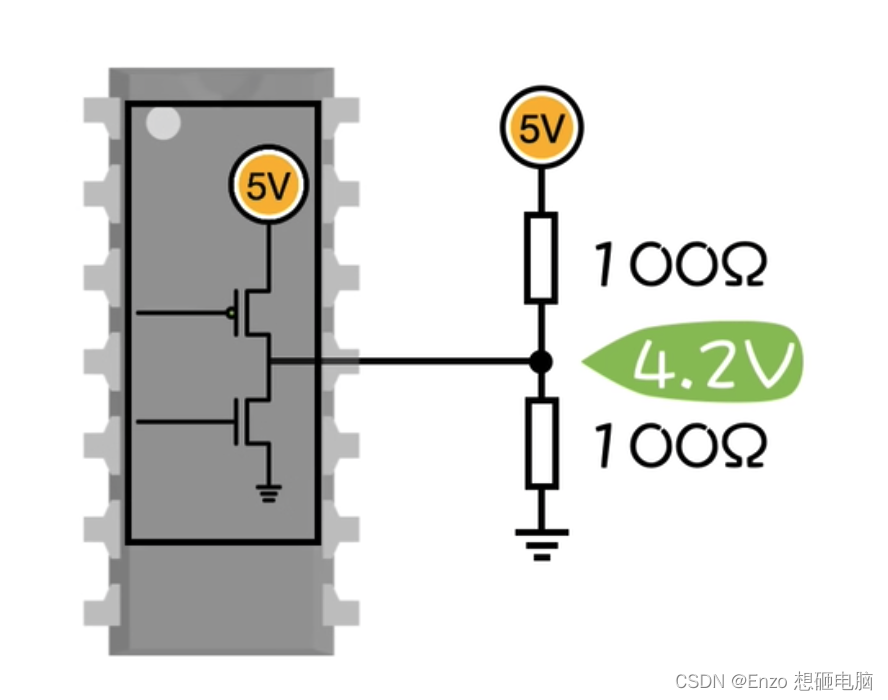
数据结构–队列的顺序实现
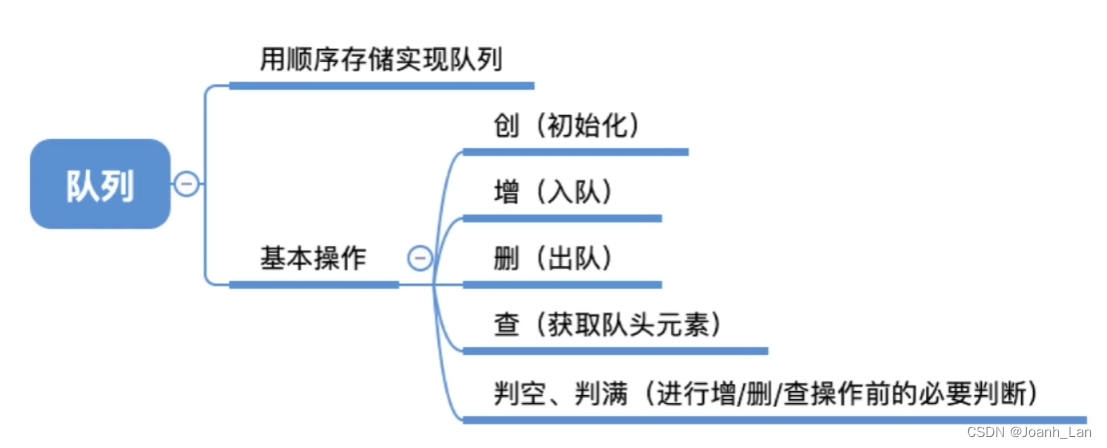
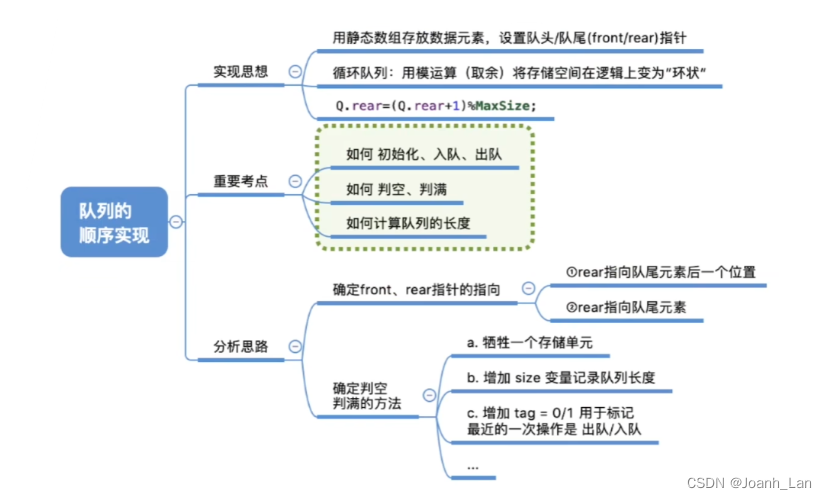
队列的顺序存储代码定义
#define MaxSize 10 //定义队列中元素最大个数
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize]; //静态数组存放队列元素
int front, rear; //对头指针 & 队尾指针
} SqQueue;

初始化操作
void InitQueue(SqQueue &Q)
{
Q.rear = Q.front = 0;
}
判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue Q)
{
return Q.rear == Q.front;
}
入队操作
bool EnQueue(SqQueue &Q, ElemType x)
{
if (队列已满) return false;
Q.data[Q.rear] = x;
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize;
return true;
}
用模运算将存储空间在逻辑上变成了
“环状”
\color{red}“环状”
“环状”
这样可以 节约空间 \color{red}节约空间 节约空间
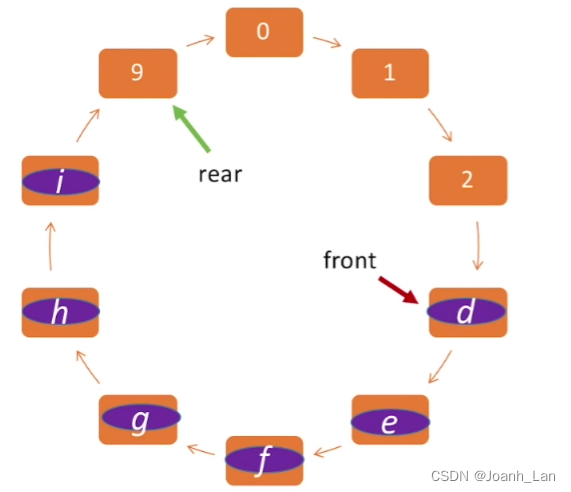
入队代码就变成这个:
