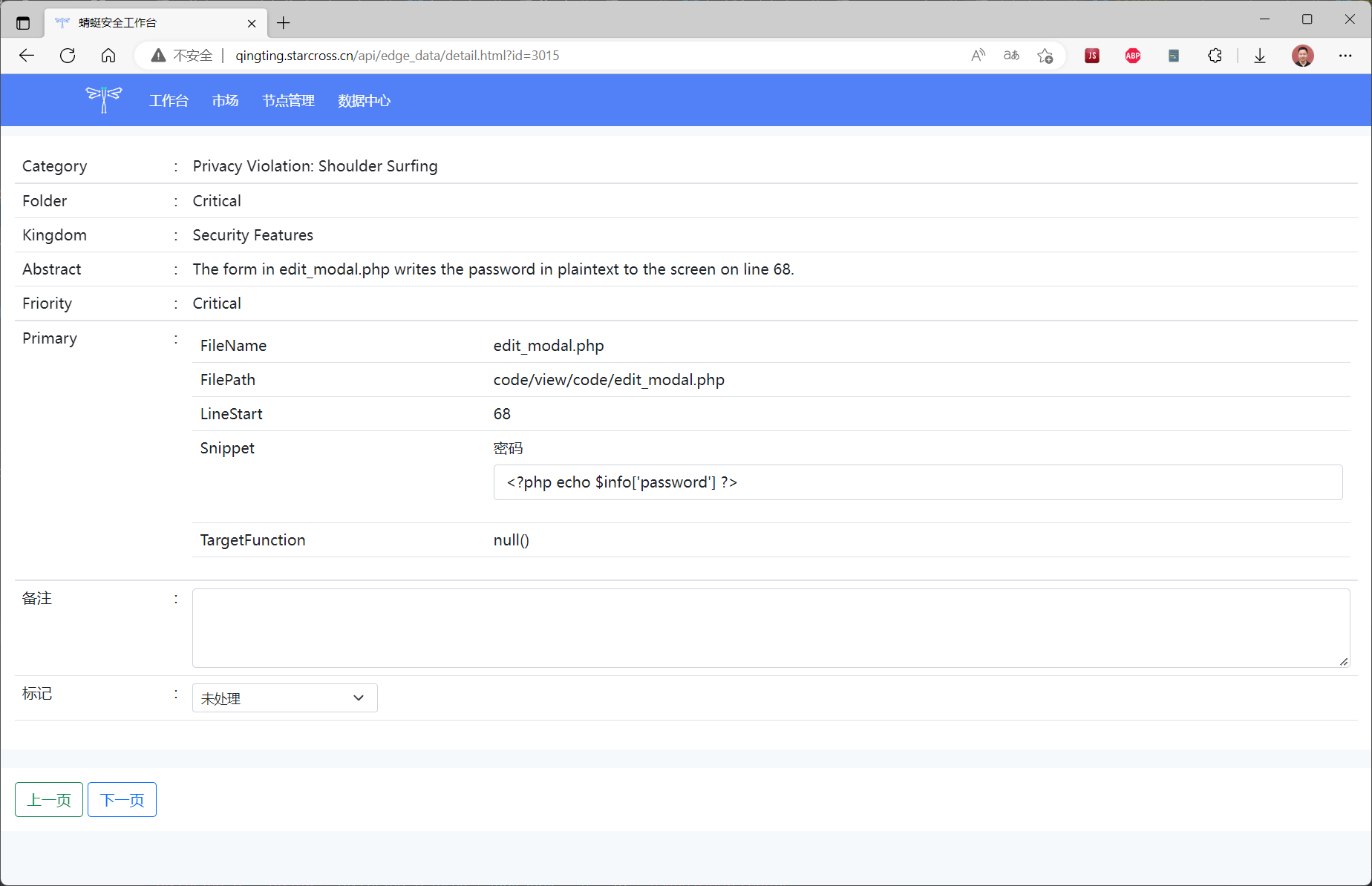
====================================================================
java.io中的对象流提供了序列化和反序列化对象的方法
对象输出流 ObjectOutputStream
构造方法:
ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out)
保存对象的方法:
void writeObject(Object obj)
对象输入流 ObjectInputStream
构造方法:
ObjectInputStream(InputStream out)
读取对象方法:
Object readObject()
-
只有实现了Serializable接口的对象,才能序列化,否则会抛出NotSerializableException
-
如果父类实现了Serializable接口,子类可以不实现该接口
-
类要序列化,类所有的属性也要序列化
-
声明为static和transient类型的属性不能被序列化
这个案例演示分别把一头大象和多头大象保存到磁盘文件中。
/**
-
大象
*/
public class Elephant implements Serializable{
/**
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2483988729860853698L;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double weight;
public String getName() {
ret

urn name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public Elephant(String name, int age, double weight) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.weight = weight;
}
public Elephant() {
super();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return “Elephont [name=” + name + “, age=” + age + “, weight=” + weight + “]”;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println(name+“在跑!!!!”);
}
}
@Test
public void testObjectOutput(){
//创建对象输出流
try(ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(“C:/xpp/object”))){
//存入Java对象
out.writeObject(new Elephant(“非洲大象”,20,5000));
//存入对象集合
List list = Arrays.asList(
new Elephant(“非洲大黑象”,10,10000),
new Elephant(“非洲小黑象”,10,10000),
new Elephant(“亚洲小黑象”,10,10000),
new Elephant(“亚洲大黑象”,10,10000),
new Elephant(“亚洲小白象”,10,10000));
out.writeObject(list);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void testObjectInput(){
//创建对象输入流
try(ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream(“C:/xpp/object”))){
//读取Java对象
Elephant elephont = (Elephant) in.readObject();
elephont.run();
//读取对象集合
List list = (List) in.readObject();
for(Elephant ele : list){
ele.run();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
我们看到无论是一个Java对象,或是一个Java集合都可以序列化到文件中,因为Java所有的集合也都实现了Serializable接口。
当一个类实现序列化接口后,IDE会出现编译警告,并提示生成一个serialVersionUID。
也就是类中的常量:
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2483988729860853698L;
那么这个常量的作用是什么呢?
集合也都实现了Serializable接口。
当一个类实现序列化接口后,IDE会出现编译警告,并提示生成一个serialVersionUID。
也就是类中的常量:
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2483988729860853698L;
那么这个常量的作用是什么呢?