问题现象
postgresql中update执行语句报错too many range table entries
源sql
with t as (select id from LZLTAB where id=8723 limit 100 )
update LZLTAB set
STATUS = '00',
FILE_ID = null,
DATE_UPDATED = localtimestamp(0)
where id in (select id from t)
如果把update改写成select,可以执行成功
with t as (select id from LZLTAB where id=8723 limit 100 )
select * from LZLTAB where id in (select id from t)
id | date_created
------+----------------------------+...
8723 | 2023-06-21 18:02:21.161687
(1 row)
主键和分区是这样,分区总共有400个
Partition key: RANGE (partition_key)
Indexes:
"pk_lzl" PRIMARY KEY, btree (id, partition_key)
...
Partitions: lzl_p20230601 FOR VALUES FROM ('20230601') TO ('20230602'),
lzl_p20230602 FOR VALUES FROM ('20230602') TO ('20230603'),
lzl_p20230603 FOR VALUES FROM ('20230603') TO ('20230604')
sql逻辑有很多优化点,但是这里不讨论优化。重点是分析为什么update会报错,和为什么select和update会有区别。
执行explain update报错如下:
explain with t as (selec tid from LZLTAB where id=8723 limit 100 )
update LZLTAB set
STATUS = '00',
FILE_ID = null,
DATE_UPDATED = localtimestamp(0)
where id in (select id from t);
ERROR: 54000: too many range table entries
LOCATION: add_rte_to_flat_rtable, setrefs.c:451
Time: 18341.171 ms (00:18.341)
explain卡了18秒,然后报错
源码分析
报错直接抛出了源码的位置LOCATION: add_rte_to_flat_rtable, setrefs.c:451 ,直接找到该源码
src/backend/optimizer/plan/setrefs.c
其注释是说setrefs.c是完成计划树后的相关工作的
/*
*Post-processing of a completed plan tree: fix references to subplan
* vars, compute regproc values for operators, etc
*/
找到第451行的函数:
/*
* Add (a copy of) the given RTE to the final rangetable
*
* In the flat rangetable, we zero out substructure pointers that are not
* needed by the executor; this reduces the storage space and copying cost
* for cached plans. We keep only the ctename, alias and eref Alias fields,
* which are needed by EXPLAIN, and the selectedCols, insertedCols,
* updatedCols, and extraUpdatedCols bitmaps, which are needed for
* executor-startup permissions checking and for trigger event checking.
*/
static void
add_rte_to_flat_rtable(PlannerGlobal *glob, RangeTblEntry *rte)
{
...
/*
* Check for RT index overflow; it's very unlikely, but if it did happen,
* the executor would get confused by varnos that match the special varno
* values.
*/
if (IS_SPECIAL_VARNO(list_length(glob->finalrtable)))
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_PROGRAM_LIMIT_EXCEEDED),
errmsg("too many range table entries")));
...
}
errmsg()就是第451行。add_rte_to_flat_rtable()看注释跟RTE有关,什么RTE呢?下面再分析。
报错的判断是IS_SPECIAL_VARNO(),直接搜索该函数,在src/include/nodes/primnodes.h中找到宏定义
/*
* Var - expression node representing a variable (ie, a table column)
*
* In the parser and planner, varno and varattno identify the semantic
* referent, which is a base-relation column unless the reference is to a join
* USING column that isn't semantically equivalent to either join input column
* (because it is a FULL join or the input column requires a type coercion).
* In those cases varno and varattno refer to the JOIN RTE. (Early in the
* planner, we replace such join references by the implied expression; but up
* till then we want join reference Vars to keep their original identity for
* query-printing purposes.)
...
*/
#define INNER_VAR 65000 /* reference to inner subplan */
#define OUTER_VAR 65001 /* reference to outer subplan */
#define INDEX_VAR 65002 /* reference to index column */
#define IS_SPECIAL_VARNO(varno) ((varno) >= INNER_VAR)
上面一段注释有点难懂,但是有段话很重要:In those cases varno and varattno refer to the JOIN RTE。varno与RTE有关系。
然后varno>=65000时,会抛出报错。(这里不扩展INNER_VAR,OUTER_VAR,INDEX_VAR的区别,因为他们的值差别不大,不影响我们继续分析)
什么是RTE?
