IPv6手工隧道配置与验证实验
【实验目的】
熟悉IPv6手工隧道的概念。
掌握IPv6和IPv4共存的实现方法。
掌握IPv6手工隧道的配置。
验证配置。
【实验拓扑】
实验拓扑如下图所示。
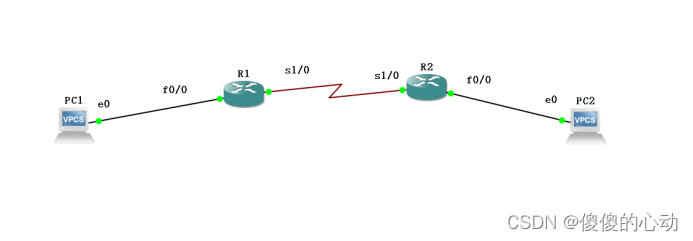
实验拓扑
设备参数如表所示。
设备参数表
| 设备 | 接口 | IPv6地址 | 子网掩码位数 | 默认网关 |
| R1 | S1/0 | 192.168.12.1 | 24 | N/A |
| F0/0 | 2000:f106:f208:12::1 | 64 | N/A | |
| R2 | S1/0 | 192.168.12.2 | 24 | N/A |
| F0/0 | 2000:f106:f208:12::2 | 64 | N/A |
【实验内容】
1.基本配置
(1)R1的基本配置
Router>en
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#hostname R1
R1(config)#interface s1/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#interface f0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2000:f106:f208:1::1/64
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#interface tunnel 0
R1(config-if)#tunnel mode ipv6ip
R1(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R1(config-if)#tunnel source s1/0
R1(config-if)#tunnel destination 192.168.12.2
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R1(config)#ipv6 route 2000:f106:f208:2::/64 tunnel0
R1(config)#end
R1#write
Building configuration...
[OK]
R1#
(2)R2的基本配置
Router>en
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#hostname R2
R2(config)#interface s0/0/0
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#interface f0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2000:f106:f208:2::1/64
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface tunnel 0
R2(config-if)#tunnel mode ipv6ip
R2(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R2(config-if)#tunnel source s0/0/0
R2(config-if)#tunnel destination 192.168.12.2
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)#ipv6 route 2000:f106:f208:2::/64 tunnel0
R2(config)#end
R2#write
Building configuration...
[OK]
R2#
R2(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)#end
R2#write
Building configuration...
[OK]
R2#
(3)PC1~2的基本配置
PC1> ip auto
GLOBAL SCOPE : 2000:f106:f208:1:2050:79ff:fe66:6800/64
ROUTER LINK-LAYER : ca:01:4e:4c:00:00
PC1> show
NAME IP/MASK GATEWAY MAC LPORT RHOST:PORT
PC1 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0 00:50:79:66:68:00 10014 127.0.0.1:10015
fe80::250:79ff:fe66:6800/64
2000:f106:f208:1:2050:79ff:fe66:6800/64 eui-64
PC1>
PC2> ip auto
GLOBAL SCOPE : 2000:f106:f208:2:2050:79ff:fe66:6801/64
ROUTER LINK-LAYER : ca:02:00:84:00:00
PC2> show
NAME IP/MASK GATEWAY MAC LPORT RHOST:PORT
PC2 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0 00:50:79:66:68:01 10016 127.0.0.1:10017
fe80::250:79ff:fe66:6801/64
2000:f106:f208:2:2050:79ff:fe66:6801/64 eui-64
PC2>
2.实验调试
(1)查看隧道信息
R1#show interfaces tunnel 0
Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is Tunnel
MTU 17920 bytes, BW 100 Kbit/sec, DLY 50000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set
Keepalive not set
Tunnel source 192.168.12.1 (Serial1/0), destination 192.168.12.2
Tunnel Subblocks:
src-track:
Tunnel0 source tracking subblock associated with Serial1/0
