flask+uwsgi+docker+nginx 云服务器部署测试平台
开发环境
本次主要是在腾讯云上进行部署,系统是CentOS 7.9 64位,主要使用的软件如下:
Python 3.9.5
Pycharm
Flask1.0.2
Mysql 5.7
nginx + uwsgi
一 安装Nginx
1.更新yum 源
sudo rpm -ivh http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-7-0.el7.ngx.noarch.rpm
2.安装
sudo yum install nginx
3.配置nginx
// 1.设置开机启动
$ sudo systemctl enable nginx
// 2.启动服务
$ sudo systemctl start nginx
// 3.停止服务
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
// 4.重新加载,因为一般重新配置之后,不希望重启服务,这时可以使用重新加载。
$ sudo systemctl reload nginx
4.docker部署
拉取镜像:docker pull nginx:1.17.9
构建容器
docker run -d --name nginx -p 8081:80
--privileged=true --restart always
-v ${PWD}/nginx/html:/usr/share/nginx/html
-v ${PWD}/nginx/logs:/var/log/nginx
nginx:1.17.9
-v ${PWD}/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
不支持直接挂载文件,可以创建后复制到容器中
5.请求转发
配置nginx
cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf.bak 备份
sudo vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 编辑
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
改为
user root;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
upstream flask {
server 101.35.129.200:5001;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost; #改为自己的域名,如果没有域名就修改为127.0.0.1 或者 localhost
location / {
proxy_pass http://101.35.129.200:5001; # 此处可以写单个主机信息(前面的gunicorn启动的ip地址),也可以写upstream的组名。
# proxy_pass http://flask;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}
}
访问
4.常见问题
// 绑定其他端口
// Nginx 默认绑定的端口是 http 协议的默认端口,端口号为:80,如果需要绑定其他端口,需要注意 SELinux 的配置
// 例如:绑定 8081 端口,但是会发现无法启动,一般的报错如下
// YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss [emerg] 46123#0: bind() to 0.0.0.0:8081 failed (13: Permission denied)
// 此时需要更改 SELinux 的设置。我们使用 SELinux 的管理工具 semanage 进行操作,比较方便。
// 安装 semanage 使用如下命令
sudo yum install policycoreutils-python
// 然后查看是否有其他协议类型使用了此端口
sudo semanage port -l | grep 8081
transproxy_port_t tcp 8081
// 返回了结果,表明已经被其他类型占用了,类型为 transproxy_port_t。
// 我们还要查看一下 Nginx 的在 SELinux 中的类型 http_port_t 绑定的端口
sudo semanage port -l | grep http_port_t
http_port_t tcp 80, 81, 443, 488, 8008, 8009, 8443, 9000
pegasus_http_port_t tcp 5988
// 第一行 http_port_t 中没有包含 8081 这个端口。因此需要修改 8081 端口到 http_port_t 类型中。
sudo semanage port -m -p tcp -t http_port_t 8081
// 如果没有其他协议类型使用想要绑定的端口,如 8001,则我们只要新增到 SELinux 中即可。
sudo semanage port -l | grep 8001
sudo semanage port -a -p tcp -t http_port_t 8001
// 此时,重新启动 Nginx 即可。
二 防火墙操作
1.查看已经开放的端口
firewall-cmd --list-ports
2.开启端口
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
3.命令含义
–zone #作用域
–add-port=80/tcp #添加端口,格式为:端口/通讯协议
–permanent #永久生效,没有此参数重启后失效
4.重启防火墙
firewall-cmd --reload #重启firewall
systemctl stop firewalld.service #停止firewall
systemctl disable firewalld.service #禁止firewall开机启动
firewall-cmd --state #查看默认防火墙状态(关闭后
作者:Oort
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/8012323b60a2
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
三 CentOS 7 安装 Python3.7
1.安装 Python3.7
yum install zlib-devel bzip2-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gcc make libffi-devel
这里面有一个包很关键libffi-devel,因为只有3.7才会用到这个包,如果不安装这个包的话,在 make 阶段会出现如下的报错:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named '_ctypes'
2.安装pip,因为 CentOs 是没有 pip 的。
#运行这个命令添加epel扩展源
yum -y install epel-release
#安装pip
yum install python-pip
3.可以用yum 安装 安装一下 wget
yum -y install wget
4.下载 python3.7的源码包
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.7.0/Python-3.7.0.tgz
#解压缩
tar -zxvf Python-3.7.0.tgz
#进入解压后的目录,依次执行下面命令进行手动编译
./configure prefix=/usr/local/python3
make && make install
如果最后没提示出错,就代表正确安装了,在/usr/local/目录下就会有python3目录
5.添加软链接
#添加python3的软链接
ln -s /usr/local/python3/bin/python3.7 /usr/bin/python3.7
#添加 pip3 的软链接
ln -s /usr/local/python3/bin/pip3.7 /usr/bin/pip3.7
#测试是否安装成功了
python -V
6.更改yum配置,因为其要用到python2才能执行,否则会导致yum不能正常使用(不管安装 python3的那个版本,都必须要做的)
vi /usr/bin/yum
把 #! /usr/bin/python 修改为 #! /usr/bin/python2
vi /usr/libexec/urlgrabber-ext-down
把 #! /usr/bin/python 修改为 #! /usr/bin/python2
7.docker安装python
Dockerfile
FROM python:3.6
LABEL maintainer="dasun"
USER root
ARG kdir=/home
WORKDIR $kdir
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
#映射端口
EXPOSE 5000
CMD ["python -version"]
四 WSGI安装配置
1.WSGI是什么?
