介绍
Atomic包是java.util.concurrent下的另一个专门为线程安全设计的Java包,包含多个原子操作类。这个包里面提供了一组原子变量类。其基本的特性就是在多线程环境下,当有多个线程同时执行这些类的实例包含的方法时,具有排他性,即当某个线程进入方法,执行其中的指令时,不会被其他线程打断,而别的线程就像自旋锁一样,一直等到该方法执行完成,才由JVM从等待队列中选择一个另一个线程进入,这只是一种逻辑上的理解。实际上是借助硬件的相关指令来实现的,不会阻塞线程(或者说只是在硬件级别上阻塞了)。可以对基本数据、数组中的基本数据、对类中的基本数据进行操作。原子变量类相当于一种泛化的volatile变量,能够支持原子的和有条件的读-改-写操作。
AtomicInteger是java.util.concurrent.atomic包下的一个提供原子操作的Integer的类。在多线程环境中,++i和i++、–i和i–操作并不是线程安全的,在使用的时候,不可避免的会用到synchronized关键字,而AtomicInteger则通过一种线程安全的加减操作接口保证在多线程环境下对整型变量的原子性操作。。
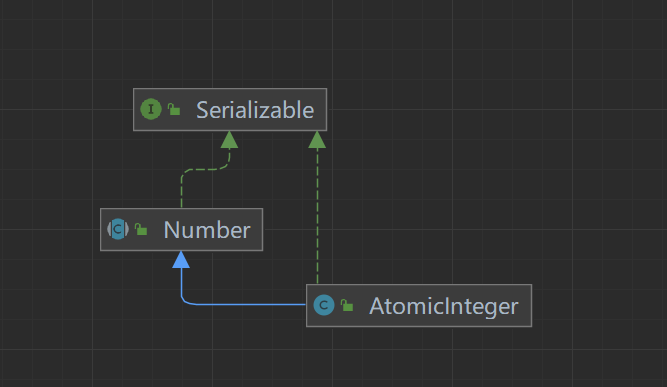
public class AtomicInteger extends Number implements java.io.Serializable
常量&变量
//序列化版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6214790243416807050L;
// setup to use Unsafe.compareAndSwapInt for updates
//unsafe常量,设置为使用Unsafe.compareAndSwapInt进行更新
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
//AtomicInteger的值在内存地址的偏移量,用它进行CAS操作
private static final long valueOffset;
//objectFieldOffset是一个本地方法,返回属性相对于对象的偏移量,这里使用反射获取属性。
static {
try {
valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AtomicInteger.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
//AtomicInteger当前的值
private volatile int value;
Unsafe 是 CAS 的核心类,Java 无法直接访问底层操作系统,而是通过本地(native)方法来访问。不过尽管如此,JVM 还是开了一个后门:Unsafe 类,它提供了硬件级别的原子操作。
Unsafe类是java中未被公开的一个类,可以使用反射来调用其方法
构造方法
/**
* Creates a new AtomicInteger with the given initial value.
*
* @param initialValue the initial value
*/
public AtomicInteger(int initialValue) {
value = initialValue;
}
/**
* Creates a new AtomicInteger with initial value {@code 0}.
*/
public AtomicInteger() {
}
常用方法
get()
获取当前值
/**
* Gets the current value.
*
* @return the current value
* 直接返回变量value
*/
public final int get() {
return value;
}
set(int newValue)
newValue表示要设置的新值。该方法会以原子方式将当前值设置为指定的值。
/**
* Sets to the given value.
*
* @param newValue the new value
* 通过参数newValue将变量value进行值的更新
*/
public final void set(int newValue) {
value = newValue;
}
lazySet(int newValue)
azySet方法是使用volatile关键字确保可见性的一种写方法,它是一种非阻塞的方法,可以减少线程间的竞争。
/**
* Eventually sets to the given value.
