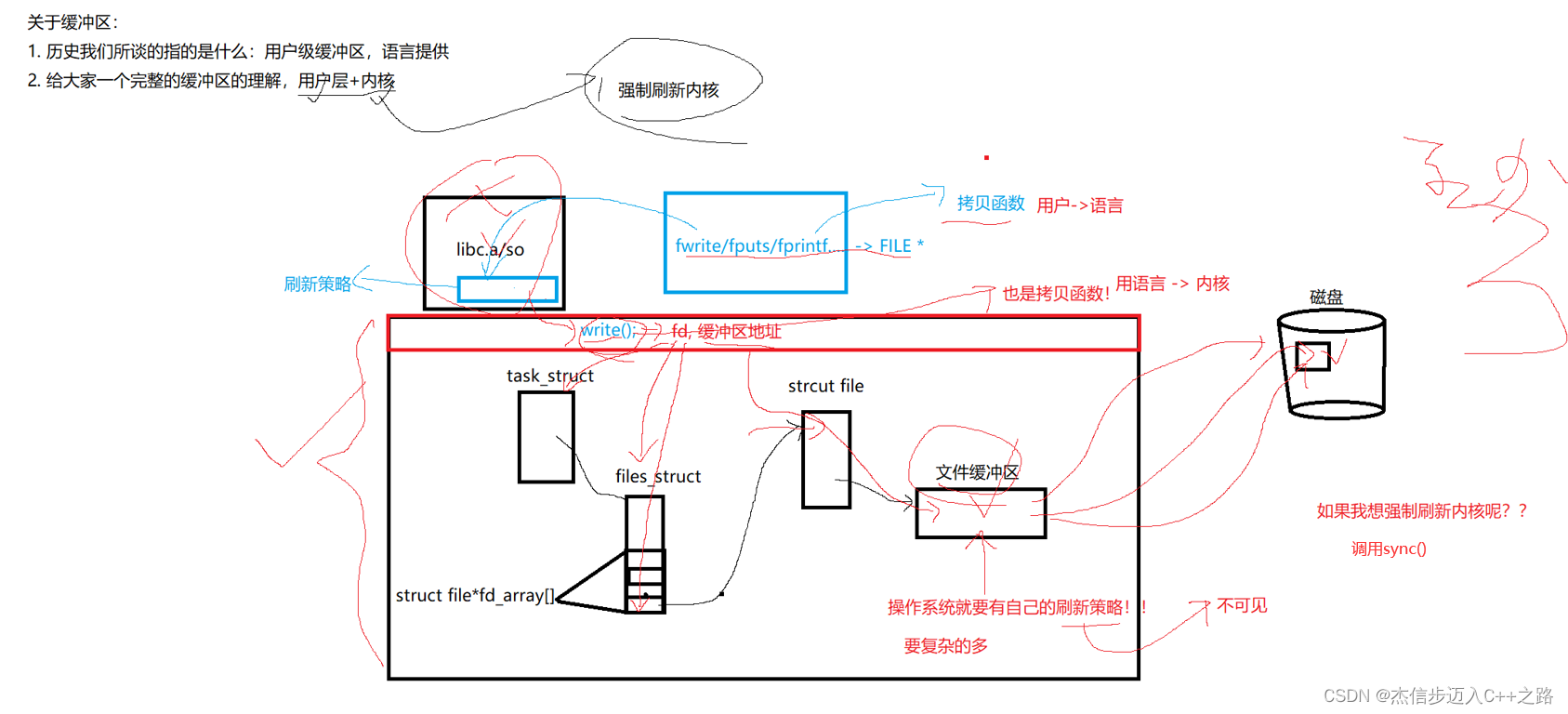
对象的初始化和清理
构造函数和析构函数
对象的初始化和清理也是两个非常重要的安全问题
一个对象或者变量没有初始化状态,对其使用后果是未知
同样的使用完一个对象或变量,没有及时清理,也会造成一定的安全问题
c++利用了构造函数和析构函数解决上述问题,这两个函数将会被编译器自动调用,完成对象初始化和清理工作。
对象的初始化和清理工作是编译器强制要我们做的事情,因此如果我们不提供构造和析构,编译器会提供编译器提供的构造函数和析构函数,只是他们都是空实现。
1、构造函数:主要作用在于创建对象时为对象的成员属性赋值,构造函数由编译器自动调用,无须手动调用。
2、析构函数:主要作用在于对象销毁前系统自动调用,执行一些清理工作。
构造函数语法:类名(){}
1、构造函数,没有返回值也不写void
2、函数名称与类名相同
3、构造函数可以有参数,因此可以发生重载
4、程序在调用对象时候会自动调用构造,无须手动调用,而且只会调用一次
构造函数语法:~类名(){}
1、析构函数,没有返回值也不写void
2、函数名称与类名相同,在名称前加上符号~
3、析构函数不可以有参数,因此不可以发生重载
4、程序在对象销毁前会自动调用析构,无须手动调用,而且只会调用一次
person.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
// 1、构造函数,没有返回值也不写void
// 2、函数名称与类名相同
// 3、构造函数可以有参数,因此可以发生重载
// 4、程序在调用对象时候会自动调用构造,无须手动调用,而且只会调用一次
Person();
// 1、析构函数,没有返回值也不写void
// 2、函数名称与类名相同,在名称前加上符号~
// 3、析构函数不可以有参数,因此不可以发生重载
// 4、程序在对象销毁前会自动调用析构,无须手动调用,而且只会调用一次
~Person();
int m_num=0;
void setnum(int num);
};
main.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "person.h"
void test01()
{
Person p1;//在栈上的数据,test01执行完毕后,释放这个对象
p1.setnum(1);
}
int main()
{
Person p2;
p2.setnum(2);
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
person.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "person.h"
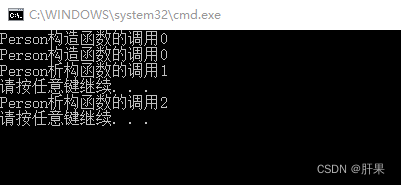
Person::Person()
{
cout << "Person构造函数的调用" << m_num << endl;
}
Person::~Person()
{
cout << "Person析构函数的调用" << m_num << endl;
}
void Person::setnum(int num)
{
m_num = num;
}
构造函数的分类及调用
两种分类方式:
按参数分为:有参构造和无参构造
按类型分为:普通构造和拷贝构造
三种调用方式:
括号法
显示法
隐式转换法
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
cout << "Person的无参数构造函数调用" << endl;//无参构造函数(默认构造函数)
}
Person(int a)
{
age = a;
cout << "Person的带参数构造函数调用" << endl;//有参构造函数
}
//拷贝构造函数
Person(const Person &p)
{
age = p.age;
age = p.age;
cout << "Person的拷贝数构造函数调用" << endl;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int age;
};
void test01()
{
//1、括号法
//Person p1;//默认构造函数调用
//Person p2(10);//有参构造函数
//Person p3(p2);
//注意事项
//调用默认构造函数时,不要加()
//因为编译器会认为是一个函数的声明,不会认为在创建对象
//cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.age << endl;
//cout << "p3的年龄为:" << p3.age << endl;
//2、显示法
//Person p1;//默认构造函数调用
//Person p2 = Person(10);//有参构造函数
//Person p3 = Person(p2);//拷贝构造函数
//注意事项
//不要利用拷贝构造函数,初始化匿名对象
//Person(10);//匿名对象 特点:当前行执行结束后,系统会立即回收掉匿名对象
//3、隐式转换法
Person p4 = 10;//相当于写了 Person p4 = Person(10);//有参构造函数
