目录
1.开启调度框架
2.ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor Bean后处理器分析
2.1 调度框架支持的Task类型
2.2 对Task进行调度执行
3.任务调度器
3.1 任务调度器获取
3.2 框架内提供的任务调度器
3.3 任务调度器执行逻辑
在实际项目开发中,有时会遇到定时调度的开发需要,这部分的功能在Spring框架中给出了较好的支持,即@EnableScheduling&Scheduled定时调度框架,本着不仅知其然还要知其所以然的指导思想,下面对该调度框架进行源码解析,以便更好的理解其执行过程;
1.开启调度框架
Spring框架中,为了开启调度框架功能,需要在配置类上标注@EnableScheduling注解,这也是Spring中Enable*模式的典型应用,下面看一下@EnableScheduling的具体实现:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import(SchedulingConfiguration.class)
@Documented
public @interface EnableScheduling {
}这里通过@Import注解,导入了配置类SchedulingConfiguration,进一步看下SchedulingConfiguration配置类的源码,如下:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class SchedulingConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TaskManagementConfigUtils.SCHEDULED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor scheduledAnnotationProcessor() {
return new ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor();
}
}可以看到,这里定义了一个Bean后处理器ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,调度框架的解析逻辑也是定义在ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor中的,下面着重对该部分进行具体分析;
2.ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor Bean后处理器分析
Bean后处理器中,主要分析下后处理器的拦截方法,如下:
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean || bean instanceof TaskScheduler ||
bean instanceof ScheduledExecutorService) {
// Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies.
return bean;
}
Class<?> targetClass = AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(bean);
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetClass) &&
AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetClass, Arrays.asList(Scheduled.class, Schedules.class))) {
Map<Method, Set<Scheduled>> annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetClass,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<Set<Scheduled>>) method -> {
Set<Scheduled> scheduledAnnotations = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedRepeatableAnnotations(
method, Scheduled.class, Schedules.class);
return (!scheduledAnnotations.isEmpty() ? scheduledAnnotations : null);
});
if (annotatedMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetClass);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @Scheduled annotations found on bean class: " + targetClass);
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
annotatedMethods.forEach((method, scheduledAnnotations) ->
scheduledAnnotations.forEach(scheduled -> processScheduled(scheduled, method, bean)));
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(annotatedMethods.size() + " @Scheduled methods processed on bean '" + beanName +
"': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
return bean;
}如上,postProcessAfterInitialization方法中,主要对标注@Scheduled和聚合注解@Schedules的类成员方法进行处理,主要分为2步:
1)识别标注@Scheduled和聚合注解@Schedules的方法;
2)对注解方法调用processScheduled方法进行处理;
方法processScheduled处理过程如下:
/**
* Process the given {@code @Scheduled} method declaration on the given bean.
