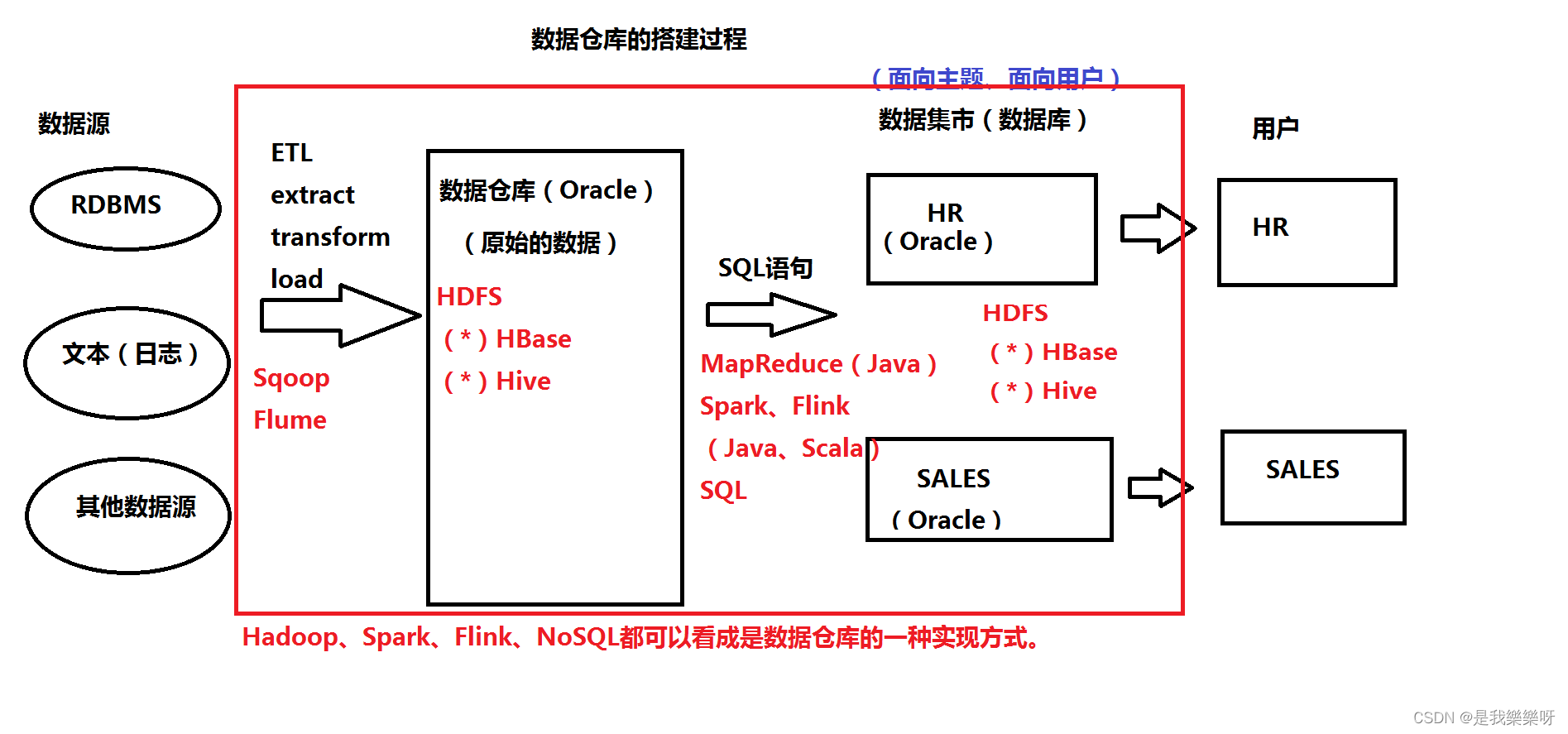
一、知识点整理
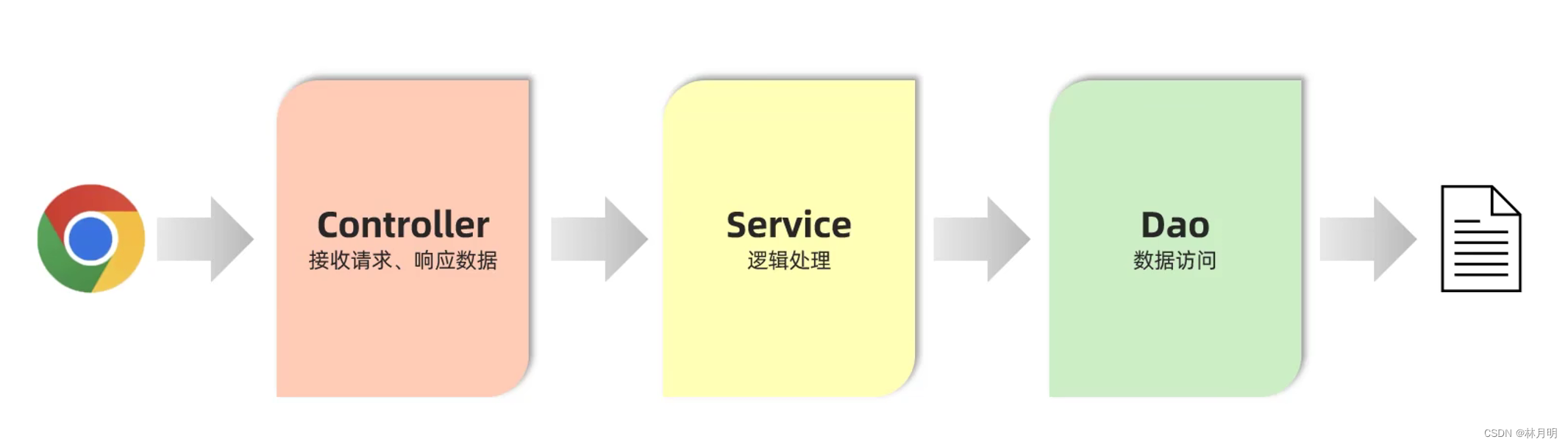
三层架构的含义
Controller: 控制层,接收前端发送的请求,对请求进行处理,并响应数据。
Service:业务逻辑层,处理具体的业务逻辑。
Dao(Data Access Object): 数据访问层(持久层),负责数据访问操作,包括数据的增、删、改、查。
二、代码实现
原EmpController.java文件中的代码:
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.pojo.Emp;
import com.example.pojo.Result;
import com.example.service.EmpService;
import com.example.service.impl.EmpServiceA;
import com.example.utils.XmlParserUtils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonTypeId;
import jdk.jshell.spi.ExecutionControl;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class EmpController {
@RequestMapping("/listEmp")
public Result list(){
//1、加载并解析emp.xml
String file=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("emp.xml").getFile();
System.out.println(file);
List<Emp> empList= XmlParserUtils.parse(file,Emp.class);
//2、对数据进行转换处理
empList.stream().forEach(emp->{
