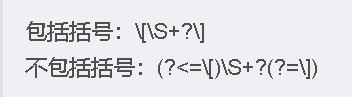目录
浏览器http请求
同步 js标签跨域、url
异步ajax、websock协议
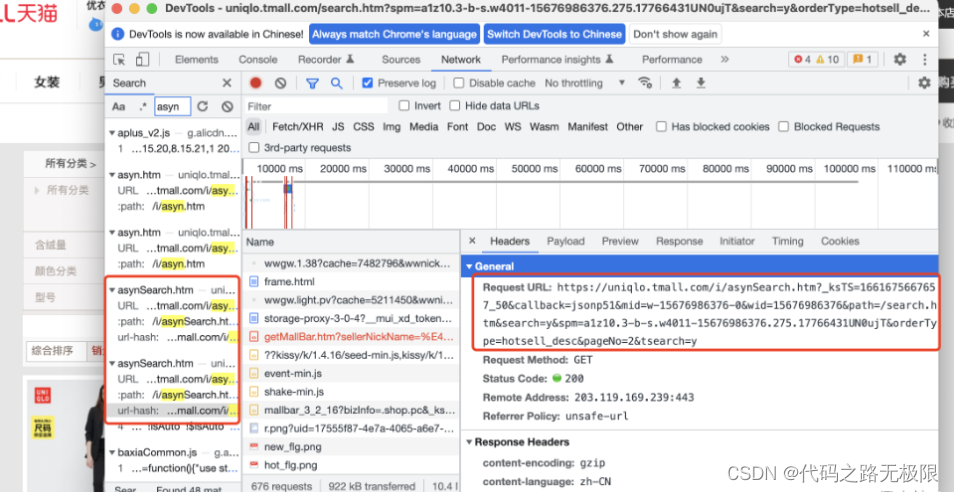
ajax是异步的技术术语,最早的api是xhr(XMLHttpRequest)
fetch es6 api
axios
封装axios
src/utils/request.ts
src/utils/func.ts
SSO(Single Sign-On)单点登录,一次登陆可访问多个相互独立的程序
正则表达式
常用字符
前/后向查找:匹配括号中的内容(不包含括号)
src/api/common.ts
src/views/components
基础知识回顾
url参数
location属性值
同源策略
A.手动
B.设置index.html
C.浏览器扩展小程序:一键获取/设置多个
浏览器的本地存储Cookie、WebStorage(localStorage、sessionStorage)
web安全
XSS跨站脚本攻击Cross-Site Scripting(登陆时执行脚本读取)
CSRF跨站请求伪造Cross-site request forgery(凭证请求)
SQL注入攻击(交表单/输域名 执行SQL命令)
DDoS攻击分布式拒绝服务 Distributed Denial of Service(请求过载)
浏览器http请求
同步 js标签跨域、url
<img src>,<link href>
异步ajax、websock协议
ajax是异步的技术术语,最早的api是xhr(XMLHttpRequest)
fetch es6 api
基于promise,简单易用
axios
- 同构,即同样的代码在nodejs端,浏览器端都可用
- 在浏览器用xhr,Node.js中使用Node的内置http模块。
// 在浏览器中,根据其Content-Type头信息,自动转换数据
axios.get('/api/data').then(response => {
// response.data 将是一个JavaScript对象
});
// 在Node.js中手动设置响应数据类型
axios.get('/api/data', { responseType: 'json' }).then(response => {
// response.data 将是一个JavaScript对象
});- axios 新版本也支持了fetch
- 第三方库都是基于原生API的,所以axios也还是基于xhr的
【JavaScript】爆肝 2 万字!一次性搞懂 Ajax、Fetch 和 Axios 的区别~ - 掘金
封装axios
src/utils/request.ts
import service from 'axios'
import { handleSSO } from '@/utils/func'
import router from '@/router/index'
// 请求拦截器
service.interceptors.request.use(
(config: any) => {
// 在请求头中添加XMLHttpRequest字段
config.headers['X-Requested-With'] = 'XMLHttpRequest'
return config
},
(error: any) => {
console.log('request:', error) // 用于调试的错误信息
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
function errorMsgTips(msg: any) {
window.$message.error(msg)
}
// 响应拦截器
service.interceptors.response.use(
(response: { data: any; config: any }) => {
const resData = response.data || {}
if (resData.code === 302) {
// 如果响应码为302,进行页面重定向到指定链接
window.location.href = `https://www.example.com/path/to/resource.html/domain=${location.host}&req=${encodeURIComponent(location.pathname)}&protocol=https${location.hash}`
} else if (resData.code == 0 || resData.code == 200) {
// 如果响应码为0或200,则直接返回响应数据
return resData
} else if (resData.code == 4004) {//自定义响应码
// 如果响应码为4004,说明没有权限,跳转至无权限页面
router.push({
