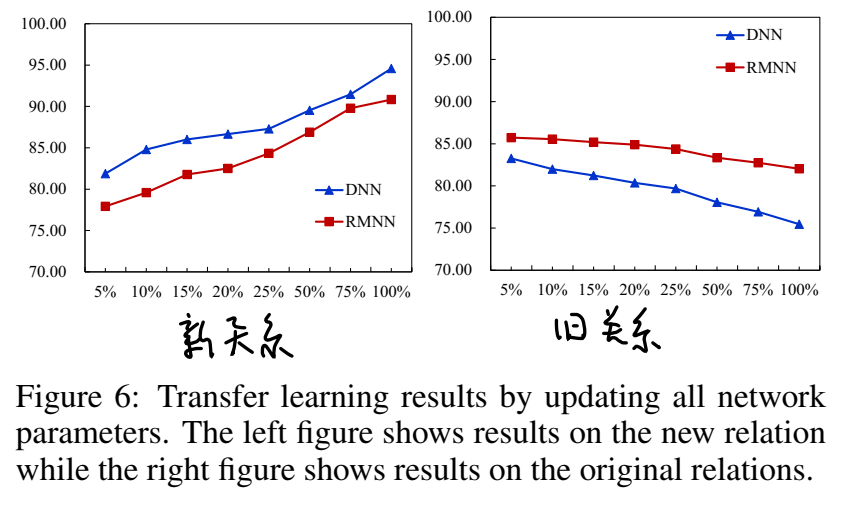
语法分析,建立并显示语法树
以识别 a = 10.01; 为例,阐述语法分析的构造过程
1. 建立AST储存结构
由a = 10.01得知,语法构成为:
SentenceList->Sentence->Exp SEMI->ID ASSIGNOP FLOAT SEMI
因此,需要储存结构如下
typedef struct ASTNode {
int kind; //保存结点类型
union {
char type_id[33]; //由标识符生成的叶结点
int type_int; //由整常数生成的叶结点
float type_float; //由浮点常数生成的叶结点
};
union {//第1指针域
struct ASTNode *Sentence; //句子
struct ASTNode *Exp1; //表达式1
struct ASTNode *ID; //标识符
};
union {//第2指针域
struct ASTNode *SentenceList; //句子集
struct ASTNode *Exp2; //表达式2
};
int type; //用以标识表达式结点的类型
int pos; //语法单位所在位置行号
} ASTNode;
2. 设定标识符
1)在parser.y文件中设定定义的词法类型
%union {
int type_int;
float type_float;
char type_id[32];
struct ASTNode *ptr;
};
2)定义符号类型
将非终结符定义为ASTNode类型
在Program ->SentenceList->Sentence->Exp SEMI->ID ASSIGNOP FLOAT SEMI
中得知
%type <ptr> program SentenceList Sentence Exp
将终结符定义为语义值类型
%token <type_id> ID /*指定ID的语义值是type_id*/
%token <type_float> FLOAT /*指定FLOAT的语义值是type_float*/
定义enum型标识符:
符号标识符有SEMI ASSIGNOP,
识别标识符(用于识别该文法类型)有SentenceList_ Sentence_
%token SentenceList_ Sentence_ SEMI ASSIGNOP
3.词法分析:标识符,=,Float,SEMI
1)Test.l文件中的一些设定:
%option yylineno. //行号自动加1
2)识别
定义段:
id [A-Za-z][A-Za-z0-9]*
floatconst [0-9]*\.?[0-9]*
规则段:
%%
"=" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return ASSIGNOP;}
{id} {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext); return ID;}
";" {return SEMI;}
{floatconst} {yylval.type_float=atof(yytext); return FLOAT;}
[ \r\t] {}
[\n] {}
. {printf("Error type A :Mysterious character \"%s\"\n\t at Line %d\n",yytext,yylineno);}
%%
4.语法分析
注:program SentenceList Sentence Exp的类型为struct ASTNode *。
在使用时,可用$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));创建内存。
使用$$->kind,$$->Sentence创造节点属性。
program: SentenceList { display($1,0);}; //显示语法树,语义分析
SentenceList: {$$=NULL;}
| Sentence SentenceList {
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = SentenceList_;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Sentence=$1;
$$->SentenceList=$2;
}
;
Sentence: Exp SEMI{
//表达式
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = Sentence_;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$1;
}
;
Exp : Exp ASSIGNOP Exp{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = ASSIGNOP;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$1;
$$->Exp2=$3;
strcpy($$->type_id,"=");
}
| ID{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind=ID;
$$->pos=yylineno;
strcpy($$->type_id,$1);
}
| FLOAT{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind=FLOAT;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->type=FLOAT;
$$->type_float=$1;
}
;
Main函数:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
yyin=fopen(argv[1],"r");
if (!yyin) return 0;
yylineno=1;
yyparse();
return 0;
}
#include<stdarg.h>
void yyerror(const char* fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
fprintf(stderr, "Grammar Error at Line %d Column %d: ", yylloc.first_line,yylloc.first_column);
vfprintf(stderr, fmt, ap);
fprintf(stderr, ".\n");
}
5.显示语法树
void display(struct ASTNode *T,int indent)
{//对抽象语法树的先根遍历
int i=1;
struct ASTNode *T0;
if (T)
{
switch (T->kind) {
case SentenceList_:
display(T->Sentence, indent);
display(T->SentenceList, indent);
break;
case Sentence_:
printf_(indent);
printf("表达式语句:");