在执行计划源码中的各个位置都能找到RTE(rangetable或RangeTblEntry)的描述,并且报错也很明显ERROR: 54000: too many range table entries也是说的RTE。那么什么是RTE?
在src/include/nodes/parsenodes.h中有一段对RTE的描述
/*--------------------
* RangeTblEntry -
* A range table is a List of RangeTblEntry nodes.
*
* A range table entry may represent a plain relation, a sub-select in
* FROM, or the result of a JOIN clause. (Only explicit JOIN syntax
* produces an RTE, not the implicit join resulting from multiple FROM
* items. This is because we only need the RTE to deal with SQL features
* like outer joins and join-output-column aliasing.) Other special
* RTE types also exist, as indicated by RTEKind.
*
* Note that we consider RTE_RELATION to cover anything that has a pg_class
* entry. relkind distinguishes the sub-cases.
*/
简单的说,RTE是执行计划中的“表”,可以是具体的表也可以是生成类的“表”,比如子查询、join结果等等。RTE超出限制65000,也就是说执行计划中生成了太多的RTE。
查看update的执行计划
由于我们知道了RTE的啥,所以查看sql的执行计划可能会有所帮助。但是由于源sql(400个分区)没有生成执行计划,我们创建一个30个分区的表,期待它能explain出来,然后观察它的执行计划。
30个分区的表执行相同的update语句
explain with t as (select id from lzl where id=8723 limit 100 )
update lzl set
STATUS = '00',
FILE_ID = null,
DATE_UPDATED = localtimestamp(0)
where id in ( select id from t);
生成的执行计划如下
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Update on lzl (cost=155.48..4980.00 rows=600 width=3042)
Update on lzl_p20230601 lzl_1
Update on lzl_p20230602 lzl_2
...
Update on lzl_p20230630 lzl_30
-> Hash Semi Join (cost=155.48..166.00 rows=20 width=3042)
Hash Cond: (lzl_1.id = t.id)
-> Seq Scan on lzl_p20230601 lzl_1 (cost=0.00..10.20 rows=20 width=2912)
-> Hash (cost=155.10..155.10 rows=30 width=40)
-> Subquery Scan on t (cost=0.14..155.10 rows=30 width=40)
-> Limit (cost=0.14..154.80 rows=30 width=8)
-> Append (cost=0.14..154.80 rows=30 width=8)
-> Index Only Scan using lzl_p20230601_pkey on lzl_p20230601 lzl_32 (cost=0.14..5.16 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (id = 8723)
-> Index Only Scan using lzl_p20230602_pkey on lzl_p20230602 lzl_33 (cost=0.14..5.16 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (id = 8723)
...
-> Index Only Scan using lzl_p20230630_pkey on lzl_p20230630 lzl_61 (cost=0.14..5.16 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (id = 8723)
...
-> Hash Semi Join (cost=155.48..166.00 rows=20 width=3042)
Hash Cond: (lzl_30.id = t_29.id)
-> Seq Scan on lzl_p20230630 lzl_30 (cost=0.00..10.20 rows=20 width=2912)
-> Hash (cost=155.10..155.10 rows=30 width=40)
-> Subquery Scan on t_29 (cost=0.14..155.10 rows=30 width=40)
-> Limit (cost=0.14..154.80 rows=30 width=8)
-> Append (cost=0.14..154.80 rows=30 width=8)
-> Index Only Scan using lzl_p20230601_pkey on lzl_p20230601 lzl_931 (cost=0.14..5.16 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (id = 8723)
-> Index Only Scan using lzl_p20230602_pkey on lzl_p20230602 lzl_932 (cost=0.14..5.16 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (id = 8723)
...
