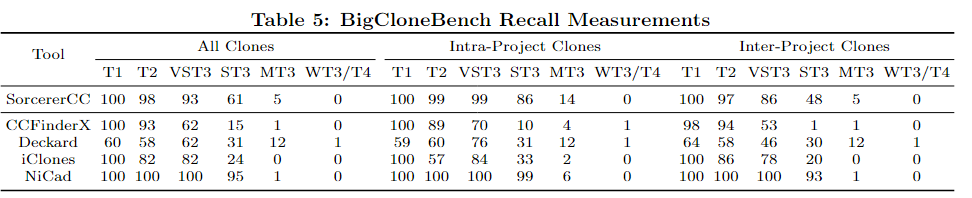
以前对于Java字符串中字符的Unicode码点、UTF编码没有仔细研究。今天研究了下。
Unicode是一个字符集,其实是一个映射,给每个字符映射了一个数值,称为码点(Code Point)。
而UTF-8、UTF-16、UTF-32则是对Unicode码点的转化格式,UTF是Unicode Transformation Format的简写。
注意:UTF后面的数字是指编码所用的最少比特位。例如,UTF-8最少用8位(即1个字节),UTF-16编码最少使用16位(即2个字节),UTF-32最少使用32位(即4个字节)。
以中文的“中”字为例,我们从Unicode官网(https://www.unicode.org/cgi-bin/GetUnihanData.pl?codepoint=4E2D)查询到码点、UTF-8、UTF-16、UTF-32编码后的十六进制表示:

下面用java代码输出码点、UTF-8编码后的值跟上面对照看看对不对:
package com.thb;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输出默认编码
System.out.println("默认编码:"+ Charset.defaultCharset());
String str = "中";
// 输出“中”这个字的的Unicode码点
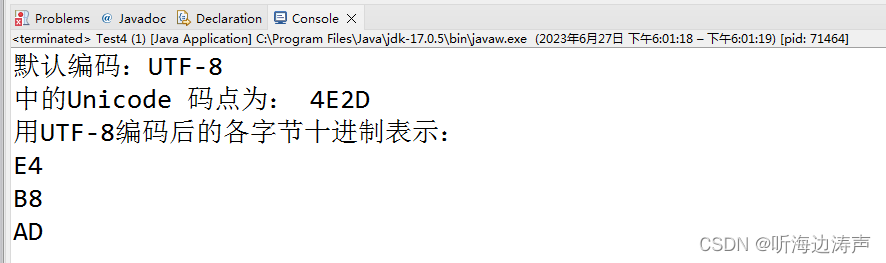
System.out.println(str + "的Unicode 码点为: " + Integer.toHexString(str.codePointAt(0)).toUpperCase());
// 输出编码后各字节的十六进制大写
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
System.out.println("用" + Charset.defaultCharset() + "编码后的各字节十进制表示:");
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(Byte.toUnsignedInt(bytes[i])).toUpperCase());
}
}
}
代码执行结果,跟官网查询的结果一致: