GraphQL
hello world
首先我们要安装好执行GraphQL的环境
因为其是运行在node服务器端的,所以我们要安装
express express-graphql graphql mongoose
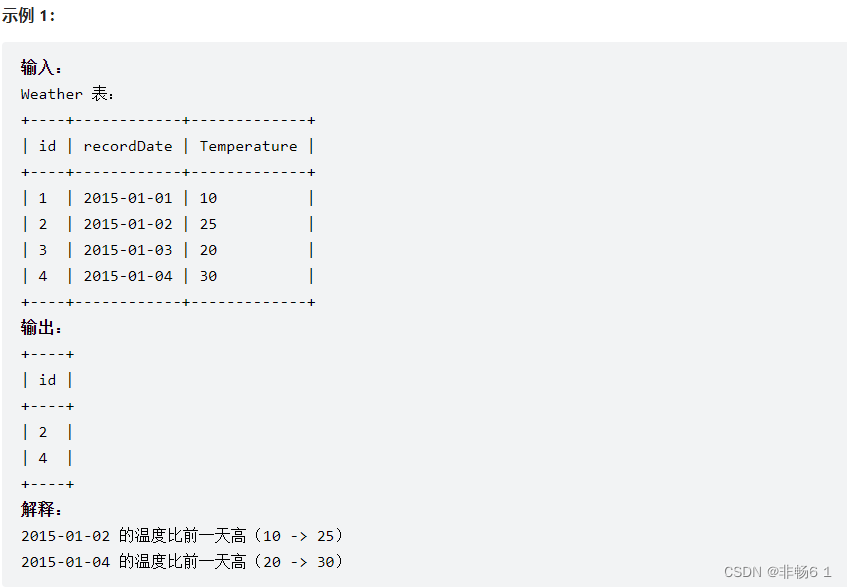
安装好后的package.json文件是这个样子的
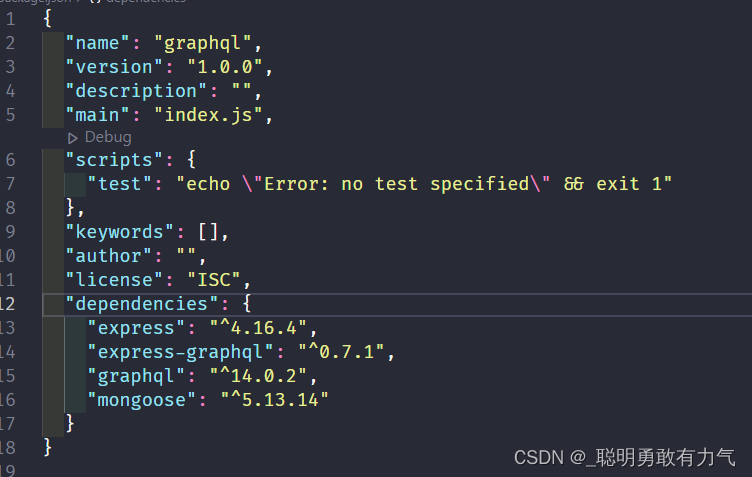
其次我们就要开始配置端口为3000的node服务器
const express = require('express')
var app = express()
app.lisiten(3000)
最后 我们结合graphql
完整代码如下
const express = require('express')
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql')
const graphqlHttp = require('express-graphql')
var Schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
hello: String,
getName: String,
getAge: Int
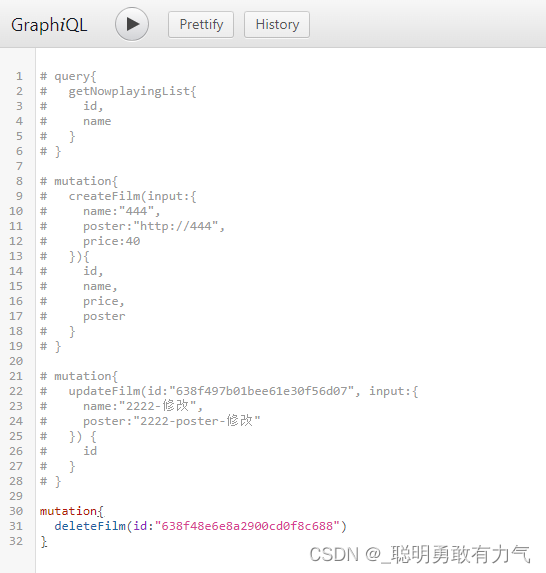
}
`)
//处理器
const root = {
hello: () => {
//通过数据库查询
var str = 'hello world111';
return str;
},
getName: () => {
return 'kobe';
},
getAge: () => {
return 100;
},
};
var app = express();
app.use(
'/graphql',
graphqlHttp({
schema: Schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
})
);
app.listen(3000);
运行此js文件
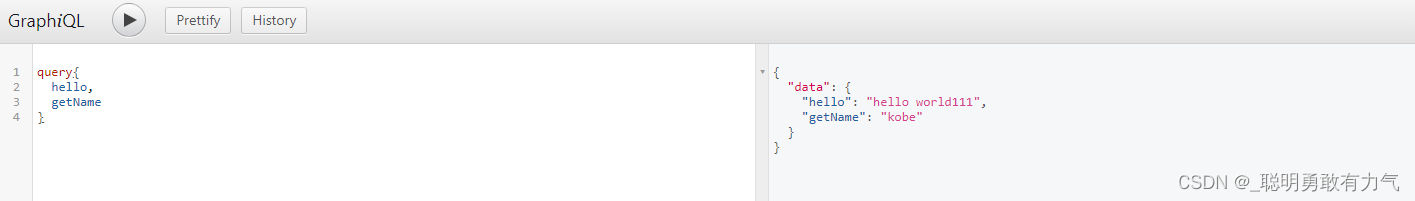
访问localhost:3000/graphql
我们就会看到如下页面,输入Query对象里面填写要查找的元素,点击运行就可以查到响应的数据
types
我们在上面的案例中可以看到
在定义Schema时 要定义类型type
那么数组是怎么定义呢?按照特定值查找又怎么定义呢?或者我们怎么自己定义一个类型呢?
这里的写法与typescript相似
我们可以使用[String] 或 [Int] 定义一个字符串数组或数字数组 我们也可以自己定义一个对象类型
type Film{
id: Int,
name: String,
poster: String,
price: Int
}
type Query{
hello: String,
getName: String,
getAge: Int,
getAllNames: [String],
getAllAges: [Int],
getAccountInfo: Account,
getNowplayingList: [Film],
getFilmDetail(id: Int!): Film
}
当我们使用!时表示此项必须传
完整代码如下
const express = require('express');
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
const graphqlHttp = require('express-graphql');
var Schema = buildSchema(`
type Account{
name: String,
age: Int,
location: String
}
type Film{
id: Int,
name: String,
poster: String,
price: Int
}
type Query{
hello: String,
getName: String,
getAge: Int,
getAllNames: [String],
getAllAges: [Int],
getAccountInfo: Account,
getNowplayingList: [Film],
getFilmDetail(id: Int!): Film
}
`);
var fakeDb = [
{
id: 1,
name: '1111',
poster: 'http://1111',
price: 100,
},
{
id: 2,
name: '2222',
poster: 'http://2222',
price: 200,
},
{
id: 1,
name: '3333',
poster: 'http://3333',
price: 300,
},
];
