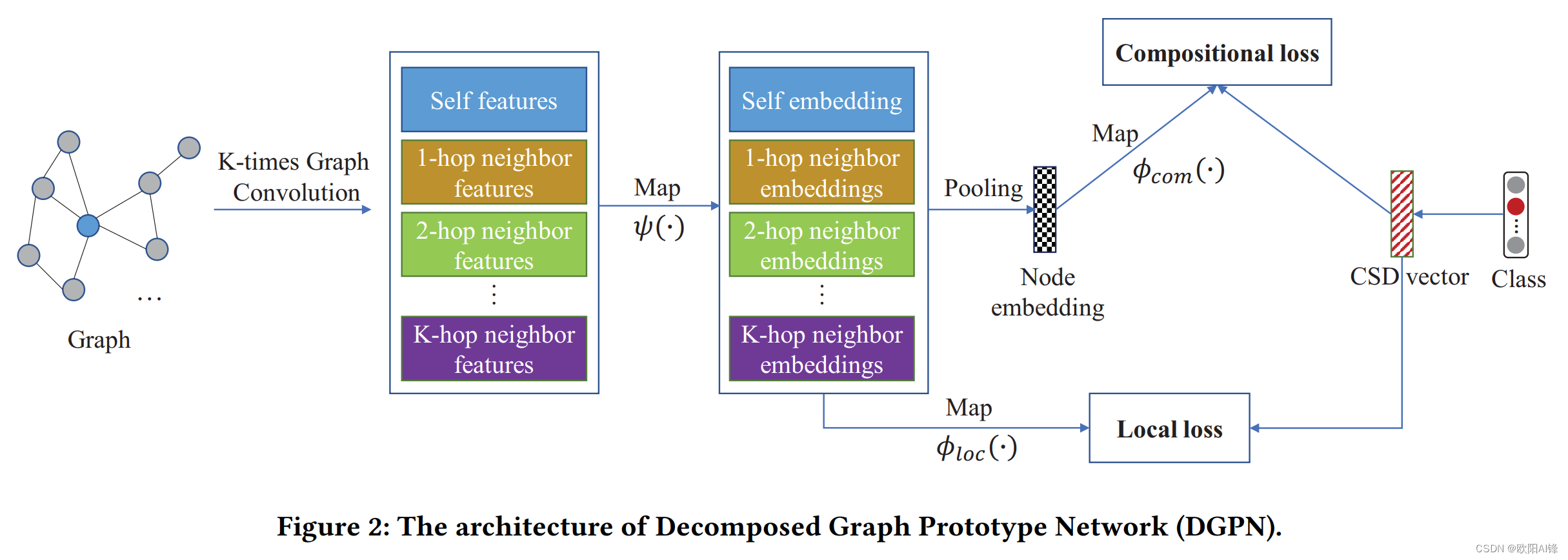
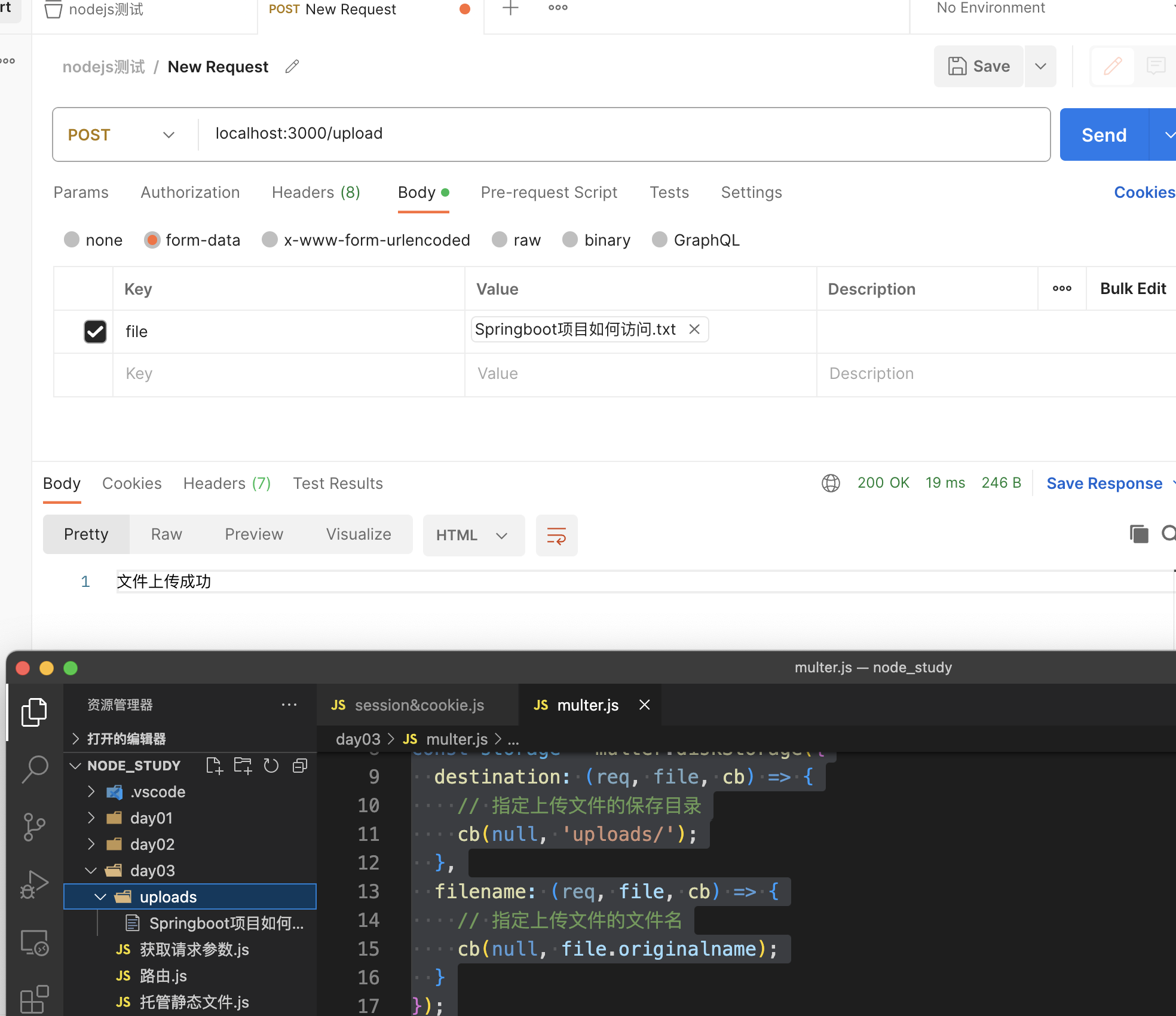
Codeforces Round 883 (Div. 3)
链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1846
A. Rudolph and Cut the Rope
There are n n n nails driven into the wall, the i i i-th nail is driven a i a_i ai meters above the ground, one end of the b i b_i bi meters long rope is tied to it. All nails hang at different heights one above the other. One candy is tied to all ropes at once. Candy is tied to end of a rope that is not tied to a nail.
To take the candy, you need to lower it to the ground. To do this, Rudolph can cut some ropes, one at a time. Help Rudolph find the minimum number of ropes that must be cut to get the candy.
The figure shows an example of the first test:

Input
The first line contains one integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains one integer n n n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 50 1 \le n \le 50 1≤n≤50) — the number of nails.
The i i i-th of the next n n n lines contains two integers a i a_i ai and b i b_i bi ( 1 ≤ a i , b i ≤ 200 1 \le a_i, b_i \le 200 1≤ai,bi≤200) — the height of the i i i-th nail and the length of the rope tied to it, all a i a_i ai are different.
It is guaranteed that the data is not contradictory, it is possible to build a configuration described in the statement.
Output
For each test case print one integer — the minimum number of ropes that need to be cut to make the candy fall to the ground.