Set of tunnels with source Serial1/0, 1 member (includes iterators), on interface <OK>
Tunnel protocol/transport IPv6/IP
//隧道模式为“ipvip”
Tunnel TTL 255
Tunnel transport MTU 1480 bytes
Tunnel transmit bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Tunnel receive bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Last input never, output 00:01:33, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 01:03:39
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/0 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
41 packets output, 4832 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 unknown protocol drops
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
//以上9行输出显示该隧道的流量收发情况
R1#
(2)调试隧道信息
R1#debug tunnel
Tunnel Interface debugging is on
R1#
*Jun 26 22:03:08.055: Tunnel0: IPv6/IP adjacency fixup, 192.168.12.1->192.168.12.2, tos set to 0x0
//对出站数据进行封装
R1#
*Jun 26 22:03:09.071: Tunnel0: IPv6/IP adjacency fixup, 192.168.12.1->192.168.12.2, tos set to 0x0
*Jun 26 22:03:10.067: Tunnel0: IPv6/IP adjacency fixup, 192.168.12.1->192.168.12.2, tos set to 0x0
R1#
*Jun 26 22:03:11.071: Tunnel0: IPv6/IP adjacency fixup, 192.168.12.1->192.168.12.2, tos set to 0x0
R1#
*Jun 26 22:03:12.087: Tunnel0: IPv6/IP adjacency fixup, 192.168.12.1->192.168.12.2, tos set to 0x0
R1#
(3)Ping测试
PC1> ping 2000:f106:f208:2:2050:79ff:fe66:6801
2000:f106:f208:2:2050:79ff:fe66:6801 icmp6_seq=1 timeout
2000:f106:f208:2:2050:79ff:fe66:6801 icmp6_seq=2 timeout
2000:f106:f208:2:2050:79ff:fe66:6801 icmp6_seq=3 timeout
2000:f106:f208:2:2050:79ff:fe66:6801 icmp6_seq=4 timeout
2000:f106:f208:2:2050:79ff:fe66:6801 icmp6_seq=5 timeout
PC2> ping 2000:f106:f208:1:2050:79ff:fe66:6800/64
2000:f106:f208:1:2050:79ff:fe66:6800 icmp6_seq=1 timeout
2000:f106:f208:1:2050:79ff:fe66:6800 icmp6_seq=2 timeout
2000:f106:f208:1:2050:79ff:fe66:6800 icmp6_seq=3 timeout
2000:f106:f208:1:2050:79ff:fe66:6800 icmp6_seq=4 timeout
2000:f106:f208:1:2050:79ff:fe66:6800 icmp6_seq=5 timeout
【知识点】
在这个实验中,涉及到以下几个知识点:
- IPv6手工隧道的概念:实验通过手工配置IPv6隧道来实现IPv6和IPv4的共存和通信。IPv6隧道是一种将IPv6数据包封装在IPv4数据包中进行传输的技术。
- IPv6和IPv4共存的实现方法:实验中使用手工隧道来实现IPv6和IPv4的共存。通过在两台设备上配置IPv6地址和IPv4地址,并创建隧道接口,将IPv6数据包封装在IPv4数据包中进行传输,实现IPv6和IPv4之间的通信。
- IPv6和IPv4的基本配置:在实验中,需要为每台设备配置IPv6地址和IPv4地址,并启用相应的接口。通过命令行配置,设置主机名、接口地址、子网掩码、默认网关等参数,确保设备能够正确地进行IPv6和IPv4通信。
- 配置IPv6隧道:在实验中,需要配置隧道接口,设置隧道模式为ipv6ip,并指定隧道的源地址和目标地址。这样,通过隧道接口可以将IPv6数据包封装在IPv4数据包中进行传输。
- 验证配置和调试隧道:实验中使用一些命令来验证配置和调试隧道。通过查看隧道接口的详细信息、调试隧道信息和封装数据的信息,可以确保隧道正常工作,并对隧道进行故障排除。
- Ping测试:实验中使用Ping测试来验证隧道的连通性。通过在PC1上ping PC2的IPv6地址,以及在PC2上ping PC1的IPv6地址,可以检查隧道是否能够正常传输数据。
以上是在这个实验中涉及到的主要知识点,包括IPv6手工隧道的概念、IPv6和IPv4的共存实现方法、配置IPv6和IPv4的基本参数、配置IPv6隧道、验证配置和调试隧道,以及使用Ping测试来验证连通性。
不要害怕犯错,因为犯错是学习的一部分。每次失败都是离成功更近一步的机会,所以勇敢地尝试吧!






![强化学习从基础到进阶-案例与实践[6]:演员-评论员算法(advantage actor-critic,A2C),异步A2C、与生成对抗网络的联系等详解](https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/818c1c2e603341f881dd57fb59e109c81702722156be4e6481b276b894c51290)