一 数据库操作框架的历程
1.1 JDBC
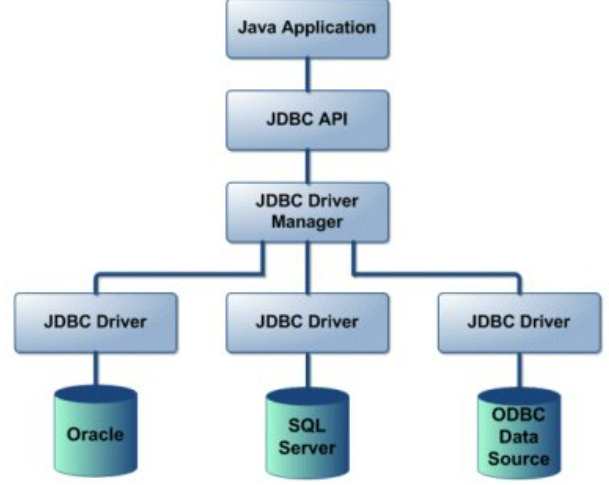
JDBC(Java Data Base Connection,java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成.JDBC提供了一种基准,据此可以构建更高级的工具和接口,使数据库开发人员能够编写数据库应用程序
- 优点:运行期:快捷、高效
- 缺点:编辑期:代码量大、繁琐异常处理、不支持数据库跨平台
jdbc核心api
- DriverManager 连接数据库
- Connection 连接数据库的抽象
- Statment 执行SQL
- ResultSet 数据结果集
1.2 DBUtils
DBUtils是Java编程中的数据库操作实用工具,小巧简单实用。
DBUtils封装了对JDBC的操作,简化了JDBC操作,可以少写代码。
DBUtils三个核心功能介绍
- QueryRunner中提供对sql语句操作的API
- ResultSetHandler接口,用于定义select操作后,怎样封装结果集
- DBUtils类,它就是一个工具类,定义了关闭资源与事务处理的方法
1.3 Hibernate
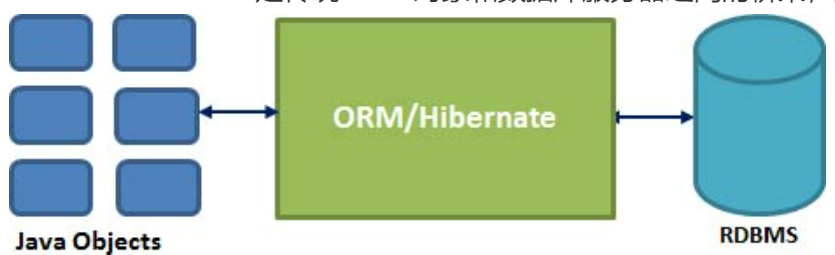
ORM 对象关系映射
- object java对象
- relational 关系型数据
- mapping 映射
- Hibernate 是由 Gavin King 于 2001 年创建的开放源代码的对象关系框架。它强大且高效的构建具有关系对象持久性和查询服务的 Java 应用程序。
- Hibernate 将 Java 类映射到数据库表中,从 Java 数据类型中映射到 SQL 数据类型中,并把开发人员从 95% 的公共数据持续性编程工作中解放出来。
- Hibernate 是传统 Java 对象和数据库服务器之间的桥梁,用来处理基于 O/R 映射机制和模式的那些对象。
Hibernate 优势
- Hibernate 使用 XML 文件来处理映射 Java 类别到数据库表格中,并且不用编写任何代码。
- 为在数据库中直接储存和检索 Java 对象提供简单的 APIs。
- 如果在数据库中或任何其它表格中出现变化,那么仅需要改变 XML 文件属性。
- 抽象不熟悉的 SQL 类型,并为我们提供工作中所熟悉的 Java 对象。
- Hibernate 不需要应用程序服务器来操作。
- 操控你数据库中对象复杂的关联。
- 最小化与访问数据库的智能提取策略。
- 提供简单的数据询问。
Hibernate劣势
- hibernate的完全封装导致无法使用数据的一些功能。
- Hibernate的缓存问题。
- Hibernate对于代码的耦合度太高。
- Hibernate寻找bug困难。
- Hibernate批量数据操作需要大量的内存空间而且执行过程中需要的对象太多
1.4 JDBCTemplate
JdbcTemplate针对数据查询提供了多个重载的模板方法,你可以根据需要选用不同的模板方法.如果你的查询很简单,仅仅是传入相应SQL或者相关参数,然后取得一个单一的结果,那么你可以选择如下一组便利的模板方法。
- 优点:运行期:高效、内嵌Spring框架中、支持基于AOP的声明式事务
- 缺点:必须于Spring框架结合在一起使用、不支持数据库跨平台、默认没有缓存
1.5 Mybatis
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架/半自动的ORM,它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
优点:
1、与JDBC相比,减少了50%的代码量
2、 最简单的持久化框架,简单易学
3、SQL代码从程序代码中彻底分离出来,可以重用
4、提供XML标签,支持编写动态SQL
5、提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库的ORM字段关系映射
6、支持缓存、连接池、数据库移植…
缺点:
1、SQL语句编写工作量大,熟练度要高
2、数据库移植性比较差,如果需要切换数据库的话,SQL语句会有很大的差异
二 MyBatis的配置文件详解
2.1 MyBatis日志配置
导入pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
添加logback配置文件
<configuration>
<!--appender 追加器 日志以哪种方式进行输出
name 取个名字
class 不同实现类会输出到不同地方
ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender 输出到控制台
-->
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<!-- 格式 -->
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{100} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!--cn.tulingxueyuan.mapper-->
<!--控制跟细粒度的日志级别 根据包\根据类-->
<logger name="cn.tulingxueyuan.mapper" level="debug"></logger>
org.apache.ibatis.transaction
<!--控制所有的日志级别-->
<root level="error">
<!-- 将当前日志级别输出到哪个追加器上面 -->
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
</root>
</configuration>
Logger LOGGER= LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
/**
* 日志级别
* TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR。
* 1 2 3 4 5
*/
@Test
public void test02(){
LOGGER.trace("跟踪级别");
LOGGER.debug("调试级别");
LOGGER.info("信息级别");
LOGGER.warn("警告级别");
LOGGER.error("异常级别");
}
2.2 mybatis-config.xml全局配置文件详解
在mybatis的项目中,我们发现了有一个mybatis-config.xml的配置文件,这个配置文件是mybatis的全局配置文件,用来进行相关的全局配置,在任何操作下都生效的配置。下面我们要针对其中的属性做详细的解释,方便大家在后续使用的时候更加熟练。
官方说明:
MyBatis 的配置文件包含了会深深影响 MyBatis 行为的设置和属性信息。 配置文档的顶层结构如下:
- configuration(配置)
- properties(属性)
- settings(设置)
- typeAliases(类型别名)
- typeHandlers(类型处理器)
- objectFactory(对象工厂)
- plugins(插件)
- environments(环境配置)
- environment(环境变量)
- transactionManager(事务管理器)
- dataSource(数据源)
- environment(环境变量)
- databaseIdProvider(数据库厂商标识)
- mappers(映射器)
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--引入外部配置文件,类似于Spring中的property-placeholder
resource:从类路径引入
url:从磁盘路径或者网络路径引入
-->
<properties resource="db.properties"></properties>
<!--用来控制mybatis运行时的行为,是mybatis中的重要配置-->
<settings>
<!--设置列名映射的时候是否是驼峰标识-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<!--typeAliases表示为我们引用的实体类起别名,默认情况下我们需要写类的完全限定名
如果在此处做了配置,那么可以直接写类的名称,在type中配置上类的完全限定名,在使用的时候可以忽略大小写
还可以通过alias属性来表示类的别名
-->
<typeAliases>
<!-- <typeAlias type="cn.tulingxueyuan.bean.Emp" alias="Emp"></typeAlias>-->
<!--如果需要引用多个类,那么给每一个类起别名肯定会很麻烦,因此可以指定对应的包名,那么默认用的是类名-->
<package name="cn.tulingxueyuan.bean"/>
</typeAliases>
<!--
在实际的开发过程中,我们可能分为开发环境,生产环境,测试环境等等,每个环境的配置可以是不一样的
environment就用来表示不同环境的细节配置,每一个环境中都需要一个事务管理器以及数据源的配置
我们在后续的项目开发中几乎都是使用spring中配置的数据源和事务管理器来配置,此处不需要研究
-->
<!--default:用来选择需要的环境-->
<environments default="development">
<!--id:表示不同环境的名称-->
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--配置数据库连接-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--使用${}来引入外部变量-->
<property name="driver" value="${driverClassname}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--
在不同的数据库中,可能sql语句的写法是不一样的,为了增强移植性,可以提供不同数据库的操作实现
在编写不同的sql语句的时候,可以指定databaseId属性来标识当前sql语句可以运行在哪个数据库中
-->
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR">
<property name="MySQL" value="mysql"/>
<property name="SQL Server" value="sqlserver"/>
<property name="Oracle" value="orcl"/>
</databaseIdProvider>
<!--将sql的映射文件适用mappers进行映射-->
<mappers>
<!--
指定具体的不同的配置文件
class:直接引入接口的全类名,可以将xml文件放在dao的同级目录下,并且设置相同的文件名称,同时可以使用注解的方式来进行相关的配置
url:可以从磁盘或者网络路径查找sql映射文件
resource:在类路径下寻找sql映射文件
-->
<!-- <mapper resource="EmpDao.xml"/>
<mapper resource="UserDao.xml"/>
<mapper class="cn.tulingxueyuan.dao.EmpDaoAnnotation"></mapper>-->
<!--
当包含多个配置文件或者配置类的时候,可以使用批量注册的功能,也就是引入对应的包,而不是具体的配置文件或者类
但是需要注意的是,
1、如果使用的配置文件的形式,必须要将配置文件跟dao类放在一起,这样才能找到对应的配置文件.