-> Index Only Scan using lzl_p20230630_pkey on lzl_p20230630 lzl_960 (cost=0.14..5.16 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (id = 8723)
(2041 rows)
执行计划非常长,总共有2041行。这个执行计划非常笨,每个分区在更新的时候,都把谓词条件在分区表中运行了一次,由于sql没有分区键,每次运行又扫描了所有分区。本身30个分区的分区表,每个分区扫描了30次,总共扫描900次分区。
从执行计划也能看到RTE表刚开始有30个,分配给update直到lzl_30;后面每次hash匹配时每个分区扫描也分配了30个RTE,比如lzl_1对应的hash下的分区扫描从lzl_32到lzl_61。这里为什么是32而不是31?因为整个分区扫描是一个子查询也是一个RTE,为t(所有的为t,t1-t_29),也是总共30个。所以执行计划中生成的RTE表总共有30+30+30*30=960个。
如果用select来看执行计划,发现跟update的执行计划有很大的不同
explain with t as (select id from lzl where id=8723 limit 100 )
select STATUS ,FILE_ID ,DATE_UPDATED from lzl where id in ( select id from t);
Hash Semi Join (cost=155.48..467.05 rows=90 width=98)
Hash Cond: (lzl.id = lzl_31.id)
-> Append (cost=0.00..309.00 rows=600 width=106)
-> Seq Scan on lzl_p20230601 lzl_1 (cost=0.00..10.20 rows=20 width=106)
-> Seq Scan on lzl_p20230602 lzl_2 (cost=0.00..10.20 rows=20 width=106)
...
-> Seq Scan on lzl_p20230630 lzl_30 (cost=0.00..10.20 rows=20 width=106)
-> Hash (cost=155.10..155.10 rows=30 width=8)
-> Limit (cost=0.14..154.80 rows=30 width=8)
-> Append (cost=0.14..154.80 rows=30 width=8)
-> Index Only Scan using lzl_p20230601_pkey on lzl_p20230601 lzl_32 (cost=0.14..5.16 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (id = 8723)
-> Index Only Scan using lzl_p20230602_pkey on lzl_p20230602 lzl_33 (cost=0.14..5.16 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (id = 8723)
...
-> Index Only Scan using lzl_p20230630_pkey on lzl_p20230630 lzl_61 (cost=0.14..5.16 rows=1 width=8)
Index Cond: (id = 8723)
(96 rows)
没有反复(笛卡尔集式地)访问表,RTE只到了61个。这也是为什么400个分区的select可以查询出来的原因,因为400*400次访问实在太多了。
所以关于之前的sql,update执行报错,而select正常的情况,可以得出结论:
- 400个分区的select,它的执行计划中的RTE有801个,没超过
INNER_VAR的值65000,它可以生成执行计划并且执行 - 400个分区的update,它的执行计划中的RTE有160160400个,远远超过
INNER_VAR的值65000,不能成功生成执行计划,抛出RTE超限的报错。
原因分析的差不多了,但是select和update的执行计划差别很大,仍然感到疑惑。下面横向对比oracle和mysql的执行计划,看看有什么差别。
ORACLE的行为
oracle库创建分区表,并使用本地索引
CREATE TABLE lzl (
id number NOT NULL,
partition_key number DEFAULT 0 NOT NULL,
...
)
PARTITION BY RANGE (partition_key)
(
PARTITION lzl_p20230601 VALUES LESS THAN ('20230602'),
PARTITION lzl_p20230602 VALUES LESS THAN ('20230603'),
...
PARTITION lzl_p20230630 VALUES LESS THAN ('20230631'));
create index PKLZL on lzl(id, partition_key) local;
alter table lzl add constraint pklzl primary key (id, partition_key) using index pklzl;
执行计划:
with t as (select id from lzl where id=8723 and rownum<= 100 )
select STATUS ,FILE_ID ,DATE_UPDATED from lzl where id in ( select id from t)
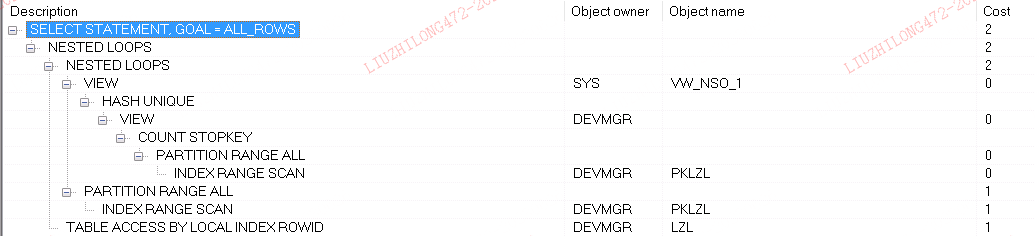
update lzl set
STATUS = '00',
FILE_ID = null,
DATE_UPDATED = sysdate
where id in (select id from lzl where id=8723 and rownum<= 100)
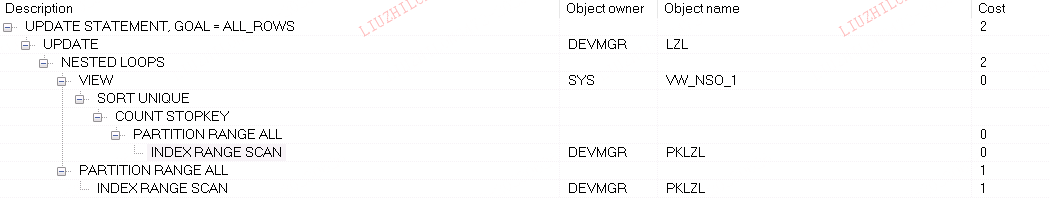
oracle里,select和update都使用了nest loop,访问所有分区partition range all,所以oracle无论是select和update,t表为驱动表,因为是in所以结果进行了排序去重,所以oracle的执行计划不是30*30次访问,而是跟驱动表里的结果集有关,如果是n条数据,那么访问n*30次分区。因为驱动表t没有什么数据,所以这个执行计划没什么问题。
mysql的行为
因为mysql只支持本地索引,所以直接建主键就行了
CREATE TABLE test (
id bigint NOT NULL,
date_created timestamp ,
...
)
PARTITION BY RANGE (partition_key)
(
PARTITION lzl_p20230601 VALUES LESS THAN (20230602),