Example
input
4
3
4 3
3 1
1 2
4
9 2
5 2
7 7
3 4
5
11 7
5 10
12 9
3 2
1 5
3
5 6
4 5
7 7
output
2
2
3
0
思路
如果 a i > b i a_i>b_i ai>bi,那么此时这个糖果就不可以到地上,因此只需要统计 a i > b i a_i>b_i ai>bi的个数即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define debug(s, x) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<pair<int, int> > a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
a[i] = {x, y};
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i].first - a[i].second > 0) cnt++;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
signed main() {
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
B. Rudolph and Tic-Tac-Toe
Rudolph invented the game of tic-tac-toe for three players. It has classic rules, except for the third player who plays with pluses. Rudolf has a 3 × 3 3 \times 3 3×3 field — the result of the completed game. Each field cell contains either a cross, or a nought, or a plus sign, or nothing. The game is won by the player who makes a horizontal, vertical or diagonal row of 3 3 3’s of their symbols.
Rudolph wants to find the result of the game. Either exactly one of the three players won or it ended in a draw. It is guaranteed that multiple players cannot win at the same time.
Input
The first line contains one integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of three lines, each of which consists of three characters. The symbol can be one of four: “X” means a cross, “O” means a nought, “+” means a plus, “.” means an empty cell.
Output
For each test case, print the string “X” if the crosses won, “O” if the noughts won, “+” if the pluses won, “DRAW” if there was a draw.
Example
input
5
+X+
OXO
OX.
O+.
+OX
X+O
.XO
OX.
+++
O.+
X.O
+..
.++
X.O
+..
output
X
O
+
DRAW
DRAW
思路
题意为3个人下3*3的棋盘,连成一条线就是赢,一个棋盘要么是平局,要么只有一个人可以赢。问是平局还是哪个人赢
依次判断3行,3列,两个对角线上的元素是否相同,如果相同并且不是’.',那么就说明那个元素获胜,否则平局。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define debug(s, x) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
char g[10][10];
void solve() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
cin >> g[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
bool ok = true;
for (int j = 2; j <= 3; j++) {
if (g[i][j] != g[i][j - 1]) ok = false;
}
if (ok &&g[i][1]!='.') {
cout << g[i][1] << endl;
return;
}
}
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
bool ok = true;
for (int i = 1; i < 3; i++) {
if (g[i][j] != g[i + 1][j]) ok = false;
}
if (ok&&g[1][j]!='.') {
cout << g[1][j] << endl;
return;
}
}
if (g[1][1] == g[2][2] && g[2][2] == g[3][3]&&g[1][1]!='.') {
cout << g[1][1] << endl;
return;
}
if (g[1][3] == g[2][2] && g[2][2] == g[3][1]&&g[2][2]!='.') {
cout << g[2][2] << endl;
return;
}
cout << "DRAW" << endl;
}
signed main() {
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
C. Rudolf and the Another Competition
Rudolf has registered for a programming competition that will follow the rules of ICPC. The rules imply that for each solved problem, a participant gets 1 1 1 point, and also incurs a penalty equal to the number of minutes passed from the beginning of the competition to the moment of solving the problem. In the final table, the participant with the most points is ranked higher, and in case of a tie in points, the participant with the lower penalty is ranked higher.
In total, n n n participants have registered for the competition. Rudolf is a participant with index 1 1 1. It is known that m m m problems will be proposed. And the competition will last h h h minutes.
A powerful artificial intelligence has predicted the values t i , j t_{i, j} ti,j, which represent the number of minutes it will take for the i i i-th participant to solve the j j j-th problem.
Rudolf realized that the order of solving problems will affect the final result. For example, if h = 120 h = 120 h=120, and the times to solve problems are [ 20 , 15 , 110 20, 15, 110 20,15,110], then if Rudolf solves the problems in the order:
- 3 , 1 , 2 {3, 1, 2} 3,1,2, then he will only solve the third problem and get 1 1 1 point and 110 110 110 penalty.
- 1 , 2 , 3 {1, 2, 3} 1,2,3, then he will solve the first problem after 20 20 20 minutes from the start, the second one after 20 + 15 = 35 20+15=35 20+15=35 minutes, and he will not have time to solve the third one. Thus, he will get 2 2 2 points and 20 + 35 = 55 20+35=55 20+35=55 penalty.
