一、前言
pytest提供的很多钩子(Hooks)方法方便我们对测试用例框架进行二次开发,可以根据自己的需求进行改造
先学习下pytest_runtest_makereport这个钩子方法,可以更清晰的了解用例的执行过程,并获取到每个用例的执行结果
二、pytest_runtest_makereport
先看下相关的源码,在_pytest/runner.py下,可以导入之后,点进去查看
from _pytest import runner
# 对应源码
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
""" return a :py:class:`_pytest.runner.TestReport` object
for the given :py:class:`pytest.Item` and
:py:class:`_pytest.runner.CallInfo`.
"""
这里item是测试用例,call是测试步骤,具体执行过程如下:
1.先执行when=’setup’ 返回setup 的执行结果
2.然后执行when=’call’ 返回call 的执行结果
3.最后执行when=’teardown’返回teardown 的执行结果
三、运行案例
conftest.py 写 pytest_runtest_makereport 内容,打印运行过程和运行结果
# conftest.py
import pytest
@pytest.hookimpl(hookwrapper=True, tryfirst=True)
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
print('------------------------------------')
# 获取钩子方法的调用结果
out = yield
print('用例执行结果', out)
# 3. 从钩子方法的调用结果中获取测试报告
report = out.get_result()
print('测试报告:%s' % report)
print('步骤:%s' % report.when)
print('nodeid:%s' % report.nodeid)
print('description:%s' % str(item.function.__doc__))
print(('运行结果: %s' % report.outcome))
test_a.py写一个简单的用例
def test_a():
'''用例描述:test_a'''
print("行行行行")
运行结果如下
D:\soft\code\pytest_jenkins_demo\demo>pytest -s
============================= test session starts =============================
platform win32 -- Python 3.6.0, pytest-4.5.0, py-1.5.4, pluggy-0.13.1
rootdir: D:\demo
plugins: html-1.19.0,
collected 1 item
test_a.py ------------------------------------
用例执行结果 <pluggy.callers._Result object at 0x0000027C547332B0>
测试报告:<TestReport 'test_a.py::test_a' when='setup' outcome='passed'>
步骤:setup
nodeid:test_a.py::test_a
description:用例描述:test_a
运行结果: passed
行行行行
------------------------------------
用例执行结果 <pluggy.callers._Result object at 0x0000027C547332B0>
测试报告:<TestReport 'test_a.py::test_a' when='call' outcome='passed'>
步骤:call
nodeid:test_a.py::test_a
description:用例描述:test_a
运行结果: passed
.------------------------------------
用例执行结果 <pluggy.callers._Result object at 0x0000027C54750A20>
测试报告:<TestReport 'test_a.py::test_a' when='teardown' outcome='passed'>
步骤:teardown
nodeid:test_a.py::test_a
description:用例描述:test_a
运行结果: passed
========================== 1 passed in 0.06 seconds ===========================
从运行结果可以看出,运行用例的过程会经历三个阶段:setup-call-teardown,每个阶段都会返回的 Result 对象和 TestReport 对象,以及对象属性
setup和teardown上面的用例默认都没有,结果都是passed
四、setup和teardown
给用例写个fixture增加用例的前置和后置操作,conftest.py内容如下
import pytest
@pytest.hookimpl(hookwrapper=True, tryfirst=True)
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
print('------------------------------------')
# 获取钩子方法的调用结果
out = yield
print('用例执行结果', out)
# 3. 从钩子方法的调用结果中获取测试报告
report = out.get_result()
print('测试报告:%s' % report)
print('步骤:%s' % report.when)
print('nodeid:%s' % report.nodeid)
print('description:%s' % str(item.function.__doc__))
print(('运行结果: %s' % report.outcome))
@pytest.fixture(scope="session", autouse=True)
def fix_a():
print("setup 前置操作")
yield
print("teardown 后置操作")
运行结果如下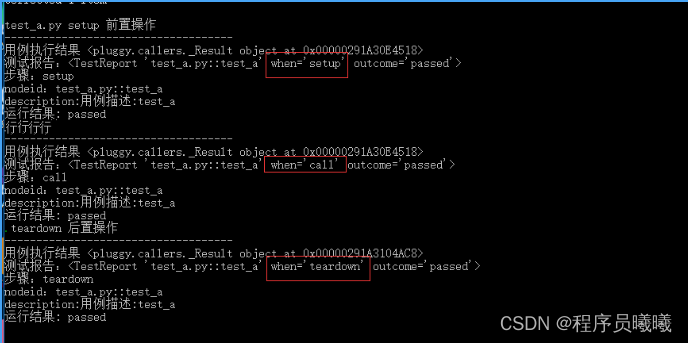
五、setup失败情况
当setup执行失败了,setup的执行结果的failed,后面的call用例和teardown都不会执行了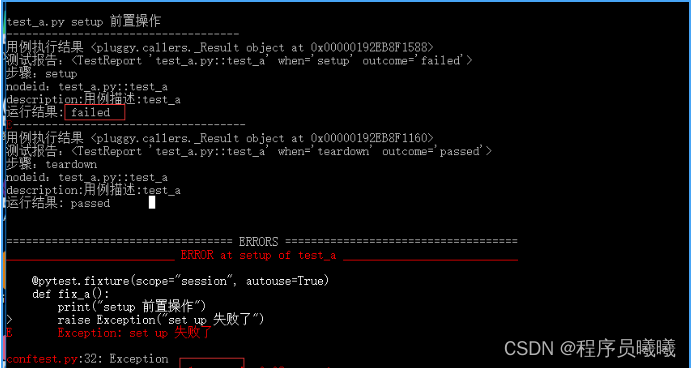
此时用例的状态是:error, 也就是用例(call)都还没开始执行,就异常了
六、call失败情况
如果setup正常执行,但是测试用例call失败了
@pytest.fixture(scope="session", autouse=True)
def fix_a():
print("setup 前置操作")
yield
print("teardown 后置操作")
test_a.py用例
def test_a():
'''用例描述:test_a'''
print("行行行行")
assert 1==0
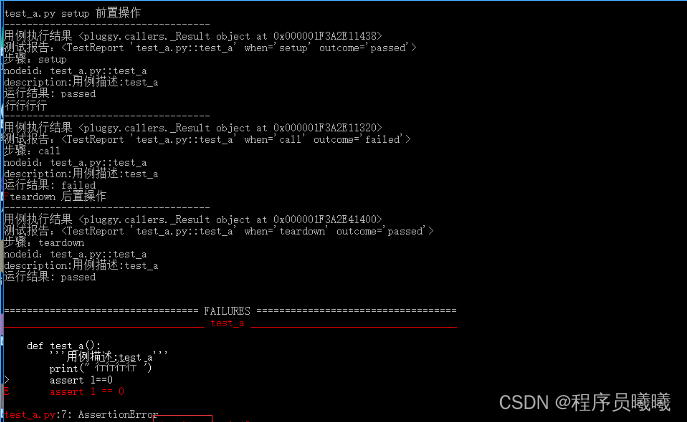
那么此时运行的结果就是failed
七、teardown失败了
如果setup正常执行,测试用例call正常执行,teardown失败了,这种情况
@pytest.fixture(scope="session", autouse=True)
def fix_a():
print("setup 前置操作")
yield
print("teardown 后置操作")
raise Exception("teardown 失败了")
teat_a.py用例
def test_a():
'''用例描述:test_a'''
print("行行行行")
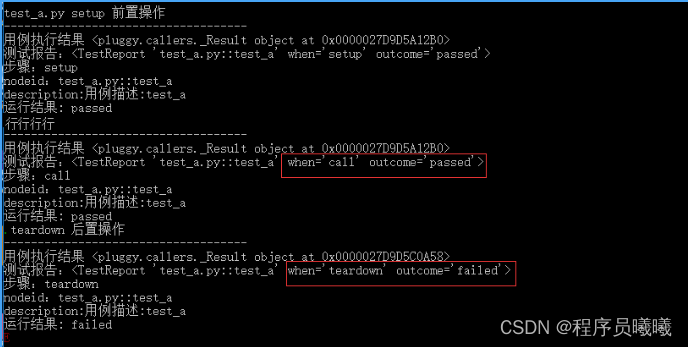
最终统计的结果:1 passed, 1 error in 0.16 seconds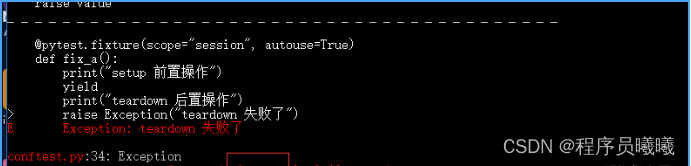
八、只获取call的结果
我们在写用例的时候,如果保证setup和teardown不报错情况,只关注测试用例本身的运行结果,前面的 pytest_runtest_makereport 钩子方法执行了三次
可以加个判断:if report.when == “call”
import pytest
from _pytest import runner
'''
# 对应源码
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
""" return a :py:class:`_pytest.runner.TestReport` object
for the given :py:class:`pytest.Item` and
:py:class:`_pytest.runner.CallInfo`.