//book 1:十二钗正册,2:十二钗副册,3:十二钗又副册
String book=emp.getBook();
if("1".equals(book)){
emp.setBook("十二钗正册");
}
else if("2".equals(book)){
emp.setBook("十二钗副册");
}
else if("3".equals(book)){
emp.setBook("十二钗又副册");
}
String job=emp.getJob();
if("1".equals(job)){
emp.setJob("夫人");
}
else if("2".equals(job)){
emp.setJob("小姐");
}
else if("3".equals(job)){
emp.setJob("丫鬟");
}
});
//3、响应数据
return Result.success(empList);
}
}
将其进行分层处理:
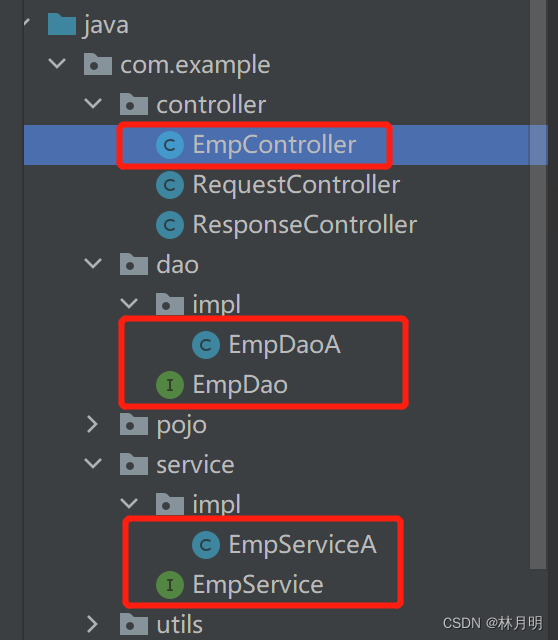
1、Dao数据访问
package com.example.dao;
import com.example.pojo.Emp;
import java.util.List;
public interface EmpDao {
//获取员工列表数据
public List<Emp> listEmp();
}
package com.example.dao.impl;
import com.example.dao.EmpDao;
import com.example.pojo.Emp;
import com.example.utils.XmlParserUtils;
import java.util.List;
public class EmpDaoA implements EmpDao {
@Override
public List<Emp> listEmp() {
//1、加载并解析emp.xml
String file=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("emp.xml").getFile();