PARTITION lzl_p20230602 VALUES LESS THAN (20230603),
...
PARTITION lzl_p20230630 VALUES LESS THAN (20230631));
alter table lzl add primary key pklzl(id,partition_key);
mysql从5.7开始执行计划会显示扫描了哪些分区,这里的版本是8.0的。
select的执行计划:
> explain with t as (select id from lzl where id=8723 limit 100 )
-> select STATUS ,FILE_ID ,DATE_UPDATED from lzl where id in ( select id from t);
+----+-------------+------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived3> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | Start temporary |
| 1 | PRIMARY | lzl | lzl_p20230601,lzl_p20230602,lzl_p20230603,lzl_p20230604,lzl_p20230605,lzl_p20230606,lzl_p20230607,lzl_p20230608,lzl_p20230609,lzl_p20230610,lzl_p20230611,lzl_p20230612,lzl_p20230613,lzl_p20230614,lzl_p20230615,lzl_p20230616,lzl_p20230617,lzl_p20230618,lzl_p20230619,lzl_p20230620,lzl_p20230621,lzl_p20230622,lzl_p20230623,lzl_p20230624,lzl_p20230625,lzl_p20230626,lzl_p20230627,lzl_p20230628,lzl_p20230629,lzl_p20230630 | ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 8 | t.id | 1 | 100.00 | End temporary |
| 3 | DERIVED | lzl | lzl_p20230601,lzl_p20230602,lzl_p20230603,lzl_p20230604,lzl_p20230605,lzl_p20230606,lzl_p20230607,lzl_p20230608,lzl_p20230609,lzl_p20230610,lzl_p20230611,lzl_p20230612,lzl_p20230613,lzl_p20230614,lzl_p20230615,lzl_p20230616,lzl_p20230617,lzl_p20230618,lzl_p20230619,lzl_p20230620,lzl_p20230621,lzl_p20230622,lzl_p20230623,lzl_p20230624,lzl_p20230625,lzl_p20230626,lzl_p20230627,lzl_p20230628,lzl_p20230629,lzl_p20230630 | ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 8 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
update的执行计划:
> explain with t as (select id from lzl where id=8723 limit 100 )
-> update lzl set
-> STATUS = '00',
-> FILE_ID = null,
-> DATE_UPDATED = localtimestamp(0) where id in ( select id from t);
+----+-------------+------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived3> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | Start temporary |
| 1 | UPDATE | lzl | lzl_p20230601,lzl_p20230602,lzl_p20230603,lzl_p20230604,lzl_p20230605,lzl_p20230606,lzl_p20230607,lzl_p20230608,lzl_p20230609,lzl_p20230610,lzl_p20230611,lzl_p20230612,lzl_p20230613,lzl_p20230614,lzl_p20230615,lzl_p20230616,lzl_p20230617,lzl_p20230618,lzl_p20230619,lzl_p20230620,lzl_p20230621,lzl_p20230622,lzl_p20230623,lzl_p20230624,lzl_p20230625,lzl_p20230626,lzl_p20230627,lzl_p20230628,lzl_p20230629,lzl_p20230630 | ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 8 | t.id | 1 | 100.00 | End temporary |
| 3 | DERIVED | lzl | lzl_p20230601,lzl_p20230602,lzl_p20230603,lzl_p20230604,lzl_p20230605,lzl_p20230606,lzl_p20230607,lzl_p20230608,lzl_p20230609,lzl_p20230610,lzl_p20230611,lzl_p20230612,lzl_p20230613,lzl_p20230614,lzl_p20230615,lzl_p20230616,lzl_p20230617,lzl_p20230618,lzl_p20230619,lzl_p20230620,lzl_p20230621,lzl_p20230622,lzl_p20230623,lzl_p20230624,lzl_p20230625,lzl_p20230626,lzl_p20230627,lzl_p20230628,lzl_p20230629,lzl_p20230630 | ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 8 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
mysql的2个执行计划都一致。但是执行计划驱动表选择有问题,const的应该为驱动表扫描次数会更少。
BUG?