//处理器
const root = {
hello: () => {
//通过数据库查询
var str = 'hello world111';
return str;
},
getName: () => {
return 'kobe';
},
getAge: () => {
return 100;
},
getAllNames: () => {
return ['xiaohu', 'xiaoming', 'xiaowei'];
},
getAllAges: () => {
return [18, 19, 300];
},
getAccountInfo() {
return {
name: 'kobe',
age: 100,
location: 'hangzhou',
};
},
getNowplayingList() {
return fakeDb;
},
getFilmDetail({ id }) {
console.log(id);
return fakeDb.filter((item) => item.id === id)[0];
},
};
var app = express();
app.use(
'/graphql',
graphqlHttp({
schema: Schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
})
);
app.listen(3000);
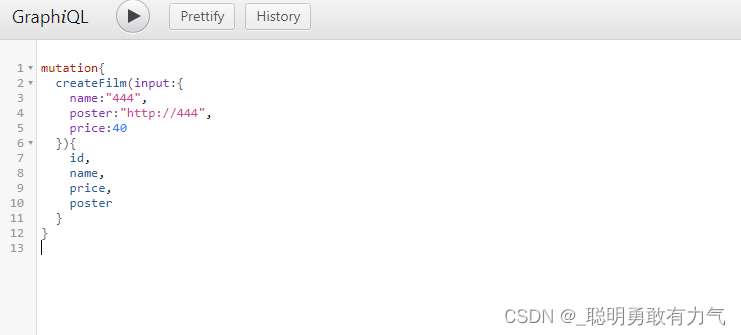
mutation
我们之前只定义了Query查找 那么怎么进行添加修改与删除呢
如果我们想要添加 就不能使用type 而是要使用input
而修改与删除则是使用Mytation
input FilmInput {
name: String,
poster: String,
price: Int
}
type Mutation {
createFilm(input: FilmInput): Film,
updateFilm(id: Int!, input: FilmInput): Film,
deleteFilm(id: Int!): Int
}
完整代码如下
const express = require('express');
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
const graphqlHttp = require('express-graphql');
var Schema = buildSchema(`
type Film {
id: Int,
name: String,
poster: String,
price: Int
}
input FilmInput {
name: String,
poster: String,
price: Int
}
type Query {
getNowplayingList: [Film],
}
type Mutation {
createFilm(input: FilmInput): Film,
updateFilm(id: Int!, input: FilmInput): Film,
deleteFilm(id: Int!): Int
}
`);
var fakeDb = [
{
id: 1,
name: '1111',
poster: 'http://1111',
price: 100,
},
{
id: 2,
name: '2222',
poster: 'http://2222',
price: 200,
},
{
id: 1,
name: '3333',
poster: 'http://3333',
price: 300,
},
];
//处理器
const root = {
getNowplayingList() {
return fakeDb;
},
createFilm({ input }) {
var obj = { ...input, id: fakeDb.length + 1 };
fakeDb.push(obj);
return obj;
},
updateFilm({ id, input }) {
console.log(id, input);
var current = null;
fakeDb = fakeDb.map((item) => {
if (item.id === id) {
current = { ...item, ...input };
return { ...item, ...input };
}
return item;
});
return current;
},
deleteFilm({ id }) {
fakeDb = fakeDb.filter((item) => item.id !== id);
return 1;
},
};
var app = express();
app.use(
'/graphql',
graphqlHttp({
