1.构造方法
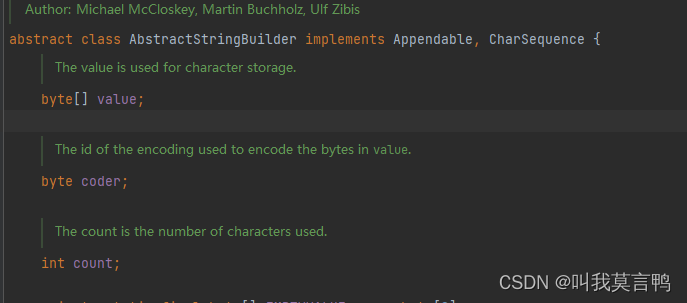
这里就看出String和Stringbuffer最主要的区别了
byte[]value不是final
// 1.空参创建 这里 默认初始长度出现了,16
public StringBuffer() {
super(16);
}
// 2.定容创建,如果知道使用长度其实还好,因为他会扩容
public StringBuffer(int capacity) {
super(capacity);
}
// 3.3和4其实一样,因为String是CharSequence的子类 4的话可以输入char数组
public StringBuffer(String str) {
super(str);
}
public StringBuffer(CharSequence seq) {
super(seq);
}
2.append
这里的apppend是将后面的字符串或者其他类型直接添加在后面。
源码太多,不做赘述
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("练习两年半");
buffer.append("的");
System.out.println("buffer = " + buffer);
buffer.append("个人练习生");
System.out.println("buffer = " + buffer);
}
后面object也能传,说明对象也能传。

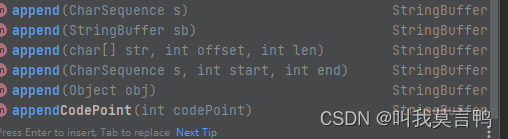
3.reverse(反转)
其实还是一个字符一个字符反转处理的 学习一下从中间向两边查找的方法
从中间向两边 j=(n-1)>>1
public synchronized StringBuffer reverse() {
toStringCache = null;
super.reverse();
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder reverse() {
byte[] val = this.value;
int count = this.count;
int n = count - 1;
if (isLatin1()) {
for (int j = (n-1) >> 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = n - j;
byte cj = val[j];
val[j] = val[k];
val[k] = cj;
}
} else {
StringUTF16.reverse(val, count);
}
return this;
}
16和阿拉伯处理方式的区别,还是字符的处理
public static void reverse(byte[] val, int count) {
checkOffset(count, val);
int n = count - 1;// 总下标
boolean hasSurrogates = false;
for (int j = (n-1) >> 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// 注意看这里,j = (n-1)/2 当字符串中字符个数位偶数时,n为基数,j以中间左边开始,count为奇数,n为偶数,这时候空掉中间的数了。
int k = n - j;
char cj = getChar(val, j);
char ck = getChar(val, k);
putChar(val, j, ck);
putChar(val, k, cj);
if (Character.isSurrogate(cj) ||
Character.isSurrogate(ck)) {
hasSurrogates = true;
}
}
if (hasSurrogates) {
reverseAllValidSurrogatePairs(val, count);
}
}
4.indexof 这里参数只能是字符串格式
这个调用的都是父类的方法,但是底层调用的还是字符串的方法。
public int indexOf(String str) {
// Note, synchronization achieved via invocations of other StringBuffer methods
return super.indexOf(str);
}
/**
* @since 1.4
*/
@Override
public synchronized int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return super.indexOf(str, fromIndex);
}
/**
* @since 1.4
*/
@Override
public int lastIndexOf(String str) {
// Note, synchronization achieved via invocations of other StringBuffer methods
return lastIndexOf(str, count);
}
/**
* @since 1.4
*/
@Override
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return super.lastIndexOf(str, fromIndex);
}
#### 5.到指定位置插入
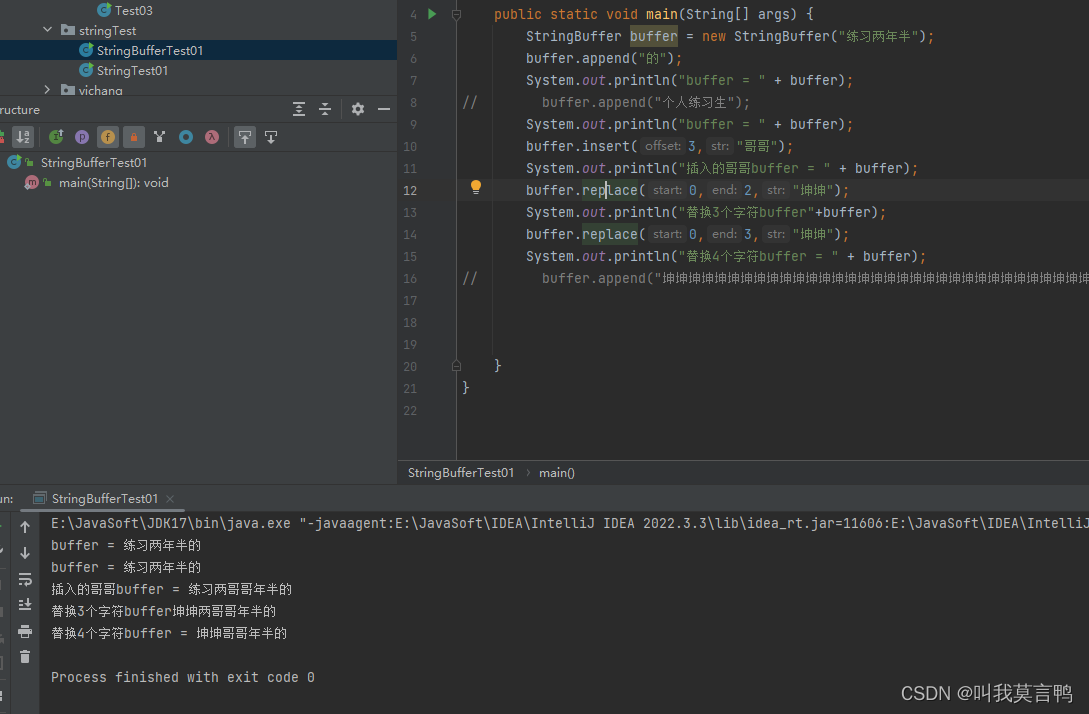
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("练习两年半");
buffer.append("的");
System.out.println("buffer = " + buffer);
// buffer.append("个人练习生");
System.out.println("buffer = " + buffer);
buffer.insert(3,"坤坤");
System.out.println("buffer = " + buffer);
}

6.length方法 注意这里是获取字符串长度,而不是容器长度
@Override
public synchronized int length() {
return count;
}
7.capacity 获取容器长度
关于扩容,晚点单独写
public synchronized int capacity() {
return super.capacity();
}
8.替换指定位置字符串
// 起始位置, 替换进去的字符串
public synchronized StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str) {
toStringCache = null;
super.replace(start, end, str);
return this;
}





![[web]前端富文本编辑器](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/475e13aa5b12402db291c96163359a2c.png)