如果是maven的项目的话,还需要添加以下配置,原因是maven在编译的文件的时候只会编译java文件
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
2、将配置文件在resources资源路径下创建跟dao相同的包名
-->
<package name="cn.tulingxueyuan.dao"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
2.3 Mybatis SQL映射文件详解
MyBatis 的真正强大在于它的语句映射,这是它的魔力所在。由于它的异常强大,映射器的 XML 文件就显得相对简单。如果拿它跟具有相同功能的 JDBC 代码进行对比,你会立即发现省掉了将近 95% 的代码。MyBatis 致力于减少使用成本,让用户能更专注于 SQL 代码。
SQL 映射文件只有很少的几个顶级元素(按照应被定义的顺序列出):
- cache – 该命名空间的缓存配置。
- cache-ref – 引用其它命名空间的缓存配置。
- resultMap – 描述如何从数据库结果集中加载对象,是最复杂也是最强大的元素。
- parameterMap – 老式风格的参数映射。此元素已被废弃,并可能在将来被移除!请使用行内参数映射。文档中不会介绍此元素。
- sql – 可被其它语句引用的可重用语句块。
- insert – 映射插入语句。
- update – 映射更新语句。
- delete – 映射删除语句。
- select – 映射查询语句。
在每个顶级元素标签中可以添加很多个属性,下面我们开始详细了解下具体的配置。
insert、update、delete元素
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| id | 在命名空间中唯一的标识符,可以被用来引用这条语句。 |
| parameterType | 将会传入这条语句的参数的类全限定名或别名。这个属性是可选的,因为 MyBatis 可以通过类型处理器(TypeHandler)推断出具体传入语句的参数,默认值为未设置(unset)。 |
| parameterMap | 用于引用外部 parameterMap 的属性,目前已被废弃。请使用行内参数映射和 parameterType 属性。 |
| flushCache | 将其设置为 true 后,只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存被清空,默认值:(对 insert、update 和 delete 语句)true。 |
| timeout | 这个设置是在抛出异常之前,驱动程序等待数据库返回请求结果的秒数。默认值为未设置(unset)(依赖数据库驱动)。 |
| statementType | 可选 STATEMENT,PREPARED 或 CALLABLE。这会让 MyBatis 分别使用 Statement,PreparedStatement 或 CallableStatement,默认值:PREPARED。 |
| useGeneratedKeys | (仅适用于 insert 和 update)这会令 MyBatis 使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键(比如:像 MySQL 和 SQL Server 这样的关系型数据库管理系统的自动递增字段),默认值:false。 |
| keyProperty | (仅适用于 insert 和 update)指定能够唯一识别对象的属性,MyBatis 会使用 getGeneratedKeys 的返回值或 insert 语句的 selectKey 子元素设置它的值,默认值:未设置(unset)。如果生成列不止一个,可以用逗号分隔多个属性名称。 |
| keyColumn | (仅适用于 insert 和 update)设置生成键值在表中的列名,在某些数据库(像 PostgreSQL)中,当主键列不是表中的第一列的时候,是必须设置的。如果生成列不止一个,可以用逗号分隔多个属性名称。 |
| databaseId | 如果配置了数据库厂商标识(databaseIdProvider),MyBatis 会加载所有不带 databaseId 或匹配当前 databaseId 的语句;如果带和不带的语句都有,则不带的会被忽略。 |
<!--如果数据库支持自增可以使用这样的方式-->
<insert id="insertUser" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into user(user_name) values(#{userName})
</insert>
<!--如果数据库不支持自增的话,那么可以使用如下的方式进行赋值查询-->
<insert id="insertUser2" >
<selectKey order="BEFORE" keyProperty="id" resultType="integer">
select max(id)+1 from user
</selectKey>
insert into user(id,user_name) values(#{id},#{userName})
</insert>
更多详细内容见下边的第三章节
三 MyBatis基于XML的详细使用-参数、返回结果处理
3.1 参数的取值方式
在xml文件中编写sql语句的时候有两种取值的方式,分别是#{}和${},下面来看一下他们之间的区别:
<!--获取参数的方式:
1.#{} ==> jdbc String sql=" SELECT id,user_name FROM EMP WHERE id=?"
1.会经过JDBC当中PreparedStatement的预编译,会根据不同的数据类型来编译成对应数据库所对应的数据。
2.能够有效的防止SQL注入。 推荐使用!!
特殊用法:
自带很多内置参数的属性:通常不会使用。了解
javaType、jdbcType、mode、numericScale、resultMap、typeHandler.
比如 需要改变默认的NULL===>OTHER:#{id,javaType=NULL}
想保留小数点后两位:#{id,numericScale=2}
2.${} ==> jdbc String sql=" SELECT id,user_name FROM EMP WHERE id="+id
1.不会进行预编译,会直接将输入进来的数据拼接在SQL中。
2.存在SQL注入的风险。不推荐使用。
特殊用法:
1.调试情况下可以临时使用。
2.实现一些特殊功能:前提一定要保证数据的安全性。
比如:动态表、动态列. 动态SQL.
-->
<select id="SelectEmp" resultType="Emp" resultMap="emp_map" >
SELECT id,user_name,create_date FROM EMP where id=#{id}
</select>
3.2 select的参数传递
<!--
参数传递的处理:
1.单个参数:SelectEmp(Integer id);
mybatis 不会做任何特殊要求
获取方式:
#:{输入任何字符获取参数}
2.多个参数:Emp SelectEmp(Integer id,String username);
mybatis 会进行封装
会将传进来的参数封装成map:
1个值就会对应2个map项 : id===> {key:arg0 ,value:id的值},{key:param1 ,value:id的值}
username===> {key:arg1 ,value:id的值},{key:param2 ,value:id的值}
获取方式:
没使用了@Param:
id=====> #{arg0} 或者 #{param1}
username=====> #{arg1} 或者 #{param2}
除了使用这种方式还有别的方式,因为这种方式参数名没有意义:
设置参数的别名:@Param(""):SelectEmp(@Param("id") Integer id,@Param("username") String username);
当使用了@Param:
id=====> #{id} 或者 #{param1}
username=====> #{username} 或者 #{param2}
3. javaBean的参数:
单个参数:Emp SelectEmp(Emp emp);
获取方式:可以直接使用属性名
emp.id=====>#{id}
emp.username=====>#{username}
多个参数:Emp SelectEmp(Integer num,Emp emp);
num===> #{param1} 或者 @Param
emp===> 必须加上对象别名: emp.id===> #{param2.id} 或者 @Param("emp")Emp emp ====>#{emp.id}
emp.username===> #{param2.username} 或者 @Param("emp")Emp emp ====>#{emp.username}
4.集合或者数组参数:
Emp SelectEmp(List<String> usernames);
如果是list,MyBatis会自动封装为map:
{key:"list":value:usernames}
没用@Param("")要获得:usernames.get(0) =====> #{list[0]}
:usernames.get(0) =====> #{agr0[0]}
有@Param("usernames")要获得:usernames.get(0) =====> #{usernames[0]}
:usernames.get(0) =====> #{param1[0]}
如果是数组,MyBatis会自动封装为map:
{key:"array":value:usernames}
没用@Param("")要获得:usernames.get(0) =====> #{array[0]}
:usernames.get(0) =====> #{agr0[0]}
有@Param("usernames")要获得:usernames.get(0) =====> #{usernames[0]}
:usernames.get(0) =====> #{param1[0]}
5.map参数
和javaBean的参数传递是一样。
一般情况下:
请求进来的参数 和pojo对应,就用pojo
请求进来的参数 没有和pojo对应,就用map
请求进来的参数 没有和pojo对应上,但是使用频率很高,就用TO、DTO(就是单独为这些参数创建一个对应的javaBean出来,使参数传递更规范、更重用)
-->
<!--
接口:SelectEmp(String username,@Param("id") Integer id);
username====> #{arg0} #{param1}
id====> #{id} #{param2}
接口:SelectEmp(@Param("beginDate") String beginDate,
String endDate,
Emp emp);
beginDate====> #{beginDate} #{param1}
endDate====> #{arg1} #{param2}
emp.id====>#{arg2.id} #{param2.id}
接口:SelectEmp(List<Integer> ids,
String[] usernames,
@Param("beginDate") String beginDate,
String endDate,);
ids.get(0)=====> #{list[0]} #{param1[0]}
usernames[0]=====> #{array[0]} #{param2[0]}
beginDate====> #{beginDate} #{param3}
end====> #{arg3} #{param4}
-->
3.3 处理集合返回结果
EmpDao.xml
<!--当返回值的结果是集合的时候,返回值的类型依然写的是集合中具体的类型-->
<select id="selectAllEmp" resultType="cn.tulingxueyuan.bean.Emp">
select * from emp
</select>
<!--在查询的时候可以设置返回值的类型为map,当mybatis查询完成之后会把列的名称作为key
列的值作为value,转换到map中
-->
<select id="selectEmpByEmpReturnMap" resultType="map">
select * from emp where empno = #{empno}
</select>
<!--注意,当返回的结果是一个集合对象的时候,返回值的类型一定要写集合具体value的类型,
同时在dao的方法上要添加@MapKey的注解,来设置key是什么结果
@MapKey("empno")
Map<Integer,Emp> getAllEmpReturnMap();-->
<select id="getAllEmpReturnMap" resultType="cn.tulingxueyuan.bean.Emp">