schema: Schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
})
);
app.listen(3000);
而且我们对于创建 修改 删除 使用的不再是query 而是mutation
真实数据库操作
上面我们的操作都是针对自己定义的假数据
现在我们对真实数据库操作
首先连接数据库 使用mongoose
var mongoose = require('mongoose')
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/suibian',{
useNewUrlParse: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
})
那个suibian是自己填的可以根据自己需要进行修改
var GilmMode = mongoose.model(
'film',
new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
poster: String,
price: Number
})
)
graphql非常好的一点是 处理器root里面的方法的返回值可以是一个promise对象
而mongoose操作返回的正好是一个promise对象 所以可以直接返回
完整代码如下
const express = require('express');
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
const graphqlHttp = require('express-graphql');
//-------------------连接数据库服务----------------------
var mongoose = require('mongoose');
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/maizuo', {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
});
//限制 数据库这个films(集合表) 只能存3个字段
var FilmModel = mongoose.model(
'film',
new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
poster: String,
price: Number,
})
);
//FilmModel.create
//FilmModel.find
//FilmModel.update
//FilmModel.delete
//-----------------------------------------------------
var Schema = buildSchema(`
type Film {
id: String,
name: String,
poster: String,
price: Int
}
input FilmInput {
name: String,
poster: String,
price: Int
}
type Query {
getNowplayingList: [Film],
}
type Mutation {
createFilm(input: FilmInput): Film,
updateFilm(id: String!, input: FilmInput): Film,
deleteFilm(id: String!): Int
}
`);
//处理器
const root = {
getNowplayingList() {
return FilmModel.find();
},
createFilm({ input }) {
/*
1.创建模型
2.操作数据库
*/
//返回一个promise对象
return FilmModel.create({
...input,
});
},
updateFilm({ id, input }) {
return FilmModel.updateOne(
{
_id: id,
},
{
...input,
}
)
.then((res) => FilmModel.find({ _id: id }))
.then((res) => res[0]);
},
deleteFilm({ id }) {
return FilmModel.deleteOne({ _id: id }).then((res) => 1);
},
};
var app = express();
app.use(
'/graphql',
graphqlHttp({
schema: Schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
})
);
app.listen(3000);