目录
0. 管道概述:
1. 管道特点
2. 管道创建:pipe函数
3. 管道的读写特点
4. 通过fcntl函数设置文件的阻塞特性
5. 查看管道缓冲区命令
总结:
0. 管道概述:
管道也叫无名管道,它是是 UNIX 系统 IPC(进程间通信) 的最古老形式,所有的 UNIX 系统都支持这种通信机制。
无名管道是创建在内核空间的,多个进程知道同一个无名管道的空间,就可以利用它来进行通信。(在32位操作系统下,任何一个进程创建时,系统都会给其分配4G的虚拟内存,3G为用户空间,1G为内核空间)
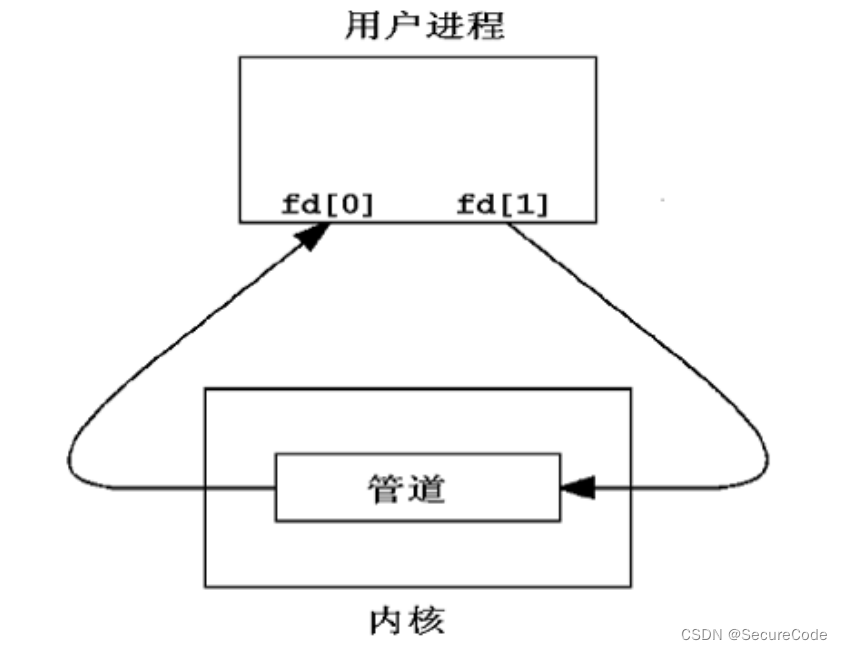
无名管道虽然是在内核空间创建的,但是会给当前用户进程两个文件描述符,一个负责执行读操作,一个负责写操作。
1. 管道特点
1) 半双工,数据在同一时刻只能在一个方向上流动。
2) 数据只能从管道的一端写入,从另一端读出。
3) 写入管道中的数据遵循先入先出的规则。
4) 管道所传送的数据是无格式的,这要求管道的读出方与写入方必须事先约定好数据的格式,如多少字节算一个消息等。
5) 管道不是普通的文件,不属于某个文件系统,其只存在于内存中。
6) 管道在内存中对应一个缓冲区。不同的系统其大小不一定相同。
7) 从管道读数据是一次性操作,数据一旦被读走,它就从管道中被抛弃,释放空间以便写更多的数据。
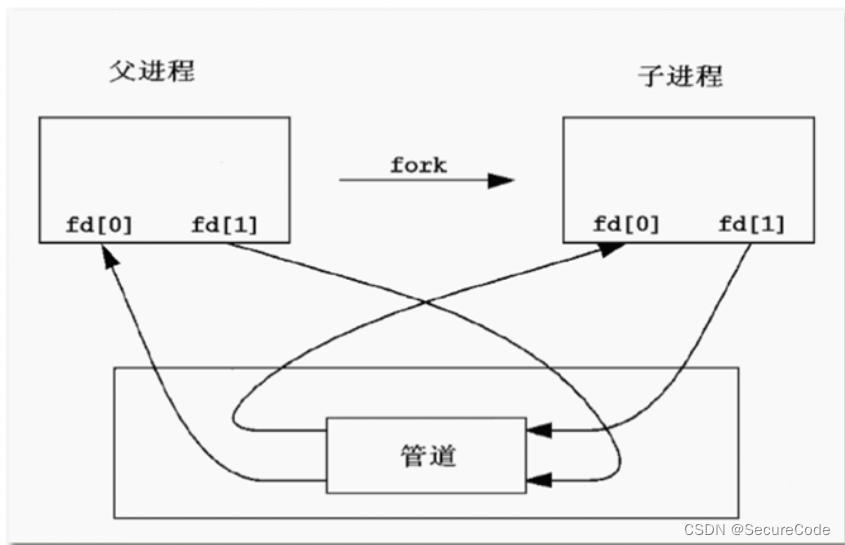
8) 管道没有名字,只能在具有公共祖先的进程(父进程与子进程,或者两个兄弟进程,具有亲缘关系)之间使用。
对于管道特点的理解,我们可以类比现实生活中管子,管子的一端塞东西,管子的另一端取东西。管道是一种特殊类型的文件,在应用层体现为两个打开的文件描述符。
2. 管道创建:pipe函数
pipe函数:
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
功能:创建无名管道,返回两个文件描述符负责对管道进行读写操作
参数:
pipefd : 为 int 型数组的首地址,其存放了管道的文件描述符 pipefd[0]、pipefd[1]。pipefd[0]:负责对管道执行读操作。
pipefd[1]:负责对管道执行写操作。
一般文件 I/O的函数都可以用来操作管道(lseek() 除外)。
返回值:
成功:0
失败:-1
代码示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fd_pipe[2];
if (pipe(fd_pipe) == -1) {
perror("fail to pipe");
exit(1);
}
printf("fd_pipe[0] = %d\n", fd_pipe[0]);
printf("fd_pipe[1] = %d\n", fd_pipe[1]);
if (write(fd_pipe[1], "hello world ", 12) == -1) {
perror("fail to write");
exit(1);
}
write(fd_pipe[1], "nihao beijing", strlen("nihao biejing") + 1);
char buf[32] = "";
ssize_t bytes;
if ((bytes = read(fd_pipe[0], buf, sizeof(buf))) == -1) {
perror("fail to read");
exit(1);
}
printf("buf = %s\n", buf);
printf("bytes = %ld\n", bytes);
return 0;
}父子进程通过管道实现数据的传输
示例代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
int pipefd[2];
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1)
{
perror("fail to pipe");
exit(1);
}
int pipeff[2];
if (pipe(pipeff) == -1)
{
perror("fail to pipe");
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
perror("fail to fork");
exit(1);
}
else if (pid > 0)
{
char buf[128] = "";
char buu[128] = "";
while (1)
{
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
if (write(pipefd[1], buf, sizeof(buf)) == -1)
{
perror("fail to write");
exit(1);
}
if (read(pipeff[0], buu, sizeof(buu)) == -1)
{
perror("fail to read ");
exit(1);
}
printf("buu = %s\n", buu);
}
}
else
{
char buf[128] = "";
