kubelet 是运行在每个节点上的主要的“节点代理”,每个节点都会启动 kubelet进程,用来处理 Master 节点下发到本节点的任务,按照 PodSpec 描述来管理Pod 和其中的容器(PodSpec 是用来描述一个 pod 的 YAML 或者 JSON 对象)。
Kubelet 以 PodSpec 的方式工作。PodSpec 是描述一个 Pod 的 YAML 或 JSON 对象。 kubelet 采用一组通过各种机制提供的 PodSpecs(主要通过 apiserver),并确保这些 PodSpecs 中描述的 Pod 正常健康运行。
kubelet 的主要功能
1、kubelet监听端口
[root@master-8 ysr]# netstat -ntlp |grep kubelet
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:10248 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2882/kubelet
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:34144 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2882/kubelet
tcp6 0 0 :::10250 :::* LISTEN 2882/kubelet
2、kubelet 主要功能:
- pod 管理:kubelet 定期从所监听的数据源获取节点上 pod/container 的期望状态(运行什么容器、运行的副本数量、网络或者存储如何配置等等),并调用对应的容器平台接口达到这个状态。
- 容器健康检查:kubelet 创建了容器之后还要查看容器是否正常运行,如果容器运行出错,就要根据 pod 设置的重启策略进行处理。
- 容器监控:kubelet 会监控所在节点的资源使用情况,并定时向 master 报告,资源使用数据都是通过 cAdvisor 获取的。知道整个集群所有节点的资源情况,对于 pod 的调度和正常运行至关重要。
kubelete工作原理
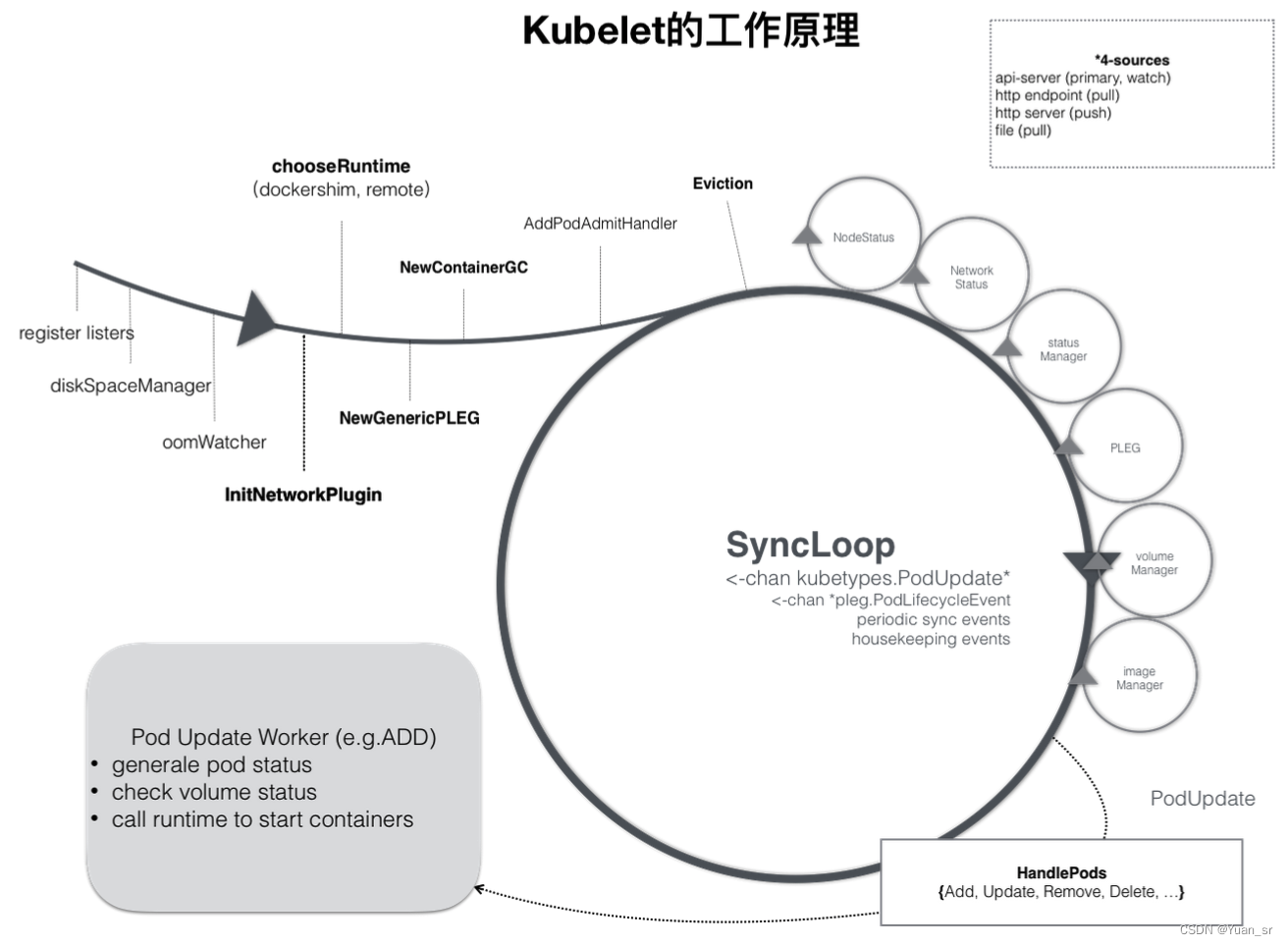
由图我们可以看到kubelet 的工作核心,就是一个控制循环,即:SyncLoop。驱动整个控制循环的事件有:pod更新事件、pod生命周期变化、kubelet本身设置的执行周期、定时清理事件等。
在SyncLoop循环上还有很多xxManager:
- PLEG(Pod Lifecycle Event Generator) PLEG 是 kubelet 的核心模块,PLEG 会一直调用 container runtime 获取本节点 containers/sandboxes 的信息,并与自身维护的 pods cache 信息进行对比,生成对应的 PodLifecycleEvent,然后输出到 eventChannel 中,通过 eventChannel 发送到 kubelet syncLoop 进行消费,然后由 kubelet syncPod 来触发 pod 同步处理过程,最终达到用户的期望状态。
- cAdvisor cAdvisor(https://github.com/google/cadvisor)是 google 开发的容器监控工具,集成在 kubelet 中,起到收集本节点和容器的监控信息,大部分公司对容器的监控数据都是从 cAdvisor 中获取的 ,cAvisor 模块对外提供了 interface 接口,该接口也被 imageManager,OOMWatcher,containerManager 等所使用。
- OOMWatcher 系统 OOM 的监听器,会与 cadvisor 模块之间建立 SystemOOM,通过 Watch方式从 cadvisor 那里收到的 OOM 信号,并产生相关事件。