select * from emp
</select>
3.4 自定义结果集—resultMap
<!--1.声明resultMap自定义结果集 resultType 和 resultMap 只能使用一个。
id 唯一标识, 需要和<select 上的resultMap 进行对应
type 需要映射的pojo对象, 可以设置别名
autoMapping 自动映射,(默认=true) 只要字段名和属性名遵循映射规则就可以自动映射,但是不建议,哪怕属性名和字段名一一对应上了也要显示的配置映射
extends 如果多个resultMap有重复映射,可以声明父resultMap,将公共的映射提取出来, 可以减少子resultMap的映射冗余
-->
<resultMap id="emp_map" type="emp" autoMapping="false" extends="common_map">
<result column="create_date" property="cjsj"></result>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="common_map" type="emp" autoMapping="false" >
<!-- <id> 主键必须使用 对底层存储有性能作用
column 需要映射的数据库字段名
property 需要映射的pojo属性名
-->
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="user_name" property="username"></result>
</resultMap>
<!--2.使用resultMap 关联 自定义结果集的id-->
<select id="SelectEmp" resultType="Emp" resultMap="emp_map" >
SELECT id,user_name,create_date FROM EMP where id=#{id}
</select>
四 MyBatis基于XML的详细使用——高级结果映射
4.1 联合查询
emp.java
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class Emp {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private LocalDate createDate;
private deptId deptId;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public LocalDate getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(LocalDate createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
public Integer getDeptId() {
return dept;
}
public void setDeptId(Integer deptId) {
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", createDate=" + createDate +
", deptId=" + deptId+
'}';
}
}
EmpMapper.xml
<!-- 实现表联结查询的方式: 可以映射: DTO -->
<resultMap id="QueryEmp_Map" type="QueryEmpDTO">
<id column="e_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="user_name" property="username"></result>
<result column="d_id" property="deptId"></result>
<result column="dept_name" property="deptName"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="QueryEmp" resultMap="QueryEmp_Map">
select t1.id as e_id,t1.user_name,t2.id as d_id,t2.dept_name from emp t1
INNER JOIN dept t2 on t1.dept_id=t2.id
where t1.id=#{id}
</select>
<!-- 实现表联结查询的方式: 可以映射map -->
<resultMap id="QueryEmp_Map" type="map">
<id column="e_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="user_name" property="username"></result>
<result column="d_id" property="deptId"></result>
<result column="dept_name" property="deptName"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="QueryEmp" resultMap="QueryEmp_Map">
select t1.id as e_id,t1.user_name,t2.id as d_id,t2.dept_name from emp t1
INNER JOIN dept t2 on t1.dept_id=t2.id
where t1.id=#{id}
</select>
QueryEmpDTO
public class QueryEmpDTO {
private String deptName;
private Integer deptId;
private Integer id;
private String username;
public String getDeptName() {
return deptName;
}
public void setDeptName(String deptName) {
this.deptName = deptName;
}
public Integer getDeptId() {
return deptId;
}
public void setDeptId(Integer deptId) {
this.deptId = deptId;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "QueryEmpDTO{" +
"deptName='" + deptName + '\'' +
", deptId=" + deptId +
", id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Test
@Test
public void test01() {
try(SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()){
// Mybatis在getMapper就会给我们创建jdk动态代理
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
QueryEmpDTO dto = mapper.QueryEmp(4);
System.out.println(dto);
}
}
4.2 嵌套结果
4.2.1 多对一
EmpMapper.xml
<!--嵌套结果 多 对 一 -->
<resultMap id="QueryEmp_Map2" type="Emp">
<id column="e_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="user_name" property="username"></result>
<!--
association 实现多对一中的 “一”
property 指定对象中的嵌套对象属性
-->
<association property="dept">
<id column="d_id" property="id"></id>
<id column="dept_name" property="deptName"></id>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="QueryEmp2" resultMap="QueryEmp_Map2">
select t1.id as e_id,t1.user_name,t2.id as d_id,t2.dept_name from emp t1
INNER JOIN dept t2 on t1.dept_id=t2.id
where t1.id=#{id}
</select>
4.2.2 一对多
<!-- 嵌套结果: 一对多 查询部门及所有员工 -->
<resultMap id="SelectDeptAndEmpsMap" type="Dept">
<id column="d_id" property="id"></id>
<id column="dept_name" property="deptName"></id>
<!--
<collection 映射一对多中的 “多”
property 指定需要映射的“多”的属性,一般声明为List
ofType 需要指定list的类型
-->
<collection property="emps" ofType="Emp" >
<id column="e_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="user_name" property="username"></result>
<result column="create_date" property="createDate"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="SelectDeptAndEmps" resultMap="SelectDeptAndEmpsMap">
select t1.id as d_id,t1.dept_name,t2.id e_id,t2.user_name,t2.create_date from dept t1
LEFT JOIN emp t2 on t1.id=t2.dept_id
where t1.id=#{id}
</select>
Emp.java
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class Emp {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private LocalDate createDate;
private Dept dept;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public LocalDate getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(LocalDate createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
public Dept getDept() {
return dept;
}
public void setDept(Dept dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", createDate=" + createDate +
", dept=" + dept +
'}';
}
}
Dept.java:
public class Dept {
private Integer id;
private String deptName;
private List<Emp> emps;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDeptName() {
return deptName;
}
public void setDeptName(String deptName) {
this.deptName = deptName;
}
public List<Emp> getEmps() {
return emps;
}
public void setEmps(List<Emp> emps) {
this.emps = emps;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dept{" +
"id=" + id +
", deptName='" + deptName + '\'' +
", emps=" + emps +
'}';
}
}
EmpMapper.java:
public interface EmpMapper {
/*徐庶老师实际开发中的实现方式*/
QueryEmpDTO QueryEmp(Integer id);
/*实用嵌套结果实现联合查询 多对一 */
