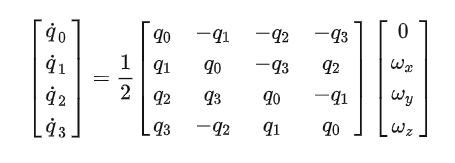树的重心

本题的本质是树的dfs, 每次dfs可以确定以u为重心的最大连通块的节点数,并且更新一下ans。
也就是说,dfs并不直接返回答案,而是在每次更新中迭代一次答案。
这样的套路会经常用到,在 树的dfs 题目中
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
const ll N = 2e6+ 10;
const ll mod =998244353;
int t,n,m,x,y,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
int h[N],ne[N],e[N],idx;
int ans;
int book[N];
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b,ne[idx] = h[a] ,h[a] = idx++;
}
// dfs 框架
/*
void dfs(int u){
st[u]=true; // 标记一下,记录为已经被搜索过了,下面进行搜索过程
for(int i=h[u];i!=-1;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(!st[j]) {
dfs(j);
}
}
}
*/
//返回以u为根的子树中节点的个数,包括u节点
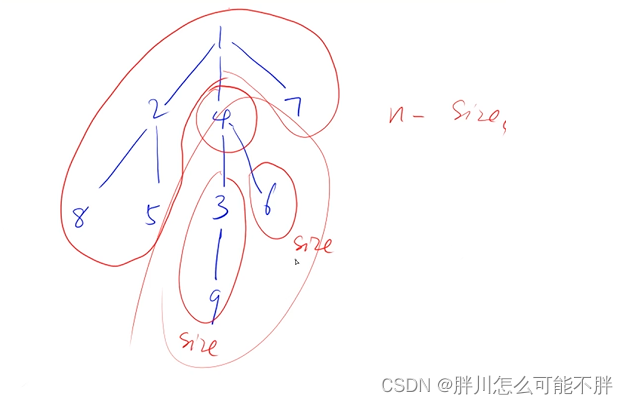
int dfs(int u)
{
int sum = 1;//存储 以u为根的树 的节点数, 包括u,如图中的4号节点
int res = 0;//存储 删掉某个节点之后,最大的连通子图节点数
book[u] = 1;
for(int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(!book[j])
{
int s = dfs(j);// u节点的单棵子树节点数
res = max(res ,s);// 记录最大联通子图的节点数
sum += s;//以j为根的树 的节点数
}
}
res = max(res ,n - sum); // 选择u节点为重心,最大的 连通子图节点数
ans = min(ans ,res);//遍历过的假设重心中,最小的最大联通子图的 节点数
return sum;
}
void fatchuan()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof(h));
ans = INF;
cin >> n;
rep(i,2,n)
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a,b),add(b,a);
}
dfs(1);
cout << ans;
}
int main()
{
IOS;
t=1;
//scanf("%d",&t);
//cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
fatchuan();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}