一、点对象和点材质基本介绍
1. 点材质(PointsMaterial):
点材质用于渲染点对象,它决定了点的颜色、透明度等属性。
常用属性有:
- color: 点的颜色,默认为白色。
- opacity: 点的透明度,默认为1。
- size: 点的大小,可以使用PointScaleAttenuation属性同时调整大小。
- sizeAttenuation: 是否使用点大小衰减(根据相机远近自动调整点的大小),默认为true。
- map: 对点纹理进行设置,可以使用贴图来代替单色点,如星空。
举例说明:
var material = new THREE.PointsMaterial({
color: 0xffffff,
size: 0.1
});
2. 点对象(Three.Point):
点对象用于渲染单个点,可以通过添加多个点对象来形成点云。
常用属性有:
- position: 点的位置,可以是THREE.Vector3类型的变量。
- color: 点的颜色,使用PointsMaterial的color属性进行设置,默认为白色。
- size: 点的大小,使用PointsMaterial的size属性进行设置,默认为1。
举例说明:
var pointGeometry = new THREE.Geometry();
pointGeometry.vertices.push( new THREE.Vector3( 0, 0, 0 ) );
var pointMaterial = new THREE.PointsMaterial( { size: 5, color: 0xff0000 } );
var point = new THREE.Points( pointGeometry, pointMaterial );
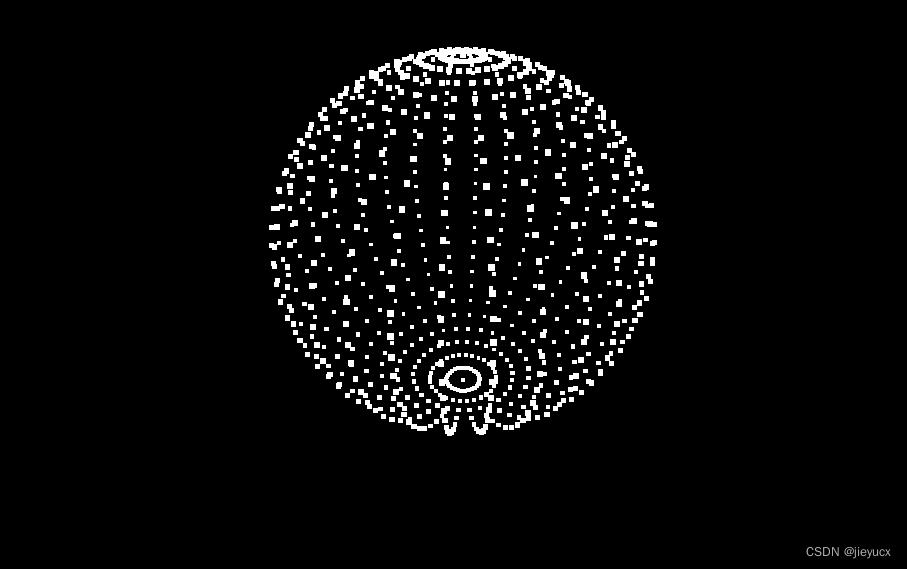
3. 基本运用示例
效果如图:
完整示例代码
import * as THREE from "three";
// 导入轨道控制器
import { OrbitControls } from "three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls";
// 导入动画库
import gsap from "gsap";
// 导入dat.gui
import * as dat from "dat.gui";
// 目标:认识pointes
const gui = new dat.GUI();
// 1、创建场景
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 2、创建相机
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
75,
window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
// 设置相机位置
camera.position.set(0, 0, 10);
scene.add(camera);
// 创建球几何体
const sphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereBufferGeometry(3, 30, 30);