- 2 , 1 , 3 {2, 1, 3} 2,1,3, then he will solve the second problem after 15 15 15 minutes from the start, the first one after 15 + 20 = 35 15+20=35 15+20=35 minutes, and he will not have time to solve the third one. Thus, he will get 2 2 2 points and 15 + 35 = 50 15+35=50 15+35=50 penalty.
Rudolf became interested in what place he will take in the competition if each participant solves problems in the optimal order based on the predictions of the artificial intelligence. It will be assumed that in case of a tie in points and penalty, Rudolf will take the best place.
Input
The first line contains an integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 3 1 \le t \le 10^3 1≤t≤103) — the number of test cases.
Then follow the descriptions of the test cases.
The first line of each test case contains three integers n , m , h n, m, h n,m,h ( 1 ≤ n ⋅ m ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 , 1 ≤ h ≤ 1 0 6 1 \le n \cdot m \le 2 \cdot 10^5, 1 \le h \le 10^6 1≤n⋅m≤2⋅105,1≤h≤106) — the number of participants, the number of problems, and the duration of the competition, respectively.
Then there are n n n lines, each containing m m m integers t i , j t_{i, j} ti,j ( 1 ≤ t i , j ≤ 1 0 6 1 \le t_{i, j} \le 10^6 1≤ti,j≤106) — the number of minutes it will take for the i i i-th participant to solve the j j j-th problem.
The sum of n ⋅ m n \cdot m n⋅m over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output an integer — Rudolf’s place in the final table if all participants solve problems in the optimal order.
Example
input
5
3 3 120
20 15 110
90 90 100
40 40 40
2 1 120
30
30
1 3 120
10 20 30
3 2 27
8 9
10 7
10 8
3 3 15
7 2 6
7 5 4
1 9 8
output
2
1
1
2
1
Note
In the first example, Rudolf will get 2 2 2 points and 50 50 50 penalty minutes. The second participant will solve only one problem and get 1 1 1 point and 90 90 90 penalty minutes. And the third participant will solve all 3 3 3 problems and get 3 3 3 points and 240 240 240 penalty minutes. Thus, Rudolf will take the second place.
In the second example, both participants will get 1 1 1 point and 30 30 30 penalty minutes. In case of a tie in points, Rudolf gets the better position, so he will take the first place.
In the third example, Rudolf is the only participant, so he will take the first place.
In the fourth example, all participants can solve two problems with penalty of 25 = 8 + ( 8 + 9 ) 25 = 8 + (8 + 9) 25=8+(8+9), 24 = 7 + ( 7 + 10 ) 24 = 7 + (7 + 10) 24=7+(7+10) and 26 = 8 + ( 8 + 10 ) 26 = 8 + (8 + 10) 26=8+(8+10), respectively, thanks to the penalty, the second participant gets the first place, and Rudolf gets the second.
思路
题目就是ACM赛制,判断排名:
- 解题数目不同:题目多的排名靠前
- 解题数目相同:
- 罚时不同:罚时低的靠前
- 罚时相同:Rudolf靠前
只需要对结构体重载 < < <排序规则即可
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define debug(s, x) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
int num, min, c;
bool operator<(const node& w) const {
if (num != w.num) return num > w.num;
if (min != w.min) return min < w.min;
return c > w.c;
}
} node;
void solve() {
int n, m, h;
cin >> n >> m >> h;
vector<node> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
vector<int> b(m + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> b[i];
sort(b.begin() + 1, b.end());
int cnt = 0, sum = 0, cur = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (cur + b[i] <= h) {
cnt++;
cur += b[i];
sum += cur;
}
}
a[i] = {cnt, sum, 0};
// cout << "i=" << i<<" " << cnt << " " << sum << endl;
if (i == 1) a[i].c = 1;
}
sort(a.begin() + 1, a.end());
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i].c == 1) {
cout << i << endl;
return;
}
}
}
signed main() {
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
D. Rudolph and Christmas Tree
Rudolph drew a beautiful Christmas tree and decided to print the picture. However, the ink in the cartridge often runs out at the most inconvenient moment. Therefore, Rudolph wants to calculate in advance how much green ink he will need.
The tree is a vertical trunk with identical triangular branches at different heights. The thickness of the trunk is negligible.