*
* @param newValue the new value
* @since 1.6
* 通过unsafe变量最终设置为给定的值。
*/
public final void lazySet(int newValue) {
unsafe.putOrderedInt(this, valueOffset, newValue);
}
方法内部使用了一个putOrderedInt方法,该方法的作用是在不需要锁定功能的前提下,将值设置到指定偏移量的int型字段中,并使用volatile语义保证该操作的可见性。
相比于set方法,lazySet方法的优势在于不需要等待写入操作完成,所以它的性能更好。但是它也存在一个缺点,即它不能保证读操作的可见性,因为它没有使用锁,因此可能出现缓存一致性问题。
getAndSet(int newValue)
获取当前值,并设置新值,这个操作是原子性的,即在多线程环境下,任何时刻只有一个线程能够执行这个操作。
/**
* Atomically sets to the given value and returns the old value.
*
* @param newValue the new value
* @return the previous value
* 先获取旧值再更新新值,还是利用unsafe的内部方法来进行操作
*/
public final int getAndSet(int newValue) {
return unsafe.getAndSetInt(this, valueOffset, newValue);
}
compareAndSet(int expect, int update)
比较当前AtomicInteger对象的值和一个期望值,如果相等,就将AtomicInteger对象的值修改为一个新值。同时,这个操作是原子性的,保证在多线程的情况下,只有一个线程能够成功修改AtomicInteger对象的值。
/**
* Atomically sets the value to the given updated value
* if the current value {@code ==} the expected value.
*
* @param expect the expected value
* @param update the new value
* @return {@code true} if successful. False return indicates that
* the actual value was not equal to the expected value.
* CAS方法,利用判断旧值符合预期值并且更新新的值
*/
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
weakCompareAndSet
AtomicInteger的weakCompareAndSet方法是一种无锁的原子操作,用于比较并设置操作。该方法比较当前AtomicInteger的值与给定的预期值,如果相等,则将AtomicInteger的值设为新值,并返回true;否则不作任何操作,返回false。与compareAndSet方法相比,weakCompareAndSet方法不保证在高并发环境下的操作的原子性,但可以提高系统的并发性能。
/**
* Atomically sets the value to the given updated value
* if the current value {@code ==} the expected value.
*
* <p><a href="package-summary.html#weakCompareAndSet">May fail
* spuriously and does not provide ordering guarantees</a>, so is
* only rarely an appropriate alternative to {@code compareAndSet}.
*
* @param expect the expected value
* @param update the new value
* @return {@code true} if successful
*/
public final boolean weakCompareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
其中,unsafe.compareAndSwapInt是Java中的一个本地方法,可以直接操作内存,实现无锁并发控制。在该方法中,参数this表示当前对象,valueOffset表示该对象内存地址中值的偏移量(由于AtomicInteger是基于内存地址进行操作的,因此需要根据偏移量来访问对象中的值),expect表示预期值,update表示更新值。如果偏移量处的值与expect相等,则将值更新为update,并返回true,否则不作任何操作,返回false。
getAndIncrement()
获取当前值,并递增1
/**
* Atomically increments by one the current value.
*
* @return the previous value
* 先获取旧值然后再旧值上加一,利用的unsafe内部方法
*/
public final int getAndIncrement() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1);
}
getAndDecrement
获取当前值,并递减1
/**
* Atomically decrements by one the current value.
*
* @return the previous value
* 将当前值自动减1
*/
public final int getAndDecrement() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, -1);
}
getAndAdd(int delta)
获取当前值,并加上delta的值
/**
* Atomically adds the given value to the current value.
*
* @param delta the value to add
* @return the previous value
* 先获取旧值然后再旧值上加上指定值,利用的unsafe内部方法
*/
public final int getAndAdd(int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta);
}
public final int addAndGet(int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta) + delta;
}
addAndGet
用于对AtomicInteger对象的值进行原子性的加操作,并返回加操作后的值。
/**
* Atomically adds the given value to the current value.
*
* @param delta the value to add
* @return the updated value
*/
public final int addAndGet(int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta) + delta;
}
incrementAndGet
递增1
/**
* Atomically increments by one the current value.
*
* @return the updated value
*/
public final int incrementAndGet() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1) + 1;
}
decrementAndGet
递减1
/**
* Atomically decrements by one the current value.
*
* @return the updated value
*/
public final int decrementAndGet() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, -1) - 1;
}