* @param scheduled the {@code @Scheduled} annotation
* @param method the method that the annotation has been declared on
* @param bean the target bean instance
* @see #createRunnable(Object, Method)
*/
protected void processScheduled(Scheduled scheduled, Method method, Object bean) {
try {
Runnable runnable = createRunnable(bean, method);
boolean processedSchedule = false;
String errorMessage =
"Exactly one of the 'cron', 'fixedDelay(String)', or 'fixedRate(String)' attributes is required";
Set<ScheduledTask> tasks = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
// Determine initial delay
long initialDelay = convertToMillis(scheduled.initialDelay(), scheduled.timeUnit());
String initialDelayString = scheduled.initialDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(initialDelayString)) {
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay < 0, "Specify 'initialDelay' or 'initialDelayString', not both");
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
initialDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(initialDelayString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initialDelayString)) {
try {
initialDelay = convertToMillis(initialDelayString, scheduled.timeUnit());
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid initialDelayString value \"" + initialDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
}
}
// Check cron expression
String cron = scheduled.cron();
if (StringUtils.hasText(cron)) {
String zone = scheduled.zone();
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
cron = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(cron);
zone = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(zone);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(cron)) {
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay == -1, "'initialDelay' not supported for cron triggers");
processedSchedule = true;
if (!Scheduled.CRON_DISABLED.equals(cron)) {
TimeZone timeZone;
if (StringUtils.hasText(zone)) {
timeZone = StringUtils.parseTimeZoneString(zone);
}
else {
timeZone = TimeZone.getDefault();
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleCronTask(new CronTask(runnable, new CronTrigger(cron, timeZone))));
}
}
}
// At this point we don't need to differentiate between initial delay set or not anymore
if (initialDelay < 0) {
initialDelay = 0;
}
// Check fixed delay
long fixedDelay = convertToMillis(scheduled.fixedDelay(), scheduled.timeUnit());
if (fixedDelay >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new FixedDelayTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedDelayString = scheduled.fixedDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedDelayString)) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedDelayString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(fixedDelayString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
try {
fixedDelay = convertToMillis(fixedDelayString, scheduled.timeUnit());
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedDelayString value \"" + fixedDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new FixedDelayTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
}
// Check fixed rate
long fixedRate = convertToMillis(scheduled.fixedRate(), scheduled.timeUnit());
if (fixedRate >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new FixedRateTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedRateString = scheduled.fixedRateString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedRateString)) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedRateString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedRateString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(fixedRateString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
try {
fixedRate = convertToMillis(fixedRateString, scheduled.timeUnit());
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedRateString value \"" + fixedRateString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new FixedRateTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
}
// Check whether we had any attribute set
Assert.isTrue(processedSchedule, errorMessage);
// Finally register the scheduled tasks
synchronized (this.scheduledTasks) {
Set<ScheduledTask> regTasks = this.scheduledTasks.computeIfAbsent(bean, key -> new LinkedHashSet<>(4));
regTasks.addAll(tasks);
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Encountered invalid @Scheduled method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}上述处理过程主要包含以下几步:
1)将调用目标方法的过程包装为ScheduledMethodRunnable类
2)构造CronTask并进行调度
3)构造FixedDelayTask并进行调度
4)构造FixedRateTask并进行调度
下面主要说明下调度任务的类型以及具体的调度方法;
2.1 调度框架支持的Task类型
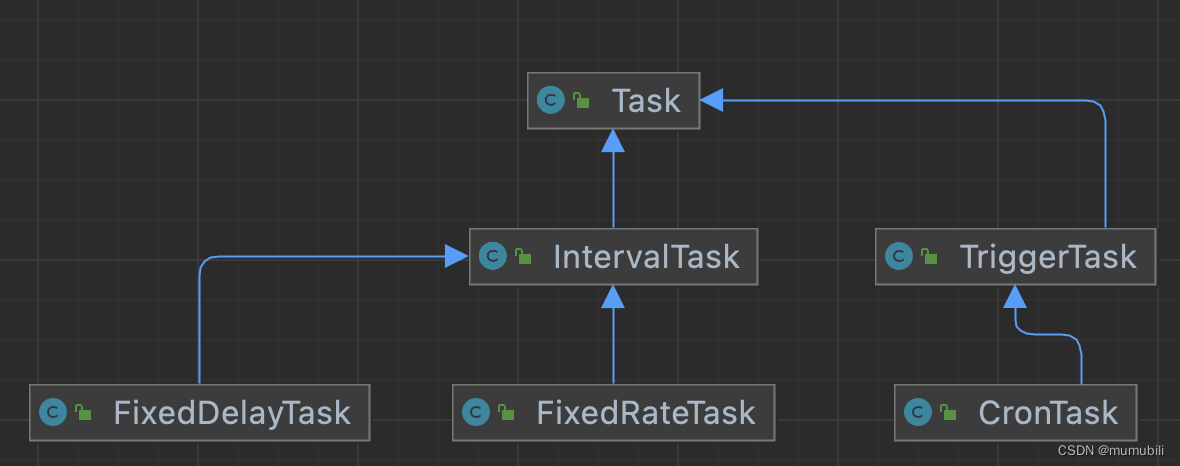
Spring调度框架中重要支持3种调度任务类型(继承结构如上图),具体说明如下:
1)CronTask:cron表达式调度的任务
2)FixedDelayTask:固定延迟时间执行的任务
3)FixedRateTask:固定速率执行的任务
2.2 对Task进行调度执行
上述3种的调度执行实现近似,下面以FixedDelayTask进行说明,该任务的调度方法为scheduleFixedDelayTask,具体实现如下:
/**
* Schedule the specified fixed-delay task, either right away if possible
* or on initialization of the scheduler.