Emp QueryEmp2(Integer id);
/*实用嵌套查询实现联合查询 多对一 */
Emp QueryEmp3(Integer id);
}
DeptMapper.java:
public interface DeptMapper {
//嵌套查询: 一对多 使用部门id查询员工
Dept SelectDeptAndEmps(Integer id);
// 嵌套查询(异步查询): 一对多 查询部门及所有员工
Dept SelectDeptAndEmps2(Integer id);
}
4.3 嵌套查询
在上述逻辑的查询中,是由我们自己来完成sql语句的关联查询的,那么,我们能让mybatis帮我们实现自动的关联查询吗?
4.3.1 多对一
EmpMapper.xml:
<!--嵌套查询(分步查询) 多 对 一
联合查询和分步查询区别: 性能区别不大
分部查询支持 懒加载(延迟加载)
需要设置懒加载,一定要使用嵌套查询的。
要启动懒加载可以在全局配置文件中设置 lazyLoadingEnabled=true
还可以单独为某个分步查询设置立即加载 <association fetchType="eager"
-->
<resultMap id="QueryEmp_Map3" type="Emp">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="user_name" property="username"></result>
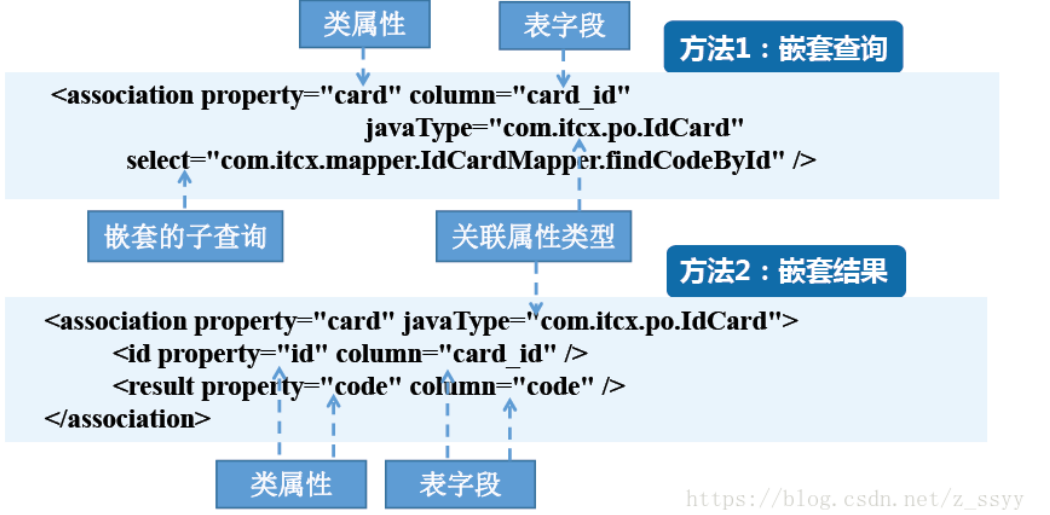
<!-- association 实现多对一中的 “一”
property 指定对象中的嵌套对象属性
column 指定将哪个字段传到分步查询中
select 指定分步查询的 命名空间+ID
以上3个属性是实现分步查询必须的属性
fetchType 可选, eager|lazy eager立即加载 lazy跟随全局配置文件中的lazyLoadingEnabled
-->
<association property="dept" column="dept_id" select="cn.tulingxueyuan.mapper.DeptMapper.SelectDept">
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="QueryEmp3" resultMap="QueryEmp_Map3">
select * from emp where id=#{id}
</select>
DeptMapper.xml
<!-- 根据部门id查询部门-->
<select id="SelectDept" resultType="dept">
SELECT * FROM dept where id=#{id}
</select>
4.3.2 一对多
DeptMapper.xml
<!-- 嵌套查询(异步查询): 一对多 查询部门及所有员工 -->
<resultMap id="SelectDeptAndEmpsMap2" type="Dept">
<id column="d_id" property="id"></id>
<id column="dept_name" property="deptName"></id>
<!--
<collection 映射一对多中的 “多”
property 指定需要映射的“多”的属性,一般声明为List
ofType 需要指定list的类型
column 需要将当前查询的字段传递到异步查询的参数
select 指定异步查询
-->
<collection property="emps" ofType="Emp" column="id" select="cn.tulingxueyuan.mapper.EmpMapper.SelectEmpByDeptId" >
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="SelectDeptAndEmps2" resultMap="SelectDeptAndEmpsMap2">
SELECT * FROM dept where id=#{id}
</select>
EmpMapper.xml
<!-- 根据部门id所有员工 -->
<select id="SelectEmpByDeptId" resultType="emp">
select * from emp where dept_id=#{id}
</select>
Emp.java
public class Emp {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private LocalDate createDate;
private Dept dept;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public LocalDate getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(LocalDate createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
public Dept getDept() {
return dept;
}
public void setDept(Dept dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", createDate=" + createDate +
", dept=" + dept +
'}';
}
}
Dept.java:
public class Dept {
private Integer id;
private String deptName;
private List<Emp> emps;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getDeptName() {
return deptName;
}
public void setDeptName(String deptName) {
this.deptName = deptName;
}
public List<Emp> getEmps() {
return emps;
}
public void setEmps(List<Emp> emps) {
this.emps = emps;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dept{" +
"id=" + id +
", deptName='" + deptName + '\'' +
", emps=" + emps +
'}';
}
}
EmpMapper.java:
public interface EmpMapper {
/*徐庶老师实际开发中的实现方式*/
QueryEmpDTO QueryEmp(Integer id);
/*实用嵌套结果实现联合查询 多对一 */
Emp QueryEmp2(Integer id);
/*实用嵌套查询实现联合查询 多对一 */
Emp QueryEmp3(Integer id);
}
DeptMapper.java:
public interface DeptMapper {
//嵌套查询: 一对多 使用部门id查询员工
Dept SelectDeptAndEmps(Integer id);
// 嵌套查询(异步查询): 一对多 查询部门及所有员工
Dept SelectDeptAndEmps2(Integer id);
}
4.4 延迟查询
当我们在进行表关联的时候,有可能在查询结果的时候不需要关联对象的属性值(select count(1)…),那么此时可以通过延迟加载来实现功能。在全局配置文件中添加如下属性
mybatis-config.xml
<!-- 开启延迟加载,所有分步查询都是懒加载 (默认是立即加载)-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--当开启式, 使用pojo中任意属性都会加载延迟查询 ,默认是false
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>-->
<!--设置对象的哪些方法调用会加载延迟查询 默认:equals,clone,hashCode,toString-->
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value=""/>
如果设置了全局加载,但是希望在某一个sql语句查询的时候不使用延时策略,可以添加fetchType下属性:
<association property="dept" fetchType="eager" column="dept_id" select="cn.tulingxueyuan.mapper.DeptMapper.SelectDept">
</association>
4.5 总结

三种关联关系都有两种关联查询的方式: 嵌套查询,嵌套结果
Mybatis的延迟加载配置, 在全局配置文件中加入下面代码
<settings>
<setting name=”lazyLoadingEnabled” value=”true” />
<setting name=”aggressiveLazyLoading” value=”false”/>
</settings>
在映射文件中,元素和元素中都已默认配置了延迟加载属性,即默认属性fetchType=”lazy”(属性fetchType=”eager”表示立即加载),所以在配置文件中开启延迟加载后,无需在映射文件中再做配置
一对一
使用元素进行一对一关联映射非常简单,只需要参考如下两种示例配置即可
一对多
<resultMap>元素中,包含了一个<collection>子元素,MyBatis就是通过该元素来处理一对多关联关系的
<collection>子元素的属性大部分与<association>元素相同,但其还包含一个特殊属性–ofType
ofType属性与javaType属性对应,它用于指定实体对象中集合类属性所包含的元素类型。
<collection >元素的使用也非常简单,同样可以参考如下两种示例进行配置,具体代码如下:
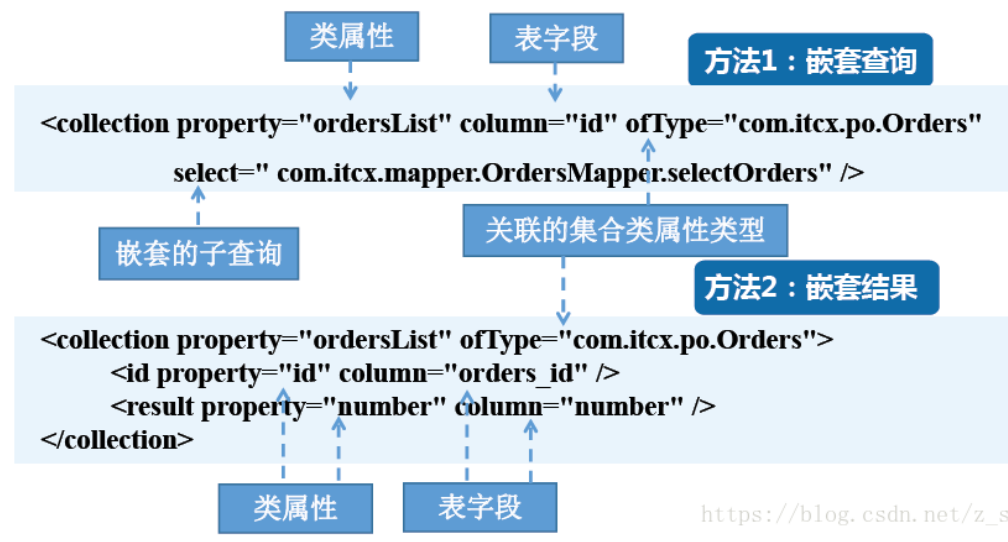
多对多
多对多的关联关系查询,同样可以使用前面介绍的元素进行处理(其用法和一对多关联关系查询语句用法基本相同)
五 动态sql
动态 SQL 是 MyBatis 的强大特性之一。如果你使用过 JDBC 或其它类似的框架,你应该能理解根据不同条件拼接 SQL 语句有多痛苦,例如拼接时要确保不能忘记添加必要的空格,还要注意去掉列表最后一个列名的逗号。利用动态 SQL,可以彻底摆脱这种痛苦。
使用动态 SQL 并非一件易事,但借助可用于任何 SQL 映射语句中的强大的动态 SQL 语言,MyBatis 显著地提升了这一特性的易用性。
如果你之前用过 JSTL 或任何基于类 XML 语言的文本处理器,你对动态 SQL 元素可能会感觉似曾相识。在 MyBatis 之前的版本中,需要花时间了解大量的元素。借助功能强大的基于 OGNL 的表达式,MyBatis 3 替换了之前的大部分元素,大大精简了元素种类,现在要学习的元素种类比原来的一半还要少。
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
- bind
- sql片段
5.1 if
EmpDao.xml
<select id="getEmpByCondition" resultType="cn.tulingxueyuan.bean.Emp">
select * from emp where
<if test="empno!=null">
empno = #{empno} and
</if>
<if test="ename!=null">
ename like #{ename} and
</if>
<if test="sal!=null">
sal > #{sal}
</if>
</select>
上边代码看起来是比较正常的,但是大家需要注意的是如果我们传入的参数值有缺失会怎么呢?这个时候拼接的sql语句就会变得有问题,例如不传参数或者丢失最后一个参数,那么语句中就会多一个where或者and的关键字,因此在mybatis中也给出了具体的解决方案:
where
where 元素只会在子元素返回任何内容的情况下才插入 “WHERE” 子句。而且,若子句的开头为 “AND” 或 “OR”,where 元素也会将它们去除。
<select id="getEmpByCondition" resultType="cn.tulingxueyuan.bean.Emp">
select * from emp
<where>
<if test="empno!=null">
empno = #{empno}
</if>
<if test="ename!=null">
and ename like #{ename}
</if>
<if test="sal!=null">
and sal > #{sal}
</if>
</where>
</select>
现在看起来没有什么问题了,但是我们的条件添加到了拼接sql语句的前后,那么我们该如何处理呢?