- probeManager probeManager 依赖于 statusManager,livenessManager,containerRefManager,会定时去监控 pod 中容器的健康状况,当前支持两种类型的探针:livenessProbe 和readinessProbe。 livenessProbe:用于判断容器是否存活,如果探测失败,kubelet 会 kill 掉该容器,并根据容器的重启策略做相应的处理。 readinessProbe:用于判断容器是否启动完成,将探测成功的容器加入到该 pod 所在 service 的 endpoints 中,反之则移除。readinessProbe 和 livenessProbe 有三种实现方式:http、tcp 以及 cmd。
- statusManager statusManager 负责维护状态信息,并把 pod 状态更新到 apiserver,但是它并不负责监控 pod 状态的变化,而是提供对应的接口供其他组件调用,比如 probeManager。
- containerRefManager 容器引用的管理,相对简单的Manager,用来报告容器的创建,失败等事件,通过定义 map 来实现了 containerID 与 v1.ObjectReferece 容器引用的映射。
- evictionManager 当节点的内存、磁盘或 inode 等资源不足时,达到了配置的 evict 策略, node 会变为 pressure 状态,此时 kubelet 会按照 qosClass 顺序来驱赶 pod,以此来保证节点的稳定性。可以通过配置 kubelet 启动参数 --eviction-hard= 来决定 evict 的策略值。
- imageGC imageGC 负责 node 节点的镜像回收,当本地的存放镜像的本地磁盘空间达到某阈值的时候,会触发镜像的回收,删除掉不被 pod 所使用的镜像,回收镜像的阈值可以通过 kubelet 的启动参数 --image-gc-high-threshold 和 --image-gc-low-threshold 来设置。
- containerGC containerGC 负责清理 node 节点上已消亡的 container,具体的 GC 操作由runtime 来实现。
- imageManager 调用 kubecontainer 提供的PullImage/GetImageRef/ListImages/RemoveImage/ImageStates 方法来保证pod 运行所需要的镜像。
- volumeManager 负责 node 节点上 pod 所使用 volume 的管理,volume 与 pod 的生命周期关联,负责 pod 创建删除过程中 volume 的 mount/umount/attach/detach 流程,kubernetes 采用 volume Plugins 的方式,实现存储卷的挂载等操作,内置几十种存储插件。
- containerManager 负责 node 节点上运行的容器的 cgroup 配置信息,kubelet 启动参数如果指定 --cgroups-per-qos 的时候,kubelet 会启动 goroutine 来周期性的更新 pod 的 cgroup 信息,维护其正确性,该参数默认为 true,实现了 pod 的Guaranteed/BestEffort/Burstable 三种级别的 Qos。
- runtimeManager containerRuntime 负责 kubelet 与不同的 runtime 实现进行对接,实现对于底层 container 的操作,初始化之后得到的 runtime 实例将会被之前描述的组件所使用。可以通过 kubelet 的启动参数 --container-runtime 来定义是使用docker 还是 rkt,默认是 docker。
- podManager podManager 提供了接口来存储和访问 pod 的信息,维持 static pod 和 mirror pods 的关系,podManager 会被statusManager/volumeManager/runtimeManager 所调用,podManager 的接口处理流程里面会调用 secretManager 以及 configMapManager。