System.out.println(file);
List<Emp> empList= XmlParserUtils.parse(file,Emp.class);
return empList;
}
}
2、Service逻辑处理
package com.example.service;
import com.example.pojo.Emp;
import java.util.List;
public interface EmpService {
//获取员工列表
public List<Emp> listEmp();
}
package com.example.service.impl;
import com.example.dao.EmpDao;
import com.example.dao.impl.EmpDaoA;
import com.example.pojo.Emp;
import com.example.service.EmpService;
import java.util.List;
public class EmpServiceA implements EmpService {
//在service中调用dao
private EmpDao empdao=new EmpDaoA();
@Override
public List<Emp> listEmp() {
//1、调用dao,获取数据
List<Emp> empList=empdao.listEmp();
//2、对数据进行转换处理
empList.stream().forEach(emp->{
//book 1:十二钗正册,2:十二钗副册,3:十二钗又副册
String book=emp.getBook();
if("1".equals(book)){
emp.setBook("十二钗正册");
}
else if("2".equals(book)){
emp.setBook("十二钗副册");
}
else if("3".equals(book)){
emp.setBook("十二钗又副册");
}
String job=emp.getJob();
if("1".equals(job)){
emp.setJob("夫人");
}
else if("2".equals(job)){
emp.setJob("小姐");
}
else if("3".equals(job)){
emp.setJob("丫鬟");
}
});
return empList;
}
}
3、Controller接收请求,响应数据
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.pojo.Emp;
import com.example.pojo.Result;
import com.example.service.EmpService;
import com.example.service.impl.EmpServiceA;
import com.example.utils.XmlParserUtils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonTypeId;
import jdk.jshell.spi.ExecutionControl;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class EmpController {
//定义面向service层的对象
private EmpService empService=new EmpServiceA();
@RequestMapping("/listEmp")
public Result list(){
//1、调用service,获取数据
List<Emp> empList=empService.listEmp();
//3、响应数据
return Result.success(empList);
}
}
package com.example.pojo;
public class Result {
private Integer code;//1:成功,0:失败
private String msg;//提示信息
private Object data;//数据
public Result(){
}
public Result(Integer code,String msg,Object data){