* @return a handle to the scheduled task, allowing to cancel it
* (or {@code null} if processing a previously registered task)
* @since 5.0.2
*/
@Nullable
public ScheduledTask scheduleFixedDelayTask(FixedDelayTask task) {
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = this.unresolvedTasks.remove(task);
boolean newTask = false;
if (scheduledTask == null) {
scheduledTask = new ScheduledTask(task);
newTask = true;
}
if (this.taskScheduler != null) {
if (task.getInitialDelay() > 0) {
Date startTime = new Date(this.taskScheduler.getClock().millis() + task.getInitialDelay());
scheduledTask.future =
this.taskScheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(task.getRunnable(), startTime, task.getInterval());
}
else {
scheduledTask.future =
this.taskScheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(task.getRunnable(), task.getInterval());
}
}
else {
addFixedDelayTask(task);
this.unresolvedTasks.put(task, scheduledTask);
}
return (newTask ? scheduledTask : null);
}这里主要包含以下几步:
1)将调度任务包装为ScheduledTask类型,其中封装了执行结果ScheduledFuture
2)存在任务调度器(taskScheduler)时,直接进行调度执行
3)不存在任务调度器(taskScheduler)时,将任务暂存到fixedDelayTasks中,待调用afterPropertiesSet方法时再进行调度执行
3.任务调度器
3.1 任务调度器获取
任务调度器支持自定义,当无自定义调度器时,调度框架提供了默认的任务调度器;
自定义任务调度器的处理逻辑在方法finishRegistration中,如下:
private void finishRegistration() {
if (this.scheduler != null) {
this.registrar.setScheduler(this.scheduler);
}
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {
Map<String, SchedulingConfigurer> beans =
((ListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory).getBeansOfType(SchedulingConfigurer.class);
List<SchedulingConfigurer> configurers = new ArrayList<>(beans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(configurers);
for (SchedulingConfigurer configurer : configurers) {
configurer.configureTasks(this.registrar);
}
}
if (this.registrar.hasTasks() && this.registrar.getScheduler() == null) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "BeanFactory must be set to find scheduler by type");
try {
// Search for TaskScheduler bean...
this.registrar.setTaskScheduler(resolveSchedulerBean(this.beanFactory, TaskScheduler.class, false));
}
catch (NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not find unique TaskScheduler bean - attempting to resolve by name: " +
ex.getMessage());
}
try {
this.registrar.setTaskScheduler(resolveSchedulerBean(this.beanFactory, TaskScheduler.class, true));
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("More than one TaskScheduler bean exists within the context, and " +
"none is named 'taskScheduler'. Mark one of them as primary or name it 'taskScheduler' " +
"(possibly as an alias); or implement the SchedulingConfigurer interface and call " +
"ScheduledTaskRegistrar#setScheduler explicitly within the configureTasks() callback: " +
ex.getBeanNamesFound());
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not find default TaskScheduler bean - attempting to find ScheduledExecutorService: " +
ex.getMessage());
}
// Search for ScheduledExecutorService bean next...