WSGI,全称 Web Server Gateway Interface,是为 Python 语言定义的 Web 服务器和 Web 应用程序或框架之间的一种简单而通用的接口。
WSGI就像是一座桥梁,一边连着web服务器,另一边连着用户的应用
2.uwsgi和uWSGI
uwsgi同WSGI一样是一种通信协议。
而uWSGI是实现了uwsgi和WSGI两种协议的Web服务器。
为什么要使用
使用flask写了一个简易的http服务用来提供接口,按照接口文档demo写好以后本地测试一切正常,但是发布到服务器以后有一串警告:WARNING:This is a developnent server. Do not use it in a production deploynent,如下图:
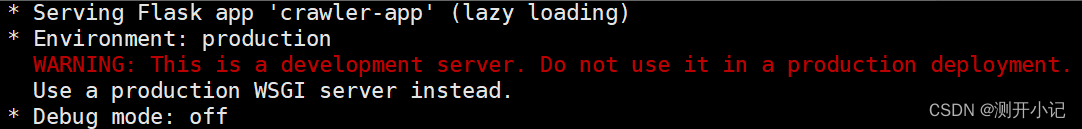
意思是我的这个启动方式不能在生产环境上使用,然后带着疑问上网查了一下,我的启动方式是
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=80)
只适用于开发模式,因为它是单线程的,生产环境影响性能,替代方案是可以用uWSGI或者pywsgi
3.三者的区别如下
1.app.run 启动的是单线程服务,性能很低
2.pywsgi服务器使用的是gevent的pywsgi模块,性能不错,配置也很简单,但是它只是把单线程改造成了单线程异步方式
3.uWSGI性能最好,配置稍微比上面难一点,但是它是支持多进程、多线程、和多协程的方式,简直就是完美,所以我选择尝试使用uWSGI服务器来替代
4.pywsgi方式实现
1.安装gevent模块
pip install gevent
2.在启动类里引入模块
from gevent import pywsgi
3.main方法里将app.run替换
server = pywsgi.WSGIServer(('0.0.0.0', 80), app)
server.serve_forever()
5.uWSGI实现
官方文档 https://uwsgi-docs-zh.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/WSGIquickstart.html#uwsgipython
5.1安装uWSGI模块
pip install uwsgi
5.2配置文件
在根目录下创建uWSGI配置文件 【uwsgi.ini】
[uwsgi]
# 使用nginx连接时使用
# socket = 0.0.0.0:8080
# 地址端口 直接作为web服务器使用
http = 0.0.0.0:80
# 项目路径
chdir = /root/projectname
# 项目启动文件 适用于flask项目部署
wsgi-file = manage.py
# 项目需要调用的启动类 router
callable = app
# 进程线程设置
processes = 4
threads = 10
# 日志文件
daemonize = /app/logs/uwsgi.log
# 保存主进程pid文件
pidfile = uwsgi.pid
# 是否需要主进程
master = true
5.3相关命令
使用uwsgi服务器启动 : uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini
停止 : uwsgi --stop uwsgi.pid
停止 : pkill -f uwsgi -9
uwsgi --http-socket :6005 --http-websockets --wsgi-file app.py --callable app --master --processes 4 --threads 2 --stats 127.0.0.1:9191
5.4配置选项
master = true #启动主进程,来管理其他进程,其它的uwsgi进程都是这个master进程的子进程,如果kill这个master进程,相当于重启所有的uwsgi进程。
chdir = /web/www/mysite #在app加载前切换到当前目录, 指定运行目录
module = mysite.wsgi # 加载一个WSGI模块,这里加载mysite/wsgi.py这个模块
py-autoreload=1 #监控python模块mtime来触发重载 (只在开发时使用)
lazy-apps=true #在每个worker而不是master中加载应用
socket = /test/myapp.sock #指定socket文件,也可以指定为127.0.0.1:9000,这样就会监听到网络套接字
processes = 2 #启动2个工作进程,生成指定数目的worker/进程
buffer-size = 32768 #设置用于uwsgi包解析的内部缓存区大小为64k。默认是4k。
daemonize = /var/log/myapp_uwsgi.log # 使进程在后台运行,并将日志打到指定的日志文件或者udp服务器
log-maxsize = 5000000 #设置最大日志文件大小
disable-logging = true #禁用请求日志记录
vacuum = true #当服务器退出的时候自动删除unix socket文件和pid文件。
listen = 120 #设置socket的监听队列大小(默认:100)
pidfile = /var/run/uwsgi.pid #指定pid文件