kubelet 调用下层容器运行时的执行过程,并不会直接调用容器运行时的 API,而是通过一组叫作 CRI(Container Runtime Interface,容器运行时接口)的 gRPC 接口来间接执行的。
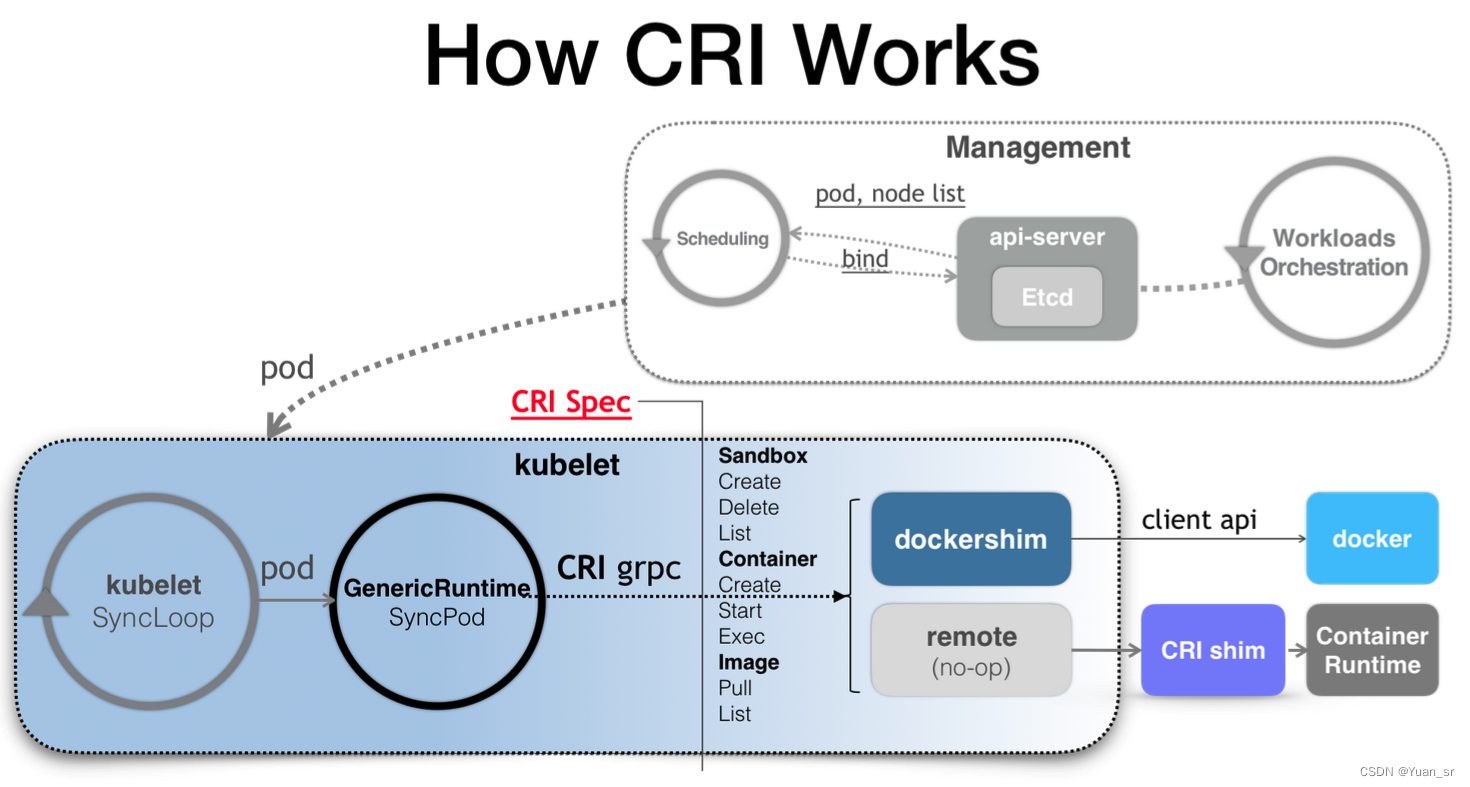
Kubelet 使用 gRPC 框架通过 Unix 套接字与容器运行时或容器运行时垫片程序通信,其中 kubelet 充当客户端,CRI 垫片程序充当服务器。
一般来说CRI接口主要包括两个 gRPC 服务:镜像服务和运行时服务:
- 镜像服务主要是容器镜像相关的操作,比如拉取镜像、删除镜像等。
- 运行时服务主要是跟容器相关的操作,比如创建、启动、删除Container、Exec等。
// PreInitRuntimeService will init runtime service before RunKubelet.
func PreInitRuntimeService(kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *Dependencies) error {
remoteImageEndpoint := kubeCfg.ImageServiceEndpoint
if remoteImageEndpoint == "" && kubeCfg.ContainerRuntimeEndpoint != "" {
remoteImageEndpoint = kubeCfg.ContainerRuntimeEndpoint
}
var err error
if kubeDeps.RemoteRuntimeService, err = remote.NewRemoteRuntimeService(kubeCfg.ContainerRuntimeEndpoint, kubeCfg.RuntimeRequestTimeout.Duration, kubeDeps.TracerProvider); err != nil {
return err
}
if kubeDeps.RemoteImageService, err = remote.NewRemoteImageService(remoteImageEndpoint, kubeCfg.RuntimeRequestTimeout.Duration, kubeDeps.TracerProvider); err != nil {
return err
}
kubeDeps.useLegacyCadvisorStats = cadvisor.UsingLegacyCadvisorStats(kubeCfg.ContainerRuntimeEndpoint)
return nil
}
下面是CRI容器运行时接口的定义规范:
// Runtime service defines the public APIs for remote container runtimes
service RuntimeService {
// Version returns the runtime name, runtime version, and runtime API version.
rpc Version(VersionRequest) returns (VersionResponse) {}
// RunPodSandbox creates and starts a pod-level sandbox. Runtimes must ensure
// the sandbox is in the ready state on success.
rpc RunPodSandbox(RunPodSandboxRequest) returns (RunPodSandboxResponse) {}
// StopPodSandbox stops any running process that is part of the sandbox and
// reclaims network resources (e.g., IP addresses) allocated to the sandbox.