try {
this.registrar.setScheduler(resolveSchedulerBean(this.beanFactory, ScheduledExecutorService.class, false));
}
catch (NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not find unique ScheduledExecutorService bean - attempting to resolve by name: " +
ex2.getMessage());
}
try {
this.registrar.setScheduler(resolveSchedulerBean(this.beanFactory, ScheduledExecutorService.class, true));
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex3) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("More than one ScheduledExecutorService bean exists within the context, and " +
"none is named 'taskScheduler'. Mark one of them as primary or name it 'taskScheduler' " +
"(possibly as an alias); or implement the SchedulingConfigurer interface and call " +
"ScheduledTaskRegistrar#setScheduler explicitly within the configureTasks() callback: " +
ex2.getBeanNamesFound());
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not find default ScheduledExecutorService bean - falling back to default: " +
ex2.getMessage());
}
// Giving up -> falling back to default scheduler within the registrar...
logger.info("No TaskScheduler/ScheduledExecutorService bean found for scheduled processing");
}
}
}
this.registrar.afterPropertiesSet();
}上述获取任务调度器的优先级顺序为:
1)当Bean后处理器中定义了任务调度器时,优先取Bean后处理器的任务调度器
2)在BeanFactory中获取Bean类型为SchedulingConfigurer的实例,在其方法configureTasks中可以自定义任务调度器
3)获取BeanFactory中TaskScheduler类型的bean(如有)
4)获取BeanFactory中ScheduledExecutorService类型的bean(如有)
5)当上述方式获取的任务调度器都不存在时,会使用框架中默认的任务调度器,如下:
if (this.taskScheduler == null) {
this.localExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
this.taskScheduler = new ConcurrentTaskScheduler(this.localExecutor);
}3.2 框架内提供的任务调度器
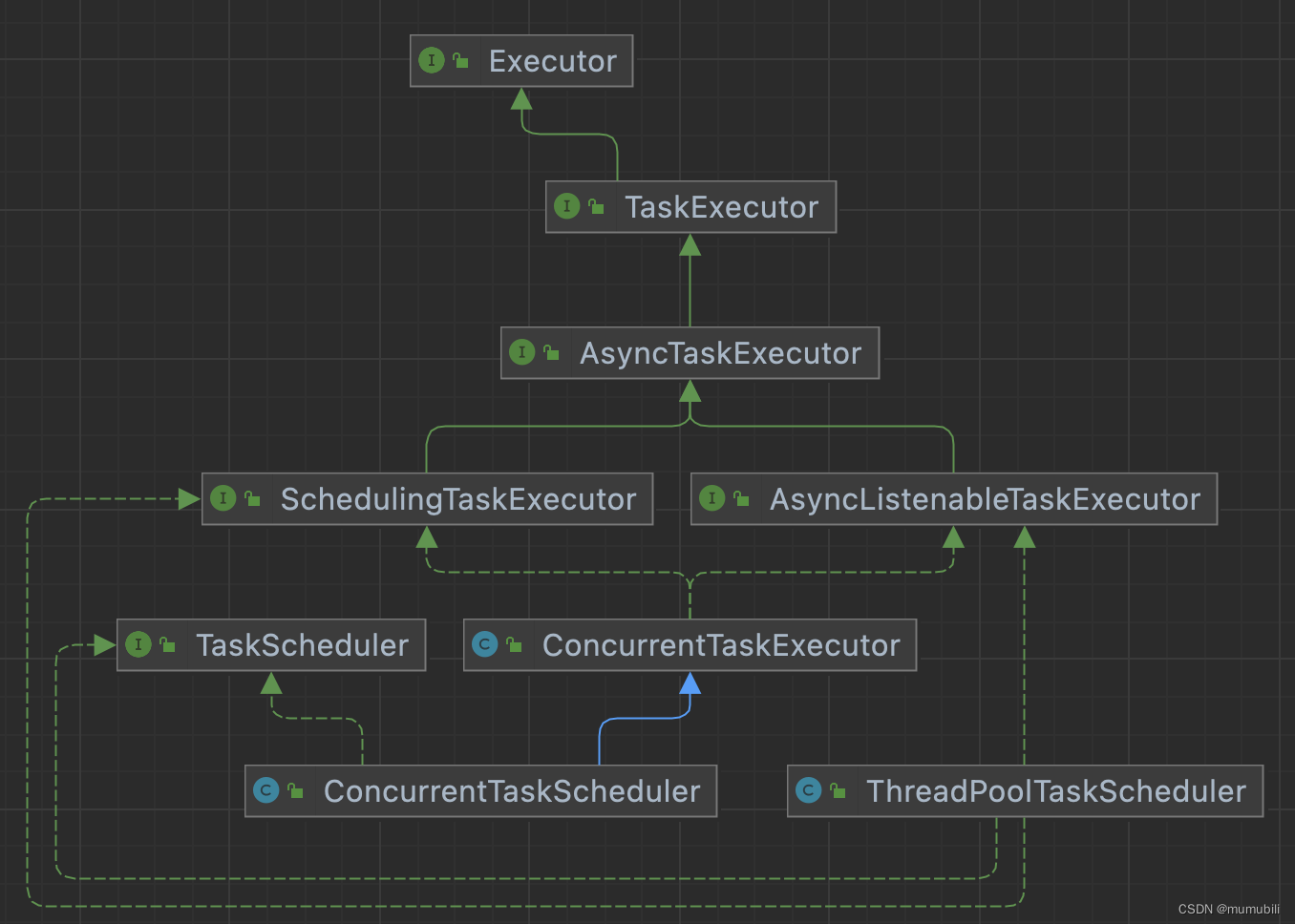