Each branch is an isosceles triangle with base d d d and height h h h, whose base is perpendicular to the trunk. The triangles are arranged upward at an angle, and the trunk passes exactly in the middle. The base of the i i i-th triangle is located at a height of y i y_i yi.
The figure below shows an example of a tree with d = 4 , h = 2 d = 4, h = 2 d=4,h=2 and three branches with bases at heights [ 1 , 4 , 5 ] [1, 4, 5] [1,4,5].

Help Rudolph calculate the total area of the tree branches.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
Then follow the descriptions of the test cases.
The first line of each test case contains three integers n , d , h n, d, h n,d,h ( 1 ≤ n , d , h ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le n, d, h \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤n,d,h≤2⋅105) — the number of branches, the length of the base, and the height of the branches, respectively.
The second line of each test case contains n n n integers y i y_i yi ( 1 ≤ y i ≤ 1 0 9 , y 1 < y 2 < . . . < y n ) (1 \le y_i \le 10^9, y_1 < y_2 < ... < y_n) (1≤yi≤109,y1<y2<...<yn) — the heights of the bases of the branches.
The sum of n n n over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output a single real number on a separate line — the total area of the tree branches. The answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 1 0 − 6 10^{-6} 10−6.
Example
input
5
3 4 2
1 4 5
1 5 1
3
4 6 6
1 2 3 4
2 1 200000
1 200000
2 4 3
9 11
output
11
2.5
34.5
199999.9999975
11.333333
思路
最上面的三角形不可能被遮挡,就加整块三角形面积。
下面的三角形:
- 如果没有和上面的重叠( a [ i ] + h < = a [ i + 1 ] a[i]+h<=a[i+1] a[i]+h<=a[i+1]),则加整个三角形面积
- 重叠了,加梯型面积:设梯型高为 h − t = a [ i ] + h − a [ i + 1 ] h-t=a[i]+h-a[i+1] h−t=a[i]+h−a[i+1](t为重叠部分的高),利用相似三角形计算上底: x d = t h \frac{x}{d}=\frac{t}{h} dx=ht,得到: x = t d h x=\frac{td}{h} x=htd,因此梯型面积为: 0.5 ∗ ( t d h + d ) ∗ ( h − t ) 0.5*(\frac{td}{h}+d)*(h-t) 0.5∗(htd+d)∗(h−t)
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define debug(s, x) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n, d, h;
cin >> n >> d >> h;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
double s = 1.0 * d * h / 2;
double res = s;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] + h <= a[i + 1]) {
res += s;
} else {
double t = a[i] + h - a[i + 1];
res += 0.5 * (t * d / h + d) * (h - t);
}
}
printf("%.10f\n", res);
}
signed main() {
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
E1. Rudolf and Snowflakes (simple version)
This is a simple version of the problem. The only difference is that in this version n ≤ 1 0 6 n \le 10^6 n≤106.
One winter morning, Rudolf was looking thoughtfully out the window, watching the falling snowflakes. He quickly noticed a certain symmetry in the configuration of the snowflakes. And like a true mathematician, Rudolf came up with a mathematical model of a snowflake.
He defined a snowflake as an undirected graph constructed according to the following rules:
- Initially, the graph has only one vertex.
- Then, more vertices are added to the graph. The initial vertex is connected by edges to k k k new vertices ( k > 1 k > 1 k>1).
- Each vertex that is connected to only one other vertex is connected by edges to k k k more new vertices. This step should be done at least once.
The smallest possible snowflake for k = 4 k = 4 k=4 is shown in the figure.

After some mathematical research, Rudolf realized that such snowflakes may not have any number of vertices. Help Rudolf check if a snowflake with n n n vertices can exist.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
Then follow the descriptions of the test cases.
The first line of each test case contains an integer n n n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 6 1 \le n \le 10^6 1≤n≤106) — the number of vertices for which it is necessary to check the existence of a snowflake.
Output
Output t t t lines, each of which is the answer to the corresponding test case — “YES” if there exists such k > 1 k > 1 k>1 for which a snowflake with the given number of vertices can be constructed; “NO” otherwise.