// If there are any running containers in the sandbox, they must be forcibly
// terminated.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if all relevant
// resources have already been reclaimed. kubelet will call StopPodSandbox
// at least once before calling RemovePodSandbox. It will also attempt to
// reclaim resources eagerly, as soon as a sandbox is not needed. Hence,
// multiple StopPodSandbox calls are expected.
rpc StopPodSandbox(StopPodSandboxRequest) returns (StopPodSandboxResponse) {}
// RemovePodSandbox removes the sandbox. If there are any running containers
// in the sandbox, they must be forcibly terminated and removed.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the sandbox has
// already been removed.
rpc RemovePodSandbox(RemovePodSandboxRequest) returns (RemovePodSandboxResponse) {}
// PodSandboxStatus returns the status of the PodSandbox. If the PodSandbox is not
// present, returns an error.
rpc PodSandboxStatus(PodSandboxStatusRequest) returns (PodSandboxStatusResponse) {}
// ListPodSandbox returns a list of PodSandboxes.
rpc ListPodSandbox(ListPodSandboxRequest) returns (ListPodSandboxResponse) {}
// CreateContainer creates a new container in specified PodSandbox
rpc CreateContainer(CreateContainerRequest) returns (CreateContainerResponse) {}
// StartContainer starts the container.
rpc StartContainer(StartContainerRequest) returns (StartContainerResponse) {}
// StopContainer stops a running container with a grace period (i.e., timeout).
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the container has
// already been stopped.
// The runtime must forcibly kill the container after the grace period is
// reached.
rpc StopContainer(StopContainerRequest) returns (StopContainerResponse) {}
// RemoveContainer removes the container. If the container is running, the
// container must be forcibly removed.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the container has
// already been removed.
rpc RemoveContainer(RemoveContainerRequest) returns (RemoveContainerResponse) {}
// ListContainers lists all containers by filters.
rpc ListContainers(ListContainersRequest) returns (ListContainersResponse) {}
// ContainerStatus returns status of the container. If the container is not
// present, returns an error.
rpc ContainerStatus(ContainerStatusRequest) returns (ContainerStatusResponse) {}
// UpdateContainerResources updates ContainerConfig of the container synchronously.
// If runtime fails to transactionally update the requested resources, an error is returned.
rpc UpdateContainerResources(UpdateContainerResourcesRequest) returns (UpdateContainerResourcesResponse) {}
// ReopenContainerLog asks runtime to reopen the stdout/stderr log file
// for the container. This is often called after the log file has been
// rotated. If the container is not running, container runtime can choose
// to either create a new log file and return nil, or return an error.
// Once it returns error, new container log file MUST NOT be created.
rpc ReopenContainerLog(ReopenContainerLogRequest) returns (ReopenContainerLogResponse) {}
// ExecSync runs a command in a container synchronously.
rpc ExecSync(ExecSyncRequest) returns (ExecSyncResponse) {}
// Exec prepares a streaming endpoint to execute a command in the container.
rpc Exec(ExecRequest) returns (ExecResponse) {}
// Attach prepares a streaming endpoint to attach to a running container.
rpc Attach(AttachRequest) returns (AttachResponse) {}
// PortForward prepares a streaming endpoint to forward ports from a PodSandbox.
rpc PortForward(PortForwardRequest) returns (PortForwardResponse) {}
// ContainerStats returns stats of the container. If the container does not
// exist, the call returns an error.
rpc ContainerStats(ContainerStatsRequest) returns (ContainerStatsResponse) {}
// ListContainerStats returns stats of all running containers.
rpc ListContainerStats(ListContainerStatsRequest) returns (ListContainerStatsResponse) {}
// PodSandboxStats returns stats of the pod sandbox. If the pod sandbox does not
// exist, the call returns an error.
rpc PodSandboxStats(PodSandboxStatsRequest) returns (PodSandboxStatsResponse) {}
// ListPodSandboxStats returns stats of the pod sandboxes matching a filter.
rpc ListPodSandboxStats(ListPodSandboxStatsRequest) returns (ListPodSandboxStatsResponse) {}
// UpdateRuntimeConfig updates the runtime configuration based on the given request.
rpc UpdateRuntimeConfig(UpdateRuntimeConfigRequest) returns (UpdateRuntimeConfigResponse) {}
// Status returns the status of the runtime.
rpc Status(StatusRequest) returns (StatusResponse) {}
// CheckpointContainer checkpoints a container
rpc CheckpointContainer(CheckpointContainerRequest) returns (CheckpointContainerResponse) {}
// GetContainerEvents gets container events from the CRI runtime
rpc GetContainerEvents(GetEventsRequest) returns (stream ContainerEventResponse) {}
// ListMetricDescriptors gets the descriptors for the metrics that will be returned in ListPodSandboxMetrics.