trim
<!--
trim截取字符串:
prefix:前缀,为sql整体添加一个前缀
prefixOverrides:去除整体字符串前面多余的字符
suffixOverrides:去除后面多余的字符串
-->
<select id="getEmpByCondition" resultType="cn.tulingxueyuan.bean.Emp">
select * from emp
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and" suffixOverrides="and">
<if test="empno!=null">
empno = #{empno} and
</if>
<if test="ename!=null">
ename like #{ename} and
</if>
<if test="sal!=null">
sal > #{sal} and
</if>
</trim>
</select>
5.2 foreach
动态 SQL 的另一个常见使用场景是对集合进行遍历(尤其是在构建 IN 条件语句的时候)。
<!--foreach是对集合进行遍历
collection="deptnos" 指定要遍历的集合
close="" 表示以什么结束
index="" 给定一个索引值
item="" 遍历的每一个元素的值
open="" 表示以什么开始
separator="" 表示多个元素的分隔符
-->
<select id="getEmpByDeptnos" resultType="Emp">
select * from emp where deptno in
<foreach collection="deptnos" close=")" index="idx" item="deptno" open="(" separator=",">
#{deptno}
</foreach>
</select>
5.3 choose、when、otherwise
有时候,我们不想使用所有的条件,而只是想从多个条件中选择一个使用。针对这种情况,MyBatis 提供了 choose 元素,它有点像 Java 中的 switch 语句。
<select id="getEmpByConditionChoose" resultType="cn.tulingxueyuan.bean.Emp">
select * from emp
<where>
<choose>
<when test="empno!=null">
empno > #{empno}
</when>
<when test="ename!=null">
ename like #{ename}
</when>
<when test="sal!=null">
sal > #{sal}
</when>
<otherwise>
1=1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
5.4 set
用于动态更新语句的类似解决方案叫做 set。set 元素可以用于动态包含需要更新的列,忽略其它不更新的列。
<update id="updateEmpByEmpno">
update emp
<set>
<if test="empno!=null">
empno=#{empno},
</if>
<if test="ename!=null">
ename = #{ename},
</if>
<if test="sal!=null">
sal = #{sal}
</if>
</set>
<where>
empno = #{empno}
</where>
</update>
5.5 bind
bind 元素允许你在 OGNL 表达式以外创建一个变量,并将其绑定到当前的上下文。比如:
<select id="selectBlogsLike" resultType="Blog">
<bind name="pattern" value="'%' + _parameter.getTitle() + '%'" />
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE title LIKE #{pattern}
</select>
5.6 sql
这个元素可以用来定义可重用的 SQL 代码片段,以便在其它语句中使用。 参数可以静态地(在加载的时候)确定下来,并且可以在不同的 include 元素中定义不同的参数值。比如:
<sql id="userColumns"> ${alias}.id,${alias}.username,${alias}.password </sql>
这个 SQL 片段可以在其它语句中使用,例如:
<select id="selectUsers" resultType="map">
select
<include refid="userColumns"><property name="alias" value="t1"/></include>,
<include refid="userColumns"><property name="alias" value="t2"/></include>
from some_table t1
cross join some_table t2
</select>
六 MyBatis缓存
6.1 缓存介绍
MyBatis 内置了一个强大的事务性查询缓存机制,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。 为了使它更加强大而且易于配置,我们对 MyBatis 3 中的缓存实现进行了许多改进。
默认情况下,只启用了本地的会话缓存,它仅仅对一个会话中的数据进行缓存。 要启用全局的二级缓存,只需要在你的 SQL 映射文件中添加一行:
<cache/>
当添加上该标签之后,会有如下效果:
- 映射语句文件中的所有 select 语句的结果将会被缓存。
- 映射语句文件中的所有 insert、update 和 delete 语句会刷新缓存。
- 缓存会使用最近最少使用算法(LRU, Least Recently Used)算法来清除不需要的缓存。
- 缓存不会定时进行刷新(也就是说,没有刷新间隔)。
- 缓存会保存列表或对象(无论查询方法返回哪种)的 1024 个引用。
- 缓存会被视为读/写缓存,这意味着获取到的对象并不是共享的,可以安全地被调用者修改,而不干扰其他调用者或线程所做的潜在修改。
在进行配置的时候还会分为一级缓存和二级缓存:
- 一级缓存:线程级别的缓存,是本地缓存,sqlSession级别的缓存
- 二级缓存:全局范围的缓存,不止局限于当前会话
6.2 一级缓存的使用
一级缓存是sqlsession级别的缓存,默认是存在的。在下面的案例中,大家发现我发送了两个相同的请求,但是sql语句仅仅执行了一次,那么就意味着第一次查询的时候已经将结果进行了缓存。
@Test
public void test01() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
List<Emp> list = mapper.selectAllEmp();
for (Emp emp : list) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
List<Emp> list2 = mapper.selectAllEmp();
for (Emp emp : list2) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
在大部分的情况下一级缓存是可以的,但是有几种特殊的情况会造成一级缓存失效:
1、一级缓存是sqlSession级别的缓存,如果在应用程序中只有开启了多个sqlsession,那么会造成缓存失效
@Test
public void test02(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
List<Emp> list = mapper.selectAllEmp();
for (Emp emp : list) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
System.out.println("================================");
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpDao mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
List<Emp> list2 = mapper2.selectAllEmp();
for (Emp emp : list2) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
sqlSession.close();
sqlSession2.close();
}
2、在编写查询的sql语句的时候,一定要注意传递的参数,如果参数不一致,那么也不会缓存结果
3、如果在发送过程中发生了数据的修改,那么结果就不会缓存
@Test
public void test03(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
Emp empByEmpno = mapper.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno);
System.out.println("================================");
empByEmpno.setEname("zhangsan");
int i = mapper.updateEmp(empByEmpno);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println("================================");
Emp empByEmpno1 = mapper.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno1);
sqlSession.close();
}
4、在两次查询期间,手动去清空缓存,也会让缓存失效
@Test
public void test03(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
Emp empByEmpno = mapper.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno);
System.out.println("================================");
System.out.println("手动清空缓存");
sqlSession.clearCache();
System.out.println("================================");
Emp empByEmpno1 = mapper.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno1);
sqlSession.close();
}
特性
一级缓存特性:
- 默认就开启了,也可以关闭一级缓存 localCacheScope=STATEMENT
- 作用域:是基于sqlSession(默认),一次数据库操作会话。
- 缓存默认实现类PerpetualCache ,使用map进行存储的
- 查询完就会进行存储
- 先从二级缓存中获取,再从一级缓存中获取
key==> sqlid+sql
一级缓存失效情况:
- 不同的sqlSession会使一级缓存失效
- 同一个SqlSession,但是查询语句不一样
- 同一个SqlSession,查询语句一样,期间执行增删改操作
- 同一个SqlSession,查询语句一样,执行手动清除缓存
6.3 二级缓存的使用
二级缓存是全局作用域缓存,默认是不开启的,需要手动进行配置。
Mybatis提供二级缓存的接口以及实现,缓存实现的时候要求实体类实现Serializable接口,二级缓存在sqlSession关闭或提交之后才会生效。
二级缓存的使用
步骤:
1、全局配置文件中添加如下配置:
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
2、需要在使用二级缓存的映射文件处使用标签标注
3、实体类必须要实现Serializable接口
@Test
public void test04(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
EmpDao mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
Emp empByEmpno = mapper.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno);
sqlSession.close();
Emp empByEmpno1 = mapper2.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno1);
sqlSession2.close();
}
缓存的属性
- eviction:表示缓存回收策略,默认是LRU
- LRU:最近最少使用的,移除最长时间不被使用的对象
- FIFO:先进先出,按照对象进入缓存的顺序来移除
- SOFT:软引用,移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象
- WEAK:弱引用,更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象
- flushInternal:刷新间隔,单位毫秒
- 默认情况是不设置,也就是没有刷新间隔,缓存仅仅调用语句时刷新
- size:引用数目,正整数
- 代表缓存最多可以存储多少个对象,太大容易导致内存溢出
- readonly:只读,true/false
- true:只读缓存,会给所有调用这返回缓存对象的相同实例,因此这些对象不能被修改。
- false:读写缓存,会返回缓存对象的拷贝(序列化实现),这种方式比较安全,默认值
//可以看到会去二级缓存中查找数据,而且二级缓存跟一级缓存中不会同时存在数据,因为二级缓存中的数据是在sqlsession 关闭之后才生效的
@Test
public void test05(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
Emp empByEmpno = mapper.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno);
sqlSession.close();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpDao mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
Emp empByEmpno2 = mapper2.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno2);
Emp empByEmpno3 = mapper2.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno3);
sqlSession2.close();
}
缓存查询的顺序是先查询二级缓存再查询一级缓存
@Test
public void test05(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
Emp empByEmpno = mapper.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno);
sqlSession.close();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
EmpDao mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
Emp empByEmpno2 = mapper2.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno2);
Emp empByEmpno3 = mapper2.findEmpByEmpno(1111);
System.out.println(empByEmpno3);
Emp empByEmpno4 = mapper2.findEmpByEmpno(7369);
System.out.println(empByEmpno4);
Emp empByEmpno5 = mapper2.findEmpByEmpno(7369);
System.out.println(empByEmpno5);
sqlSession2.close();
}
二级缓存的作用范围
如果设置了全局的二级缓存配置,那么在使用的时候需要注意,在每一个单独的select语句中,可以设置将查询缓存关闭,以完成特殊的设置
1、在setting中设置,是配置二级缓存开启,一级缓存默认一直开启
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
2、select标签的useCache属性:
在每一个select的查询中可以设置当前查询是否要使用二级缓存,只对二级缓存有效
3、sql标签的flushCache属性
增删改操作默认值为true,sql执行之后会清空一级缓存和二级缓存,而查询操作默认是false
4、sqlSession.clearCache()
只是用来清除一级缓存
二级缓存特性
- 默认开启了,没有实现
- 作用域:基于全局范围,应用级别。
- 缓存默认实现类PerpetualCache ,使用map进行存储的但是二级缓存根据不同的mapper命名空间多包了一层map
: org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#caches key:mapper命名空间 value:erpetualCache.map
key==> sqlid+sql
- 事务提交的时候(sqlSession关闭)
- 先从二级缓存中获取,再从一级缓存中获取
实现:
- 开启二级缓存
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> - 在需要使用到二级缓存的映射文件中加入,基于Mapper映射文件来实现缓存的,基于Mapper映射文件的命名空间来存储的
- 在需要使用到二级缓存的javaBean中实现序列化接口implements Serializable
配置成功就会出现缓存命中率 同一个sqlId: 从缓存中拿出的次数/查询总次数
失效:
- 同一个命名空间进行了增删改的操作,会导致二级缓存失效
但是如果不想失效:可以将SQL的flushCache 这是为false,但是要慎重设置,因为会造成数据脏读问题,除非你能保证查询的数据永远不会执行增删改 - 让查询不缓存数据到二级缓存中useCache=“false”
- 如果希望其他mapper映射文件的命名空间执行了增删改清空另外的命名空间就可以设置:
<cache-ref namespace="cn.tulingxueyuan.mapper.DeptMapper"/>
6.4 整合第三方缓存
整合redis
添加redis-mybatis 缓存适配器 依赖
<dependencies>
<!--添加依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
添加redis.properties在resources根目录
host=localhost
port=6379
connectionTimeout=5000
soTimeout=5000
password=无密码可不填
database=0
clientName=
设置mybatis二级缓存实现类
<cache
...
type="org.mybatis.caches.redis.RedisCache" ......
