛选点数少于等于1的gt,更新gt_names和gt_boxes
if 'gt_boxes' in info:
if self.dataset_cfg.get('FILTER_MIN_POINTS_IN_GT', False):
mask = (info['num_lidar_pts'] > self.dataset_cfg.FILTER_MIN_POINTS_IN_GT - 1)
else:
mask = None
input_dict.update({
'gt_names': info['gt_names'] if mask is None else info['gt_names'][mask],
'gt_boxes': info['gt_boxes'] if mask is None else info['gt_boxes'][mask]
})
此时的data_dict结构如下:

随后会进行prepare_data操作,这包含了点云数据增强、特征选择、点云数据处理,将点云场景量化为voxel的几个操作,操作完后的data_dict更下如下:

此时,算是处理完了一个scenes场景,在同时处理完batch_size个之后,就会执行collect_batch函数,将多个scene数据重建成多维矩阵,进行矩阵的并行计算。这里我设置的batch_size是4,所以这里一个batch数据的最高维度是4,如下所示:

这里的point和voxek_coords由于在对应的维度中添加了一列来区分其所属的scenes,所以直接拼接起来就好了。随后,这个batch_data的数据就会丢给模型来进行处理,处理的是voxel这个特征,其他的key是用来辅助的。
2. nuScenes CreateDatabase
以上过程是介绍了从pkl序列信息读取内容到batch数据的构建整个过程,那么如果构建从pkl文件是这里的内容。首先在pycharm中进行设置,以实现可以debug一些子模块


这一部分包含了两个函数的处理,一个是create_groundtruth_database来进行gt sample的数据增强,另外的是create_nuscenes_info函数来进行nuScenes数据集的处理,来生成nuscenes_infos_10sweeps_train.pkl文件,随后在nuScense数据集处理的时候进行初始化的操作。
2.1 create_nuscenes_info
create_nuscenes_info函数的核心其实是调用了nuscenes_utils.fill_trainval_infos函数,在此之前create_nuscenes_info函数对nuScenes mini版本中划分的训练集和测试集的scenes场景路径进行判断,看是否存在