bug描述
https://postgrespro.com/list/thread-id/2482006
通过报错很容易就能搜到这个bug。这个bug还是德哥在2020年提交的,后面是两个源码大佬对这个bug的讨论,讨论内容比较长,总结一下:pg并不支持无限制的分区表,这在真实世界中也是能理解的,如果分区过多性能可能会急速下降。但是社区还是认为需要调整这个限制,并对源码中的INNER_VAR、Var.varno等进行了讨论。
误导性
这个bug标题有一定的误导性,BUG #16302: too many range table entries - when count partition table(65538 childs)
bug看上去说分区表的分区不能超过65538个,在讨论中也有PG can handle up to 64K relations in a query,一个查询不能有超过64K的relation。
这个就很奇怪,因为我这里的表是400个分区,然后就抛出报错了。实际上上面两个描述不太准确。因为64K的限制指的是执行计划中“表”,不全等于真实的表。当然如果表或者分区已经超过这个数,那么当然会有问题。但是如果没有超过64K,也可能是有问题的,就像我这里的案例一样,它只有400个分区。
修复
bug提交的是12.2版本,我的环境是13.2版本的。
这个bug在pg15中修复,src/include/nodes/primnodes.h源码跟之前不一样了
#define INNER_VAR (-1) /* reference to inner subplan */
#define OUTER_VAR (-2) /* reference to outer subplan */
#define INDEX_VAR (-3) /* reference to index column */
#define ROWID_VAR (-4) /* row identity column during planning */
#define IS_SPECIAL_VARNO(varno) ((int) (varno) < 0)
跟社区讨论的一样,15中不仅把几个VAR都改成了负数,还把varno转换成了32位(40亿),之前是16位的(也就是65536)。
而在抛出报错的函数中,src/backend/optimizer/plan/setrefs.c中的add_rte_to_flat_rtable()函数中的报错代码已经被删除了!整个15的源码都没有too many range table entries!
总结
- pg对于分区表的优化还有提升空间。pg对于分区表的分区,跟oracle、mysql不一样,它仍然子分区当成普通表来处理,而oracle只是把子分区当成一个段来处理,跟表是有差别的。这也导致pg在生产分区表执行计划时把每一个分区的访问方式都写了出来(在不会裁剪的情况下),分区特别多时执行计划会非常的长;而oracle只需要写
partition range all就行了;mysql也会打印所有分区,但是不会像pg那样把每个分区的访问当成一个子查询,从而降低了执行计划的复杂度。 - 即使分区没有达到64K,也可能报错
too many range table entries。这个限制其实是执行计划RTE个数,而不是分区个数(当然分区达到这个数,RTE也到达了,就像上面说的,pg打印了所有分区的访问方式) too many range table entries报错在pg15解决- 如果是15以下的版本,确实不要建太多的分区!当然也可以利用分区裁剪来减少分区的访问,就像这个案例,把where逻辑中加上分区键条件就可以了。



![[RocketMQ] Broker接收消息入口源码 (九)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cd572fe87f2f44fd8c0c082719ee6999.png)