Example
input
9
1
2
3
6
13
15
255
10101
1000000
output
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO
思路
从题目可以看出,出现的n只可能是 1 + k + k 2 + k 3 + . . . + k x ( k > = 2 , x > = 2 ) 1+k+k^2+k^3+...+k^x(k>=2,x>=2) 1+k+k2+k3+...+kx(k>=2,x>=2)
n最多到 1 e 6 1e6 1e6,因此 k k k最多到 1 e 3 1e3 1e3,
只需要遍历 k ∈ [ 2 , 1000 ] k\in[2,1000] k∈[2,1000],计算式的值,如果 > 1 e 6 >1e6 >1e6就跳出,继续判断下一个k,可以塞到set里面,每次输入n,判断是否在set里即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define debug(s, x) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
set<int> s;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
if (s.count(n)) yes else no
}
signed main() {
for (int k = 2; k <= 1000; k++) {
int res = 1 + k + k * k;
if (res <= 1e6) s.insert(res);
for (int i = 3;; i++) {
res += pow(k, i);
if (res <= 1e6)
s.insert(res);
else
break;
}
}
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
E2. Rudolf and Snowflakes (hard version)
思路
1 + k + k 2 + k 3 + . . . + k x 显然是一个等比数列 1+k+k^2+k^3+...+k^x显然是一个等比数列 1+k+k2+k3+...+kx显然是一个等比数列,
等比数列求和公式为 s n = a 1 1 − q n 1 − q s_n=a_1\frac{1-q^n}{1-q} sn=a11−q1−qn
计算得到 S n = k x − 1 k − 1 S_n=\frac{k^x-1}{k-1} Sn=k−1kx−1,因为 S n S_n Sn不会超过 1 0 18 10^{18} 1018,因此指数x最多取到64,我们可以遍历指数 x ∈ [ 2 , 64 ] x\in[2,64] x∈[2,64],当指数不变的时候,显然k越大,这个雪花图就会越大,顶点就越多,因此当指数不变的时候,顶点具有单调性,可以二分 k ∈ [ 2 , 1 0 9 ] k \in [2,10^9] k∈[2,109];
注意计算的时候会爆long long ,可以使用__int128进行计算,一旦__超过longlong最大值,可以直接返回,当作一个技巧吧。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) \
if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
int check(int k, int x) {
__int128 t = 1, cur = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++) {
cur *= k;
t += cur;
if (t >= 2e18) {
return 2e18;
}
}
return (int)t;
}
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int x = 2; x <= 63; x++) {
int l = 2, r = 1e9;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int t = check(mid, x);
if (t >= n)
r = mid;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
if (check(l, x)==n) {
yes return;
}
}
no;
}
signed main() {
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
F. Rudolph and Mimic
This is an interactive task.
Rudolph is a scientist who studies alien life forms. There is a room in front of Rudolph with n n n different objects scattered around. Among the objects there is exactly one amazing creature — a mimic that can turn into any object. He has already disguised himself in this room and Rudolph needs to find him by experiment.
The experiment takes place in several stages. At each stage, the following happens:
- Rudolf looks at all the objects in the room and writes down their types. The type of each object is indicated by a number; there can be several objects of the same type.
- After inspecting, Rudolph can point to an object that he thinks is a mimic. After that, the experiment ends. Rudolph only has one try, so if he is unsure of the mimic’s position, he does the next step instead.
- Rudolf can remove any number of objects from the room (possibly zero). Then Rudolf leaves the room and at this time all objects, including the mimic, are mixed with each other, their order is changed, and the mimic can transform into any other object (even one that is not in the room).
- After this, Rudolf returns to the room and repeats the stage. The mimic may not change appearance, but it can not remain a same object for more than two stages in a row.
Rudolf’s task is to detect mimic in no more than five stages.
Input
The first line contains one integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1000 ) (1 \le t \le 1000) (1≤t≤1000) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains one integer n n n ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 200 ) (2 \le n \le 200) (2≤n≤200) — the number of objects in the room.
The second line of each test case contains n n n integers a 1 a_1 a1, a 2 a_2 a2,…, a n a_n an ( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 9 ) (1 \le a_i \le 9) (1≤ai≤9) — object types.