"""
'''
@pytest.hookimpl(hookwrapper=True, tryfirst=True)
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
print('------------------------------------')
# 获取钩子方法的调用结果
out = yield
# print('用例执行结果', out)
# 3. 从钩子方法的调用结果中获取测试报告
report = out.get_result()
if report.when == "call":
print('测试报告:%s' % report)
print('步骤:%s' % report.when)
print('nodeid:%s' % report.nodeid)
print('description:%s' % str(item.function.__doc__))
print(('运行结果: %s' % report.outcome))
@pytest.fixture(scope="session", autouse=True)
def fix_a():
print("setup 前置操作")
yield
print("teardown 后置操作")
运行结果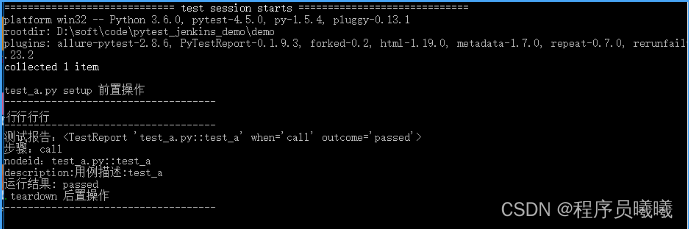
【下面是我整理的2023年最全的软件测试工程师学习知识架构体系图】
一、Python编程入门到精通
二、接口自动化项目实战
三、Web自动化项目实战
四、App自动化项目实战
五、一线大厂简历
六、测试开发DevOps体系
七、常用自动化测试工具
八、JMeter性能测试
九、总结(尾部小惊喜)
生命不息,奋斗不止。每一份努力都不会被辜负,只要坚持不懈,终究会有回报。珍惜时间,追求梦想。不忘初心,砥砺前行。你的未来,由你掌握!
生命短暂,时间宝贵,我们无法预知未来会发生什么,但我们可以掌握当下。珍惜每一天,努力奋斗,让自己变得更加强大和优秀。坚定信念,执着追求,成功终将属于你!
只有不断地挑战自己,才能不断地超越自己。坚持追求梦想,勇敢前行,你就会发现奋斗的过程是如此美好而值得。相信自己,你一定可以做到!
【软件测试技术交流(免费领取全套软件测试资料)】:320231853(备注C)![]() http://qm.qq.com/cgi-bin/qm/qr?_wv=1027&k=H1j6mp_9eGG23LNX5PwlX0JnVzwPdmlf&authKey=hJdPzdWN04zNIbuFtmCSDUbpu7hA9R%2FwR9jM9KGZGganFcm%2FC14SGNfjVddllBqy&noverify=0&group_code=320231853
http://qm.qq.com/cgi-bin/qm/qr?_wv=1027&k=H1j6mp_9eGG23LNX5PwlX0JnVzwPdmlf&authKey=hJdPzdWN04zNIbuFtmCSDUbpu7hA9R%2FwR9jM9KGZGganFcm%2FC14SGNfjVddllBqy&noverify=0&group_code=320231853