// This list should be static at startup: either the client and server restart together when
// adding or removing metrics descriptors, or they should not change.
// Put differently, if ListPodSandboxMetrics references a name that is not described in the initial
// ListMetricDescriptors call, then the metric will not be broadcasted.
rpc ListMetricDescriptors(ListMetricDescriptorsRequest) returns (ListMetricDescriptorsResponse) {}
// ListPodSandboxMetrics gets pod sandbox metrics from CRI Runtime
rpc ListPodSandboxMetrics(ListPodSandboxMetricsRequest) returns (ListPodSandboxMetricsResponse) {}
}
// ImageService defines the public APIs for managing images.
service ImageService {
// ListImages lists existing images.
rpc ListImages(ListImagesRequest) returns (ListImagesResponse) {}
// ImageStatus returns the status of the image. If the image is not
// present, returns a response with ImageStatusResponse.Image set to
// nil.
rpc ImageStatus(ImageStatusRequest) returns (ImageStatusResponse) {}
// PullImage pulls an image with authentication config.
rpc PullImage(PullImageRequest) returns (PullImageResponse) {}
// RemoveImage removes the image.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the image has
// already been removed.
rpc RemoveImage(RemoveImageRequest) returns (RemoveImageResponse) {}
// ImageFSInfo returns information of the filesystem that is used to store images.
rpc ImageFsInfo(ImageFsInfoRequest) returns (ImageFsInfoResponse) {}
}
容器的创建和状态维护
什么是PLEG
kubelet (Kubernetes) 中的 PLEG 模块根据每个匹配的 pod 级别事件调整容器运行时状态,并通过应用更改来保持 pod 缓存最新。
让我们看一下过程图中下面的红色虚线。
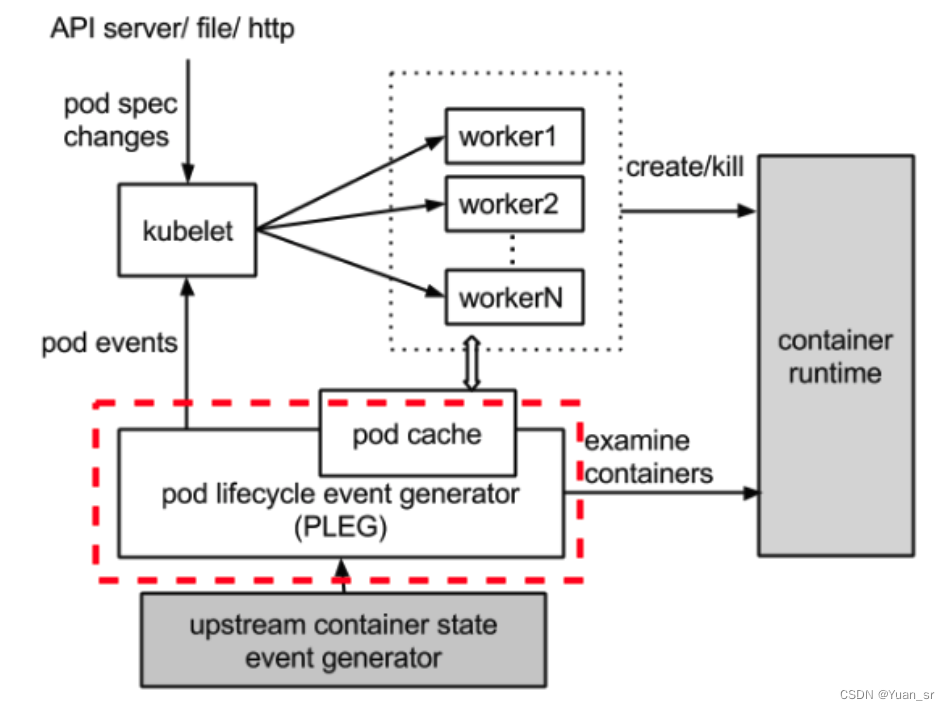 kubele通过调用SyncLoop()不断检查PLEG的健康状况,Healthy()通过检查relist(PLEG关键任务)完成时间是否在设定的阈值内判断PLEG的健康状况。
kubele通过调用SyncLoop()不断检查PLEG的健康状况,Healthy()通过检查relist(PLEG关键任务)完成时间是否在设定的阈值内判断PLEG的健康状况。
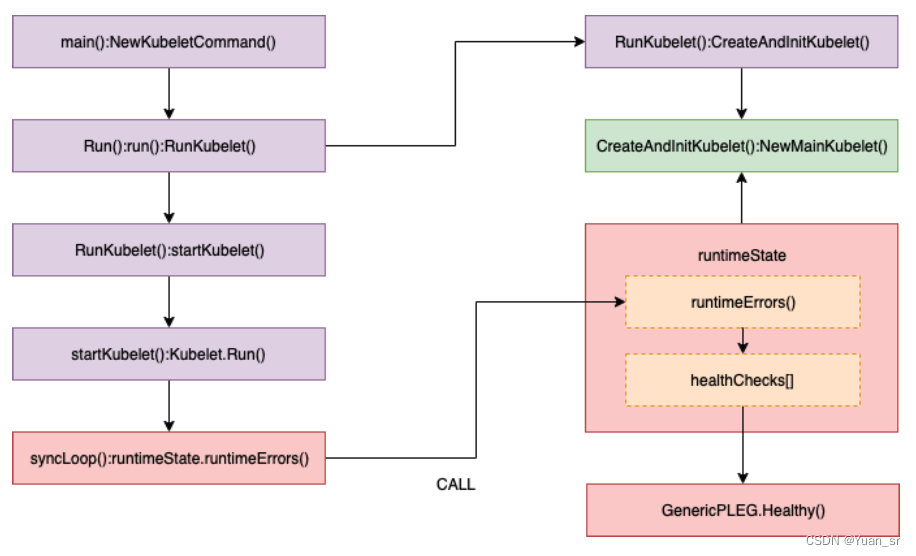
// Healthy check if PLEG work properly.