/>
整合ehcache
导入对应的maven依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.ehcache/ehcache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.caches/mybatis-ehcache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>
导入ehcache配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd">
<!-- 磁盘保存路径 -->
<diskStore path="D:\ehcache" />
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="1"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>
<!--
属性说明:
l diskStore:指定数据在磁盘中的存储位置。
l defaultCache:当借助CacheManager.add("demoCache")创建Cache时,EhCache便会采用<defalutCache/>指定的的管理策略
以下属性是必须的:
l maxElementsInMemory - 在内存中缓存的element的最大数目
l maxElementsOnDisk - 在磁盘上缓存的element的最大数目,若是0表示无穷大
l eternal - 设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断
l overflowToDisk - 设定当内存缓存溢出的时候是否将过期的element缓存到磁盘上
以下属性是可选的:
l timeToIdleSeconds - 当缓存在EhCache中的数据前后两次访问的时间超过timeToIdleSeconds的属性取值时,这些数据便会删除,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大
l timeToLiveSeconds - 缓存element的有效生命期,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB 这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小.默认是30MB.每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区.
l diskPersistent - 在VM重启的时候是否启用磁盘保存EhCache中的数据,默认是false。
l diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds - 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。每个120s,相应的线程会进行一次EhCache中数据的清理工作
l memoryStoreEvictionPolicy - 当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入的时候, 移除缓存中element的策略。默认是LRU(最近最少使用),可选的有LFU(最不常使用)和FIFO(先进先出)
-->
在mapper文件中添加自定义缓存
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"></cache>
七 MyBatis分页插件&逆向工程
7.1 分页插件
MyBatis 通过提供插件机制,让我们可以根据自己的需要去增强MyBatis 的功能。需要注意的是,如果没有完全理解MyBatis 的运行原理和插件的工作方式,最好不要使用插件,因为它会改变系底层的工作逻辑,给系统带来很大的影响。
MyBatis 的插件可以在不修改原来的代码的情况下,通过拦截的方式,改变四大核心对象的行为,比如处理参数,处理SQL,处理结果。
Mybatis插件典型适用场景
分页功能
mybatis的分页默认是基于内存分页的(查出所有,再截取),数据量大的情况下效率较低,不过使用mybatis插件可以改变该行为,只需要拦截StatementHandler类的prepare方法,改变要执行的SQL语句为分页语句即可;
公共字段统一赋值
一般业务系统都会有创建者,创建时间,修改者,修改时间四个字段,对于这四个字段的赋值,实际上可以在DAO层统一拦截处理,可以用mybatis插件拦截Executor类的update方法,对相关参数进行统一赋值即可;
性能监控
对于SQL语句执行的性能监控,可以通过拦截Executor类的update, query等方法,用日志记录每个方法执行的时间;
其它
其实mybatis扩展性还是很强的,基于插件机制,基本上可以控制SQL执行的各个阶段,如执行阶段,参数处理阶段,语法构建阶段,结果集处理阶段,具体可以根据项目业务来实现对应业务逻辑。
实现思考:
第一个问题:
不修改对象的代码,怎么对对象的行为进行修改,比如说在原来的方法前面做一点事情,在原来的方法后面做一点事情?
答案:大家很容易能想到用代理模式,这个也确实是MyBatis 插件的原理。
第二个问题:
我们可以定义很多的插件,那么这种所有的插件会形成一个链路,比如我们提交一个休假申请,先是项目经理审批,然后是部门经理审批,再是HR 审批,再到总经理审批,怎么实现层层的拦截?
答案:插件是层层拦截的,我们又需要用到另一种设计模式——责任链模式。
在之前的源码中我们也发现了,mybatis内部对于插件的处理确实使用的代理模式,既然是代理模式,我们应该了解MyBatis 允许哪些对象的哪些方法允许被拦截,并不是每一个运行的节点都是可以被修改的。只有清楚了这些对象的方法的作用,当我们自己编写插件的时候才知道从哪里去拦截。在MyBatis 官网有答案,我们来看一下:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html#plugins
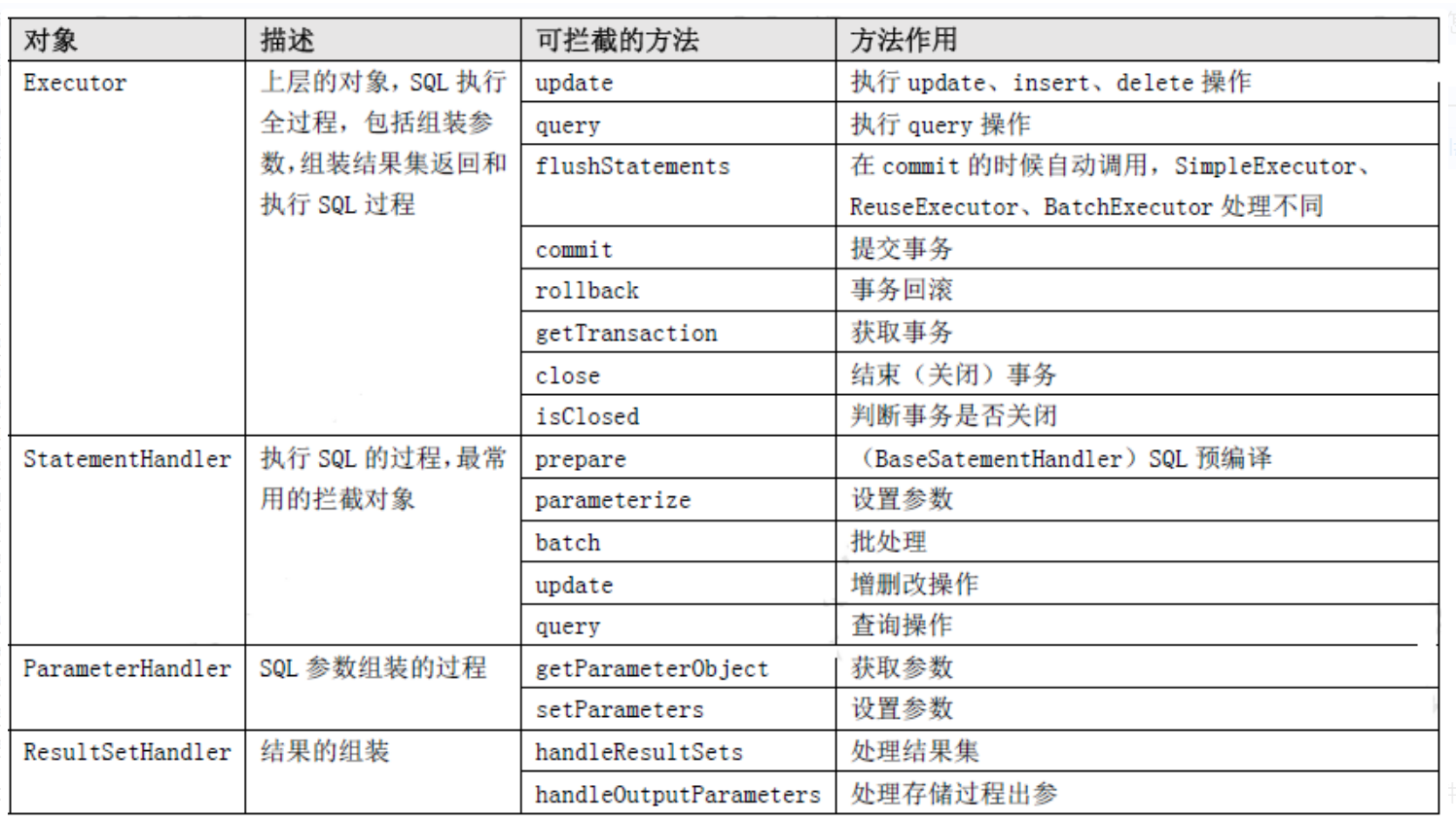
Executor 会拦截到CachingExcecutor 或者BaseExecutor。因为创建Executor 时是先创建CachingExcecutor,再包装拦截。从代码顺序上能看到。我们可以通过mybatis的分页插件来看看整个插件从包装拦截器链到执行拦截器链的过程。
在查看插件原理的前提上,我们需要来看看官网对于自定义插件是怎么来做的,官网上有介绍:通过 MyBatis 提供的强大机制,使用插件是非常简单的,只需实现 Interceptor 接口,并指定想要拦截的方法签名即可。这里本人踩了一个坑,在Springboot中集成,同时引入了pagehelper-spring-boot-starter 导致RowBounds参数的值被刷掉了,也就是走到了我的拦截其中没有被设置值,这里需要注意,拦截器出了问题,可以Debug看一下Configuration配置类中拦截器链的包装情况。
自定义分页插件
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class,method = "query" ,args ={MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class} ), // 需要代理的对象和方法
@Signature(type = Executor.class,method = "query" ,args ={MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class} ) // 需要代理的对象和方法
})
public class MyPageInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("简易版的分页插件:逻辑分页改成物理分页");
// 修改sql 拼接Limit 0,10
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
// MappedStatement 对mapper映射文件里面元素的封装
MappedStatement ms= (MappedStatement) args[0];
// BoundSql 对sql和参数的封装
Object parameterObject=args[1];
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// RowBounds 封装了逻辑分页的参数 :当前页offset,一页数limit
RowBounds rowBounds= (RowBounds) args[2];
// 拿到原来的sql语句
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
String limitSql=sql+ " limit "+rowBounds.getOffset()+","+ rowBounds.getLimit();
//将分页sql重新封装一个BoundSql 进行后续执行
BoundSql pageBoundSql = new BoundSql(ms.getConfiguration(), limitSql, boundSql.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
// 被代理的对象
Executor executor= (Executor) invocation.getTarget();
CacheKey cacheKey = executor.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, pageBoundSql);
// 调用修改过后的sql继续执行查询
return executor.query(ms,parameterObject,rowBounds, (ResultHandler) args[3],cacheKey,pageBoundSql);
}
}