path: '/notPermission'
})
} else {
// 其他情况下,显示错误提示消息
errorMsgTips(resData.message || '接口错误,请稍后重试')
}
},
(error: any) => {
if (service.isCancel(error)) {
console.log('取消请求 error -> ', error)
return
}
if (error && error.response && error.response.status === 302) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
// 如果是开发环境,并且错误码为302,显示替换SSO_SESSION_ID的提示
errorMsgTips('请替换Cookies里的SSO_SESSION_ID')
return
} else {
// 非开发环境下,进行单点登录重定向
window.location.href = handleSSO('login')
}
} else if (error && error.stack.includes('timeout')) {
// 如果错误信息中包含"timeout",显示接口超时错误提示
errorMsgTips('接口超时')
return
} else if (error && error.stack.includes('Network')) {
// 如果错误信息中包含"Network",显示网络异常错误提示
errorMsgTips('网络异常')
return
}
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
export default service
src/utils/func.ts
/**
* 清除会话
* @param
*/
function clearSession() {
//匹配不包含空格和分号的字符,该字符后面必须跟着一个等号。这会返回一个由cookie键组成的数组。
const keys = document.cookie.match(/[^ =;]+(?=\=)/g)
if (keys) {
for (let i = keys.length; i--; )
//) 创建了一个代表时间戳 0 的 JavaScript Date 对象,并将其转换为 UTC 字符串。
//这个时间对应于 1970 年 1 月 1 日 协调世界时 (UTC) 时间 00:00:00。
document.cookie = keys[i] + '=0;expires=' + new Date(0).toUTCString()
}
sessionStorage.clear()
localStorage.clear()
}
/**
* SSO登入登出
* @param SSOtype
* login登入
* logout登出
*/
export function handleSSO(SSOtype: string): string {
const hostStr = 'passport.example.com'
clearSession()
return `https://${hostStr}/${SSOtype}?service=` + encodeURIComponent(window.location.origin)
}SSO(Single Sign-On)单点登录,一次登陆可访问多个相互独立的程序
通常靠token/cookie实现
正则表达式
常用字符
·匹配除换行字符外的任何单个字符
*匹配前一个字符零或多次。例如,"zo*”与"z”或"zoo”匹配。
+匹配前一个字符一次或多次。例如,"zo+"与"zoo”匹配,但和"z”不匹配。
?匹配前一个字符零或一次。例如,"a?ve?”和"never"中的“"ve”匹配。
x|y 匹配x或y
{n}匹配n次。n是非负整数
{n,} n是一个非负整数。至少匹配n次。例如,"o{2,)"和"Bob”中的"o”不匹配,但和"foooood"中的所有o匹配。"o{1}”与"o+”等效。"o{0,}”和"o*”等效。
{n,m}m和n是非负整数。至少匹配n次而至多匹配 m次。例如,"o{1,3]"和"fooooood”中的前三个o匹配。"o{0,1}”和“o?”等效。
[xyz]匹配括号内的任一字符。例如,"[abc]"和"plain”中的"a”匹配。
[^xyz]匹配非括号内的任何字符。例如,"[^abc]"和“plain”中的"p”匹配。
[a-z]字符范围。和指定范围内的任一字符匹配。例如,"[a-z]”匹配"a"到"z"范围内的任一小写的字母表字符。
[^m-z]否定字符范围。匹配不在指定范围内的任何字符。例如,"[m-z]”匹配不在"m"到"z"范围内的任何字符。
前/后向查找:匹配括号中的内容(不包含括号)
后向查找:(?<=exp)是以exp开头的字符串, 但不包含本身.
前向查找:(?=exp)就匹配为exp结尾的字符串, 但不包含本身.