Interaction
After you have read the description of the input data set, you must make no more than 5 5 5 queries. Reading the input data is considered the beginning of the first stage, and the mimic may already begin to change.
The request is a line. The first character of the line indicates the request type. To remove objects, print “-”. After that print the number k k k — how many objects you want to remove. Then there are k k k numbers — indexes of objects in their current location. Indexing starts from one. You can remove the mimic, but in this case you will not be able to point to it and will get “Wrong answer” verdict.
In response to the request you will receive a line containing integers — the objects remaining in the room after removal and mixing.
To indicate the position of a mimic, print “!”, then print the index of the object that is the mimic.
The task will be considered solved if the position of the mimic is specified correctly.
If you make more than five requests, or make an invalid request, the solution will get “Wrong answer” verdict.
After outputting a query or the answer do not forget to output the end of line and flush the output. Otherwise, you will get “Idleness limit exceeded”. To do this, use:
- fflush(stdout) or cout.flush() in C++;
- System.out.flush() in Java;
- flush(output) in Pascal;
- stdout.flush() in Python;
- see documentation for other languages.
Hacks
You can hack a solution with the following input format.
The first line contains one integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1000 ) (1 \le t \le 1000) (1≤t≤1000) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n n n, k k k ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 200 , 1 ≤ k ≤ n 2 \le n \le 200, 1 \le k \le n 2≤n≤200,1≤k≤n) — the number of objects and the position of the mimic.
The second line contains of each test case n n n integers a 1 a_1 a1, a 2 a_2 a2,…, a n a_n an ( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 9 1 \le a_i \le 9 1≤ai≤9) – initial array of objects.
Example
input
3
5
1 1 2 2 3
2 1 1 2
2 2 2
2
8
1 2 3 4 3 4 2 1
4 3 4 3 2 2 1 3
2 3 3 2
5 3 2
2 5
15
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 7 9 5 4 3 2 1
output
- 1 5
- 1 3
- 2 1 2
! 1
- 0
- 4 1 3 7 8
- 1 4
- 1 2
! 2
- 0
! 10
思路
因为物品不可以连续超过两个回合不变为其他的,因此可以
- 先一直输出 − 0 - 0 −0,即不删除任何元素,直到这个物品变为其他物品,这个操作一定不会超过两次,此时统一每个物品的个数,会有一个比一开始多一个,这个就是变化来的物品,
- 接着可以输出
- cnt个 cnt个元素,即把变化的那个物品之外的其他物品全部删除。 - 接着继续一直输出
- 0,不删除元素,物品不超过两个回合会变成其他的,因此编号也会和其他的不同,此时可以得到物品的位置。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) \
if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int idx;
vector<int> a(n + 1), cnt(20);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
cnt[a[i]]++;
}
while (1) {
cout << "- 0" << endl;
vector<int> b(20);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
b[a[i]]++;
}
bool ok = false;
for (idx = 1; idx <= 9; idx++) {
if (b[idx] == cnt[idx]+1) {
ok = true;
break;
}
}
if (ok) break;
}
int t = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i] != idx) {
t++;
}
}
cout << "- " << t << " ";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i] != idx) {
cout << i << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
n -= t;
while (1) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i] != idx) {
cout << "! " << i << endl;
return;
}
}
cout << "- 0" << endl;
}
}
signed main() {
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
G. Rudolf and CodeVid-23
A new virus called “CodeVid-23” has spread among programmers. Rudolf, being a programmer, was not able to avoid it.
There are n n n symptoms numbered from 1 1 1 to n n n that can appear when infected. Initially, Rudolf has some of them. He went to the pharmacy and bought m m m medicines.
For each medicine, the number of days it needs to be taken is known, and the set of symptoms it removes. Unfortunately, medicines often have side effects. Therefore, for each medicine, the set of symptoms that appear when taking it is also known.
After reading the instructions, Rudolf realized that taking more than one medicine at a time is very unhealthy.
Rudolph wants to be healed as soon as possible. Therefore, he asks you to calculate the minimum number of days to remove all symptoms, or to say that it is impossible.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 100 ) (1 \le t \le 100) (1≤t≤100) — the number of test cases.