char buu[128] = "";
while (1)
{
if (read(pipefd[0], buf, sizeof(buf)) == -1)
{
perror("fail to read ");
exit(1);
}
printf("buf = %s\n", buf);
fgets(buu, sizeof(buu), stdin);
buu[strlen(buu) - 1] = '\0';
if (write(pipeff[1], buu, sizeof(buu)) == -1)
{
perror("fail to write");
exit(1);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
3. 管道的读写特点
使用管道需要注意以下4种特殊情况(假设都是阻塞I/O操作,没有设置O_NONBLOCK标志):
1. 读写端都存在,只读不写:
//读写端都存在,只读不写
//如果管道中有数据,会正常读取数据
//如果管道中没有数据,则读操作会阻塞等待,直到有数据为止
2. 读写端都存在,只写不读
//读写端都存在,只写不读
//如果一直执行写操作,则无名管道对应的缓冲区会被写满,写满之后,write函数也会阻塞等待
//默认无名管道的缓冲区64K字节
3. 只有读端
//关闭文件描述符,只有读端
//如果管道中有数据,则读操作正常读取数据
//如果管道中没有数据,则read函数返回0
4. 只有写段
//关闭读端,只有写端
//关闭读端,一旦执行写操作,立刻产生一个SIGPIPE(管道破裂)
//这个信号默认处理方式是退出进程
读写端都存在,只读不写
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
int pipefd[2];
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1)
{
perror("fail to pipe");
exit(1);
}
//读写端都存在,只读不写
//如果管道中有数据,会正常读取数据
//如果管道中没有数据,则读操作会阻塞等待,直到有数据为止
write(pipefd[1], "hello world", 11);
char buf[128] = "";
if (read(pipefd[0], buf, sizeof(buf)) == -1)
{
perror("fail to read");
exit(1);
}
printf("buf = %s\n", buf);
if (read(pipefd[0], buf, sizeof(buf)) == -1)
{
perror("fail to read");
exit(1);
}
printf("buf = %s\n", buf);
return 0;
}
~读写端都存在,只写不读
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
int pipefd[2];
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1)
{
perror("fail to pipe");
exit(1);
}
//读写端都存在,只写不读
//如果一直执行写操作,则无名管道对应的缓冲区会被写满,写满之后,write函数也会阻塞等待
//默认无名管道的缓冲区64K字节
int num = 0;
while (1)
{
if (write(pipefd[1], "666", 1024) == -1)
{
perror("fail to write");
exit(1);
}
num++;
printf("num = %d\n", num);
}
return 0;
}只有读端
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
int pipefd[2];
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1)
{
perror("fail to pipe");
exit(1);
}
write(pipefd[1], "hello world", 11);
//关闭文件描述符,只有读端
//如果管道中有数据,则读操作正常读取数据
//如果管道中没有数据,则read函数返回0
close(pipefd[1]);
char buf[128] = "";
ssize_t bytes;
if ((bytes = read(pipefd[0], buf, sizeof(buf))) == -1)
{
perror("fail to read");
exit(1);
}
printf("bytes = %ld\n", bytes);
printf("buf = %s\n", buf);
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
if ((bytes = read(pipefd[0], buf, sizeof(buf))) == -1)
{
perror("fail to read");
exit(1);
}
printf("bytes = %ld\n", bytes);