display(T->Exp1, indent + 4);
break;
case ID:
printf_(indent);
printf("变量:%s",T->type_id);
break;
case FLOAT:
printf_(indent);
printf("浮点常量:%.6f",T->type_float);
break;
case ASSIGNOP:
printf_(indent);
printf("%s",T->type_id);
display(T->Exp1,indent+4);
display(T->Exp2,indent+4);
break;
}
}
}
6.在此基础上按照1~5的步骤添加其他语法
IF LP Exp RP Sentence ELSE Sentence
WHILE LP Exp RP LC SentenceList RC
SCAN ID SEMI
PRINT Exp SEMI
等
7.编译运行
使用bat语言进行命令行输入,代码文件名为lex.l、parser.y,生成文件parser.exe。
@echo on
flex lex.l
bison -d parser.y
gcc -o parser lex.yy.c parser.tab.c ast.c
实现编译,编译文件为test.c.
parser test.c
完整代码
lex.l
%option yylineno
%{
#include "parser.tab.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "def.h"
int yycolumn=1;
int lastToken;
%}
id [A-Za-z][A-Za-z0-9]*
intconst [0-9]+
floatconst [0-9]*\.?[0-9]*([eE][-+]?[0-9]+)?
%%
"int" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return TYPE;}
"float" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return TYPE;}
"return" {return RETURN;}
"if" {return IF;}
"else" {return ELSE;}
"while" {return WHILE;}
"for" {return FOR;}
"scan" {return SCAN;}
"print" {return PRINT;}
{id} {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext); return ID;}
";" {return SEMI;}
"," {return COMMA;}
">"|"<"|">="|"<="|"=="|"!=" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return RELOP;}
"=" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return ASSIGNOP;}
"++" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return DPLUS;}
"+" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return PLUS;}
"-" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return MINUS;}
"*" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return STAR;}
"/" {strcpy(yylval.type_id, yytext);return DIV;}
"&&" {return AND;}
"||" {return OR;}
"!" {return NOT;}
"(" {return LP;}
")" {return RP;}
"{" {return LC;}
"}" {return RC;}
{intconst} {yylval.type_int=atoi(yytext); return INT;}
{floatconst} {yylval.type_float=atof(yytext); return FLOAT;}
[ \r\t] {}
[\n] {yycolumn=1;}
. {printf("Error type A :Mysterious character \"%s\"\n\t at Line %d\n",yytext,yylineno);}
%%
int yywrap()
{
return 1;
}
parser.y
%error-verbose
%locations
%{
#include "stdio.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "def.h"
extern int yylineno;
extern char *yytext;
extern FILE *yyin;
void yyerror(const char* fmt, ...);
void display(struct ASTNode *,int);
int yylex();
%}
%union {
int type_int;
float type_float;
char type_id[32];
struct ASTNode *ptr;
};
// %type 定义非终结符的语义值类型
%type <ptr> program SentenceList Sentence Exp
//% token 定义终结符的语义值类型
%token <type_int> INT /*指定INT的语义值是type_int,有词法分析得到的数值*/
%token <type_id> ID RELOP TYPE /*指定ID,RELOP 的语义值是type_id,有词法分析得到的标识符字符串*/
%token <type_float> FLOAT /*指定ID的语义值是type_id,有词法分析得到的标识符字符串*/
//GE GT LE LT NE LB RB
%token DPLUS LP RP LC RC SEMI COMMA /*用bison对该文件编译时,带参数-d,生成的exp.tab.h中给这些单词进行编码,可在lex.l中包含parser.tab.h使用这些单词种类码*/
%token SCAN PRINT PLUS MINUS STAR DIV ASSIGNOP AND OR NOT IF ELSE WHILE RETURN STRUCT FOR SWITCH CASE COLON DEFAULT
/*以下为接在上述token后依次编码的枚举常量,作为AST结点类型标记*/
%token SentenceList_ Sentence_ IF_ELSE UMINUS
//%token FUNC_CALL ARGS FUNCTION PARAM ARG CALL LABEL GOTO JLT JLE JGT JGE EQ NEQ
%left ASSIGNOP
%left OR
%left AND
%left RELOP
%left PLUS MINUS
%left STAR DIV