Then follow the descriptions of the test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n , m n, m n,m ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 10 , 1 ≤ m ≤ 1 0 3 ) (1 \le n \le 10, 1 \le m \le 10^3) (1≤n≤10,1≤m≤103) — the number of symptoms and medicines, respectively.
The second line of each test case contains a string of length n n n consisting of the characters 0 0 0 and 1 1 1 — the description of Rudolf’s symptoms. If the i i i-th character of the string is 1 1 1, Rudolf has the i i i-th symptom, otherwise he does not.
Then follow 3 ⋅ m 3 \cdot m 3⋅m lines — the description of the medicines.
The first line of each medicine description contains an integer d d d ( 1 ≤ d ≤ 1 0 3 ) (1 \le d \le 10^3) (1≤d≤103) — the number of days the medicine needs to be taken.
The next two lines of the medicine description contain two strings of length n n n, consisting of the characters 0 0 0 and 1 1 1 — the description of the symptoms it removes and the description of the side effects.
In the first of the two lines, 1 1 1 at position i i i means that the medicine removes the i i i-th symptom, and 0 0 0 otherwise.
In the second of the two lines, 1 1 1 at position i i i means that the i i i-th symptom appears after taking the medicine, and 0 0 0 otherwise.
Different medicines can have the same sets of symptoms and side effects. If a medicine relieves a certain symptom, it will not be among the side effects.
The sum of m m m over all test cases does not exceed 1 0 3 10^3 103.
Output
For each test case, output a single integer on a separate line — the minimum number of days it will take Rudolf to remove all symptoms. If this never happens, output − 1 -1 −1.
Example
input
4
5 4
10011
3
10000
00110
3
00101
00000
3
01010
00100
5
11010
00100
4 1
0000
10
1011
0100
2 2
11
2
10
01
3
01
10
2 3
11
3
01
10
3
10
00
4
10
01
output
8
0
-1
6
思路
n为10,考虑状态压缩,一共有 2 n 2^n 2n个状态 即 2 n 2^n 2n个点, 药剂可以看成可以让你从一种状态变为另外一种状态,天数就是这两个状态的边的权值。
考虑初始状态为 u ∈ [ 0 , 2 n − 1 ] u \in [0,2^n-1] u∈[0,2n−1],一种药的正作用为A,副作用为B,最终得到的状态为 v v v
- 在正作用的作用下:将A的二进制各位取反,然后与u进行与操作,即 v = u & ( ~ A ) v=u\&(~A) v=u&(~A),可以将A中可以消除的病在u中消除
- 在副作用的作用下:上一步得到的 v v v与B只要有一个为1,则这个病就不可以消除,即 v = v ∣ B v=v|B v=v∣B
最后从起点 s s s开始,计算变化到 0 0 0的最短路径,可以使用 d i j k s t r a dijkstra dijkstra算法进行求解。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) \
if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
const int N = 1200;
typedef struct node {
int y, w;
} node;
vector<node> e[N];
vector<int> dist(N);
int n, m;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i++) e[i].clear();
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i++) dist[i] = 1e18;
string s;
cin >> s;
auto cal = [&](string s) -> int {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = res * 2 + s[i] - '0';
}
return res;
};
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int d;
cin >> d;
string a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int A = cal(a), B = cal(b);
for (int u = 0; u < (1 << n); u++) {
int v = (u & (~A)) | B;
e[u].push_back({v, d});
}
}
vector<bool> st(1 << n);
int begin = cal(s);
int end = 0;
priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, greater<>> q;
q.push({0, begin});
dist[begin] = 0;
while (q.size()) {
auto [d, x] = q.top();
q.pop();
if (st[x]) continue;
st[x] = true;
for (auto [y, w] : e[x]) {
if (dist[y] > dist[x] + w) {
dist[y] = dist[x] + w;
q.push({dist[y], y});
}
}
}
if (dist[0] == 1e18) {
dist[0] = -1;
}
cout << dist[0] << endl;
}
signed main() {
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}







![[NOI2014] 随机数生成器(模拟+贪心)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/14190904ddd04d929c8b64d1437a1f47.png)