拦截签名跟参数的顺序有严格要求,如果按照顺序找不到对应方法会抛出异常:
org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.PersistenceException:
### Error opening session. Cause: org.apache.ibatis.plugin.PluginException:
Could not find method on interface org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor named queryv
MyBatis 启动时扫描 标签, 注册到Configuration 对象的 InterceptorChain 中。property 里面的参数,会调用setProperties()方法处理。
分页插件使用
添加pom依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>
插件注册,在mybatis-config.xml 中注册插件:
<configuration>
<plugins>
<!-- com.github.pagehelper为PageHelper类所在包名 -->
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper">
<property name="helperDialect" value="mysql" />
<!-- 该参数默认为false -->
<!-- 设置为true时,会将RowBounds第一个参数offset当成pageNum页码使用 -->
<!-- 和startPage中的pageNum效果一样 -->
<property name="offsetAsPageNum" value="true" />
<!-- 该参数默认为false -->
<!-- 设置为true时,使用RowBounds分页会进行count查询 -->
<property name="rowBoundsWithCount" value="true" />
<!-- 设置为true时,如果pageSize=0或者RowBounds.limit = 0就会查询出全部的结果 -->
<!-- (相当于没有执行分页查询,但是返回结果仍然是Page类型) -->
<property name="pageSizeZero" value="true" />
<!-- 3.3.0版本可用 - 分页参数合理化,默认false禁用 -->
<!-- 启用合理化时,如果pageNum<1会查询第一页,如果pageNum>pages会查询最后一页 -->
<!-- 禁用合理化时,如果pageNum<1或pageNum>pages会返回空数据 -->
<property name="reasonable" value="true" />
<!-- 3.5.0版本可用 - 为了支持startPage(Object params)方法 -->
<!-- 增加了一个`params`参数来配置参数映射,用于从Map或ServletRequest中取值 -->
<!-- 可以配置pageNum,pageSize,count,pageSizeZero,reasonable,不配置映射的用默认值 -->
<!-- 不理解该含义的前提下,不要随便复制该配置 -->
<property name="params" value="pageNum=start;pageSize=limit;" />
</plugin>
</plugins>
</configuration>
调用
// 获取配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis/mybatis-config.xml");
// 通过加载配置文件获取SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// Mybatis在getMapper就会给我们创建jdk动态代理
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
PageHelper.startPage(1, 5);
List<Emp> list=mapper.selectAll();
PageInfo<ServiceStation> info = new PageInfo<ServiceStation>(list, 3);
System.out.println("当前页码:"+info.getPageNum());
System.out.println("每页的记录数:"+info.getPageSize());
System.out.println("总记录数:"+info.getTotal());
System.out.println("总页码:"+info.getPages());
System.out.println("是否第一页:"+info.isIsFirstPage());
System.out.println("连续显示的页码:");
int[] nums = info.getNavigatepageNums();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
System.out.println(nums[i]);
}
}
代理和拦截是怎么实现的?
上面提到的可以被代理的四大对象都是什么时候被代理的呢?Executor 是openSession() 的时候创建的; StatementHandler 是SimpleExecutor.doQuery()创建的;里面包含了处理参数的ParameterHandler 和处理结果集的ResultSetHandler 的创建,创建之后即调用InterceptorChain.pluginAll(),返回层层代理后的对象。代理是由Plugin 类创建。在我们重写的 plugin() 方法里面可以直接调用returnPlugin.wrap(target, this);返回代理对象。
单个插件的情况下,代理能不能被代理?代理顺序和调用顺序的关系? 可以被代理。
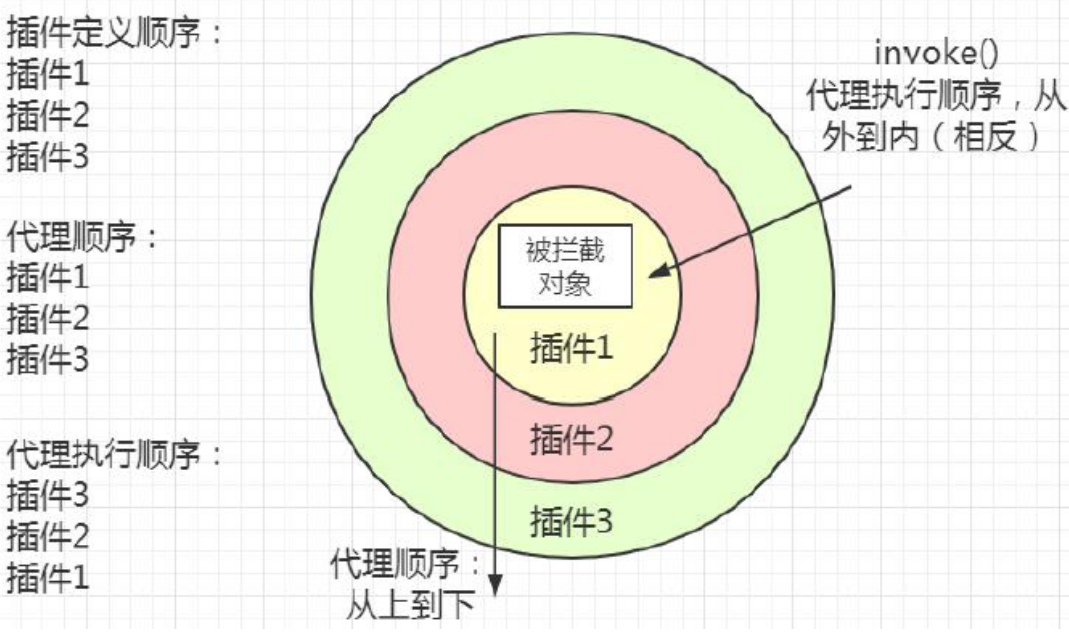
因为代理类是Plugin,所以最后调用的是Plugin 的invoke()方法。它先调用了定义的拦截器的intercept()方法。可以通过invocation.proceed()调用到被代理对象被拦截的方法。
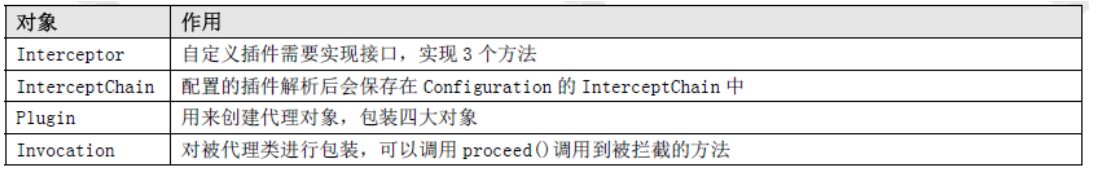
调用流程时序图:
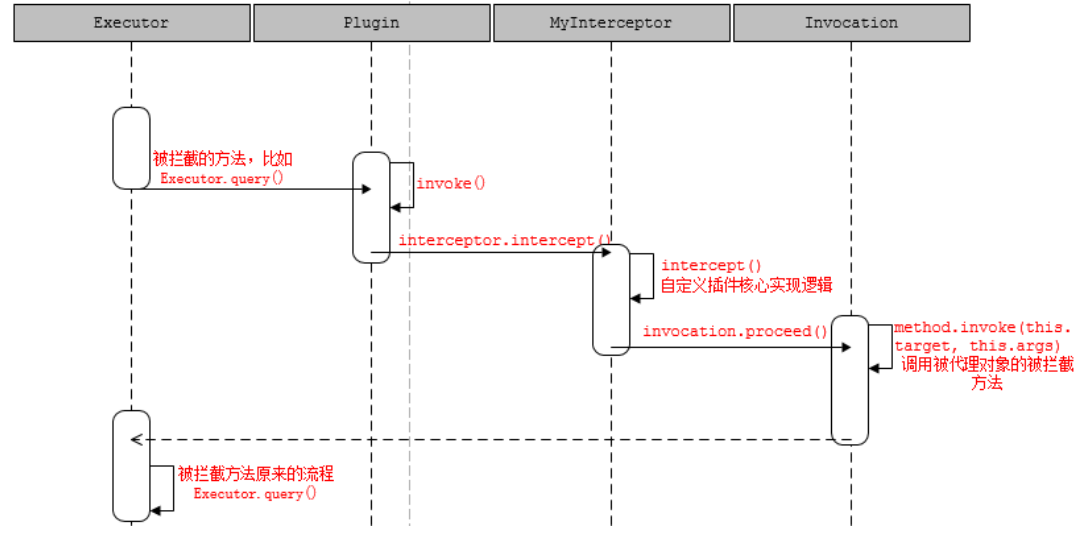
PageHelper 原理
先来看一下分页插件的简单用法:
PageHelper.startPage(1, 3);
List<Blog> blogs = blogMapper.selectBlogById2(blog);
PageInfo page = new PageInfo(blogs, 3);
对于插件机制我们上面已经介绍过了,在这里我们自然的会想到其所涉及的核心类 :PageInterceptor。拦截的是Executor 的两个query()方法,要实现分页插件的功能,肯定是要对我们写的sql进行改写,那么一定是在 intercept 方法中进行操作的,我们会发现这么一行代码:
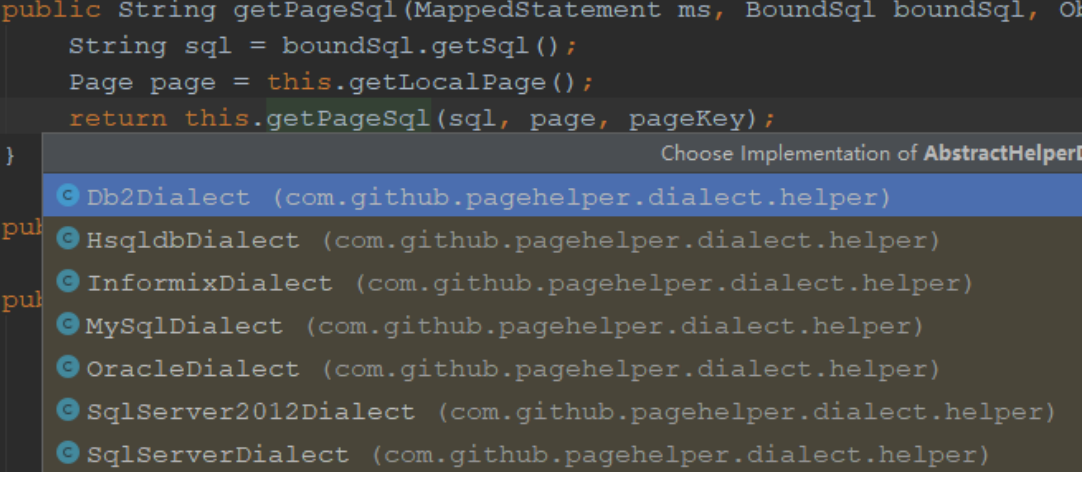
String pageSql = this.dialect.getPageSql(ms, boundSql, parameter, rowBounds, cacheKey);
调用到 AbstractHelperDialect 中的 getPageSql 方法:
public String getPageSql(MappedStatement ms, BoundSql boundSql, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, CacheKey pageKey) {
// 获取sql
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
//获取分页参数对象
Page page = this.getLocalPage();
return this.getPageSql(sql, page, pageKey);
}
这里可以看到会去调用 this.getLocalPage(),我们来看看这个方法:
public <T> Page<T> getLocalPage() {
return PageHelper.getLocalPage();
}
//线程独享
protected static final ThreadLocal<Page> LOCAL_PAGE = new ThreadLocal();
public static <T> Page<T> getLocalPage() {
return (Page)LOCAL_PAGE.get();
}
可以发现这里是调用的是PageHelper的一个本地线程变量中的一个 Page对象,从其中获取我们所设置的 PageSize 与 PageNum,那么他是怎么设置值的呢?请看:
PageHelper.startPage(1, 3);
public static <E> Page<E> startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize) {
return startPage(pageNum, pageSize, true);
}
public static <E> Page<E> startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize, boolean count, Boolean reasonable, Boolean pageSizeZero) {
Page<E> page = new Page(pageNum, pageSize, count);
page.setReasonable(reasonable);
page.setPageSizeZero(pageSizeZero);