%right UMINUS NOT DPLUS
%nonassoc ELSE
%%
program: SentenceList { display($1,0);}; //显示语法树,语义分析
SentenceList: {$$=NULL;}
| Sentence SentenceList {
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = SentenceList_;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Sentence=$1;
$$->SentenceList=$2;
//printf("SentenceList: ->Sentence SentenceList\n");
}
;
Sentence: Exp SEMI{
//表达式
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = Sentence_;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$1;
//printf("Sentence: ->Exp SEMI\n");
}
| SCAN ID SEMI{
//scan输入
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = SCAN;
$$->pos=yylineno;
strcpy($$->type_id,$2);
//printf("Sentence:->SCAN ID\n");
}
| PRINT Exp SEMI{
//print输出
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = PRINT;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->ID = $2;
//printf("Sentence:->PRINT ID\n");
}
| IF LP Exp RP Sentence ELSE Sentence{
//if-else语句
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = IF_ELSE;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1 = $3;
$$->SentenceIF = $5;
$$->SentenceElse = $7;
//printf("Sentence:->IF LP Exp RP SentenceList ELSE SentenceList\n");
}
| WHILE LP Exp RP LC SentenceList RC{
//While语句
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = WHILE;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1 = $3;
$$->SentenceListWhile= $6;
}
;
Exp : Exp ASSIGNOP Exp{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = ASSIGNOP;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$1;
$$->Exp2=$3;
strcpy($$->type_id,"=");
//printf("Exp = Exp \n");
}
| MINUS Exp %prec UMINUS{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = UMINUS;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$2;
strcpy($$->type_id,"-");
//printf("-Exp \n");
}
| LP Exp RP{
$$=$2;
//printf("(Exp) \n");
}
| Exp RELOP Exp{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = RELOP;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$1;
$$->Exp2=$3;
strcpy($$->type_id,$2);
//printf("Exp %s Exp\n",$2);
}
| Exp MINUS Exp{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = MINUS;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$1;
$$->Exp2=$3;
strcpy($$->type_id,"-");
//printf("Exp - Exp\n");
}
| Exp PLUS Exp{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = PLUS;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$1;
$$->Exp2=$3;
strcpy($$->type_id,"+");
//printf("Exp + Exp\n");
}
| Exp STAR Exp{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = STAR;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$1;
$$->Exp2=$3;
strcpy($$->type_id,"*");
//printf("Exp * Exp\n");
}
| Exp DIV Exp{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind = DIV;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->Exp1=$1;
$$->Exp2=$3;
strcpy($$->type_id,"/");
//printf("Exp / Exp\n");
}
| ID{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind=ID;
$$->pos=yylineno;
strcpy($$->type_id,$1);
//printf("Exp :->ID,ID = %s\n",$1);
}
| FLOAT{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind=FLOAT;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->type=FLOAT;
$$->type_float=$1;
//printf("FLOAT = %f\n",$1);
}
| INT{
$$=(ASTNode *)malloc(sizeof(ASTNode));
$$->kind=INT;
$$->pos=yylineno;
$$->type=INT;