负后向查找:(?<!exp) ,在之前被指定的子表达式不能被匹配到。
负前向查找::(?!exp),在之后被指定的子表达式不能被匹配到。
正向先行断言 (?=\=) 表示在匹配等号 = 前面的位置进行断言,即正向这个位置后面必须跟着等号 = 才能进行匹配。这种断言不会消耗实际的字符。
前向查找 (?==) 表示匹配等号 =,并且把等号 = 包含在匹配结果中。这种查找会消耗等号 = 这个字符。
src/api/common.ts
import request from '@/utils/request'
const baseUrl = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ? '/test' : ''
const mock = false
// 查看自己信息接口
export const commonQuery = (data: any) => {
const url = mock ? `${baseUrl}/common/query` : `${baseUrl}/mock/query`
return request.post(url, data)
}
// 查看自己信息接口
export const getUserInfo = () => {
const url = `${baseUrl}/menu/userInfo`
return request.get(url)
}
src/views/components
import * as API from "@/api/common"
...
API.commonQuery(params).then((res: any) => {
console.log('res::::', res)
})基础知识回顾
url参数
http://example.com/page?param1=value1¶m2=value2#section1
| ? | 分隔实际的URL和参数 |
| & | URL中指定的参数间的分隔符 |
| = | 左边为参数名、右边参数值 |
| # | 锚点(Anchor),用于标识文档中的特定位置或元素, 仅在客户端使用,并且由浏览器处理,不发送到服务器 指示浏览器滚动到具有 |
location属性值
window的全局对象,表示当前页面http://www.example.com/path/index.html
window.location.href:获取/设置 url
window.location.orgin:协议、主机名和端口号部分
//https://www.example.com:8080/page.html
// :// :
//https%3A%2F%2Fwww.example.com%3A8080。
encodeURIComponent(window.location.origin)
//encodeURIComponent用于将字符串中的特殊字符(空格、&、+、= 、?)转换为编码形式,确保URL中不包含任何无效字符
//查询参数时 或者 动态参数时 需要encodeURIComponent
const url = 'https://example.com/api?param=' + encodeURIComponent(queryParam);
window.location.href =`https://www.example.com/path/to/resource.html/domain=${location.host}&req=${encodeURIComponent(location.pathname)}&protocol=https${location.hash}`window.location.protocol: 协议http
window.location.host:主机+端口(host:8080)/IP地址(127.123.32.1唯一)/域名(www.example.com助记)
window.location.hostname:主机host
window.location.port:端口8080
window.location.pathname: 资源路径path/index.html,资源index.html
window.location.hash:
window.location.search: 搜索
var searchParams = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search);
console.log(searchParams.get('name')); // 输出 "John"同源策略
同源/域:顾名思义,域名包括前缀都要相同,自然也包括端口号
但是cookie从端口号开始就可以不同
跨域请求默认情况下不会携带 Cookie。
然而,可以通过设置 CORS(跨源资源共享)头部来允许携带 Cookie 进行跨域请求。
withCredentials 属性为 true,以告知浏览器在请求中携带 Cookie。
token和cookie
| 凭证 | token | cookie |
| 跨域 | token 完全由应用管理,所以它可以避开同源策略 | 服务器端生成管理,不能跨域 |
| 与session | 移动端对 cookie 的支持不是很好,所以移动端常用的是 token | session 需要基于 cookie 实现 |
替换cookie(开发中模拟不同权限的用户)
A.手动
B.设置index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="">
<head>
...
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
document.cookie = 'sso_ticket=xx'
</script>
</body>
</html>C.浏览器扩展小程序:一键获取/设置多个
浏览器的本地存储Cookie、WebStorage(localStorage、sessionStorage)
web安全
XSS跨站脚本攻击Cross-Site Scripting(登陆时执行脚本读取)
解决:
- url参数使用encodeURIComponent方法转义
- 尽量不用InnerHtml插入HTML内容
CSRF跨站请求伪造Cross-site request forgery(凭证请求)
解决:添加验证码、使用token
SQL注入攻击(交表单/输域名 执行SQL命令)
解决:表单输入时通过正则表达式将一些特殊字符进行转换
DDoS攻击分布式拒绝服务 Distributed Denial of Service(请求过载)
解决:
- 限制单IP请求频率。
- 检查特权端口的开放