this.code=code;
this.msg=msg;
this.data=data;
}
public Integer getCode(){return code;}
public void setCode(Integer code){this.code=code;}
public String getMsg() {return msg;}
public void setMsg(String msg) {this.msg = msg;}
public Object getData() {return data;}
public void setData(Object data) {this.data = data;}
public static Result success(Object data){
return new Result(1,"success",data);
}
public static Result success(){
return new Result(0,"success",null);
}
public static Result error(String msg){
return new Result(0,msg,null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Result{"+
"code="+code+
",msg="+msg+'\''+
",data="+data+
"}";
}
}
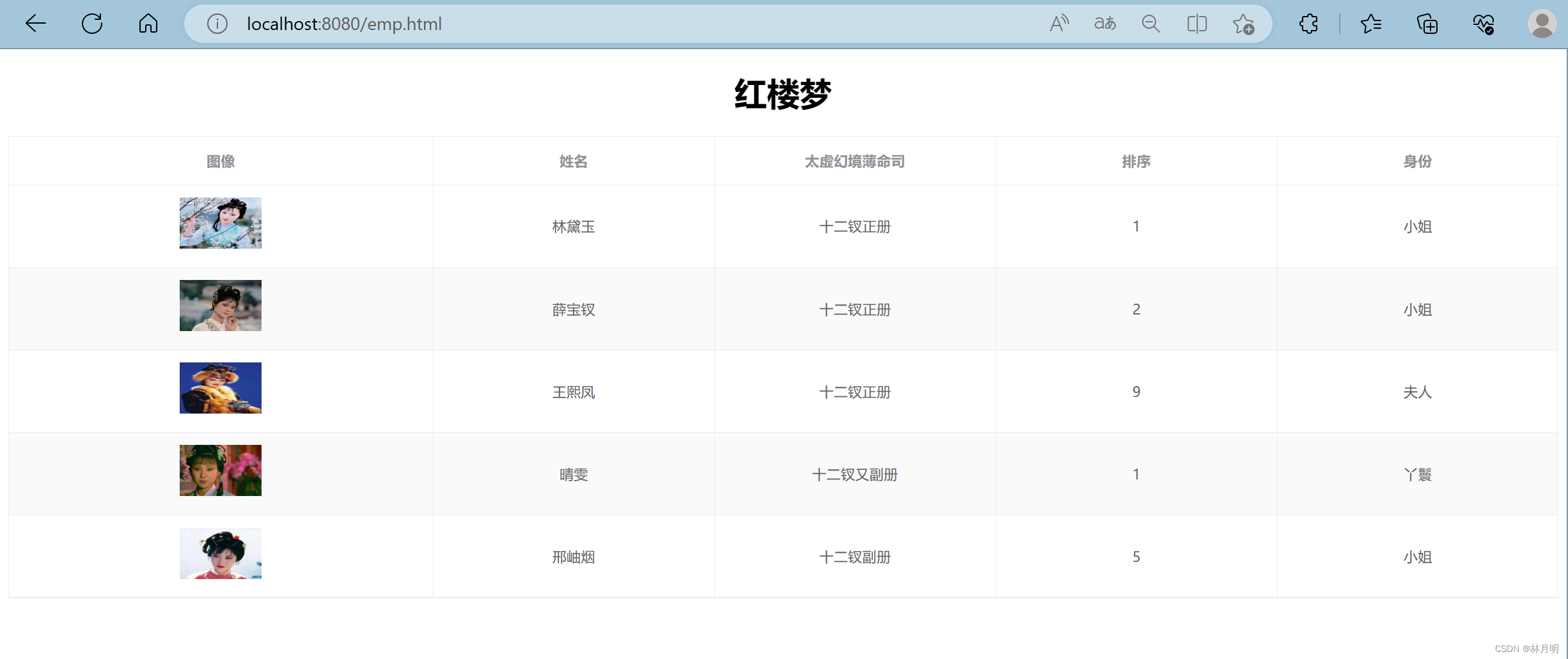
4、运行效果
三、总结
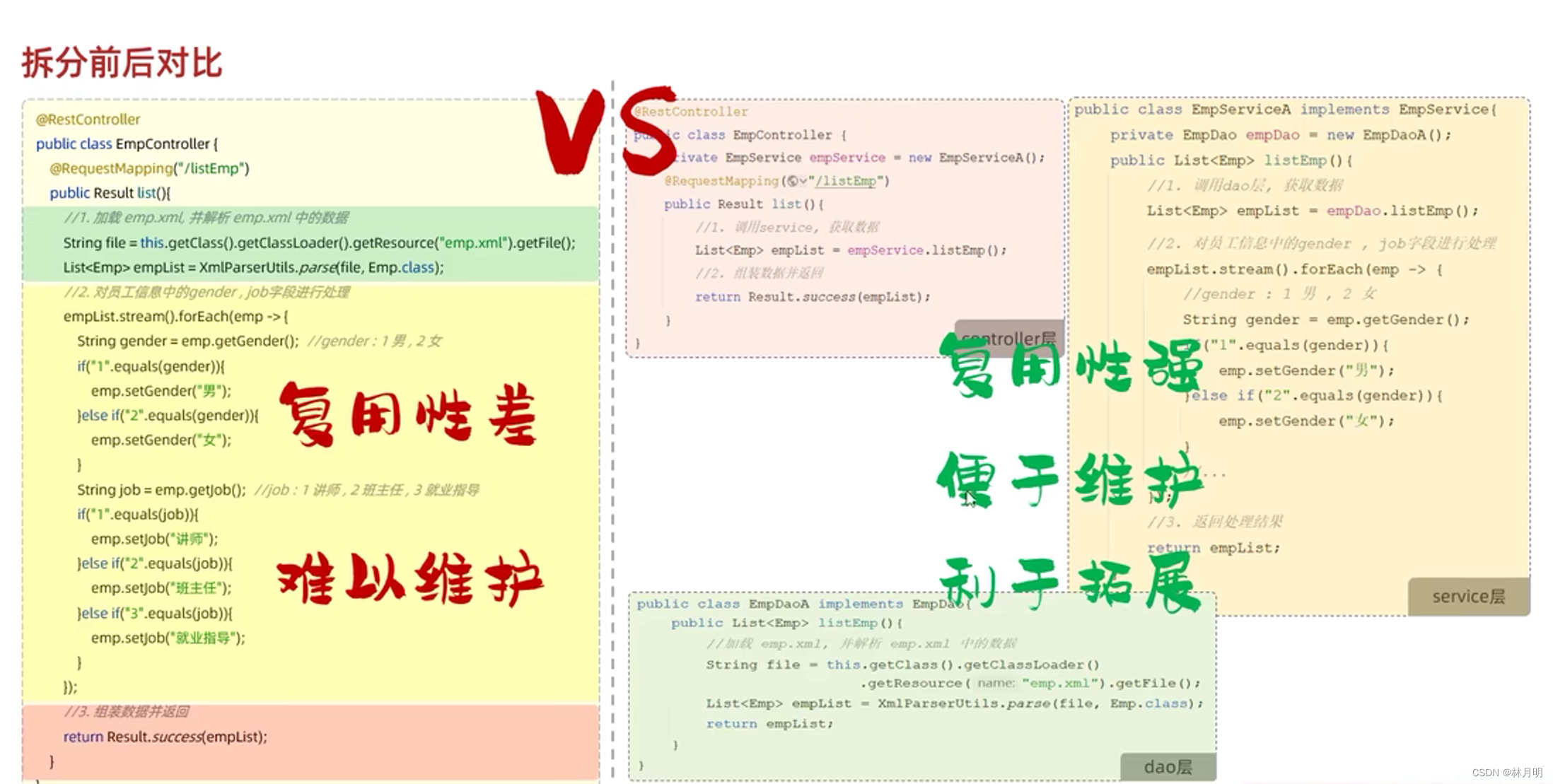
三层架构优点:
1、复用性强
2、便于维护
3、利于拓展
四、学习教程
分层解耦https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1m84y1w7Tb?p=76&spm_id_from=pageDriver&vd_source=841fee104972680a6cac4dbdbf144b50