$$->type_int=$1;
//printf("INT = %d\n",$1);
}
;
%%
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
yyin=fopen(argv[1],"r");
if (!yyin) return 0;
yylineno=1;
yyparse();
return 0;
}
#include<stdarg.h>
void yyerror(const char* fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
fprintf(stderr, "Grammar Error at Line %d Column %d: ", yylloc.first_line,yylloc.first_column);
vfprintf(stderr, fmt, ap);
fprintf(stderr, ".\n");
}
def.h
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "stdarg.h"
#include "parser.tab.h"
typedef struct ASTNode {
//以下对结点属性定义没有考虑存储效率,只是简单地列出要用到的一些属性
int kind;
union {
char type_id[33]; //由标识符生成的叶结点
int type_int; //由整常数生成的叶结点
float type_float; //由浮点常数生成的叶结点
};
union {//第1指针域
struct ASTNode *Sentence;
struct ASTNode *Exp1;
struct ASTNode *ID; //标识符
};
union {//第2指针域
struct ASTNode *SentenceList;
struct ASTNode *Exp2; //表达式2
struct ASTNode *SentenceIF;
struct ASTNode *SentenceListWhile;
};
union {//第3指针域
struct ASTNode* SentenceElse;
};
int type; //用以标识表达式结点的类型
int pos; //语法单位所在位置行号
} ASTNode;
ast.c
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "def.h"
#include "parser.tab.h"
int Enter = 0;
void printf_(int indent) {
if (Enter == 1) {
printf("\n");
}
else {
Enter = 1;
}
if (indent != 0) {
printf("%*c", indent, ' ');
}
}
void display(struct ASTNode *T,int indent)
{//对抽象语法树的先根遍历
int i=1;
struct ASTNode *T0;
if (T)
{
switch (T->kind) {
case SentenceList_:
display(T->Sentence, indent);
display(T->SentenceList, indent);
break;
case Sentence_:
printf_(indent);
printf("表达式语句:");
display(T->Exp1, indent + 4);
break;
case ID:
printf_(indent);
printf("变量:%s",T->type_id);
break;
case INT:
printf_(indent);
printf("整型常量:%d",T->type_int);
break;
case FLOAT:
printf_(indent);
printf("浮点常量:%.6f",T->type_float);
break;
case ASSIGNOP:
case AND:
case OR:
case RELOP:
case PLUS:
case MINUS:
case STAR:
case DIV:
printf_(indent);
printf("%s",T->type_id);
display(T->Exp1,indent+4);
display(T->Exp2,indent+4);
break;
case UMINUS:
printf_(indent);
printf("单目%s", T->type_id);
display(T->Exp1, indent + 4);
break;
case SCAN:
printf_(indent);
printf("输入变量:%s", T->type_id);
break;
case PRINT:
printf_(indent);
printf("输出表达式:");
display(T->ID, indent + 4);
break;
case IF_ELSE:
printf_(indent);
printf("条件语句(if_then_else):");
printf_(indent+4);
printf("条件:");
display(T->Exp1, indent + 8);
printf_(indent+4);
printf("if子句:");
display(T->SentenceIF, indent + 8);
printf_(indent+4);
printf("else子句:");
display(T->SentenceElse, indent + 8);
break;
case WHILE:
printf_(indent);
printf("循环语句:");
printf_(indent + 4);
printf("条件:");
display(T->Exp1, indent + 8);
printf_(indent + 4);
printf("循环体:");
display(T->SentenceListWhile, indent + 8);
break;
}
}
}
测试文件test.c
a = 10.1;
scan b;
if (a > b)
max = a;
else max = b;
print max;
i = 1;
sum = 0;
while (i <= 10)
{
sum = sum + i;
i = i + 1;
}
print sum;
a = (1 + 3) * 2 / -(13.56 - 5) > 100 == 1;
test.bat
@echo on
flex lex.l
bison -d parser.y
gcc -o parser lex.yy.c parser.tab.c ast.c
运行结果
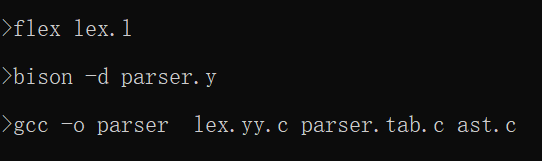
编译成功
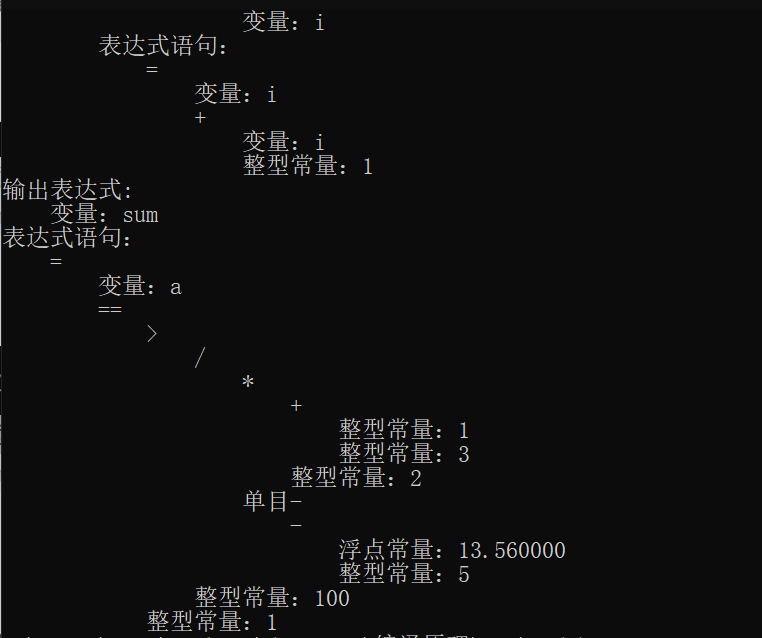
运行成功
实验总结:
熟悉了flex、bison的使用,联合使用,以及和其他文件(.c)的联合使用,学会了创建语法树,实现语法树的显示输出。






![[选型] 实时数仓之技术选型](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/41ccfc03b487d599a67a2b148245156b.png)