enable-threads = true #允许用内嵌的语言启动线程。这将允许你在app程序中产生一个子线程
reload-mercy = 8 #设置在平滑的重启(直到接收到的请求处理完才重启)一个工作子进程中,等待这个工作结束的最长秒数。这个配置会使在平滑地重启工作子进程中,如果工作进程结束时间超过了8秒就会被强行结束(忽略之前已经接收到的请求而直接结束)
max-requests = 5000 #为每个工作进程设置请求数的上限。当一个工作进程处理的请求数达到这个值,那么该工作进程就会被回收重用(重启)。你可以使用这个选项来默默地对抗内存泄漏
limit-as = 256 #通过使用POSIX/UNIX的setrlimit()函数来限制每个uWSGI进程的虚拟内存使用数。这个配置会限制uWSGI的进程占用虚拟内存不超过256M。如果虚拟内存已经达到256M,并继续申请虚拟内存则会使程序报内存错误,本次的http请求将返回500错误。
harakiri = 60 #一个请求花费的时间超过了这个harakiri超时时间,那么这个请求都会被丢弃,并且当前处理这个请求的工作进程会被回收再利用(即重启)
5.5运行
查看进程 : ps -aux | grep uwsgi
root 14281 0.4 2.3 272640 42000 ? S 16:06 0:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini
root 14370 0.0 2.1 936228 37452 ? Sl 16:06 0:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini
root 14371 0.0 2.1 936228 37456 ? Sl 16:06 0:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini
root 14381 0.0 2.1 936228 37452 ? Sl 16:06 0:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini
root 14382 0.0 2.1 936228 37456 ? Sl 16:06 0:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini
root 14383 0.0 2.0 273124 37096 ? S 16:06 0:00 uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini
root 18126 0.0 0.0 112824 980 pts/0 S+ 16:07 0:00 grep --color=auto uwsgi
S代表一个主进程, Sl代表四个子进程
常见问题总结
运行uwsgi时出错 open(“./python_plugin.so”)
运行uwsgi时出错:
open(“./python_plugin.so”): No such file or directory [core/utils.c line 3713]
UNABLE to load uWSGI plugin: ./python_plugin.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory!
原因:这可能是uwsgi的配置问题
解决:1. 若是使用的uwsgi 的配置文件是 .ini 类型时,注释
# plugin = python
-
若是配置文件是 .xml 类型时,删除 python 。
-
其他配置文件类型还有 .json 及 .yaml 文件。
-
若是以上配置文件没问题,那么就是没有安装好 uwsgi 或者uwsgi 服务没有启动,启动uwsgi 服务:
systemctl start uwsgi
再次运行命令是否可行。若还是不可行,那么按照以下步骤:
首先查询是否已存在uwsgi,并卸载:
rpm -qa|grep uwsgi
yum remove -y uwsgi*
若之前是pip 安装的话,执行:
pip uninstall uwsgi
重新安装:
Ubuntu 的Python3 :
apt-get install -y uwsgi-plugin-python3
注:这里可能还有个所有可用的plugin:sudo apt-get install uwsgi-plugins-all
centos环境:
sudo yum install -y uwsgi-plugin-python
查看 uwsgi 服务是否启动:
systemctl status uwsgi
若没有则启动之。
server配置
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
server = make_server('127.0.0.1', 5000, app)
server.serve_forever()
app.run(host='127.0.0.1',port=5000)
Docker容器一起动就退出的解决方案
docker run -dit --name testplatformapi --network testplatform -p 5001:5001 testplatformapi:v1 /bin/bash
添加-it 参数交互运行
添加-d 参数后台运行
这样就能启动一个一直停留在后台运行的Centos了。