// relistThreshold is the maximum interval between two relist.
func (g *GenericPLEG) Healthy() (bool, error) {
relistTime := g.getRelistTime()
if relistTime.IsZero() {
return false, fmt.Errorf("pleg has yet to be successful")
}
// Expose as metric so you can alert on `time()-pleg_last_seen_seconds > nn`
metrics.PLEGLastSeen.Set(float64(relistTime.Unix()))
elapsed := g.clock.Since(relistTime)
if elapsed > g.relistDuration.RelistThreshold {
return false, fmt.Errorf("pleg was last seen active %v ago; threshold is %v", elapsed, g.relistDuration.RelistThreshold)
}
return true, nil
}
接下来看看PLEG的关键任务Relist:
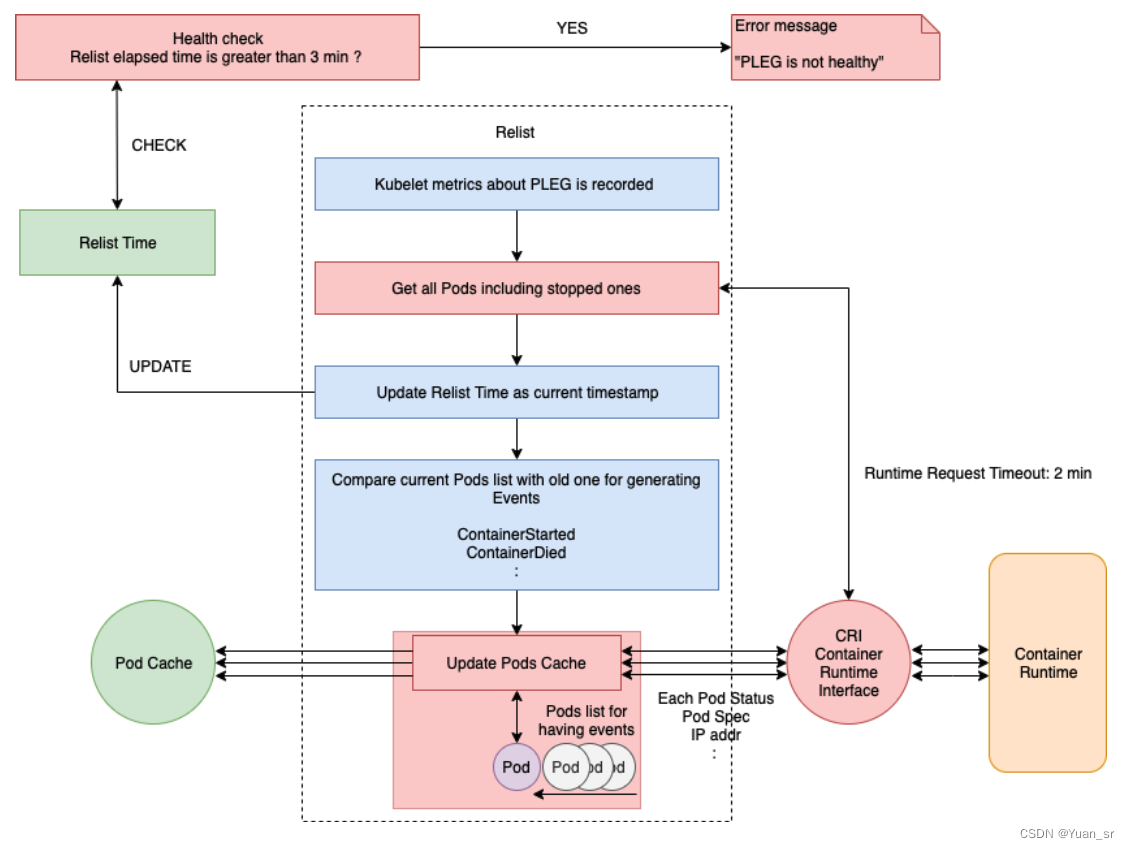 Relist函数的作用是查询容器运行时获取一组Pod和容器的列表,然后与内部存储的Pod和容器进行比较,并根据比较结果生成相应的事件。
Relist函数的作用是查询容器运行时获取一组Pod和容器的列表,然后与内部存储的Pod和容器进行比较,并根据比较结果生成相应的事件。
具体而言,Relist函数的主要功能包括:
- 获取所有的Pod列表,并将其转换为kubecontainer.Pods类型。
- 更新正在运行的Pod和容器的计数指标。
- 更新podRecords中的当前Pod列表。
- 比较旧的Pod和当前Pod,并生成相应的事件。
- 如果启用了缓存,将与Pod相关的事件更新到缓存中。
- 更新内部存储并发送事件。
- 在容器完成时记录容器的退出码。
- 如果启用了缓存,重新检查之前检查失败的Pod。