// 设置点材质
const pointsMaterial = new THREE.PointsMaterial();
pointsMaterial.size = 0.1; // 设置点的尺寸大小,默认为1
// 相机深度而衰减
pointsMaterial.sizeAttenuation = true;
const points = new THREE.Points(sphereGeometry, pointsMaterial); // 将几何体和材质传入点对象
scene.add(points);
// 初始化渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
// 设置渲染的尺寸大小
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
// 开启场景中的阴影贴图
renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true;
renderer.physicallyCorrectLights = true;
// 将webgl渲染的canvas内容添加到body
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// 创建轨道控制器
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
// 设置控制器阻尼,让控制器更有真实效果,必须在动画循环里调用.update()。
controls.enableDamping = true;
function render() {
controls.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
// 渲染下一帧的时候就会调用render函数
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
render();
// 监听画面变化,更新渲染画面
window.addEventListener("resize", () => {
// console.log("画面变化了");
// 更新摄像头
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
// 更新摄像机的投影矩阵
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
// 更新渲染器
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
// 设置渲染器的像素比
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
});
如上面的示例,我们用点材质(pointsMaterial)和点对象(point)结合 球体(THREE.SphereBufferGeometry(3, 30, 30))实现了以点的形式构建一个球体,我们放大球体看看
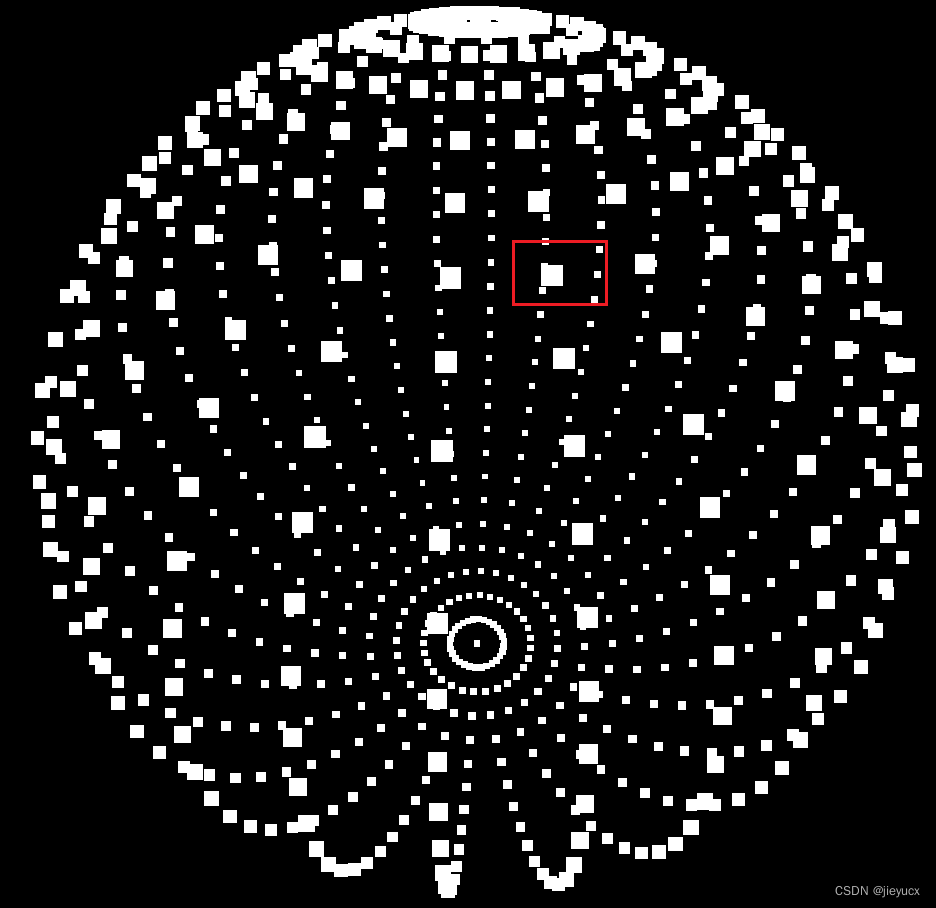
可以看到每个点其实是由小立方体组成的。
好啦 本章节就介绍这么多,下一章详细介绍一下点材质的各个属性的作用