随后将name转化成token的形式,传入nuscenes_utils.fill_trainval_infos函数进行pkl文件的生成处理。(这里的filter内置函数配置lambda的写法很值得学习)
train_scenes = list(filter(lambda x: x in available_scene_names, train_scenes))
val_scenes = list(filter(lambda x: x in available_scene_names, val_scenes))
train_scenes = set([available_scenes[available_scene_names.index(s)]['token'] for s in train_scenes]) # 将name转化成token的形式来表示
val_scenes = set([available_scenes[available_scene_names.index(s)]['token'] for s in val_scenes])
- 相关信息保存
在nuscenes_utils.fill_trainval_infos函数中,会依次遍历每个nusc.sample,随后将相关信息构造成一个info的字典,随后存储在一个列表中。
for index, sample in enumerate(nusc.sample): # len(nusc.sample): 404
progress_bar.update()
ref_sd_token = sample['data'][ref_chan]
ref_sd_rec = nusc.get('sample_data', ref_sd_token)
ref_cs_rec = nusc.get('calibrated_sensor', ref_sd_rec['calibrated_sensor_token'])
ref_pose_rec = nusc.get('ego_pose', ref_sd_rec['ego_pose_token'])
ref_time = 1e-6 * ref_sd_rec['timestamp']
ref_lidar_path, ref_boxes, _ = get_sample_data(nusc, ref_sd_token)
ref_cam_front_token = sample['data']['CAM_FRONT']
ref_cam_path, _, ref_cam_intrinsic = nusc.get_sample_data(ref_cam_front_token)
# Homogeneous transform from ego car frame to reference frame
ref_from_car = transform_matrix(
ref_cs_rec['translation'], Quaternion(ref_cs_rec['rotation']), inverse=True
)
# Homogeneous transformation matrix from global to _current_ ego car frame
car_from_global = transform_matrix(
ref_pose_rec['translation'], Quaternion(ref_pose_rec['rotation']), inverse=True,
)
# 构建每个sample的info列表
info = {
'lidar_path': Path(ref_lidar_path).relative_to(data_path).__str__(),
'cam_front_path': Path(ref_cam_path).relative_to(data_path).__str__(),
'cam_intrinsic': ref_cam_intrinsic,
'token': sample['token'],
'sweeps': [],
'ref_from_car': ref_from_car,
'car_from_global': car_from_global,
'timestamp': ref_time,
}
- sweep信息保存
此外,由于每个sample场景多有多个密集的sweep帧与之相匹配,这里还会筛选挑选MAX_SWEEP个sweep场景的点云与sample的点进行拼接操作。并且,首个sample是没有prev的,所以这里会重复的采样同一个sweep,而其他用prev的会重复采样不同的max_sweeps个sweep场景。
sample_data_token = sample['data'][chan]
curr_sd_rec = nusc.get('sample_data', sample_data_token)
sweeps = []
while len(sweeps) < max_sweeps - 1: # 挑选sweep(不超过max_sweeps)
if curr_sd_rec['prev'] == '':
if len(sweeps) == 0:
sweep = {
'lidar_path': Path(ref_lidar_path).relative_to(data_path).__str__(),
'sample_data_token': curr_sd_rec['token'],
'transform_matrix': None,
'time_lag': curr_sd_rec['timestamp'] * 0,
}
sweeps.append(sweep)
else:
sweeps.append(sweeps[-1])
else:
curr_sd_rec = nusc.get('sample_data', curr_sd_rec['prev'])
# Get past pose
current_pose_rec = nusc.get('ego_pose', curr_sd_rec['ego_pose_token'])
global_from_car = transform_matrix(
current_pose_rec['translation'], Quaternion(current_pose_rec['rotation']), inverse=False,
)
# Homogeneous transformation matrix from sensor coordinate frame to ego car frame.
current_cs_rec = nusc.get(
'calibrated_sensor', curr_sd_rec['calibrated_sensor_token']
)
car_from_current = transform_matrix(
current_cs_rec['translation'], Quaternion(current_cs_rec['rotation']), inverse=False,
)
tm = reduce(np.dot, [ref_from_car, car_from_global, global_from_car, car_from_current])
lidar_path = nusc.get_sample_data_path(curr_sd_rec['token'])
time_lag = ref_time - 1e-6 * curr_sd_rec['timestamp']
sweep = {
'lidar_path': Path(lidar_path).relative_to(data_path).__str__(),
'sample_data_token': curr_sd_rec['token'],
'transform_matrix': tm,
'global_from_car': global_from_car,
'car_from_current': car_from_current,
'time_lag': time_lag,
}
sweeps.append(sweep)
info['sweeps'] = sweeps
- gt信息保存
随后,对当前sample的gt进行统计,利用的是get_sample_data函数来实现。
def get_sample_data(nusc, sample_data_token, selected_anntokens=None):
"""
Returns the data path as well as all annotations related to that sample_data.
Note that the boxes are transformed into the current sensor's coordinate frame.
Args:
nusc:
sample_data_token: Sample_data token.
selected_anntokens: If provided only return the selected annotation.
Returns:
"""
# Retrieve sensor & pose records
sd_record = nusc.get('sample_data', sample_data_token)
cs_record = nusc.get('calibrated_sensor', sd_record['calibrated_sensor_token'])
sensor_record = nusc.get('sensor', cs_record['sensor_token'])
pose_record = nusc.get('ego_pose', sd_record['ego_pose_token'])
data_path = nusc.get_sample_data_path(sample_data_token)
if sensor_record['modality'] == 'camera':
cam_intrinsic = np.array(cs_record['camera_intrinsic'])
imsize = (sd_record['width'], sd_record['height'])
else:
cam_intrinsic = imsize = None
# Retrieve all sample annotations and map to sensor coordinate system.
if selected_anntokens is not None:
boxes = list(map(nusc.get_box, selected_anntokens))
else:
boxes = nusc.get_boxes(sample_data_token)
# Make list of Box objects including coord system transforms.
box_list = []
for box in boxes:
box.velocity = nusc.box_velocity(box.token)
# Move box to ego vehicle coord system
box.translate(-np.array(pose_record['translation']))
box.rotate(Quaternion(pose_record['rotation']).inverse)
# Move box to sensor coord system
box.translate(-np.array(cs_record['translation']))
box.rotate(Quaternion(cs_record['rotation']).inverse)
box_list.append(box)
return data_path, box_list, cam_intrinsic
annotations的结构信息如下所示:

这里将相关的信息,比如位置,尺寸,旋转角度,速度的信息拼接在一起组成了gt的维度信息,这里的维度是9维,相比与KITTI数据集多了两个维度。
if not test:
annotations = [nusc.get('sample_annotation', token) for token in sample['anns']]
# the filtering gives 0.5~1 map improvement
num_lidar_pts = np.array([anno['num_lidar_pts'] for anno in annotations])
num_radar_pts = np.array([anno['num_radar_pts'] for anno in annotations])
mask = (num_lidar_pts + num_radar_pts > 0)
# 构造gt信息(dim=8)
locs = np.array([b.center for b in ref_boxes]).reshape(-1, 3)
dims = np.array([b.wlh for b in ref_boxes]).reshape(-1, 3)[:, [1, 0, 2]] # wlh == > dxdydz (lwh)
velocity = np.array([b.velocity for b in ref_boxes]).reshape(-1, 3)
rots = np.array([quaternion_yaw(b.orientation) for b in ref_boxes]).reshape(-1, 1)
names = np.array([b.name for b in ref_boxes])
tokens = np.array([b.token for b in ref_boxes])
gt_boxes = np.concatenate([locs, dims, rots, velocity[:, :2]], axis=1)
assert len(annotations) == len(gt_boxes) == len(velocity)
info['gt_boxes'] = gt_boxes[mask, :]
info['gt_boxes_velocity'] = velocity[mask, :]
info['gt_names'] = np.array([map_name_from_general_to_detection[name] for name in names])[mask]
info['gt_boxes_token'] = tokens[mask]
info['num_lidar_pts'] = num_lidar_pts[mask]
info['num_radar_pts'] = num_radar_pts[mask]
if sample['scene_token'] in train_scenes:
train_nusc_infos.append(info) # 追加train序列信息
else:
val_nusc_infos.append(info) # 追加val序列信息
2.2 create_groundtruth_database
现在获取到当前数据集中的待处理sample的序列信息,那么可以对这些sample的gt构建出一个database来进行gt的数据增强。
首选依次读取每一个sample的序列信息,对每个sample及其sweep场景的点云进行拼接操作,提取出其gt和gt_name
for idx in tqdm(range(len(self.infos))):
sample_idx = idx
info = self.infos[idx]
points = self.get_lidar_with_sweeps(idx, max_sweeps=max_sweeps)
gt_boxes = info['gt_boxes']
gt_names = info['gt_names']
随后利用roiaware_pool3d_utils.points_in_boxes_gpu函数来对每个点的所属的gt进行判别,已实现后续每个gt的点提取。-1表示背景点,不属于任何一个gt,其他根据gt位置尺寸一一进行判别,当前的sample的gt数量是66,那么该函数的返回结果中,最大值就是65,表示第65个gt的点。
box_idxs_of_pts = roiaware_pool3d_utils.points_in_boxes_gpu( # 判断每个点在哪个gt中,-1表示背景,其他的属于哪一类就为i
torch.from_numpy(points[:, 0:3]).unsqueeze(dim=0).float().cuda(),
torch.from_numpy(gt_boxes[:, 0:7]).unsqueeze(dim=0).float().cuda()
).long().squeeze(dim=0).cpu().numpy()
随后,在拼接后的sample场景中,开始对其gt进行一一遍历。分别提取出每个gt的点,随后将其平移到原点坐标上,保存点序列文件。随后保存在对于类别的列表all_db_infos中。
for i in range(gt_boxes.shape[0]): # 对sample场景每个gt均进行构建
filename = '%s_%s_%d.bin' % (sample_idx, gt_names[i], i)
filepath = database_save_path / filename
gt_points = points[box_idxs_of_pts == i]
gt_points[:, :3] -= gt_boxes[i, :3]
with open(filepath, 'w') as f: # gt点云序列的提取
gt_points.tofile(f)
if (used_classes is None) or gt_names[i] in used_classes:
db_path = str(filepath.relative_to(self.root_path)) # gt_database/xxxxx.bin
db_info = {'name': gt_names[i], 'path': db_path, 'image_idx': sample_idx, 'gt_idx': i, # gt信息保存在对应的类别列表中
'box3d_lidar': gt_boxes[i], 'num_points_in_gt': gt_points.shape[0]}
if gt_names[i] in all_db_infos:
all_db_infos[gt_names[i]].append(db_info)
else:
all_db_infos[gt_names[i]] = [db_info]
这里的列表有9个表示设置了检测9个类别,所有的sample场景的gt全部都会保存在这个gt列表中,最后会将这个序列信息进行保存,后续在进行preprare_data函数中进行gt_sample读取时再进行操作,来实现gt的采样操作实现copy_paste的数据增强。