Page<E> oldPage = getLocalPage();
if (oldPage != null && oldPage.isOrderByOnly()) {
page.setOrderBy(oldPage.getOrderBy());
}
//设置页数,行数信息
setLocalPage(page);
return page;
}
protected static void setLocalPage(Page page) {
//设置值
LOCAL_PAGE.set(page);
}
在我们调用 PageHelper.startPage(1, 3); 的时候,系统会调用 LOCAL_PAGE.set(page) 进行设置,从而在分页插件中可以获取到这个本地变量对象中的参数进行 SQL 的改写,由于改写有很多实现,我们这里用的Mysql的实现:
在这里我们会发现分页插件改写SQL的核心代码,这个代码就很清晰了,不必过多赘述:
public String getPageSql(String sql, Page page, CacheKey pageKey) {
StringBuilder sqlBuilder = new StringBuilder(sql.length() + 14);
sqlBuilder.append(sql);
if (page.getStartRow() == 0) {
sqlBuilder.append(" LIMIT ");
sqlBuilder.append(page.getPageSize());
} else {
sqlBuilder.append(" LIMIT ");
sqlBuilder.append(page.getStartRow());
sqlBuilder.append(",");
sqlBuilder.append(page.getPageSize());
pageKey.update(page.getStartRow());
}
pageKey.update(page.getPageSize());
return sqlBuilder.toString();
}
PageHelper 就是这么一步一步的改写了我们的SQL 从而达到一个分页的效果。
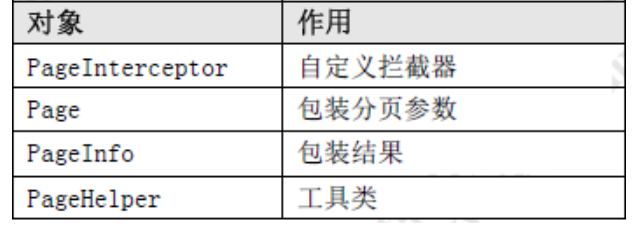
关键类总结:
7.2 MyBatis逆向工程
引入pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-core</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
编写配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd">
<generatorConfiguration>
<!-- 指定数据库驱动
用java代码的方式生成可以不指定(只需要吧mybatis-generator和数据库驱动依赖到项目)
<classPathEntry location ="F:\java\jar\mysql-connector-java-5.1.22-bin.jar" /> -->
<!-- targetRuntime
MyBatis3 可以生成通用查询,可以指定动态where条件
MyBatis3Simple 只生成CURD
-->
<context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<!-- 关于注释的生成规则 -->
<commentGenerator>
<!-- 设置不生成注释 -->
<property name="suppressAllComments" value="true"/>
</commentGenerator>
<!-- 数据库的连接信息 -->
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bookstore"
userId="root"
password="root">
</jdbcConnection>
<!-- java类型生成方式 -->
<javaTypeResolver >
<!-- forceBigDecimals
true 当数据库类型为decimal 或number 生成对应的java的BigDecimal
false 会根据可数据的数值长度生成不同的对应java类型
useJSR310Types
false 所有数据库的日期类型都会生成java的 Date类型
true 会将数据库的日期类型生成对应的JSR310的日期类型
比如 mysql的数据库类型是date===>LocalDate
必须jdk是1.8以上
-->
<property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false" />
</javaTypeResolver>
<!-- pojo的生成规则 -->
<javaModelGenerator
targetPackage="cn.tuling.pojo" targetProject="./src/main/java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" />
<property name="trimStrings" value="true" />
</javaModelGenerator>
<!-- sql映射文件的生成规则 -->
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="cn.tuling.mapper" targetProject="./src/main/resources">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" />
</sqlMapGenerator>
<!-- dao的接口生成规则 UserMapper-->
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="cn.tuling.mapper" targetProject="./src/main/java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" />
</javaClientGenerator>
<table tableName="emp" domainObjectName="Emp" mapperName="EmpMapper" ></table>
<table tableName="dept" domainObjectName="Dept" mapperName="DeptMapper" ></table>
</context>
</generatorConfiguration>
编写测试类
public class MBGTest {
@Test
public void test01() throws Exception {
List<String> warnings = new ArrayList<String>();
boolean overwrite = true;
File configFile = new File("generatorConfig.xml");
ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings);
Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(configFile);
DefaultShellCallback callback = new DefaultShellCallback(overwrite);
MyBatisGenerator myBatisGenerator = new MyBatisGenerator(config, callback, warnings);
myBatisGenerator.generate(null);
}
}
调用
@Test
public void test01() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// Mybatis在getMapper就会给我们创建jdk动态代理
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
Emp emp = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(4);
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
/**
* Mybatis3生成调用方式
*/
@Test
public void test02() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// Mybatis在getMapper就会给我们创建jdk动态代理
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
// 使用Example实现动态条件语句
EmpExample empExample=new EmpExample();
EmpExample.Criteria criteria = empExample.createCriteria();
criteria.andUserNameLike("%帅%")
.andIdEqualTo(4);
List<Emp> emps = mapper.selectByExample(empExample);
System.out.println(emps);
}
}


![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计水果销售管理网站(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1f1b4176e966486ca34655121fd5ddbe.png)






![[附源码]计算机毕业设计考试系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2d5623fc7680479a8c78832f77730a61.png)