bool EnQueue(SqQueue &Q, ElemType x)
{
if ((Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize == Q.front) return false;
Q.data[Q.rear] = x;
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize;
return true;
}
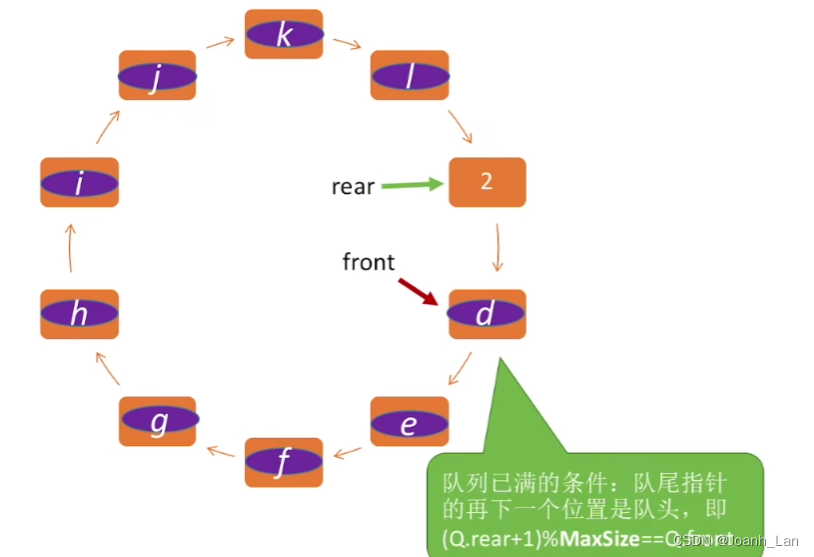
我们可以发现这种逻辑会牺牲一个存储空间
解决方法:
方法一:引进队列元素个数
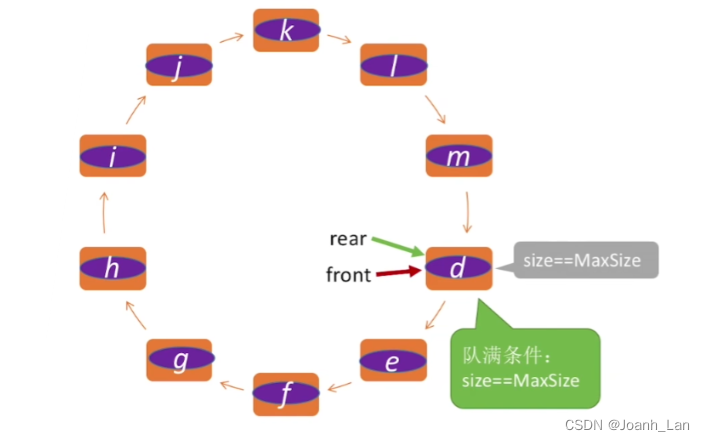
方法二:
记录上一次操作是插入 or 删除
只有删除操作,才可能导致队空
只有插入操作,才可能导致队满
出队操作
bool DeQueue(SqQueue &Q, ElemType &x)
{
if (Q.rear == Q.rear) return false;
x = Q.data[Q.front];
Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % MaxSize;
return true;
}
获取队头元素
bool GetHead(SqQueue Q, ElemType &x)
{
if(Q.rear == Q.front) return false;
x = Q.data[Q.front];
return true;
}
ps:要根据实际的逻辑来书写代码,注意是否需要保证 不牺牲存储空间
知识点回顾与重要考点