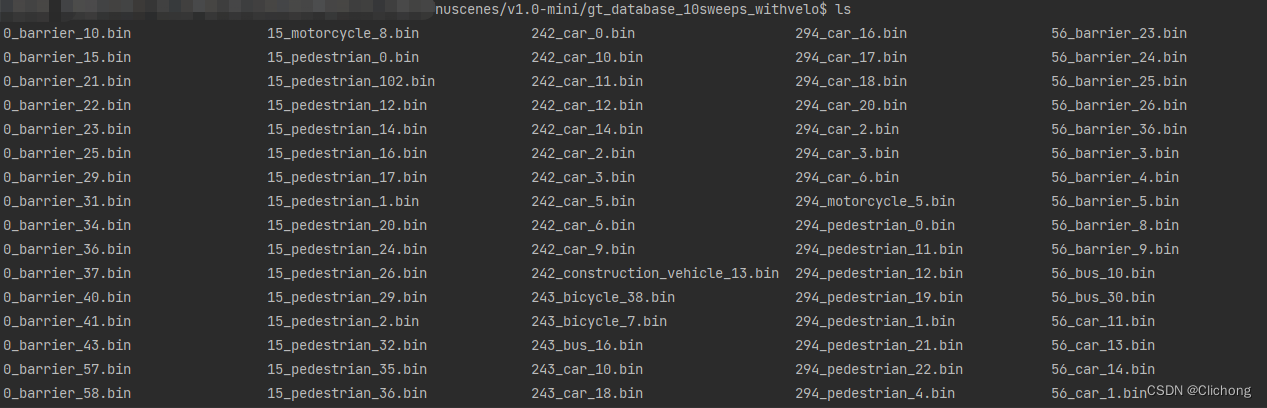
其中gt的database文件夹中存储的是每一个gt的点信息,也就是一个bin文件。完整的处理代码如下所示:
def create_groundtruth_database(self, used_classes=None, max_sweeps=10):
import torch
database_save_path = self.root_path / f'gt_database_{max_sweeps}sweeps_withvelo'
db_info_save_path = self.root_path / f'nuscenes_dbinfos_{max_sweeps}sweeps_withvelo.pkl'
database_save_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
all_db_infos = {}
for idx in tqdm(range(len(self.infos))):
sample_idx = idx
info = self.infos[idx]
points = self.get_lidar_with_sweeps(idx, max_sweeps=max_sweeps)
gt_boxes = info['gt_boxes']
gt_names = info['gt_names']
box_idxs_of_pts = roiaware_pool3d_utils.points_in_boxes_gpu( # 判断每个点在哪个gt中,-1表示背景,其他的属于哪一类就为i
torch.from_numpy(points[:, 0:3]).unsqueeze(dim=0).float().cuda(),
torch.from_numpy(gt_boxes[:, 0:7]).unsqueeze(dim=0).float().cuda()
).long().squeeze(dim=0).cpu().numpy()
for i in range(gt_boxes.shape[0]): # 对sample场景每个gt均进行构建
filename = '%s_%s_%d.bin' % (sample_idx, gt_names[i], i)
filepath = database_save_path / filename
gt_points = points[box_idxs_of_pts == i]
gt_points[:, :3] -= gt_boxes[i, :3]
with open(filepath, 'w') as f: # gt点云序列的提取
gt_points.tofile(f)
if (used_classes is None) or gt_names[i] in used_classes:
db_path = str(filepath.relative_to(self.root_path)) # gt_database/xxxxx.bin
db_info = {'name': gt_names[i], 'path': db_path, 'image_idx': sample_idx, 'gt_idx': i, # gt信息保存在对应的类别列表中
'box3d_lidar': gt_boxes[i], 'num_points_in_gt': gt_points.shape[0]}
if gt_names[i] in all_db_infos:
all_db_infos[gt_names[i]].append(db_info)
else:
all_db_infos[gt_names[i]] = [db_info]
for k, v in all_db_infos.items():
print('Database %s: %d' % (k, len(v)))
with open(db_info_save_path, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(all_db_infos, f)
其中,all_db_infos最后的处理结果如下所示,保存的也是这个序列信息。

其中gt_database生成的文件所存储的内容如下所示,前面的数值表示属于第几个sample的,中间表示属于的类别,最后的数字表示是gt中的第几个。