框架内提供的任务调度器主要包括:
1)ConcurrentTaskExecutor
2)ThreadPoolTaskScheduler
继承结构如下:
3.3 任务调度器执行逻辑
以上述框架默认的ConcurrentTaskScheduler进行说明,在调用调度器方法scheduleWithFixedDelay执行时,具体执行逻辑为:
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable task, Date startTime, long delay) {
long initialDelay = startTime.getTime() - this.clock.millis();
try {
return this.scheduledExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(decorateTask(task, true), initialDelay, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
throw new TaskRejectedException("Executor [" + this.scheduledExecutor + "] did not accept task: " + task, ex);
}
}这里主要包含2部分:
1)首先把task任务包装为DelegatingErrorHandlingRunnable类型(支持嵌入错误处理器逻辑),具体是在方法decorateTask中实现的,如下:
private Runnable decorateTask(Runnable task, boolean isRepeatingTask) {
Runnable result = TaskUtils.decorateTaskWithErrorHandler(task, this.errorHandler, isRepeatingTask);
if (this.enterpriseConcurrentScheduler) {
result = ManagedTaskBuilder.buildManagedTask(result, task.toString());
}
return result;
}
public static DelegatingErrorHandlingRunnable decorateTaskWithErrorHandler(
Runnable task, @Nullable ErrorHandler errorHandler, boolean isRepeatingTask) {
if (task instanceof DelegatingErrorHandlingRunnable) {
return (DelegatingErrorHandlingRunnable) task;
}
ErrorHandler eh = (errorHandler != null ? errorHandler : getDefaultErrorHandler(isRepeatingTask));
return new DelegatingErrorHandlingRunnable(task, eh);
}2)调用线程池方法scheduleWithFixedDelay进行调度执行
至此,Spring调度框架整体的处理过程总结如下:
- 开启调度框架(@EnableScheduling)
- 利用bean后处理器识别@Scheduled注解,并包装为Task任务
- 利用任务调度器(TaskScheduler,自定义或框架默认)进行调度执行
Over~~






![[补充]托福口语21天——day2 课堂内容](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9e5d18b5b2854a9b91a7d38655da988a.png)