printf("buf = %s\n", buf);
return 0;
}只有写
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<signal.h>
void handler(int sig) {
printf("SIGPIPE发生了,管道破裂\n");
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGPIPE, handler);
int pipefd[2];
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1)
{
perror("fail to pipe");
exit(1);
}
//关闭读端,只有写端
//关闭读端,一旦执行写操作,立刻产生一个SIGPIPE(管道破裂)
//这个信号默认处理方式是退出进程
close(pipefd[0]);
int num = 0;
while (1)
{
if (write(pipefd[1], "hello", 1024) == -1)
{
perror("fail to write");
exit(1);
}
num++;
printf("num = %d\n", num);
}
return 0;
}
4. 通过fcntl函数设置文件的阻塞特性
设置为阻塞:
fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,0);
设置为非阻塞:
fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,O_NONBLOCK);
非阻塞:如果是阻塞,管道中没有数据,read会一直等待,直到有数据才会继续运行,否则一直等待。
设置方法:
//获取原来的flags
int flags = fcntl(fd[0], F_GETFL);
// 设置新的flags
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
// flags = flags | O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fd[0], F_SETFL, flags);结论: 如果写端没有关闭,读端设置为非阻塞, 如果没有数据,直接返回-1。
如果是非阻塞,read函数运行时,会先看一下管道中是否有数据,如果有数据,则正常运行读取数据,如果管道中没有数据,则read函数会立即返回,继续下面代码运行。
include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd_pipe[2];
char buf[] = "hello world";
pid_t pid;
if (pipe(fd_pipe) == -1)
{
perror("fail to pipe");
exit(1);
}
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
perror("fail to fork");
exit(1);
}
else if (pid > 0)
{
fcntl(fd_pipe[0], F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
while (1)
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(fd_pipe[0], buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("buf = %s\n", buf);
sleep(1);
}
}
else
{
while (1)
{
sleep(5);
write(fd_pipe[1], buf, strlen(buf));
}
}
return 0;
}5. 查看管道缓冲区命令
可以使用ulimit -a 命令来查看当前系统中创建管道文件所对应的内核缓冲区大小。

查看管道缓冲区函数
#include <unistd.h>
long fpathconf(int fd, int name);
功能:该函数可以通过name参数查看不同的属性值
参数:
fd:文件描述符
name:
_PC_PIPE_BUF,查看管道缓冲区大小
_PC_NAME_MAX,文件名字字节数的上限
返回值:
成功:根据name返回的值的意义也不同。
失败: -1示例:
int main()
{
int fd[2];
int ret = pipe(fd);
if (ret == -1)
{
perror("pipe error");
exit(1);
}
long num = fpathconf(fd[0], _PC_PIPE_BUF);
printf("num = %ld\n", num);
return 0;
}总结:
无名管道是一种强大且基础的进程间通信机制,它使得具有亲缘关系的进程之间能够方便地共享数据。无名管道的使用,无论是在简单的Shell命令,还是在复杂的多进程应用中,都有着广泛的应用。
注意:无名管道只能在具有公共祖先的进程之间使用,且只能实现单向通信。