- 更新缓存的时间戳。
总的来说,Relist函数的目的是通过与容器运行时的查询结果进行比较,及时更新内部存储的Pod和容器状态,并生成相应的事件。这样可以确保Kubelet能够及时了解到Pod和容器的变化,并做出相应的处理。
其中获取所有Pod列表的方法GetPods()调用堆栈如下:
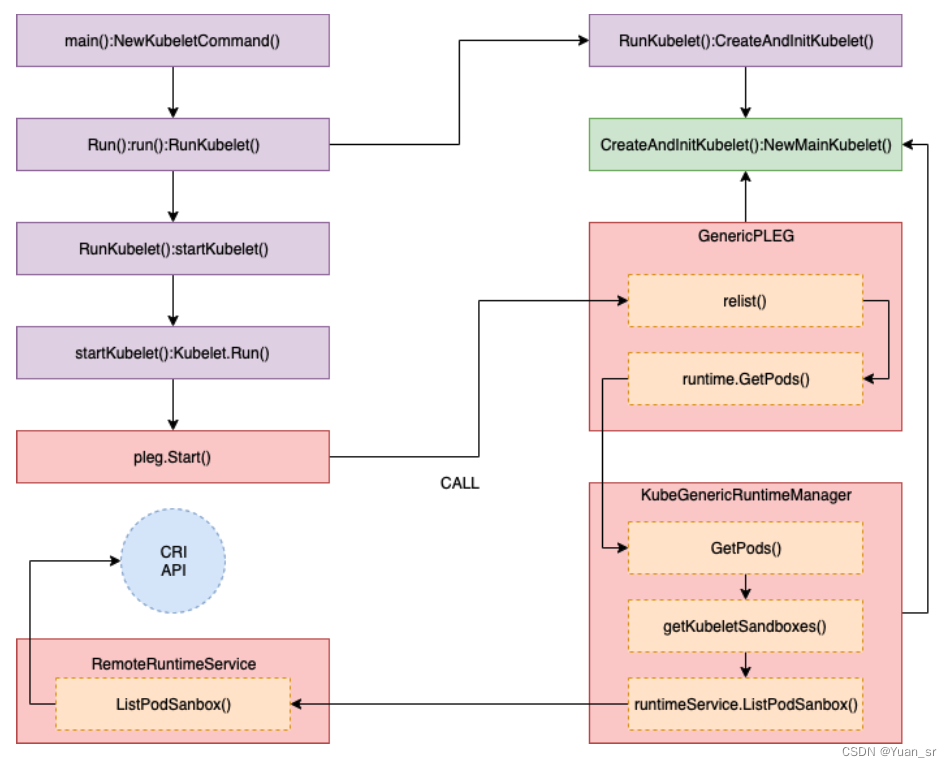
GetPods函数的作用是返回一个按照Pod分组的容器列表。该函数接受一个布尔参数all,用于指定运行时是否返回所有容器,包括已经退出和已经死亡的容器(用于垃圾回收)。
该函数首先通过调用getKubeletSandboxes函数获取所有的沙箱(sandbox),然后遍历沙箱列表。对于每个沙箱,它会将其转换为kubecontainer.Pod类型,并将其添加到对应的Pod中。如果Pod不存在,则创建一个新的Pod,并将其添加到Pod列表中。最后,它通过调用getKubeletContainers函数获取所有的容器,并将每个容器转换为kubecontainer.Container类型,并将其添加到对应的Pod中。
最后,函数将Pod列表转换为一个有序的列表,并按照创建时间的降序排列。然后返回该列表作为结果。
总结来说,GetPods函数的主要功能是获取运行时中的所有Pod及其包含的容器,并按照创建时间的降序排列返回。
getKubeletSandboxes函数的作用是列出kubelet管理的所有(或只是正在运行的)沙箱。该函数接受一个上下文对象和一个布尔值参数all,用于指定是否列出所有沙箱。如果all为false,则只列出状态为SANDBOX_READY的沙箱。
函数首先根据all参数的值创建一个过滤器对象filter。如果all为false,则将过滤器的状态设置为SANDBOX_READY。然后,函数调用runtimeService.ListPodSandbox方法,传入上下文对象和过滤器对象,以获取沙箱列表。
如果调用成功,函数将返回一个runtimeapi.PodSandbox类型的切片,其中包含列出的沙箱。如果调用失败,函数将返回一个错误对象。
总结来说,getKubeletSandboxes函数的主要功能是获取kubelet管理的沙箱列表,并根据需要进行过滤。