Person p5 = p4;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
拷贝构造函数的调用时机
C++中拷贝构造函数调用时机通常有三种情况
1、使用一个已经创建完毕的对象来初始化一个新对象
2、值传递的方式给函数传值
3、以值方式返回局部对象
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
cout << "Person的无参数构造函数调用" << endl;//无参构造函数(默认构造函数)
}
Person(int age)
{
m_Age = age;
cout << "Person的带参数构造函数调用" << endl;//有参构造函数
}
//拷贝构造函数
Person(const Person &p)
{
m_Age = p.m_Age;
cout << "Person的拷贝数构造函数调用" << endl;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
//1、使用一个已经创建完毕的对象来初始化一个新对象
void test01()
{
Person p1(20);
Person p2(p1);
}
//2、值传递的方式给函数传值
void doWork(Person p)
{
}
void test02()
{
Person p;
doWork(p);
}
//3、以值方式返回局部对象
Person doWork2()
{
Person p1;
return p1;
}
void test03()
{
Person p = doWork2();
}
int main()
{
//test01();
//test02();
test03();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
自行探索:☆
1、当类中有任意一个构造函数时,编译器就不会在添加默认构造函数了。
2、当类中程序员自己写了一个拷贝构造函数后,若这个拷贝函数中并没有将所有成员变量的赋值给另一个需要拷贝的类,那么在调用值传递的时候,这些常量的值将不会被拷贝过去。
构造函数的调用规则
默认情况下,c++编译器至少给一个类添加3个函数
1、默认构造函数(无参,函数体为空)
2、默认析构函数(无参,函数体为空)
3、默认拷贝构造函数,对属性进行值拷贝
构造函数调用规则如下:
1、如果用户定义有参构造函数,c++不再提供默认无参构造,但是会提供默认拷贝构造
2、如果用户定义拷贝构造函数,c++不会再提供其他构造函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
cout << "Person的无参数构造函数调用" << endl;//无参构造函数(默认构造函数)
}
Person(int age)
{
m_Age = age;
cout << "Person的带参数构造函数调用" << endl;//有参构造函数
}
//Person(const Person &p)//*(Person* const p)
//{
// m_Age = p.m_Age;
// cout << "Person的拷贝数构造函数调用" << endl;//拷贝构造函数
//}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
Person p;
p.m_Age = 18;
Person p2(p);
cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.m_Age << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
//Person()
//{
// cout << "Person的无参数构造函数调用" << endl;//无参构造函数(默认构造函数)
//}
Person(int age)
{
m_Age = age;
cout << "Person的带参数构造函数调用" << endl;//有参构造函数
}
//Person(const Person &p)//*(Person* const p)
//{
// m_Age = p.m_Age;
// cout << "Person的拷贝数构造函数调用" << endl;//拷贝构造函数
//}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
//void test01()
//{
// Person p;//报错
// p.m_Age = 18;
// Person p2(p);
// cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.m_Age << endl;
//}
void test02()
{
Person p(28);
Person p2(p);
cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.m_Age << endl;
}
int main()
{
//test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}