一、实验目标
生成拉普拉斯分布的噪声,并分析它的概率密度函数
二、解决思路
(1)拉普拉斯分布可以由指数分布生成
拉普拉斯的概率密度函数为
f
(
x
;
μ
,
λ
)
=
1
2
λ
e
−
∣
x
−
μ
∣
λ
f(x;\mu,\lambda)=\frac{1}{2 \lambda} e^{-\frac{|x-\mu|}{\lambda}}
f(x;μ,λ)=2λ1e−λ∣x−μ∣
而指数分布的概率密度函数为
f
(
x
)
=
λ
e
−
λ
x
,
x
>
0
f
(
x
)
=
0
,
x
≤
0
\begin{gathered} f(x)=\lambda e^{-\lambda x}, x>0 \\ f(x)=0, x \leq 0 \end{gathered}
f(x)=λe−λx,x>0f(x)=0,x≤0
由上可知,当
μ
=
0
\mu = 0
μ=0时,拉普拉斯分布的正半部分是尺度参数为
1
/
λ
1/\lambda
1/λ的指数分布的一半。
且拉普拉斯分布的概率密度函数是左右对称的,由此可以通过指数分布生成拉普拉斯分布。
(2)使用ksdensity函数估计生成的拉普拉斯变量的概率密度函数
三、实验代码
主函数:main.m
close all;clc;clear all;
%% 参数设置
length = 5000000;
lambda = 1;
%% 生成噪声
y = randlap(length,lambda); % 生成拉普拉斯噪声
%% 概率密度计算
% 估计概率密度
[yy,x]=ksdensity(y);
% 计算概率密度理论值
xx = transpose(-5:1e-1:5);
miu = 0;
probablity = 1 / ( 2*lambda ) * exp( -abs(xx-miu) / lambda );
%% 作图
figure;xlabel('x');ylabel('PDF');
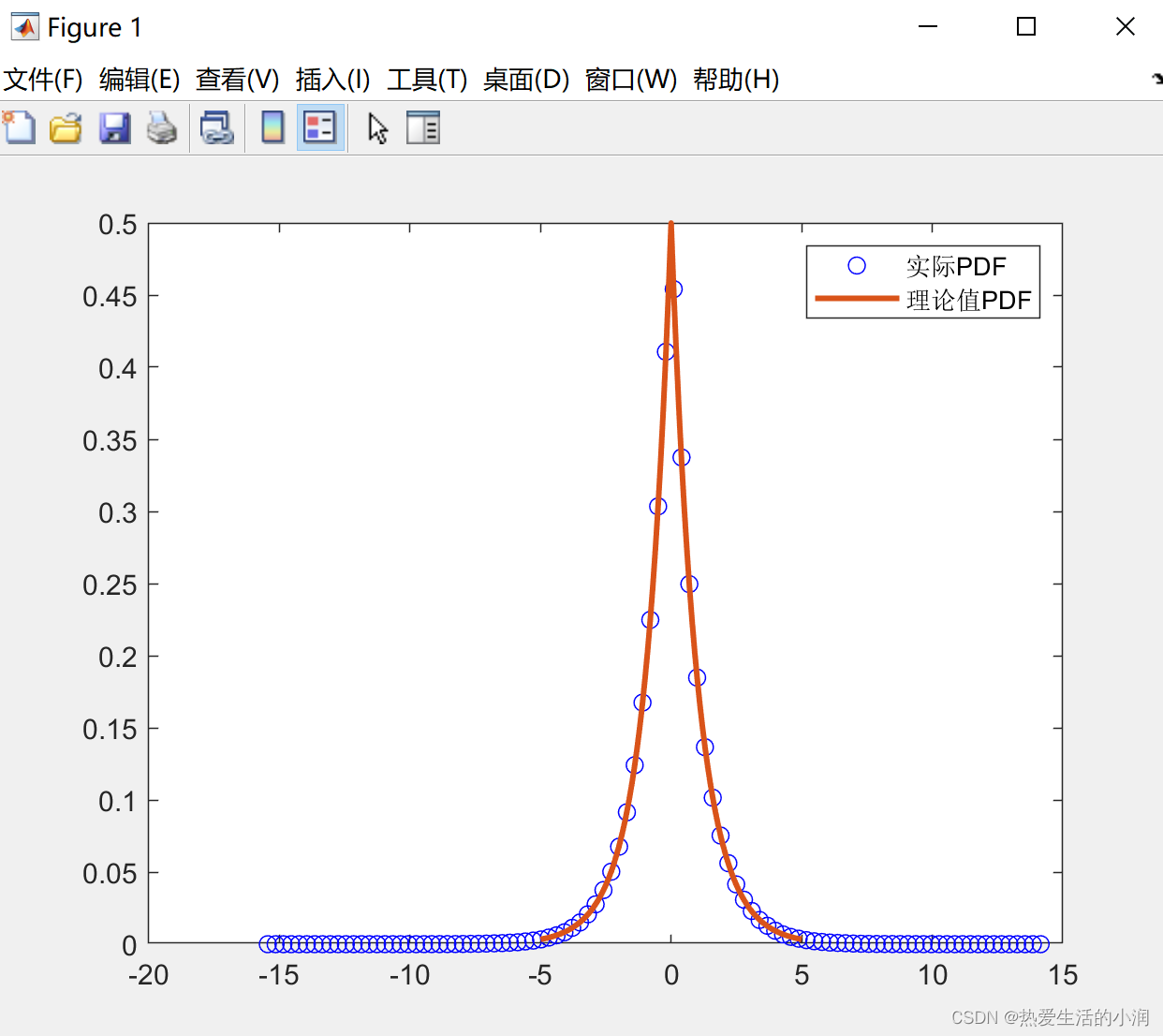
plot (x,yy,'bo'); % 做概率分布折线图
hold on;
plot (xx,probablity,'LineWidth',2);
legend('实际PDF','理论值PDF');
子函数:randlap.m
function x = randlap(siz,lambda)
% lambda就是lambda,siz是维度,这里默认miu是0
% RANDL random numbers distributed according to the Laplace distribution
% RANDL(N) will return an NxN matrix containing pseudo-random values
% drawn from a Laplace distribution with zero mean and standard deviation
% one. RAND([M,N,...,P]) will return an MxNx...xP matrix.
% RANDL([M,N,...,P],lambda) will return an MxNx...xP matrix of
% pseudo-random numbers with parameter lambda. CAUTION: the pdf is
% assumed as
% pdf = lambda/2 * exp(-lambda*abs(x))
%
% The Laplace random numbers are generated using the the RAND function to
% generate uniformly distributed numbers in (0,1) and then the probability
% integral transformation, i.e. using the fact that
% if Fx(x) is the cdf of a random variable x, then the RV z=Fx(x) is
% uniformly distributed in (0,1).
%
% In order to generate random numbers with mean mu and variance v, then
% generate the random numbers X with mean 0 and variance 1 and then
% X = X*sqrt(v)+mu;
%
% C. Saragiotis, Oct 2008
% 23-07-03 大概明白的,就是用了一个指数分布的形式去生成的
if nargin==1
lambda = sqrt(2); % this gives a std=var=1.
end
% z = rand(siz);
% x = zeros(siz);
% 23-07-03 改为
z = rand(siz,1);
x = zeros(siz,1);
in = z<=.5;
ip = z> .5;
x(in) = 1/lambda *log(2*z(in));
x(ip) = -1/lambda *log(2*(1-z(ip)));
四、实验结果