ListPodSanbox调用CRI接口获取所有pod。
其中更新Pod缓存的方法updateCache()调用堆栈如下:
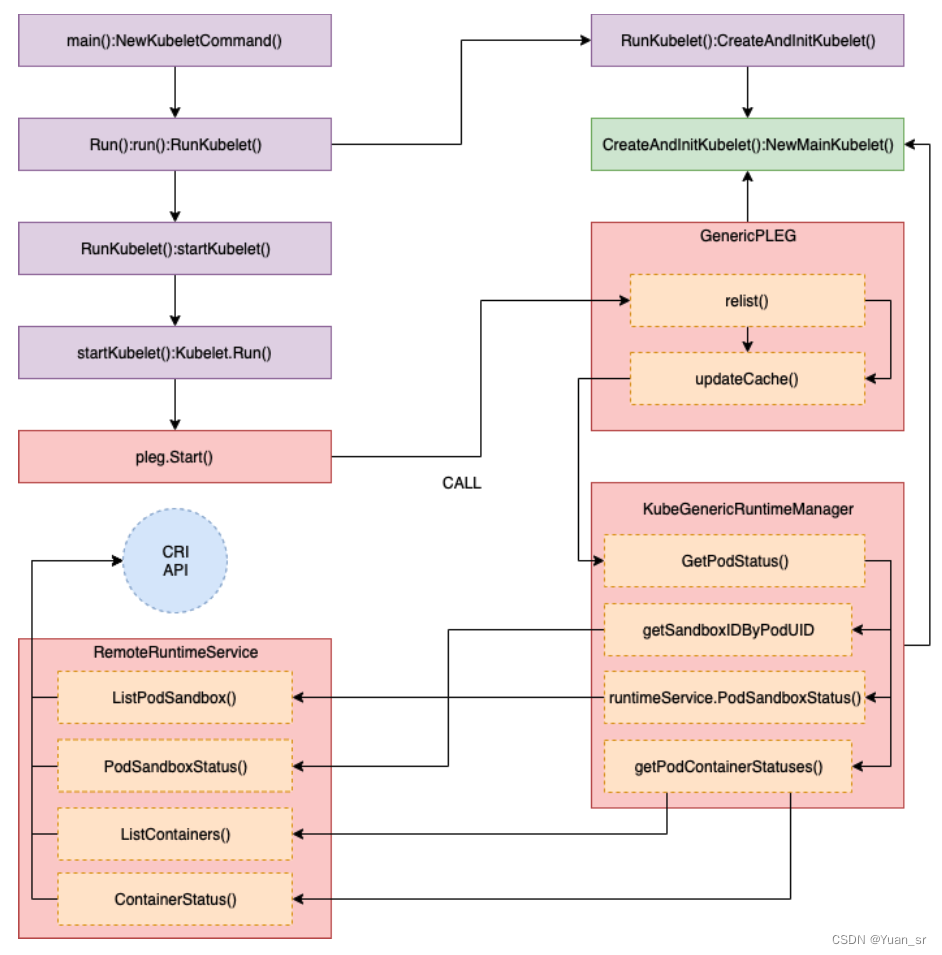 这个函数的入参是pod对象和缓存中pod的 UID,作用是尝试更新 kubelet 缓存中的 pod 状态,并返回一个布尔值来表示是否成功更新了缓存。如果 pod 不存在,则会从缓存中删除该 pod 的状态。
这个函数的入参是pod对象和缓存中pod的 UID,作用是尝试更新 kubelet 缓存中的 pod 状态,并返回一个布尔值来表示是否成功更新了缓存。如果 pod 不存在,则会从缓存中删除该 pod 的状态。
具体来说,这个函数的功能如下:
- 首先,它会检查传入的 pod 是否为 nil。如果是 nil,则表示当前的 pod 列表中没有该 pod,即该 pod 没有可见的容器(活动或非活动)。
- 在这种情况下,函数会使用 pod 的 UID 删除缓存中的状态,并返回 nil 和 true。
- 如果 pod 不为 nil,则会获取当前时间戳,并调用 runtime.GetPodStatus 方法获取 pod 的状态。
- 如果获取状态的过程中出现错误,则会使用 klog.ErrorS 记录错误日志。
- 如果获取状态成功,则会使用 klog.V(6).InfoS 或 klog.V(4).InfoS 记录状态日志,并将获取到的状态赋值给变量 status。
-
接下来,函数会调用 g.getPodIPs 方法,将获取到的 pod 状态中的 IP 地址赋值给 status.IPs。这样做是为了在缓存更新时保留 pod 的 IP 地址,以满足 Kubernetes API 的要求。
-
最后,函数会根据是否启用了 features.EventedPLEG 和 isEventedPLEGInUse() 的结果来决定是否更新时间戳。如果启用了 Evented PLEG 并且正在使用它,则会将 status.TimeStamp 赋值给 timestamp。
-
最终,函数会调用 g.cache.Set 方法将 pod 的 ID、状态、错误和时间戳存储到缓存中,并返回错误和布尔值。
总结起来,这个函数的主要功能是更新 kubelet 缓存中的 pod 状态,并根据不同的情况进行相应的处理。